Home>Garden Essentials>What Is Landscaping Architecture


Garden Essentials
What Is Landscaping Architecture
Modified: October 27, 2024
Discover the art of garden landscaping architecture and transform your outdoor space. Our experts create stunning garden designs that enhance the beauty and functionality of your property.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Welcome to the world of landscaping architecture, where creativity, design, and nature blend together to create stunning outdoor spaces. Whether you have a small backyard or a vast estate, landscaping architecture has the power to transform your surroundings into a picturesque oasis.
Landscaping architecture is a multidisciplinary field that combines elements of art, science, and horticulture to design and create outdoor spaces that are not only aesthetically pleasing but also functional and sustainable. From parks and gardens to residential and commercial properties, landscaping architecture plays a vital role in enhancing the beauty and functionality of outdoor areas.
With a rich history dating back centuries, landscaping architecture has evolved from simple garden layouts to complex and intricate designs that incorporate various elements of nature. From formal gardens with symmetrical patterns to naturalistic landscapes that mimic the beauty of the wilderness, landscaping architecture offers endless possibilities for creating unique and captivating outdoor spaces.
In this article, we will explore the principles, elements, and techniques of landscaping architecture. We will delve into the importance of landscaping architecture in enhancing the quality of life, as well as its role in promoting sustainability and environmental stewardship. We will also highlight the difference between landscaping and landscape architecture and provide insights into the steps involved in the landscape design process.
So, whether you are a landscaping enthusiast looking to beautify your own backyard or a curious mind eager to learn more about this fascinating field, join us as we embark on a journey into the world of landscaping architecture.
Key Takeaways:
- Landscaping architecture blends art, science, and sustainability to create visually captivating and functional outdoor spaces, enhancing beauty, environmental quality, and community interaction.
- Sustainable landscaping practices promote water conservation, native plants, and biodiversity, contributing to cost-effective, resilient, and visually appealing landscapes that harmonize with nature.
Definition of Landscaping Architecture
Landscaping architecture, also known as landscape architecture, is the art and science of designing, planning, and managing outdoor spaces. It involves the integration of natural and built elements to create aesthetically pleasing and functional landscapes.
At its core, landscaping architecture seeks to harmonize human activities with the natural environment. It considers the cultural, social, ecological, and economic aspects of a site to craft outdoor spaces that are not only visually appealing but also sustainable and practical.
Landscaping architecture combines various disciplines, including architecture, horticulture, engineering, urban planning, and ecology. It requires a deep understanding of spatial design, plant selection, grading, drainage, and construction techniques.
The role of a landscaping architect is to envision and create outdoor spaces that fulfill the needs and desires of clients while considering environmental factors and long-term sustainability. They work closely with clients to understand their preferences, goals, and budget, and then translate those into a cohesive and functional design plan.
Landscaping architecture encompasses a wide range of projects, from small residential gardens to large-scale public parks and urban landscapes. It can involve the design of elements such as pathways, water features, seating areas, lighting, and plantings, all of which are carefully selected and arranged to enhance the overall aesthetic and function of the space.
One of the key principles of landscaping architecture is the concept of “place-making,” which focuses on creating outdoor spaces that foster a sense of identity, community, and connection to the natural environment. It seeks to create environments that not only serve practical purposes but also evoke emotional responses and enrich the lives of those who interact with them.
Overall, landscaping architecture is a dynamic and creative profession that blends artistry and technical knowledge to transform outdoor spaces into beautiful, sustainable, and functional environments. Its impact can be seen in both urban and rural landscapes, where carefully designed outdoor spaces enhance the quality of life for individuals and communities alike.
Historical Background
The practice of landscaping architecture can be traced back to ancient civilizations, where the design and arrangement of outdoor spaces held cultural and symbolic significance. Throughout history, different cultures and civilizations have left their marks on the landscape through their unique approaches to landscaping and garden design.
One of the earliest recorded instances of landscape design dates back to ancient Egypt, where gardens were created as sacred spaces around temples and tombs. The gardens of ancient Egypt featured meticulously planned layouts, geometric patterns, and carefully selected plantings.
In ancient Persia, now modern-day Iran, the concept of paradise gardens emerged. These gardens were designed as enclosed spaces with lush vegetation, water features, and pavilions, providing a sanctuary for relaxation and contemplation.
The influence of Greek and Roman civilizations on landscaping architecture cannot be overstated. The Greeks were known for their symmetrical and ordered gardens, blending natural elements with architectural features. The Romans, on the other hand, introduced the concept of extensive gardens and created grand landscapes to showcase their wealth and power.
During the Renaissance period in Europe, landscaping architecture underwent a significant transformation. Inspired by the revival of classical art and culture, European nobility and aristocrats began creating elaborate gardens that reflected their wealth and status. These gardens featured geometric patterns, intricate sculptures, and carefully cultivated plantings.
In the 18th and 19th centuries, landscape design took on a more naturalistic approach with the rise of the English Landscape Garden movement. Influenced by the romantic ideals of nature, landscape architects such as Capability Brown in England and André Le Nôtre in France created sweeping parklands with rolling hills, lakes, and strategically planted trees. This movement emphasized the harmonious integration of natural elements and the creation of picturesque vistas.
Fast forward to the modern era, landscaping architecture has seen further evolution and diversification. The emergence of urban planning and environmental concerns has influenced the field’s focus on sustainable design, incorporating ecological principles and promoting biodiversity in urban landscapes.
