Home>Garden Essentials>How To Choose Plants For Landscaping


Garden Essentials
How To Choose Plants For Landscaping
Modified: March 29, 2024
Learn how to choose the perfect garden plants for landscaping your outdoor space. Discover expert tips and advice for creating a beautiful and thriving garden.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Welcome to the world of landscaping, where nature’s beauty meets human creativity. Choosing the right plants for your landscape is crucial in achieving the stunning and harmonious outdoor space of your dreams. Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or a beginner in the world of landscaping, understanding the key factors to consider when selecting plants will help you create a thriving and visually appealing garden.
When it comes to landscaping, plants are the stars of the show. They provide color, texture, and structure to your outdoor space, creating a vibrant and inviting atmosphere. But with so many plant species to choose from, how do you know which ones are the best fit for your landscape?
In this article, we will explore the various factors to consider when choosing plants for landscaping. From sunlight requirements and soil conditions to climate compatibility and maintenance needs, we’ll cover everything you need to know to make informed decisions and create a thriving garden.
Key Takeaways:
- Choose plants that match your garden’s specific conditions, such as sunlight, soil, and climate, to create a thriving and visually appealing landscape that reflects your personal style and enhances your outdoor living experience.
- Incorporate low-maintenance plants, such as native species, succulents, and ornamental grasses, to create a beautiful and thriving garden with minimal time and effort, allowing you to spend more time relaxing and enjoying your outdoor space.
Read more: How To Choose A Landscape Architect
Factors to Consider When Choosing Plants for Landscaping
When selecting plants for your landscaping project, it’s important to consider several factors to ensure their success and harmonious integration into your outdoor space. Let’s take a closer look at these factors:
- Sunlight requirements: Different plants have varying sunlight needs. Some thrive in full sun, while others prefer partial or full shade. Consider the available sunlight in your garden and select plants accordingly. This will ensure that your plants receive the proper amount of light for optimal growth.
- Soil conditions: Assessing the soil conditions in your garden is crucial for plant selection. Some plants prefer well-drained soil, while others thrive in moist or clayey soil. Conduct a soil test to determine its pH level and nutritional content. This will help you choose plants that are well-suited to your specific soil type.
- Climate compatibility: Every plant has its own climate preferences. Consider your region’s climate, including average temperature, humidity, and frost dates. Choose plants that are native or well-adapted to your climate to ensure their long-term survival and reduce the need for extensive maintenance.
- Watering needs: Some plants require frequent watering, while others are more drought-tolerant. Consider the availability of water in your area and select plants that match your watering capabilities. Native plants or those adapted to your region are often a good choice as they have evolved to thrive in the local climate.
- Maintenance and growth rate: Assess your willingness and ability to maintain your garden. Some plants require regular pruning, fertilizing, or pest control. Consider your available time and resources for garden maintenance. Additionally, consider the growth rate of the plants to ensure they won’t outgrow the space or require frequent trimming.
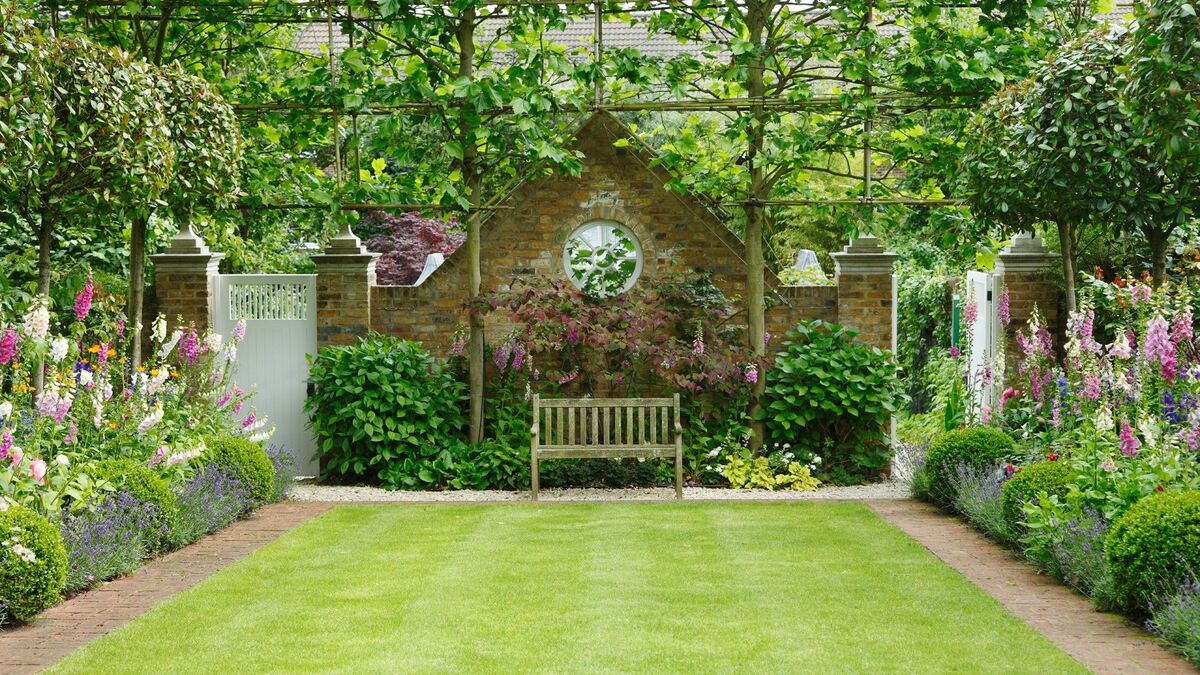
- Size and scale: Determine the desired size and scale of your garden to select plants that complement the overall design. Taller plants can provide vertical interest or act as screens, while lower-growing plants create a sense of balance and fill in empty spaces. Consider the mature size of the plants to avoid overcrowding or underutilizing the space.
- Color, texture, and form: Plants bring visual interest to your garden through their colors, textures, and forms. Consider the color palette you want to achieve in your landscape and choose plants that complement or contrast with one another. Mix plants with varying leaf shapes and textures to create an engaging and dynamic visual appeal.
- Diversity and variety: A diverse plant selection adds depth and interest to your garden. Aim for a mix of trees, shrubs, perennials, and annuals to create a multi-layered landscape that blooms throughout the year. Incorporate plants with different bloom times, foliage colors, and growth habits to maintain visual interest in every season.
