Home>Garden Essentials>What Is Urban Infill Development


Garden Essentials
What Is Urban Infill Development
Modified: March 7, 2024
Discover the concept of urban infill development and how it fosters sustainable growth. Learn how incorporating garden spaces enhances livability and promotes environmental awareness.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
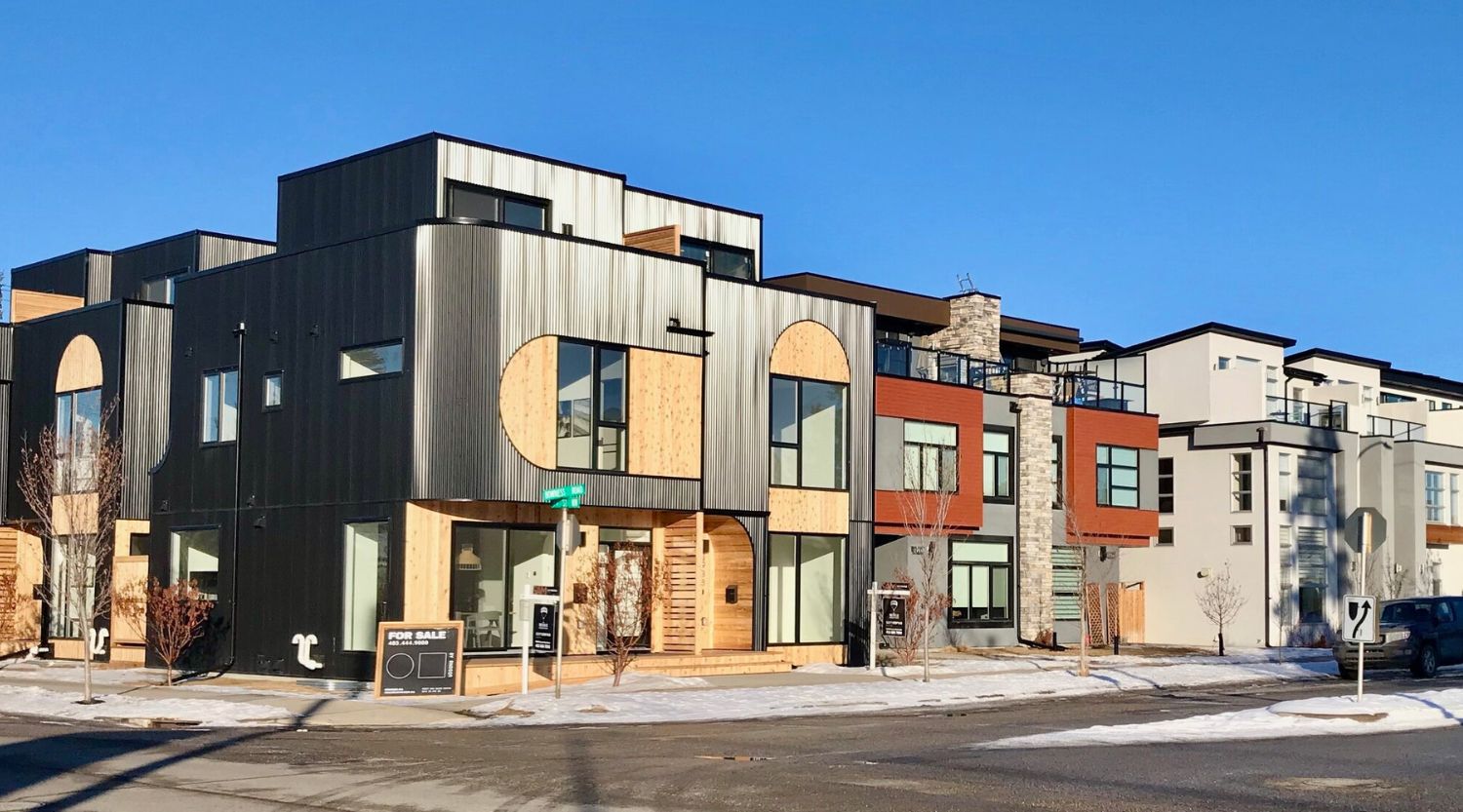
Welcome to the world of urban infill development, where creativity and innovation intersect with the ever-evolving needs of our cities. In this article, we will explore the concept of urban infill development, its definition, and the benefits and challenges it brings. Urban infill development is a vital approach to sustainable city growth, supporting the efficient use of existing land and resources. By revitalizing underutilized or abandoned spaces within established urban areas, it helps create vibrant and livable communities.