Today, landscaping architecture continues to evolve, embracing technological advancements and incorporating new design principles. It plays a critical role in addressing contemporary challenges such as urbanization, climate change, and the need for green spaces in urban environments. Landscape architects work on projects ranging from urban parks and rooftop gardens to sustainable design initiatives that prioritize water conservation and ecological restoration.
The historical background of landscaping architecture provides a rich tapestry of influences and inspirations from different cultures and time periods. It has shaped the field into what it is today, a discipline that blends art, science, and sustainability to create beautiful and functional outdoor spaces.
Principles of Landscaping Architecture
Landscaping architecture is guided by a set of principles that serve as the foundation for designing and creating harmonious and functional outdoor spaces. These principles encompass a range of considerations, including aesthetics, functionality, sustainability, and cultural context. Here are some key principles of landscaping architecture:
- Unity: The principle of unity focuses on creating a cohesive and harmonious design that ties together various elements in the landscape. It involves the integration of different components, such as plantings, hardscaping, and structures, to create a sense of unity and visual coherence.
- Balance: Achieving balance in landscaping architecture involves distributing visual elements evenly throughout the landscape. This can be done through symmetrical or asymmetrical design techniques, balancing the mass, color, and texture of plantings and structures.
- Scale and Proportion: Scale refers to the relationship between the size of elements within the landscape and the overall space. Proportion involves ensuring that the size and scale of different elements are visually pleasing and relate well to each other and the surrounding environment.
- Rhythm and Repetition: Rhythm creates a sense of movement and visual flow within the landscape. It can be achieved through the repetition of certain elements, such as plantings, colors, or patterns. This repetition helps establish a rhythm that guides the viewer’s eye through the landscape.
- Hierarchy: Hierarchy involves the organization and arrangement of elements in the landscape according to their importance or significance. This can be achieved through the use of focal points, such as a striking tree or a water feature, that draw attention and create visual interest.
- Functionality: A major principle of landscaping architecture is ensuring that the outdoor space is functional and serves its intended purpose. This involves careful consideration of how people will use the space, whether it’s for relaxation, recreation, or social gatherings. Accessibility, seating areas, pathways, and lighting are all elements that contribute to the functionality of the landscape.
- Biodiversity: Creating landscapes that support biodiversity and ecological health is an important principle of landscaping architecture. This involves selecting a variety of plants and creating habitats that can attract and support local wildlife. Biodiverse landscapes are not only visually appealing but also contribute to the overall health and resilience of the ecosystem.
- Sustainability: With environmental concerns becoming increasingly important, sustainability has become a crucial principle in landscaping architecture. It involves designing landscapes that minimize the use of water, energy, and other resources, and promote practices such as rainwater harvesting, use of native plants, and eco-friendly materials.
- Cultural Context: Landscaping architecture takes into account the cultural context and history of a site. It incorporates elements and design motifs that reflect and respect the local cultural heritage, ensuring that the landscape is a meaningful and relevant reflection of the community it serves.
By adhering to these principles, landscaping architects create outdoor spaces that are visually appealing, functional, and sustainable. They strike a balance between artistry and practicality, resulting in landscapes that enhance the quality of life for individuals and communities while respecting the natural environment.
Elements of Landscaping Architecture
Landscaping architecture is comprised of several key elements that come together to create visually striking and functional outdoor spaces. These elements are the building blocks that form the foundation of a well-designed landscape. Understanding and incorporating these elements is crucial in creating a balanced and harmonious outdoor environment. Here are the main elements of landscaping architecture:
- Plantings: Plants play a central role in landscaping architecture. They provide beauty, texture, color, and create a sense of seasonality. Selecting the right plants and arranging them in a visually appealing way is essential in creating a vibrant and dynamic landscape.
- Hardscaping: Hardscaping refers to the non-living elements in a landscape, such as pathways, walls, fences, and structures. These elements add structure and define the functionality of the space. The selection of materials, such as stone, wood, or concrete, and their placement is vital in creating a cohesive design.
- Water Features: Water features, such as fountains, ponds, or streams, add a sense of serenity and movement to the landscape. They provide a focal point and create a soothing ambiance, while also attracting wildlife and promoting a sense of tranquility.
- Lighting: Lighting is a crucial element in landscaping architecture, as it enhances the aesthetics and functionality of outdoor spaces. Well-designed lighting can highlight architectural features, create a warm and inviting atmosphere, and extend the usability of the landscape into the evening.
- Seating Areas: Seating areas are essential for enjoying and interacting with the landscape. Whether it’s a comfortable outdoor lounge or a simple bench, seating areas provide a place for relaxation, socializing, and contemplation.