- Planting zones: Familiarize yourself with your planting zone, which indicates the climate conditions your garden experiences. Consider plants that are recommended for your specific zone to ensure they are well-suited to the local climate.
- Budget considerations: Your budget may also influence your plant selection. Some plants are more expensive than others, especially rare or exotic varieties. Consider the long-term costs associated with maintenance and replacements when selecting plants to fit your budget.
By taking these factors into account, you can make informed decisions when choosing plants for your landscaping project. This will help you create a visually stunning and thriving garden that brings joy and tranquility to your outdoor space.
Sunlight Requirements
Understanding the sunlight requirements of plants is essential when choosing the right plants for your landscaping project. The amount of sunlight a plant receives directly affects its growth, flowering, and overall health. Here are some key points to consider:
Full Sun: Plants that require full sun need at least six hours of direct sunlight each day. These plants thrive in open areas with abundant sunlight and typically have vibrant flowers and lush foliage. Examples of full sun plants include roses, lavender, sunflowers, and succulents.
Partial Sun/Partial Shade: Plants that prefer partial sun or partial shade thrive in locations that receive three to six hours of direct sunlight daily. They can tolerate some shade during certain times of the day. These plants are a great choice for gardens with partially shaded areas or for areas that receive filtered sunlight. Examples include hydrangeas, hostas, begonias, and impatiens.
Full Shade: Plants that thrive in full shade require less than three hours of direct sunlight each day. They will flourish in areas with heavy tree cover, north-facing walls, or dense shade caused by tall buildings. These plants have adapted to low-light conditions and usually have lush green foliage. Examples of full shade plants include ferns, astilbes, hostas, and bleeding hearts.
It’s important to observe the lighting conditions in your garden throughout the day to determine the sun exposure in different areas. Keep in mind that the position of the sun changes with the seasons, so a spot that receives full sun in the summer may become partially shaded in the winter.
When considering sunlight requirements, it’s also crucial to account for potential obstructions that can cast shade, such as nearby buildings, trees, or tall structures. These obstructions can create microclimates within your garden, resulting in varying levels of sunlight throughout the day.
By understanding the specific sunlight requirements of plants, you can ensure that they are placed in optimal locations and receive the amount of sunlight necessary for healthy growth. This will help to ensure the success and vitality of your landscape.
Soil Conditions
When choosing plants for your landscaping project, it’s crucial to consider the soil conditions in your garden. Soil provides the necessary nutrients, water, and support for plants to grow and thrive. Understanding your soil’s composition and characteristics will help you select plants that are well-suited to your specific soil conditions. Here are some key factors to consider:
Soil pH: The pH level of your soil is a measure of its acidity or alkalinity. Different plants have varying pH preferences. Some plants prefer acidic soil (pH below 7), while others thrive in alkaline soil (pH above 7). Most plants prefer a slightly acidic to neutral pH range, around 6 to 7. Conduct a soil test to determine the pH level of your soil and choose plants that are adapted to that particular pH range.
Soil Structure: The structure of your soil refers to its texture and composition. It can range from sandy to clayey, with loamy soil being the ideal balance in between. Sandy soil drains quickly and tends to be less fertile, while clayey soil retains water for longer periods and may require amendments to improve drainage. Loamy soil is well-draining, rich in organic matter, and provides an optimal growing environment for a wide variety of plants.
Organic Matter: The presence of organic matter in your soil is essential for plant health and growth. Organic matter improves soil fertility, moisture retention, and drainage. If your soil lacks organic matter, consider incorporating compost, leaf mold, or well-rotted manure to improve its structure and nutrient content.
Moisture Retention: Some plants prefer moist soil, while others tolerate dry conditions. Assess the moisture retention characteristics of your soil to select plants that can thrive in those conditions. You can check the soil’s moisture level by digging a small hole and observing its moisture content. Sandy soils tend to drain quickly and may require more frequent watering, while clayey soils retain moisture for longer periods.
Soil Nutrients: Soil nutrients play a vital role in plant growth. Conduct a soil test to determine the levels of essential nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. These macronutrients are crucial for overall plant health, and their availability in the soil can affect plant growth and flowering. Depending on the test results, you may need to amend your soil with organic fertilizers or mineral-based fertilizers to provide a balanced nutrient profile for your plants.
Soil Drainage: Proper soil drainage is crucial for the health of your plants. Excess water can lead to root rot and other plant diseases. Ensure that your soil drains well by improving its structure or creating drainage channels if necessary. Plants that prefer well-drained soil, such as succulents and certain herbs, will not thrive in waterlogged conditions.
By understanding the soil conditions in your garden, you can select plants that are well-adapted to those conditions. This will enhance their growth and ensure their long-term success in your landscape. If you have challenging soil conditions, such as heavy clay or sandy soil, consider incorporating raised beds or containers to create a more favorable environment for your plants.
Climate Compatibility
When choosing plants for your landscaping project, considering climate compatibility is crucial for their long-term survival and thriving. Every plant has specific climate requirements, and selecting plants that are well-adapted to your region’s climate will increase their chances of thriving in your garden. Here are key factors to consider:
Average Temperature: Different plants have varying temperature tolerances. Some plants thrive in hot climates, while others prefer cooler temperatures. Consider the average temperature range in your region throughout the year and choose plants that can withstand those conditions. This will help ensure that your plants can tolerate both summer heat and winter cold.
Humidity: Humidity levels can greatly affect plant health. Some plants thrive in high humidity, while others prefer drier conditions. Assess the average humidity levels in your region and select plants that are adapted to those conditions. If you live in an area with high humidity, it’s important to choose plants that are less susceptible to fungal diseases caused by excessive moisture.
Frost Dates: Frost dates indicate the average date of the last frost in spring and the first frost in fall. These dates are crucial to understand when choosing plants, as frost can damage or kill frost-sensitive plants. Determine the frost dates in your region and select plants that can withstand the frost-free period in your area.
Microclimates: Microclimates are localized climate conditions within your garden that may differ from the general climate of your region. Factors such as wind patterns, proximity to bodies of water, and the presence of shade can create microclimates. Assess your garden for potential microclimates and choose plants that are well-suited to those specific conditions.
Hardiness Zones: Hardiness zones are geographical areas that are defined by their average minimum winter temperatures. They serve as a guide to determine which plants are most likely to thrive in specific regions. Consult a hardiness zone map to identify your region’s zone and choose plants that are recommended for that particular zone.