Urban infill development involves the redevelopment of vacant or underutilized land within already developed urban areas. Instead of expanding into greenfield sites on the outskirts of cities, infill development focuses on making more efficient use of existing urban spaces. This includes the redevelopment of brownfields, the conversion of industrial sites into mixed-use developments, and the repurposing of abandoned buildings for residential or commercial purposes.
One of the key benefits of urban infill development is its ability to support sustainable growth. By utilizing existing infrastructure, such as roads, utilities, and public transportation networks, infill projects reduce the need for costly new infrastructure development and decrease the strain on environmental resources. This approach minimizes urban sprawl, conserves open spaces, and promotes walkability and public transit usage.
Additionally, urban infill development can contribute to the economic revitalization of urban areas. By breathing new life into underutilized spaces, these projects create opportunities for new businesses, job creation, and increased tax revenues. The development of mixed-use projects in infill locations further enhances the vibrancy of urban communities, offering a blend of residential, commercial, and recreational spaces all within close proximity.
However, urban infill development also poses its fair share of challenges. The limited availability of land in urban areas, along with the higher cost of acquiring and developing infill sites, can make these projects financially challenging. Additionally, navigating through complex zoning regulations and community resistance to change can be time-consuming and cumbersome.
When undertaking an urban infill development project, there are several factors to consider. The site’s location, accessibility, and existing infrastructure are crucial in determining its suitability for development. Conducting a thorough feasibility study and engaging with stakeholders and the local community are essential steps to ensure a successful outcome.
In the following sections, we will delve into the strategies for successful urban infill development, examine case studies of notable projects, and conclude with a summary of the benefits and future potential of this approach.
Key Takeaways:
- Urban infill development repurposes unused city spaces, creating vibrant communities and reducing environmental impact. It faces challenges like limited land availability and zoning regulations, but benefits outweigh obstacles.
- Successful urban infill projects require thoughtful planning, community engagement, and sustainable design. Examples like The High Line in NYC and Kings Cross Central in London showcase the transformative power of infill development.
Read more: What Is An Infill Development Site
Definition of Urban Infill Development
Urban infill development refers to the process of revitalizing and repurposing underutilized or vacant land within existing urban areas. Instead of expanding cities outward into greenfield sites, infill development focuses on maximizing the use of available space within established urban regions.
It involves the redevelopment of brownfields, adaptive reuse of existing buildings, and the transformation of abandoned or vacant lots into vibrant and functional spaces. Urban infill development aims to create sustainable, mixed-use communities that meet the evolving needs of residents, businesses, and the broader urban ecosystem.
Key characteristics of urban infill development include:
- Density: Infill projects typically aim to increase the density of an area by maximizing land use. This can include adding multi-story buildings, mixed-use developments, or increasing the number of residential units on a given parcel of land.
- Existing Infrastructure: Infill development leverages existing infrastructure such as roads, utilities, and public transportation systems. By utilizing these resources, it reduces the need for costly new infrastructure and promotes increased walkability and access to amenities.
- Mixed-Use Spaces: Infill projects often incorporate a mix of residential, commercial, and recreational spaces within a compact area. This mix of land uses helps create vibrant and dynamic communities that cater to diverse needs and preferences.
- Sustainability: Urban infill development promotes sustainable growth by reducing urban sprawl, conserving open spaces, and minimizing the environmental impact associated with new construction on undeveloped land.
- Collaboration: Successful infill development requires collaboration among various stakeholders, including developers, local communities, government bodies, and environmental organizations. Engaging with these groups ensures that projects align with community needs and values.
Urban infill development plays a crucial role in revitalizing older urban neighborhoods, repurposing unused spaces, and creating dynamic urban environments. By breathing new life into underutilized areas, these projects contribute to the economic, social, and environmental sustainability of cities. They help alleviate urban sprawl, promote public transportation utilization, and create walkable communities that foster a sense of belonging and connectivity.
As cities continue to grow and evolve, urban infill development will become increasingly important in meeting the housing, commercial, and recreational needs of residents while ensuring the efficient use of resources. By repurposing existing urban land, infill development supports the creation of vibrant and sustainable communities that thrive in today’s fast-paced urban environments.
Benefits of Urban Infill Development
Urban infill development offers a wide range of benefits for both the community and the environment. By reimagining and repurposing underutilized spaces within established urban areas, infill projects contribute to the creation of vibrant, sustainable, and thriving communities. Here are some key benefits of urban infill development:
- Sustainable Land Use: Infill development focuses on making efficient use of existing land and infrastructure, reducing the need for urban sprawl and the consumption of undeveloped land on the outskirts of cities. By utilizing underutilized areas, infill projects help preserve open spaces, agricultural land, and natural habitats, promoting a more sustainable approach to development.