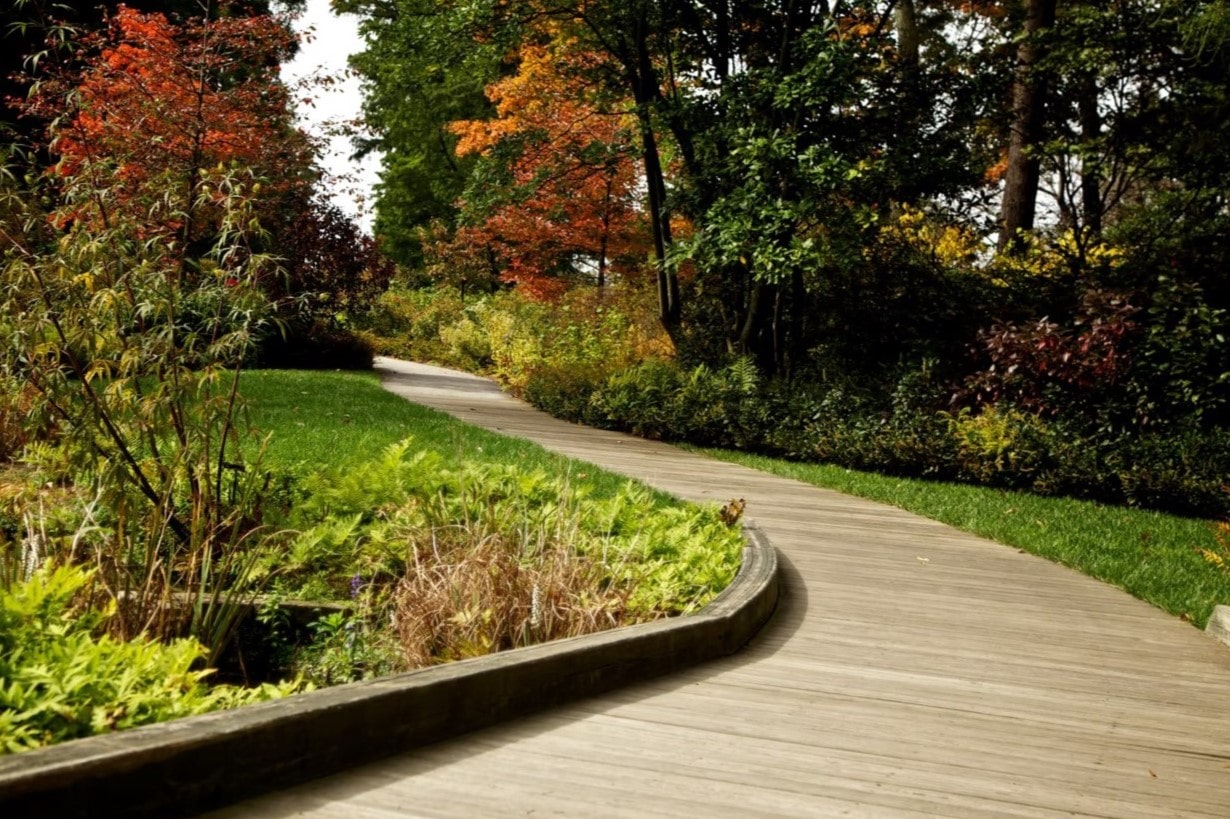
- Pathways: Pathways serve both practical and aesthetic purposes in landscaping architecture. They create a sense of direction and guide people through the landscape while also adding visual interest and defining the flow of the space. The choice of materials, such as gravel, pavers, or natural stone, can significantly impact the overall aesthetic.
- Garden Structures: Garden structures, such as pergolas, gazebos, or trellises, add vertical interest and architectural beauty to the landscape. They provide shade, privacy, and serve as a framework for climbing plants or hanging gardens.
- Art and Sculpture: Incorporating art and sculptures into the landscape adds a layer of creativity and personal expression. They can serve as focal points, create visual interest, and reflect the overall theme or concept of the landscape.
- Color and Texture: Color and texture are essential elements in landscaping architecture. They add depth, visual interest, and create a sense of harmony. The choice of plantings, materials, and surfaces should be carefully considered to achieve a cohesive and visually pleasing design.
By incorporating these elements into a landscape, landscaping architects can create inviting, functional, and visually striking outdoor spaces. Each element contributes to the overall design and plays a role in enhancing the beauty and functionality of the landscape. Balancing these elements is key to achieving harmony and creating a remarkable landscape that inspires and delights.
Read more: What Is Landscaping In Construction
Importance of Landscaping Architecture
Landscaping architecture plays a crucial role in enhancing the quality of life and creating sustainable and visually captivating outdoor spaces. Its importance extends beyond mere aesthetics, as it contributes to numerous aspects of human well-being, environmental sustainability, and community development. Here are some key reasons why landscaping architecture is important:
- Enhancing Beauty and Aesthetics: One of the primary functions of landscaping architecture is to create visually appealing and aesthetically pleasing outdoor spaces. Well-designed landscapes can transform ordinary spaces into extraordinary ones, providing joy, inspiration, and a connection to nature. Beautiful landscapes enhance our surroundings and uplift our spirits.
- Improving Environmental Quality: Landscaping architecture promotes environmental sustainability by incorporating green spaces, trees, and plants into the landscape. These elements help mitigate air and water pollution, provide shade to reduce the urban heat island effect, and support biodiversity by creating habitats for wildlife.
- Creating Functional Outdoor Spaces: Landscaping architecture considers the practical aspects of outdoor spaces, ensuring they are designed for functionality and usability. Whether it’s providing seating areas for relaxation, creating pathways for navigation, or designing recreational spaces for activities, well-designed landscapes enhance the functionality and usability of outdoor areas.
- Supporting Health and Well-being: Interacting with nature has been proven to have numerous physical and mental health benefits. Landscaping architecture provides opportunities for physical activity, stress reduction, and relaxation. Access to green spaces and well-designed landscapes can improve mental health, reduce stress levels, and promote a sense of well-being.