Native and Adapted Plants: Native plants are species that naturally occur in a specific region and are well-adapted to the local climate. These plants have evolved to thrive in the specific conditions of their native areas. By incorporating native plants into your landscape, you can create a garden that is not only beautiful but also supports the local ecosystem. Additionally, consider using plants that are adapted to your region, even if they are not native. These plants have been selected or bred to tolerate specific climate conditions and can perform well in your garden.
By considering climate compatibility, you can choose plants that are best suited to your region’s climate. This will increase their chances of thriving and reduce the need for extensive maintenance or special care. Additionally, selecting climate-appropriate plants promotes sustainability by conserving water and reducing the need for artificial climate control measures in your garden.
Read more: How To Group Plants In Landscaping
Watering Needs
Water is an essential element for plant growth, and understanding the watering needs of plants is vital for their health and vitality in your landscaping project. Different plants have varying water requirements, and matching their needs to your watering capabilities will help ensure their success. Here are some key points to consider:
Drought-tolerant Plants: Some plants are naturally adapted to survive in dry conditions and require less frequent watering. These plants have developed mechanisms to conserve water and can withstand extended periods of drought. Choosing drought-tolerant plants is a great option for water-efficient landscaping, especially in regions with limited water resources.
Water-loving Plants: On the other hand, some plants have high water requirements and prefer consistently moist soil. These plants thrive in areas with high rainfall or regular irrigation. If you have a water source readily available and are willing to provide regular watering, you can include water-loving plants in your landscaping design.
Planting Zones and Water Availability: Consider your region’s climate and water availability when selecting plants. Choose plants that are native or well-adapted to your region’s specific climate conditions. Native plants are often more tolerant of local water availability and have evolved to thrive in those conditions.
Soil Drainage: The drainage characteristics of your soil can affect watering needs. Well-draining soils require less frequent watering, as excess water can quickly drain away. In contrast, compacted or clayey soils may retain water for extended periods, necessitating less frequent watering. Understanding your soil’s drainage capabilities will help you adjust your watering schedule accordingly.
Mulching: Applying mulch to your garden beds can help conserve moisture and reduce evaporation. Mulch acts as a protective layer, reducing weed growth and maintaining a more consistent soil temperature. It also helps retain moisture, reducing the frequency of watering. Consider using organic mulch, such as wood chips or straw, to improve water efficiency in your garden.
Watering Methods: There are different methods for watering plants, including overhead sprinklers, drip irrigation, or hand watering. Consider the watering method that best suits your needs and the specific requirements of your plants. Drip irrigation, for example, provides water directly to the plant’s root zone, reducing water waste through evaporation and ensuring efficient water delivery.
Monitoring: Regularly monitor your plants’ water needs by checking the soil moisture level. Stick your finger into the soil to a depth of about one inch. If it feels dry, it’s time to water. Be cautious not to overwater your plants, as this can lead to root rot and other problems. It’s better to water deeply and less frequently, allowing the soil to dry out slightly between watering sessions.
By understanding the watering needs of your plants and matching them to your water availability and capabilities, you can maintain healthy and thriving plants in your landscape. Water-efficient practices not only conserve this precious resource but also contribute to sustainable gardening and reduce water-related costs and efforts.
Maintenance and Growth Rate
Consideration of the maintenance and growth rate of plants is essential when choosing plants for your landscaping project. Different plants have varying maintenance requirements, and understanding their growth rate will help you plan for future growth and maintenance needs. Here are some key points to consider:
Maintenance Requirements: Plants can have different maintenance needs, including pruning, fertilizing, and pest control. Some plants require regular pruning to maintain their shape and size, while others may need periodic fertilization to encourage healthy growth. Consider your willingness and ability to dedicate time and effort to maintain your garden. If you’re looking for low-maintenance options, select plants that are known for their minimal care requirements.
Growth Rate: Understanding the growth rate of plants is essential for planning the long-term development of your landscape. Some plants have rapid growth rates, while others grow more slowly. Consider the available space in your garden and how the plants will fill it over time. Avoid overcrowding by choosing plants that match the desired size and growth rate for your landscape. This will help prevent the need for frequent pruning or removal of plants that have outgrown their space.
Invasive Species: Some plants have aggressive growth habits and can become invasive, taking over your garden and potentially causing ecological harm. Avoid choosing invasive plant species, especially in areas where they can escape into natural habitats. Research the plants you’re considering to ensure they are not known to be invasive in your region.
Plant Longevity: Consider the expected lifespan of the plants you choose. Some plants are short-lived, while others can provide enjoyment for many years. This is especially important for trees and shrubs, which form the backbone of your landscape. Plan for the future by selecting long-lived plants that will continue to enhance your landscape for years to come.
Personal Preferences: Personal preference plays a role in determining the maintenance level you are willing to commit to. Some gardeners enjoy spending time in their garden, tending to plants and nurturing their growth. Others prefer a more hands-off approach, opting for low-maintenance plants that require minimal care. Consider your own gardening style and choose plants that align with your preferences.
Native Plants: Native plants are often a good choice for low-maintenance gardening as they are well-adapted to the local climate and soil conditions. They require less water, fertilizer, and maintenance once established. Consider incorporating native plants into your landscape to minimize maintenance efforts while supporting local biodiversity.
By considering the maintenance requirements and growth rate of plants, you can create a landscape that suits your lifestyle and preferences. Selecting plants that align with your desired level of maintenance will help you create a beautiful and enjoyable garden that suits your needs and provides long-term satisfaction.
Size and Scale
Considering the size and scale of plants is crucial when choosing plants for your landscaping project. The size of the plants you select can greatly impact the overall visual appeal and functionality of your garden. Here are some key points to consider:
Mature Size: It’s important to consider the mature size of plants when planning your landscape. Every plant has a specific growth habit and size at maturity. Make sure to research the expected height and spread of plants to ensure they fit within the available space in your garden. Avoid planting trees or shrubs that will outgrow their allocated space or obstruct views or walkways.
Vertical Interest: Incorporating plants of varying heights adds visual interest to your landscape. Taller plants can create vertical elements, adding depth and drama to your garden. Consider using trees or tall shrubs as anchor points and focal features. Balance them with mid-height plants and groundcovers to create a visually appealing composition.
Low-Growing Plants: Low-growing plants are well-suited for groundcovers or as borders for pathways and garden beds. These plants typically have a spreading growth habit and stay relatively short in height. They create a sense of cohesion and help define different areas of your garden.