- Revitalization of Neighborhoods: Urban infill projects can breathe new life into older neighborhoods, helping to revitalize and rejuvenate communities. By redeveloping vacant lots, abandoned buildings, or brownfield sites, infill development brings economic investment, new businesses, and job opportunities to a neighborhood, enhancing its overall desirability and quality of life for residents.
- Increased Housing Options: Infill development provides opportunities to increase the supply of housing in high-demand urban areas. By developing multi-story residential buildings or repurposing existing structures for residential use, infill projects help address housing shortages and offer diverse housing options to accommodate a variety of needs and preferences.
- Enhanced Walkability and Connectivity: Infill development often focuses on creating mixed-use spaces that blend residential, commercial, and recreational elements. This approach promotes walkability and reduces dependency on automobiles, as essential amenities and services are within close proximity. Improved connectivity through the integration of public transportation infrastructure further enhances accessibility and reduces traffic congestion.
- Economic Growth and Job Creation: Urban infill development stimulates economic growth by attracting new businesses, creating job opportunities, and generating increased tax revenues for local governments. The activation of previously underutilized or abandoned spaces can act as a catalyst for economic activity, supporting local businesses, fostering entrepreneurship, and driving investment in the area.
- Preservation of Cultural Heritage: Infill development offers opportunities to repurpose and preserve historically significant buildings and sites, helping to maintain a community’s cultural heritage and character. By integrating the old with the new, infill projects contribute to the conservation of architectural and historical landmarks, creating a sense of place and preserving a city’s unique identity.
By capitalizing on the existing urban fabric, urban infill development maximizes the use of resources, promotes sustainable growth, and supports the creation of vibrant and livable communities. It addresses the challenges associated with urban sprawl, promotes efficient land use, and enhances the overall quality of life for residents. Through a thoughtful and community-driven approach, infill development has the potential to transform underutilized spaces into thriving, inclusive, and sustainable urban environments.
Challenges of Urban Infill Development
While urban infill development offers numerous benefits, it also comes with its fair share of challenges. These challenges often require careful planning, collaboration, and innovative solutions to overcome. Here are some key challenges associated with urban infill development:
- Land Availability and Cost: Finding suitable land for infill development within established urban areas can be a significant challenge. The limited availability of vacant or underutilized land, coupled with the higher costs associated with acquiring and developing these sites, can make infill projects financially challenging.
- Zoning and Regulatory Hurdles: Navigating complex zoning regulations, building codes, and other regulatory constraints can be a time-consuming and challenging process for infill developers. Infill projects often need to comply with specific height restrictions, setbacks, and other land-use regulations that may differ from surrounding areas.
- Community Resistance to Change: Infill development projects often face resistance from the local community, especially when they involve changes to the existing neighborhood fabric or introduce higher-density developments. Community engagement and transparent communication are crucial to address concerns and build support for infill projects.
- Infrastructure Upgrades: Infill development may require upgrades to existing infrastructure, such as roads, utilities, and public transportation systems, to accommodate increased density and population. Coordinating these upgrades with local authorities and utility companies can be complex and may add to the overall cost and timeline of an infill project.
- Environmental Considerations: Infill development should carefully consider environmental factors, especially when repurposing brownfield sites or areas with existing contamination. Site remediation, waste management, and sustainable design practices may be necessary to ensure the safety and sustainability of the development.
- Community and Public Services: The increased population density associated with infill development can put pressure on existing community and public services, such as schools, healthcare facilities, and parks. Ensuring that these services can accommodate the additional demand is crucial to maintain the quality of life for residents.
Addressing these challenges requires a comprehensive and collaborative approach that involves developers, local government entities, community stakeholders, and environmental organizations. Engaging with the community, conducting feasibility studies, and working closely with regulatory bodies can help mitigate potential hurdles and ensure the success of urban infill projects.
Despite the challenges, the benefits of urban infill development far outweigh the obstacles. With thoughtful planning, innovative design, and community engagement, infill projects can create sustainable, vibrant, and inclusive urban spaces that meet the needs of today while preserving the heritage and character of established neighborhoods.
Factors to Consider in Urban Infill Development
Urban infill development requires careful consideration of various factors to ensure its success and alignment with the surrounding community. By addressing these factors, developers can create sustainable, functional, and cohesive infill projects that enhance the urban environment. Here are key factors to consider in urban infill development:
- Location: The location of an infill development plays a crucial role in its viability and success. Factors to consider include proximity to amenities, public transportation, schools, and employment centers. Choosing a location that aligns with the needs and lifestyles of future residents is essential.