- Promoting Community Interaction: Landscaping architecture plays a vital role in creating gathering spaces and fostering community interaction. Well-designed parks, public squares, and community gardens provide a platform for social connection, community events, and recreational activities. They contribute to a sense of belonging and cultural identity within neighborhoods and communities.
- Increasing Property Values: Well-maintained and aesthetically pleasing landscapes have been shown to increase the value of residential and commercial properties. Landscaping architecture enhances curb appeal, attracts potential buyers or tenants, and creates a positive first impression. It is an investment that can yield significant returns.
- Supporting Sustainability: Landscaping architecture plays a crucial role in promoting sustainable design practices. By incorporating techniques such as rainwater harvesting, use of native and drought-tolerant plants, and efficient irrigation systems, landscapes can reduce water consumption and minimize environmental impact. Sustainable landscapes contribute to conservation efforts and help address environmental challenges.
- Preserving and Celebrating Cultural Heritage: Landscaping architecture can incorporate elements that respect and celebrate the cultural heritage of a region. By integrating design motifs, materials, and themes that reflect local traditions and history, landscapes become a means to preserve and promote cultural identity. This fosters a sense of pride and connection to the community.
Landscaping architecture is a multidimensional practice that encompasses aesthetics, functionality, sustainability, and community development. Its importance lies in creating beautiful, functional, and sustainable outdoor spaces that contribute to our well-being, the environment, and the sense of community. Whether for residential, commercial, or public spaces, landscaping architecture has the power to transform ordinary spaces into extraordinary ones.
Landscaping architecture involves designing outdoor spaces to be both functional and aesthetically pleasing. It includes elements such as plants, hardscaping, and water features to create a cohesive and beautiful environment.
Difference between Landscaping and Landscape Architecture
While often used interchangeably, landscaping and landscape architecture are two distinct fields that focus on different aspects of creating and designing outdoor spaces. Understanding the differences between the two can help clarify their roles and the level of expertise involved. Here are the key differences between landscaping and landscape architecture:
Scope and Scale: Landscaping typically refers to the process of transforming outdoor spaces on a smaller scale, such as residential properties, small gardens, or commercial landscapes. It involves activities such as planting, hardscaping, and maintenance to beautify and enhance the functionality of the landscape. Landscape architecture, on the other hand, encompasses a broader scope and deals with larger-scale projects, such as urban parks, public spaces, and master planning. Landscape architects are involved in the conceptualization, planning, and management of these larger projects.
Educational Background: Landscaping often requires hands-on experience and practical skills acquired through training or apprenticeships. Many landscapers may not have formal educational backgrounds in landscape design or architecture. Landscape architecture, on the other hand, typically requires a formal education in landscape architecture or a related field. Landscape architects possess a deep understanding of design principles, ecology, site planning, and project management.
Design Approach: Landscaping primarily focuses on the aesthetic aspects of outdoor spaces, seeking to create visually appealing and functional landscapes. It is often driven by the preferences and requirements of clients and aims to enhance the existing features of the landscape. Landscape architecture takes a more comprehensive approach, considering a broader range of factors such as site analysis, environmental impact, cultural context, and long-term sustainability. Landscape architects integrate art, science, and design principles to create landscapes that are not only visually pleasing but also environmentally responsible and functional.
Regulation and Licensing: In many regions, landscape architecture is a regulated profession requiring licensure. Landscape architects must meet specific educational and professional experience requirements and pass a licensing examination. This is to ensure that they have the necessary knowledge and expertise to undertake complex projects and protect the public interest. Landscaping, on the other hand, may not require specific licensing or certifications, although some landscapers may choose to pursue certifications or join professional organizations.
Collaboration and Project Management: Given the larger scale and complexity of landscape architecture projects, landscape architects often work in collaboration with other professionals, including architects, engineers, urban planners, and environmental consultants. They oversee the entire design process, from initial concept development to construction and maintenance. Landscaping projects, while potentially involving collaboration with other professionals, are often more focused on implementation and may not require the same level of project management and coordination.
Level of Expertise: Landscape architects are trained professionals with a deep understanding of design principles, plant ecology, construction techniques, and project management. They possess the expertise to handle complex projects, address environmental considerations, and create landscapes that are both aesthetically pleasing and sustainable. Landscapers, while skilled in their craft, may have a narrower focus on implementing and maintaining the landscaping elements designed by landscape architects or clients.
While both landscaping and landscape architecture contribute to the creation of beautiful outdoor spaces, they differ in their scope, educational background, design approach, regulation, and level of expertise. Understanding these differences helps establish clear roles and expectations when undertaking landscaping or landscape architecture projects.