Scale with Structures: Consider the surrounding structures, such as buildings or fences, when choosing plants for your landscape. Select plants that will complement the scale and architecture of these structures. For example, tall plants can provide privacy or act as a screen against a fence, while smaller plants are better suited for window boxes or small garden beds near a patio.
Balance and Proportion: Achieving a sense of balance and proportion is crucial in creating a visually appealing landscape. Consider the overall size and shape of your garden and aim for a harmonious distribution of plants. Avoid overcrowding the space with too many plants or using plants that are disproportionately large or small compared to the rest of the garden.
Plant Spacing: Proper plant spacing is essential for healthy growth and adequate airflow between plants. When planting, refer to the recommended spacing guidelines for each plant species. This will help prevent competition for resources and ensure optimal growing conditions for each plant.
Container Gardens: If you have limited space or want more flexibility in your garden design, consider incorporating container gardens. Containers provide the opportunity to select plants of varying sizes and arrange them in a visually pleasing way. They can be placed strategically to create focal points or add greenery to smaller patios or balconies.
Time Considerations: Keep in mind that plants will grow and change over time. Some may start off small but eventually reach a substantial size. Plan for the future growth of your plants to avoid the need for frequent transplanting or removal of overcrowded plants.
By considering the size and scale of plants, you can create a well-balanced and visually appealing landscape. Whether you’re aiming for a grand garden with towering trees or a cozy courtyard with low-growing plants, careful selection and placement of plants will help you achieve the desired ambiance and functionality in your outdoor space.
Color, Texture, and Form
Color, texture, and form are important elements that contribute to the visual appeal and overall design of your landscaping project. When choosing plants, considering these factors will help create a vibrant and harmonious garden. Here’s what you should keep in mind:
Color: Color plays a crucial role in creating eye-catching and visually pleasing landscapes. Consider the color scheme you want to achieve in your garden. You can opt for a monochromatic color palette, using variations of a single color, or go for a more contrasting scheme by combining complementary colors. Choose plants that bloom in colors that align with your desired color scheme, whether it’s vibrant and bold or soft and pastel. Also think about the foliage color, as it adds interest even when plants aren’t in bloom.
Texture: Plant textures can be categorized as coarse, medium, or fine. Coarse textures have large, bold leaves or prominent flowers, while medium textures have average-sized leaves or blooms. Fine textures are characterized by small, delicate foliage or intricate flower structures. Consider the desired texture in your garden to add visual interest and create depth. Combining plants with different textures creates contrast and adds richness to the overall design.
Form: Plant form refers to the shape and growth habit of plants. It includes considerations of height, width, and overall structure. Plants can have an upright form, spreading form, cascading form, or even a weeping form. Consider the desired form or shapes in your landscape. For example, vertical plants can create an accent or focal point, while rounded or mounding plants add softness and fill in spaces. Offering a variety of plant forms will create a dynamic and visually interesting garden.
Combining Colors, Textures, and Forms: When selecting plants, aim for a harmonious combination of color, texture, and form. Choose plants that complement each other in color, creating a pleasing visual contrast or a unified color scheme. Mix plant textures, combining coarse, medium, and fine textures for added interest. Consider the forms of plants, using a mix of upright, spreading, and cascading forms to create a balanced and visually appealing composition.
Seasonal Interest: Think about the seasonal interest various plants can bring to your landscape. Choose plants that offer a sequence of blooming or changing foliage throughout the seasons. This ensures that your garden remains visually appealing and dynamic throughout the year.
Balance and Scale: Consider the overall balance of colors, textures, and forms in your garden. Aim for a mix of these elements that creates a sense of harmony and avoids visual overload. Also, be mindful of the scale of plants in relation to their surroundings. Ensure they are proportionate to the size of your garden, structures, and other plants.
By carefully selecting plants based on color, texture, and form, you can create a visually stunning landscape that captivates and delights the senses. Pay attention to the interplay of these elements and experiment with different combinations to find the perfect balance in your garden design.
Consider the climate, soil type, and sunlight levels in your area when choosing plants for landscaping. Select native plants for low maintenance and to support local wildlife.
Read more: Where To Buy Landscaping Plants
Diversity and Variety
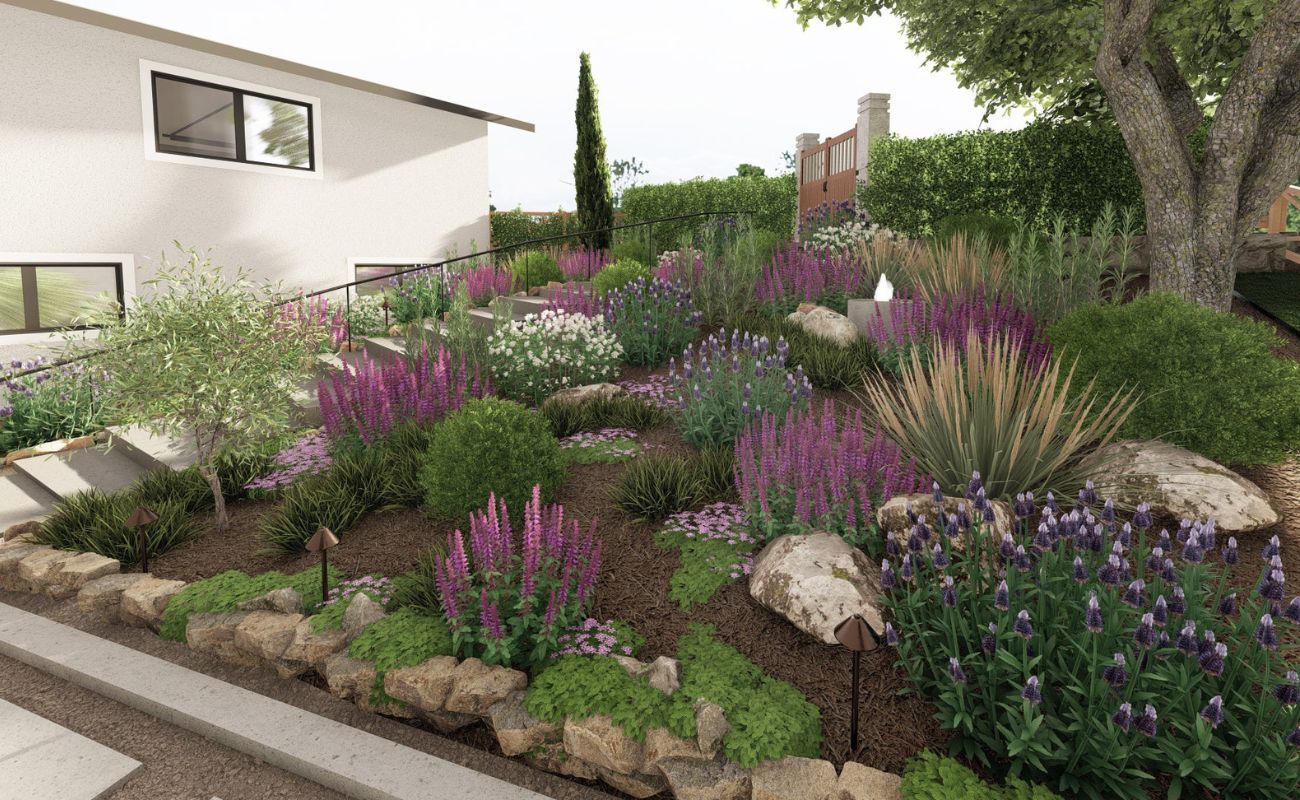
Creating a diverse and varied landscape is key to a visually intriguing and ecologically beneficial garden. Incorporating a range of plant species adds depth, interest, and resilience to your landscape. Here are some reasons why diversity and variety are important when choosing plants for your landscaping project:
Ecological Benefits: A diverse garden supports a variety of beneficial insects, birds, and other wildlife. Different plant species attract different pollinators, helping to maintain a healthy and balanced ecosystem. By selecting a variety of plants that flower at different times, you can provide a continuous source of nectar and pollen throughout the seasons, supporting pollinators like bees and butterflies.