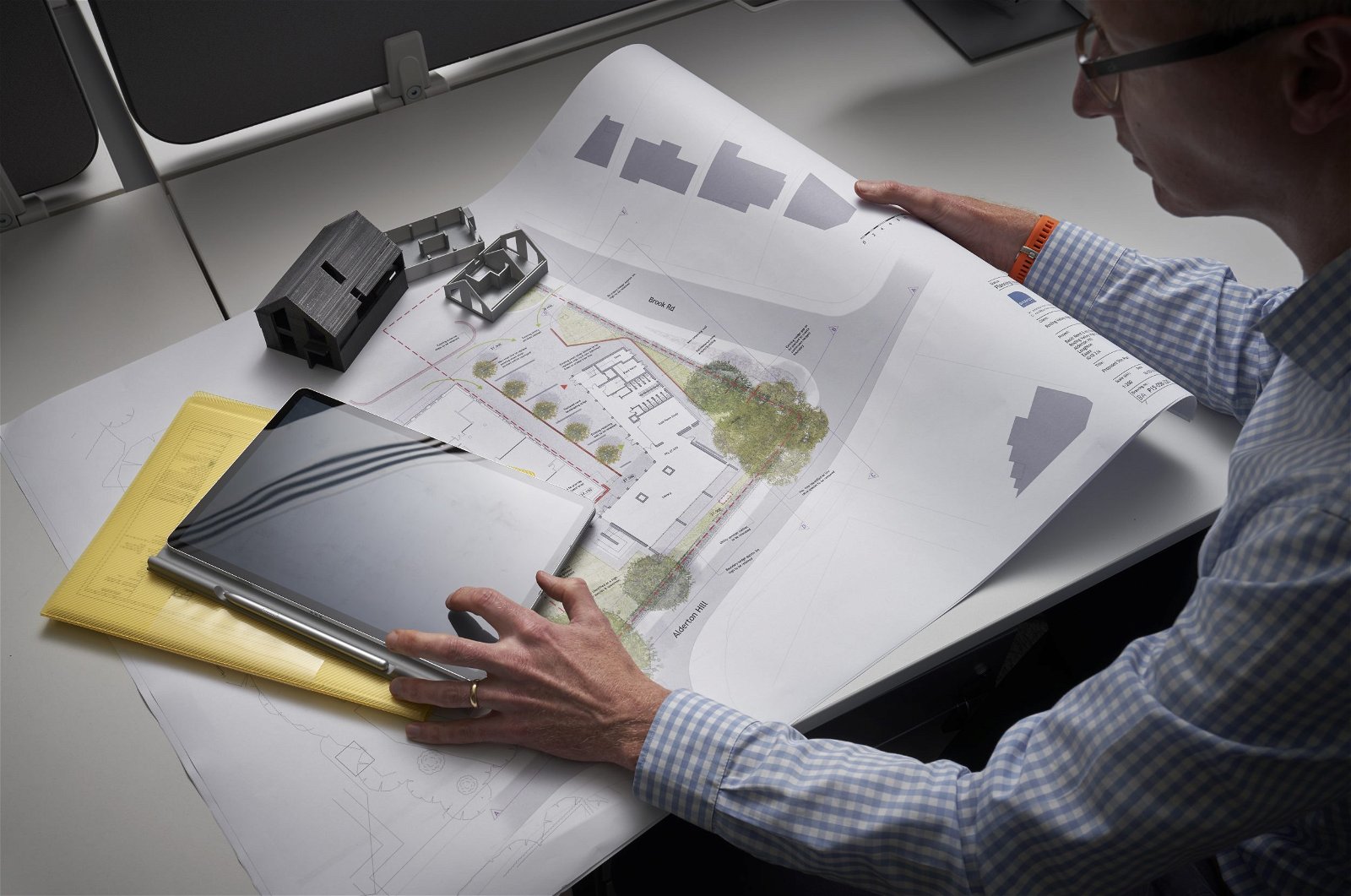
Steps Involved in Landscape Design Process
The landscape design process encompasses a series of steps that guide the creation of a well-planned and visually striking outdoor space. Each step builds upon the previous one, ensuring a comprehensive and cohesive approach to landscape design. Here are the key steps involved in the landscape design process:
- Site Analysis: The first step in landscape design is conducting a thorough site analysis. This involves assessing the existing conditions of the site, including topography, soil composition, drainage patterns, and existing vegetation. Understanding the site’s unique characteristics and constraints is crucial in determining the design possibilities and addressing any challenges.
- Goal Identification and Client Consultation: This step involves engaging with the client to identify their goals, needs, and preferences for the outdoor space. The designer gathers information on how the client intends to use the space, their desired aesthetic style, and any specific functional requirements. This consultation helps shape the design direction and ensures that the final landscape meets the client’s expectations.