Reduced Disease and Pest Problems: Monocultures, or gardens with a limited range of plant species, are more susceptible to the spread of diseases and pests. In contrast, a diverse garden is more resilient to pests and diseases, as they are less likely to spread quickly from one plant to another. Planting a variety of species creates a natural defense system, making it harder for pests or diseases to establish themselves.
Extended Seasonal Interest: Diversity in plant selection ensures that your garden remains visually interesting throughout the year. By including plants with varying bloom times and foliage colors, you can create a garden that offers seasonal interest, with different plants taking the spotlight at different times. This provides year-round beauty and enjoyment in your landscape.
Textural and Visual Appeal: A diverse garden offers a wide range of textures, colors, and forms, making it visually appealing. By mixing plants with different leaf shapes, flower types, and growth habits, you can create a tapestry of visual interest. Incorporating plants with contrasting foliage colors or interesting bark textures adds depth to your garden design. Whether it’s the delicate fronds of a fern, the bold flowers of a coneflower, or the graceful arching branches of a weeping willow, diverse plants add richness and uniqueness to your landscape.
Learning and Discovery: A garden filled with a variety of plants provides an opportunity for learning and discovery. It allows you to explore different plant species, their unique characteristics, and how they interact with each other. It encourages a deeper understanding and appreciation of the natural world and can be a source of inspiration for future gardening endeavors.
Sustainable Gardening: Sustainability is enhanced by creating a diverse garden. By using a range of plant species, you reduce the reliance on a single species and promote a more resilient and self-sustaining ecosystem. This leads to reduced water usage, decreased pest problems, and a more balanced garden ecosystem.
When selecting plants for your landscape, consider incorporating a diverse range of species to create a vibrant and multifaceted garden. Embrace a variety of colors, textures, and forms that support a healthy environment and offer year-round interest. By celebrating diversity and variety in your garden, you can create a truly captivating and sustainable outdoor space.
Planting Zones
Understanding planting zones is essential when choosing plants for your landscaping project. Planting zones provide a geographic guide to determine which plants are most likely to thrive in specific regions. Here are key points to consider when it comes to planting zones:
What are Planting Zones?
Planting zones, also known as hardiness zones, are geographical regions that classify areas based on their average minimum winter temperatures. The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) developed the USDA Hardiness Zone Map, which divides North America into 13 different zones, ranging from Zone 1 (coldest) to Zone 13 (warmest). These zones provide a rough guide to which plants are most likely to survive and thrive in specific areas.
Choosing Plants for Your Zone:
When selecting plants for your landscape, consult the USDA Hardiness Zone Map or similar zone maps specific to your country or region. The map indicates the recommended zone for each plant species. Choosing plants that are recommended for your zone increases their chances of success and reduces the risk of frost or extreme cold damage.
Microclimates and Planting Zones:
Keep in mind that microclimates within your garden can affect the overall hardiness of plants. Factors such as wind, sunlight, and proximity to structures or bodies of water can create localized climate variations. These microclimates may allow you to experiment with plants that are rated for zones slightly different from your own. For example, a south-facing wall or a sheltered spot may create a slightly warmer microclimate, enabling you to grow plants rated for slightly warmer zones.
Plant Adaptation:
Plants that are native to your specific region are typically well-adapted to the local climate and can thrive in the corresponding hardiness zone. Consider incorporating native plants into your landscape, as they often require less maintenance, have natural defenses against local pests, and support the local ecosystem. Native plants can contribute to the preservation of regional biodiversity and create habitats for local wildlife.
Changing Climate and Planting Zones:
It’s important to note that climate change can affect traditional hardiness zones. Over time, some areas may experience shifts in temperature patterns, altering the suitability of certain plant species. Stay updated with local climate information and consult updated zone maps or local gardening resources that consider changing climate conditions in your region.
By considering the planting zone of your area, you can select plants that are better adapted to the climate conditions in your region. This will increase the chances of success in your garden and ensure that your plants thrive in their intended environment.
Budget Considerations
When planning your landscaping project, it’s crucial to consider your budget. Landscaping can involve various expenses, such as purchasing plants, soil amendments, tools, and hiring professional services. Here are some key budget considerations to keep in mind:
Plant Costs: The cost of plants can vary greatly depending on factors such as plant size, species rarity, and local availability. Some plants, especially exotic or rare varieties, tend to be more expensive. Consider your budget and prioritize the plants that are within your price range. You can also look for more cost-effective alternatives or choose to invest in a smaller number of higher-priced specimens as focal points in your landscape.
Maintenance Costs: Different plants require varying levels of maintenance, which can impact your ongoing expenses. High-maintenance plants may require regular pruning, fertilizing, pest control, or irrigation. Consider the long-term costs associated with maintaining the plants you choose. If you have a limited budget or prefer low-maintenance gardening, select plants that require minimal care once established.
Hardscaping and Infrastructure: In addition to plants, landscaping often involves the installation of hardscape elements such as pathways, patios, retaining walls, or irrigation systems. These features can incur significant costs. Evaluate your budget to determine the extent of hardscaping you can afford, and prioritize the elements that are essential for your landscape design.
Soil Amendments and Fertilizers: Assess the quality of your existing soil and consider any necessary amendments. Adding organic matter, such as compost or manure, can improve soil fertility and structure. However, these amendments may come with additional costs. Similarly, if your soil lacks essential nutrients, you may need to invest in fertilizers or soil conditioners to provide the necessary elements for plant growth.
Professional Services: Depending on the complexity of your landscaping project, you may require the assistance of professionals, such as landscape designers, architects, or contractors. These services can be an additional expense but can also ensure a well-planned and executed design. Evaluate your budget and determine whether professional help is necessary or if you can undertake the project yourself.
Long-Term Considerations: Keep in mind the long-term costs of maintaining your landscape. Some plants require replacement after a certain number of years, while others may outgrow their allocated space and require transplanting. Assess the potential costs associated with plant replacements or necessary adjustments to ensure that your garden remains healthy and aesthetically pleasing over time.
Smart Budgeting Tips: Consider purchasing plants during sales or clearance periods to take advantage of discounted prices. Look for local plant nurseries or gardening clubs that may offer cost-effective options or plant exchanges. Additionally, planning and prioritizing your landscaping project can help you allocate your budget most efficiently.
By considering your budget and making thoughtful choices, you can create a beautiful and well-designed landscape that fits within your financial means. Remember, a well-planned and maintained garden can bring joy and value to your property regardless of the size of your budget.
Choosing Plants for Specific Landscaping Purposes
When designing your landscape, different areas may have specific purposes or requirements. Selecting plants that serve these specific purposes will help you create a functional and visually appealing outdoor space. Here are some common landscaping purposes and the plants that are well-suited for them:
Plants for Shade Gardens: If you have areas in your garden that receive limited sunlight, such as under trees or along north-facing walls, choose shade-loving plants. These plants can thrive in low-light conditions and add beauty to shady spots. Some popular choices for shade gardens include hostas, ferns, astilbes, heucheras, and Japanese forest grass.
Plants for Water Gardens: Water gardens provide a unique opportunity to incorporate plants that thrive in or around water. Consider aquatic plants like water lilies, lotus, water irises, or floating plants like water lettuce and duckweed. These plants not only add beauty to your water feature but also help maintain a healthy ecosystem. Additionally, consider marginal plants like cattails and rushes that can be placed at the edges of your water garden.
Plants for Privacy: Creating boundaries or screening off certain areas in your landscape for privacy is common practice. Choose plants that offer dense foliage and grow to the desired height. Evergreen trees and shrubs such as arborvitae, leyland cypress, or holly are popular choices for creating privacy screens. Bamboo and ornamental grasses can also be used to create natural privacy barriers.
Plants for Low-Maintenance Landscapes: If you’re looking for a low-maintenance landscape, choose plants that require minimal care and attention. Native plants are often a great choice as they are adapted to the local climate and require less water, fertilizer, and maintenance once established. Succulents, ornamental grasses, and many perennial flowers like daylilies, coneflowers, and sedums are also known for their low-maintenance attributes.
Plants for Drought-Resistant Landscapes: In regions with limited water resources or dry climates, choosing drought-resistant plants is essential. Succulents such as agaves and yuccas, Mediterranean plants like lavender and rosemary, and ornamental grasses like fountain grass and Mexican feather grass are excellent choices. These plants have adapted to arid conditions, requiring less water and making them more resilient during periods of drought.
Plants for Butterfly or Pollinator Gardens: If you want to attract butterflies, bees, and other pollinators to your garden, choose plants that provide nectar, pollen, and habitat for these creatures. Look for plants with brightly colored flowers and a long blooming period. Native wildflowers such as echinacea, coneflowers, milkweed, and bee balm are popular choices for creating vibrant butterfly and pollinator gardens.
Plants for Edible Landscaping: Incorporating edible plants into your landscape allows you to enjoy fresh produce while adding beauty to your garden. Consider planting fruit-bearing trees, such as apple or cherry trees, or shrubs like blueberries or raspberries. Herbs like basil, rosemary, and thyme can be used as attractive border plantings. Vegetable plants, such as tomatoes or lettuce, can also be intermixed with ornamental plants to create a visually appealing and productive garden.
By choosing plants that align with specific landscaping purposes, you can create a garden that is not only visually stunning but also functional and fulfilling. Consider the unique requirements of each area in your landscape and select plants that will thrive in those specific conditions, enhancing the overall beauty and usability of your outdoor space.
Read more: Landscape Design: How To Group Plants
Plants for Shade Gardens
Shade gardens, with their cool and tranquil atmosphere, provide a unique opportunity to cultivate plants that thrive in low-light conditions. Whether you have areas under trees, along a north-facing wall, or in the shadow of tall structures, selecting the right plants for shade gardens is crucial for their successful growth and beauty. Here are some wonderful plant choices that will flourish in shade:
Hostas (Hosta spp.): Hostas are popular shade-loving plants known for their elegant foliage. Available in a variety of sizes, colors, and textures, hostas can add interest and beauty to any shade garden. Their broad leaves range from solid green to variegated patterns, offering striking contrast and visual appeal.
Ferns: Ferns are versatile plants that thrive in shade gardens. Their delicate, feathery foliage creates a lush and natural look. There are countless fern species to choose from, including the popular Boston fern (Nephrolepis exaltata), maidenhair fern (Adiantum spp.), and autumn fern (Dryopteris erythrosora).
Astilbes (Astilbe spp.): Astilbes are renowned for their fluffy plumes of flowers that rise above their fern-like foliage. These perennials come in a range of colors, including pinks, purples, and whites. Astilbes can add a soft and romantic touch to shade gardens and are perfect for creating visual interest in the middle to back of borders.
Heucheras (Heuchera spp.): Heucheras, also known as coral bells, are compact perennial plants with vibrant and colorful foliage. They come in a wide array of hues, such as shades of green, purple, bronze, and even variegated combinations. Heucheras add a pop of color to shade gardens and are excellent for edging or container gardening.
Japanese Forest Grass (Hakonechloa spp.): Japanese forest grass is a graceful and cascading ornamental grass that thrives in shaded areas. Its slender arching foliage adds texture and movement to shade gardens. The golden varieties, such as Hakonechloa macra ‘Aureola,’ provide a beautiful contrast against the darker foliage of other shade-loving plants.