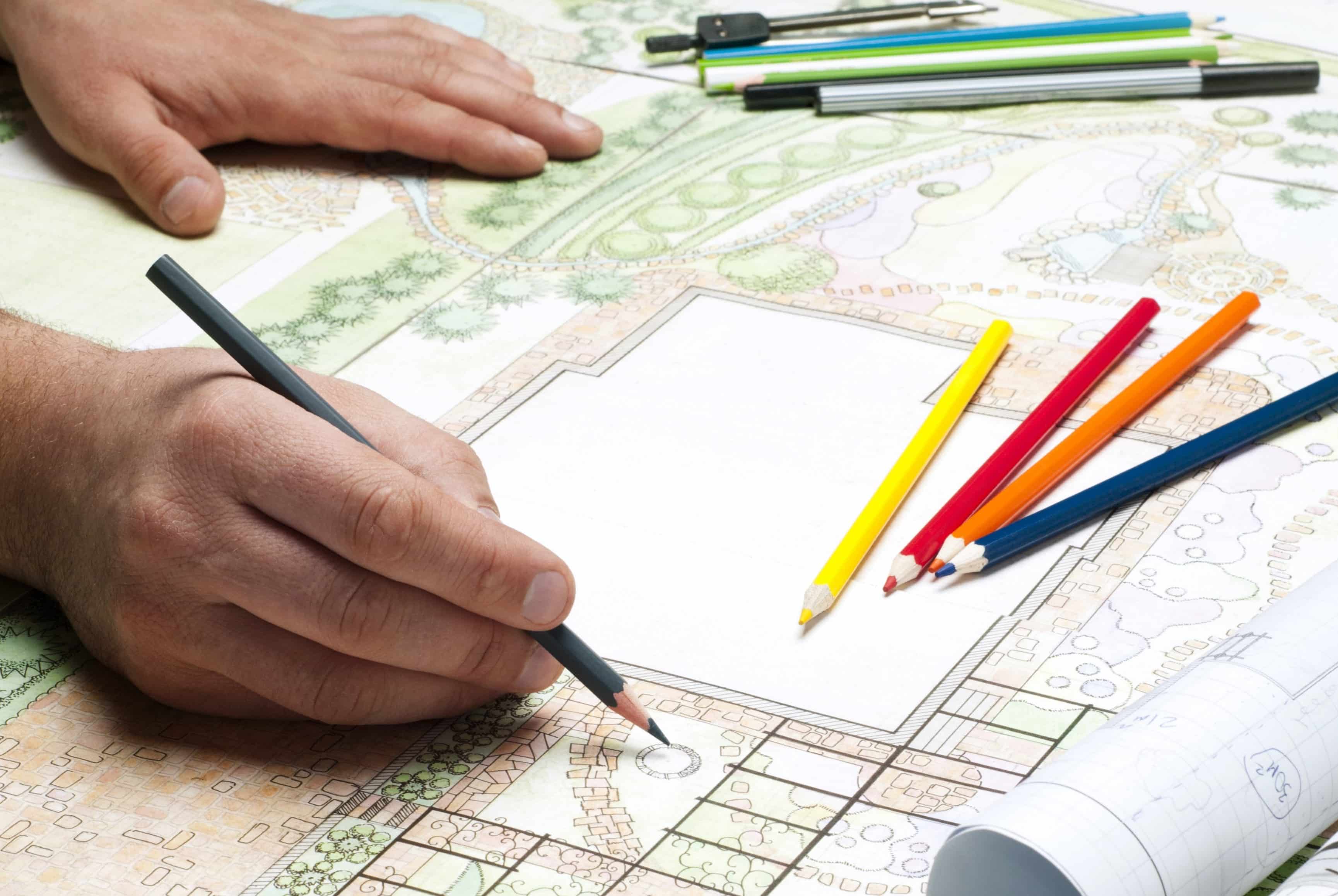
- Concept Development: Based on the site analysis and client consultation, the landscape designer develops a concept for the landscape. This involves generating ideas, creating sketches or renderings, and exploring various design options. The concept serves as a visual representation of the design direction and helps the client visualize the end result.
- Preliminary Design: In this step, the concept is further developed into a preliminary design. This includes the selection and arrangement of plantings, hardscape elements, water features, lighting, and other design components. The preliminary design serves as a blueprint for the final landscape and includes dimensions, materials, and layouts.
- Design Refinement: The preliminary design is reviewed and refined based on feedback from the client. Adjustments are made to the design to ensure that it aligns with the client’s vision and functional requirements. Collaboration and communication between the landscape designer and client are central to this step, which ensures that any revisions are incorporated to achieve the desired end result.
- Construction Documentation: Once the design is finalized, detailed construction documentation is prepared. This includes technical drawings, specifications, and material selections. The documentation serves as a guide for contractors, installers, and other professionals involved in the construction process, ensuring that the design is accurately implemented.
- Construction Oversight: During the construction phase, the landscape designer may provide oversight to ensure that the design is being implemented according to the specifications. They work closely with contractors, coordinating the installation of plantings, hardscape elements, lighting, and other features. This step involves regular site visits, addressing any design-related issues, and ensuring that the final result matches the intended design.
- Planting and Installation: Once the construction is complete, the planting and installation of the landscape elements are carried out. This includes the installation of plants, trees, shrubs, and the placement of hardscape elements, such as pathways, seating areas, and water features. Proper planting techniques and attention to detail ensure the success and longevity of the landscape.
- Maintenance and Management: The final step involves developing a maintenance and management plan for the landscape. This includes instructions on watering, pruning, fertilization, and other maintenance practices to ensure the ongoing health and vitality of the landscape. Regular maintenance helps preserve the design intent and allows the landscape to flourish over time.
The landscape design process is a dynamic and iterative one, with each step informing and influencing the next. From the initial site analysis to the final installation and ongoing maintenance, each stage is critical in creating a visually captivating, functional, and sustainable outdoor space that meets the client’s goals and enhances the surrounding environment.
Common Techniques Used in Landscaping Architecture
Landscaping architecture employs a variety of techniques to create visually appealing and functional outdoor spaces. These techniques draw from principles of design, horticulture, and construction, and are used to enhance the overall aesthetic and functionality of the landscape. Here are some common techniques used in landscaping architecture:
- Plant Selection and Arrangement: Choosing the right plants for a landscape is crucial in creating a visually appealing and sustainable design. Landscape architects consider factors such as climate, soil conditions, and maintenance requirements when selecting plants. They also take into account the color, texture, and form of plants to create visually dynamic and harmonious arrangements.
- Hardscaping: Hardscaping refers to the use of non-living elements in the landscape, such as pathways, walls, and structures. Techniques such as the use of different materials (e.g., stone, wood, or concrete), patterns, and textures can be employed to create visually striking hardscape features. Skillfully incorporating hardscapes into the landscape helps define spaces, create visual interest, and provide functionality.