Bleeding Hearts (Dicentra spp.): Bleeding hearts are old-fashioned favorites in shade gardens, known for their heart-shaped flowers that dangle delicately from arching stems. They come in shades of pink and white and bring charm and elegance to shady corners and woodland garden settings.
Brunnera (Brunnera macrophylla): Brunnera, also known as Siberian bugloss, is a versatile shade-loving perennial. It features clusters of small, sky-blue flowers that rise above heart-shaped leaves. Brunnera adds a splash of color and forms dense groundcovers that fill in empty spaces in shade gardens.
Hellebores (Helleborus spp.): Hellebores, or Lenten roses, are early-blooming perennials that thrive in shade. They offer an array of flower colors, including shades of white, pink, purple, and green. With their long-lasting flowers and evergreen foliage, hellebores add beauty and interest to shade gardens even during the colder months.
Virginia Bluebells (Mertensia virginica): Virginia bluebells are spring-flowering perennials that thrive in shade gardens. Their clusters of bell-shaped blue flowers create a carpet of color in early spring. These native plants naturalize well, providing a burst of beauty year after year.
Epimedium (Epimedium spp.): Epimediums, also known as barrenworts or fairy wings, are shade-loving plants appreciated for their delicate flowers and attractive foliage. Their dainty flowers come in various colors, including shades of pink, yellow, and white. Epimediums are ideal for adding layers and ground coverage in shade gardens.
Remember to assess the specific growing conditions in your shade garden, such as moisture levels, soil type, and sun exposure. By selecting plants that thrive in shaded areas, you can create a lush and captivating garden that showcases the beauty of shade-loving plants.
Plants for Water Gardens
Water gardens offer a serene and captivating environment that can be enhanced with the right selection of plants. These plants are well-suited to growing in or around water, adding beauty, texture, and ecological balance to your aquatic oasis. When choosing plants for your water garden, consider these options:
Water Lilies (Nymphaea spp.): Water lilies are iconic plants in water gardens, known for their captivating floating leaves and vibrant flowers. They come in a variety of colors, including white, yellow, pink, and red. Water lilies provide shade and shelter for aquatic wildlife while adding a touch of elegance to your water garden.
Lotus (Nelumbo spp.): Lotus plants are renowned for their majestic beauty and cultural significance. These aquatic plants have large, striking flowers that come in an array of colors. Lotus leaves provide shade and create a dramatic presence in water gardens. Ensure you have enough space for these vigorous plants, as they can spread quickly.
Water Irises (Iris spp.): Water irises are ideal for the edges of water gardens, providing a burst of color and vertical interest. They have striking flowers in various hues, including blue, white, yellow, and purple. Water irises also tolerate moist soil and offer a delightful fragrance to your water garden.
Bog Plants: Bog plants thrive in shallow water or at the water’s edge, offering a graceful transition between land and water. Some popular choices include Canna lilies, Japanese primroses (Primula japonica), Marsh marigolds (Caltha palustris), and Cardinal flowers (Lobelia cardinalis). These plants not only add beauty to your water garden but also provide habitat and food for pollinators.
Floating Plants: Floating plants are an essential component of water gardens as they help control algae growth and provide habitat for fish and other wildlife. Water Lettuce (Pistia spp.) and Water Hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) are popular choices. These plants have long, trailing roots that provide shelter for aquatic creatures while creating a stunning natural carpet on the water’s surface.
Marginal Plants: Marginal plants, also known as shallow water or emergent plants, grow at the water’s edge and add texture and dimension to water gardens. Some examples include Yellow Flag Iris (Iris pseudacorus), Pickerelweed (Pontederia cordata), and Sweet Flag (Acorus spp.). These plants provide vertical interest, stabilize the water’s edge, and attract a variety of wildlife.
Pond Grasses and Rushes: Ornamental grasses and rushes add a sense of movement and grace to water gardens. Blue Rush (Juncus inflexus), Giant Reed (Arundo donax), and Zebra Rush (Scirpus tabernaemontani ‘Zebrinus’) are suitable choices. These grasses offer vertical texture and can be planted at the water’s edge or in shallow water.
Aquatic Moss and Ferns: Aquatic mosses and ferns provide a lush and natural look to water features. Java Moss (Taxiphyllum barbieri) and Water Fern (Azolla caroliniana) are popular options. These plants can be attached to rocks or driftwood in your water garden, adding a soft and vibrant texture.
Remember to consider the specific needs of each plant, such as sunlight requirements and water depth, to ensure they thrive in your water garden. By carefully choosing these water-loving plants, you can create a vibrant and harmonious aquatic sanctuary that enhances the beauty and tranquility of your outdoor space.
Plants for Privacy
Creating privacy in your outdoor space is essential for creating a sense of seclusion and tranquility. Whether you have nosy neighbors, a busy street, or simply want to define your property boundaries, incorporating plants for privacy is a natural and visually appealing solution. Here are some plant options that can help you achieve the desired level of privacy in your landscape:
Evergreen Trees: Evergreen trees are an excellent choice for creating privacy screens, as they provide year-round coverage and structure. Select trees that are suitable for your climate and space. Popular evergreen options include Leyland cypress (Cupressus leylandii), Thuja varieties such as Thuja occidentalis ‘Emerald Green,’ and Arborvitae (Thuja plicata).
Hedges: Hedges offer a classic and elegant solution for creating privacy in your landscape. They can be formal or informal, depending on the desired look. Select dense-growing shrubs that can be trimmed to form a solid barrier. Popular hedge plant options include Boxwood (Buxus), Privet (Ligustrum), and Holly (Ilex). Consider the height and width requirements of the selected shrubs to ensure they will provide adequate privacy.
Bamboo: Bamboo is a fast-growing plant that forms thick, dense screens, making it ideal for creating privacy. There are various types of bamboo, such as Clumping Bamboo (Bambusa) and Running Bamboo (Phyllostachys). When choosing bamboo, be mindful of the spreading habit of certain varieties and use containment techniques if needed to prevent them from invading neighboring areas.
Ornamental Grasses: Ornamental grasses can be an attractive option for creating privacy screens while adding a touch of elegance to your landscape. Select taller grasses with dense growth habits, such as Feather Reed Grass (Calamagrostis acutiflora), Miscanthus, or Northern Sea Oats (Chasmanthium latifolium). These grasses provide height and movement, creating a stunning visual impact.
Climbing Vines: Climbing vines can be utilized to cover structures like fences, trellises, or pergolas, offering privacy and a lush backdrop. Consider fast-growing vines such as Clematis, Jasmine, Honeysuckle (Lonicera), or Trumpet Vine (Campsis radicans). These vines will quickly cover fences or walls, providing both privacy and beauty.
Privacy Shrubs: There are several shrubs that can be used to create privacy screens. Consider options like American holly (Ilex opaca), Cherry Laurel (Prunus laurocerasus), Wax Myrtle (Myrica cerifera), or Japanese Snowball Viburnum (Viburnum plicatum). These shrubs have dense foliage and can be planted close together to form a solid barrier.
Living Walls: If space is limited, consider creating a living wall using plants such as espalier fruit trees or climbing roses. These plants can be trained to grow against walls or fences, providing both beauty and privacy. Vertical gardens with trailing plants like Ivy or Creeping Fig can also be utilized to cover walls and create an effective privacy barrier.
Grasses with Tall Seed Heads: Incorporating ornamental grasses with tall seed heads, such as Pampas Grass (Cortaderia selloana) or Giant Miscanthus (Miscanthus giganteus), can create privacy with a touch of drama. These grasses offer height and density, blocking views while adding visual interest with their distinctive plumes.
Remember to evaluate the specific needs of these plants, including sunlight requirements, soil conditions, and growth habits, to ensure they will thrive in your specific landscape. By selecting the appropriate plants for privacy, you can create a secluded outdoor retreat and enjoy your outdoor space with peace of mind.
Plants for Low-Maintenance Landscapes
Creating a low-maintenance landscape doesn’t mean compromising on beauty. By carefully selecting plants that require minimal care and attention, you can create a beautiful and thriving garden that fits seamlessly into your busy lifestyle. Here are some plant options that are known for their low-maintenance characteristics:
Native Plants: Native plants are well-adapted to the local climate and require less water, fertilizer, and maintenance once established. They are naturally resistant to local pests and diseases, making them an ideal choice for low-maintenance landscapes. Research the native plants in your region and include them in your garden design for a sustainable and low-maintenance landscape.
Succulents: Succulents have become increasingly popular due to their unique and captivating forms, as well as their minimal care requirements. These plants are specifically adapted to retain water in their fleshy leaves and can tolerate drought conditions. Examples of low-maintenance succulents include Echeverias, Sedums, Aloe vera, and Agave.
Ornamental Grasses: Ornamental grasses offer a range of textures, forms, and colors while requiring minimal care. These grasses are drought-tolerant, generally pest-resistant, and provide visual interest throughout the year. Some low-maintenance ornamental grasses include Feather Reed Grass (Calamagrostis spp.), Miscanthus, and Fountain Grass (Pennisetum).
Perennial Flowers: Many perennial flowers require less maintenance compared to annuals. Once established, they will return year after year, reducing the need for replanting. Choose perennial flowers known for their hardiness and low-maintenance requirements, such as Daylilies (Hemerocallis spp.), Coneflowers (Echinacea spp.), Black-eyed Susans (Rudbeckia spp.), and Sedums.
Lavender: Lavender is a versatile and low-maintenance plant that offers fragrant blooms and attractive foliage. These plants thrive in sunny and well-draining conditions, requiring minimal watering and maintenance. Lavender varieties like English Lavender (Lavandula angustifolia) and French Lavender (Lavandula stoechas) are excellent choices for low-maintenance landscaping.
Shrubs: Choosing low-maintenance shrubs can significantly reduce the amount of pruning and care required in your landscape. Seek out slow-growing and compact varieties that require minimal shaping and pruning. Some low-maintenance shrubs include Dwarf Korean Lilac (Syringa meyeri ‘Palibin’), Butterfly Bush (Buddleja davidii), and Spirea (Spiraea).
Groundcovers: Groundcovers offer multiple benefits in low-maintenance landscapes, such as suppressing weeds, reducing erosion, and minimizing the need for mowing or mulching. Consider low-growing plants like Creeping Thyme (Thymus serpyllum), Juniper (Juniperus horizontalis), or Creeping Jenny (Lysimachia nummularia).
Herbs: Herbs not only add fragrance and culinary value to your landscape but can also be low-maintenance options. Many herbs, such as Rosemary, Sage, Oregano, and Thyme, are drought-tolerant and require little attention once established. They provide a fruitful and attractive addition to any low-maintenance garden.
Mulching and Weed Control: Using mulch in your garden beds helps retain moisture, suppress weeds, and reduce the need for frequent watering. Apply a layer of organic mulch, such as wood chips or straw, to help maintain soil moisture and minimize weed growth.
By incorporating these low-maintenance plants into your landscape design and implementing smart gardening techniques, you can enjoy a beautiful and thriving garden with minimal time and effort. Remember, a low-maintenance landscape allows you to spend more time relaxing and enjoying your outdoor space.
Read more: Landscape Design: Where To Plant Lilies
Conclusion
Creating a beautiful and thriving garden is a rewarding endeavor, and choosing the right plants is essential for achieving your landscaping goals. By considering factors such as sunlight requirements, soil conditions, climate compatibility, and maintenance needs, you can select plants that are well-suited to your specific landscape and lifestyle.
Whether you’re looking to create shade gardens, water gardens, privacy screens, low-maintenance landscapes, or any other landscaping purpose, there are plants available to meet your needs. From the elegant hostas and ferns for shade gardens to the majestic water lilies for water gardens, the variety of plants offers endless possibilities for creating stunning and functional landscapes.
Remember to also consider the color, texture, form, diversity, and variety of plants in your garden. These elements add depth, interest, and visual appeal to your landscape design. Furthermore, being mindful of your budget allows you to make informed choices while considering cost-effective options.
By selecting the right plants for your specific landscaping purposes, you can create a thriving and captivating outdoor space that brings joy and tranquility. Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or a beginner in the world of landscaping, the knowledge and understanding of plant selection will help you create a garden that reflects your personal style and enhances your outdoor living experience. Embrace your creativity, experiment with different combinations, and let nature’s beauty shine in your garden.
So, roll up your sleeves, dig into the world of gardening, and watch as your landscape transforms into a vibrant and inviting haven for both nature and yourself.
Frequently Asked Questions about How To Choose Plants For Landscaping
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.










0 thoughts on “How To Choose Plants For Landscaping”