- Grading and Drainage: Proper grading and drainage are essential elements in landscaping architecture. Landscape architects use techniques such as contouring the land, creating slopes, and installing drainage systems to ensure proper water runoff and prevent issues such as erosion or pooling. Thoughtful grading and drainage techniques contribute to the longevity and health of the landscape.
- Outdoor Lighting: Lighting is a powerful tool in enhancing the aesthetics and functionality of outdoor spaces. Landscape architects use lighting techniques to highlight architectural features, create ambiance, and extend the usability of the landscape into the evening. Techniques such as uplighting, downlighting, and pathway lighting can be used to create various lighting effects that enhance the overall design.
- Water Features: Water features such as ponds, fountains, and waterfalls add a sense of tranquility and movement to the landscape. Landscape architects use techniques such as proper placement, circulation, and filtration systems to create visually appealing and sustainable water features. Incorporating water features can help create focal points, mask noise, and attract wildlife.
- Terracing and Retaining Walls: In landscapes with varying elevations, terracing and retaining walls are commonly used techniques to create level areas for different activities. These techniques involve the construction of walls or terraces using various materials, such as stone or concrete blocks. Terracing can enhance the visual appeal of the landscape, create functional spaces, and prevent soil erosion.
- Edging and Borders: Edging and border techniques define and separate different areas within the landscape. Landscape architects use materials such as stone, wood, or metal to create distinct edges around flower beds, pathways, or other landscape features. Edging and borders create clean lines, highlight design elements, and help organize the landscape into distinct zones.
- Xeriscaping and Sustainable Design: Xeriscaping is a technique that focuses on water conservation and the use of drought-tolerant plants. Landscape architects utilize xeriscaping techniques such as proper soil preparation, efficient irrigation, and strategic plant selection to create sustainable and water-efficient landscapes. These techniques help reduce water consumption, maintenance requirements, and promote environmental stewardship.
- Sculpture and Art Installations: The incorporation of sculptures, art installations, and other artistic elements adds an extra layer of creativity and visual interest to the landscape. Landscape architects use techniques such as strategic placement, scale considerations, and complementary materials to showcase art within the natural environment. Sculptures and art installations become focal points and stimulate the senses in the landscape.
- Seasonal Plantings and Color Schemes: Using seasonal plantings and color schemes is a technique that adds vibrancy and visual interest to the landscape throughout the year. Landscape architects strategically select plants that bloom or change foliage in different seasons, creating dynamic displays of color and texture. Techniques such as color harmonization, contrasting hues, and careful plant placement contribute to visually striking landscapes.
These are just a few of the many techniques employed in landscaping architecture to create beautiful and functional outdoor spaces. Landscape architects use their expertise and creativity to combine these techniques, tailoring them to the specific goals and needs of each project. The result is a landscape that not only captivates the eye but also provides a harmonious and enjoyable environment.
Sustainable Landscaping Practices
Sustainable landscaping practices are vital in promoting environmental stewardship, conserving resources, and creating landscapes that are both beautiful and ecologically responsible. These practices prioritize long-term sustainability, biodiversity, and the preservation of natural resources. Here are some key sustainable landscaping practices:
- Water Conservation: Conserving water is a critical aspect of sustainable landscaping. Techniques such as installing efficient irrigation systems, incorporating drought-tolerant plants, and practicing proper watering techniques, such as deep watering and mulching, help reduce water consumption in the landscape. Capturing and reusing rainwater through rain barrels or cisterns is another effective method of water conservation.
- Native Plants: Incorporating native plants into the landscape is essential for supporting biodiversity and promoting a healthy ecosystem. Native plants are adapted to local climate, soil conditions, and pest resistance, requiring less water, fertilizers, and pesticides. They provide habitats for native wildlife, attract pollinators, and contribute to the overall ecological balance of the landscape.
- Soil Improvement: Healthy soil is the foundation of a sustainable landscape. Practices such as composting, adding organic matter, and minimizing chemical inputs help improve soil structure and fertility. Healthy soil supports plant growth, improves water infiltration, and reduces the need for synthetic fertilizers and pesticides.
- Plant Diversity: Including a variety of plant species in the landscape promotes resilience and reduces the risk of pests and diseases. Biodiverse landscapes are visually appealing and contribute to the overall health of the ecosystem. Planting a mix of trees, shrubs, perennials, and groundcovers creates habitats for different species, enhances pollination, and improves overall ecosystem functioning.
- Reduced Chemical Use: Minimizing the use of chemicals, such as synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, is crucial in sustainable landscaping. Integrated Pest Management (IPM) practices focus on biological control methods, cultural practices, and the use of organic or natural alternatives to manage pests and diseases effectively while reducing chemical inputs. This promotes a healthier environment for humans, wildlife, and beneficial insects.
- Wildlife Habitat Creation: Designing landscapes that provide habitat for wildlife is an essential aspect of sustainable landscaping. Incorporating elements such as bird feeders, birdhouses, butterfly gardens, and native plantings that provide food and shelter attract and support local wildlife. These habitats contribute to biodiversity conservation and create opportunities for wildlife observation and enjoyment.
- Recycling and Waste Management: Sustainable landscaping practices include proper waste management and recycling. Grass clippings, leaves, and organic debris can be composted and used as natural fertilizers. Recycling materials such as rocks, bricks, or wood for hardscaping elements reduces waste and promotes resource conservation. Using recycled materials for mulch, decking, or furniture further enhances sustainability efforts.
- Energy Efficiency: Integrating sustainable technologies and practices into the landscape design can improve energy efficiency. Techniques such as strategic placement of trees for shade, using reflective materials for hardscaping to reduce heat absorption, and the installation of solar-powered lighting can reduce energy consumption and create a more sustainable outdoor environment.
- Education and Outreach: Promoting awareness and educating others on sustainable landscaping practices is vital for broader adoption and positive environmental impact. Sharing knowledge, organizing workshops, and engaging with the community cultivates a culture of sustainable landscaping and encourages responsible practices in outdoor environments.
Sustainable landscaping practices not only benefit the environment but also create landscapes that are cost-effective, resilient, and visually appealing. By integrating these practices into landscape design and maintenance, we can create outdoor spaces that harmonize with nature, conserve resources, and contribute to the overall well-being of our planet.
Notable Landscape Architects
The field of landscape architecture has seen the contributions of many talented and innovative professionals who have shaped the discipline and left a lasting impact on the design industry. Their work has ranged from iconic public spaces to private gardens, showcasing their creativity, vision, and commitment to creating harmonious outdoor environments. Here are a few notable landscape architects:
- Frederick Law Olmsted: Considered the father of American landscape architecture, Frederick Law Olmsted is renowned for his designs of iconic public spaces, including Central Park in New York City and the Emerald Necklace parks in Boston. His landscapes were designed to provide accessible green spaces for all to enjoy, emphasizing the importance of nature in urban environments.
- André Le Nôtre: André Le Nôtre was a French landscape architect known for his work in the 17th century, particularly in the creation of the elaborate gardens at the Palace of Versailles. His designs featured grand axial perspectives, geometric patterns, and intricate water features, elevating landscape design to an art form.
- Thomas Church: Thomas Church was a prominent American landscape architect known for his innovative designs during the mid-20th century. His approach emphasized the integration of indoor and outdoor spaces, creating outdoor “rooms” that seamlessly blended with the surrounding architecture. His designs influenced the modernist movement in landscape architecture.
- Roberto Burle Marx: Roberto Burle Marx, a Brazilian landscape architect, was a pioneer in the use of native plants and modernist design principles. His work showcased the vibrant colors and textures of Brazilian flora, and he is known for his iconic designs for the Roberto Burle Marx Park in Rio de Janeiro and the Copacabana Beach promenade.
- Mihael Blanuša: Mihael Blanuša is a contemporary landscape architect known for his innovative and sustainable approaches to design. He is recognized for his emphasis on ecological restoration and the use of native plants in his projects. Blanuša’s work focuses on creating environmentally responsible landscapes that provide both beauty and ecological benefits.
- Gustafson Porter + Bowman: Gustafson Porter + Bowman is a renowned landscape architecture firm recognized for their contemporary designs that blend nature, art, and urban environments. Their projects include the Diana, Princess of Wales Memorial Fountain in London and the Valencia Parque Central in Spain. The firm’s work emphasizes integration with the surrounding landscape and a commitment to sustainability.
These landscape architects represent a small sample of the influential designers who have made significant contributions to the field. Their work exemplifies the breadth and diversity of landscape architecture, showcasing how it can transform outdoor spaces into inspiring and harmonious environments that enrich people’s lives and promote the connection between nature and the built environment.
Conclusion
Landscaping architecture is a dynamic and multidisciplinary field that blends art, science, and sustainability to create visually captivating and functional outdoor spaces. It encompasses a wide range of elements, principles, and techniques that come together to transform ordinary landscapes into extraordinary ones.
Throughout history, the practice of landscaping architecture has evolved, drawing inspiration from various cultures and time periods. From ancient civilizations to modern-day designers, landscape architects have left their mark on the world through their creativity, innovation, and commitment to enhancing the natural environment.
The importance of landscaping architecture cannot be understated. It enhances the beauty and aesthetics of outdoor spaces, improves environmental quality, and promotes community interaction. Sustainable landscaping practices play a vital role in conserving resources, supporting biodiversity, and creating landscapes that are both visually striking and ecologically responsible.
The process of landscape design requires careful planning, site analysis, and collaboration with clients and other professionals. Each step in the design process is crucial in creating a landscape that meets the client’s goals and maximizes the potential of the site.
Notable landscape architects have left a lasting legacy through their iconic designs and innovative approaches. From Frederick Law Olmsted and his transformative work in Central Park to contemporary designers like Mihael Blanuša and his emphasis on ecological restoration, these designers have shaped the field and inspired generations of landscape architects.
As we continue to navigate urbanization, environmental challenges, and the need for sustainable design, the role of landscape architecture becomes increasingly important. By integrating the principles of unity, balance, functionality, and sustainability into our outdoor spaces, we can create landscapes that are not only visually stunning but also support the well-being of individuals and communities.
In conclusion, landscaping architecture is an art form that harmonizes with nature, contributing to the beauty, functionality, and sustainability of our outdoor environments. It is an essential profession that combines creativity, expertise, and a deep appreciation for the natural world, resulting in landscapes that enrich our lives and foster a deep connection to the environment around us.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is Landscaping Architecture
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.













0 thoughts on “What Is Landscaping Architecture”