- Site Feasibility: Conducting a thorough feasibility study is crucial to identify any site-specific challenges that may impact the development. This includes assessing the site’s infrastructure, environmental conditions, zoning restrictions, and any potential regulatory hurdles that need to be navigated.
- Community Engagement: Engaging with the local community and stakeholders early in the planning process is essential to gather input, address concerns, and build support for the infill project. This collaborative approach fosters positive relationships and ensures that the development aligns with local needs and values.
- Design and Architecture: The design of an infill project should carefully consider the existing architectural character and scale of the surrounding neighborhood. Thoughtful design can help seamlessly integrate the development into its urban fabric while ensuring functional and visually appealing spaces for residents and users.
- Infrastructure Integration: Assessing the capacity of existing infrastructure, such as roads, utilities, and public transportation, is crucial to ensure that the development can be accommodated without overburdening the existing systems. Coordination with local authorities and utility companies for necessary upgrades or additions is essential.
- Sustainability: Embracing sustainable design principles in infill development contributes to the long-term environmental and economic viability of the project. This includes incorporating green building practices, utilizing renewable energy sources, implementing water conservation measures, and prioritizing efficient land use.
- Neighborhood Compatibility: The compatibility of the infill project with the surrounding neighborhood is critical for its success and acceptance. Consideration should be given to factors such as building height, setbacks, architectural style, and density, ensuring that the development harmonizes with the existing community and contributes positively to its character.
- Phasing and Implementation: In larger-scale infill projects, careful phasing of development and implementation strategies can help manage construction disruption, minimize community impact, and ensure that necessary amenities and services are delivered in tandem with the project’s progress.
By considering these factors in the planning and design stages of urban infill development, developers can create projects that are sensitive to the needs and desires of the community while maximizing the potential of underutilized urban spaces. This comprehensive approach fosters sustainable, vibrant, and livable communities that thrive in today’s evolving urban landscape.
Strategies for Successful Urban Infill Development
Successful urban infill development requires a thoughtful and strategic approach that takes into account the unique characteristics and challenges of each project. By implementing the following strategies, developers can maximize the potential of underutilized urban spaces and create successful infill projects:
- Comprehensive Planning: Thorough planning is the foundation for a successful infill development project. This includes conducting extensive research, analyzing market demand, and understanding the needs and preferences of the target community. By gathering and analyzing data, developers can make informed decisions about the project’s size, design, and amenities.
- Community Engagement: Engaging with the local community and stakeholders is crucial for building support and gathering valuable input. Hosting public meetings, workshops, and design charrettes can help incorporate community feedback into the project’s design and ensure that the development aligns with the community’s aspirations and values.
- Sustainable Design: Incorporating sustainable design principles into infill projects is essential for their long-term success. This includes features such as energy-efficient buildings, green spaces, sustainable stormwater management, and the use of recycled materials. Sustainable design practices not only benefit the environment but also enhance the quality of life for residents.
- Mixed-Use Development: Integrating mixed-use components, such as residential, retail, and office spaces, within an infill project can create a vibrant and cohesive community. This promotes walkability, reduces the need for commuting, and enhances the accessibility of essential services and amenities for residents.
- Preserve and Enhance Existing Assets: Whenever possible, infill development should seek to preserve and enhance existing historic or architecturally significant buildings. Adaptive reuse and renovation projects can bring new life to old structures, contributing to the character and charm of the neighborhood while reducing waste and preserving local heritage.
- Collaboration and Partnerships: Collaboration with various stakeholders, including local government, nonprofit organizations, and private entities, can provide valuable resources and expertise. Public-private partnerships can be particularly effective in addressing infrastructure needs, securing funding, and navigating regulatory processes.
- Phased Development: Complex infill projects can benefit from a phased development approach. This allows for the gradual implementation of different stages of the project, reducing financial risks and providing opportunities for adjustments based on evolving market conditions and community feedback.
- Attention to Detail: Paying attention to the small details can greatly impact the success of an infill project. Factors such as attractive landscaping, pedestrian-friendly design, and high-quality materials contribute to the overall aesthetic and desirability of the development.
Implementing these strategies requires a comprehensive understanding of the local context, market dynamics, and community needs. By incorporating these considerations into the planning and design stages, developers can create successful urban infill projects that contribute to the revitalization and sustainable growth of cities.
When considering urban infill development, it’s important to research local zoning laws and regulations to ensure your project complies with the area’s requirements.
Case Studies of Urban Infill Development Projects
Examining successful case studies of urban infill development projects can provide insights into the strategies and approaches that have yielded positive outcomes. Here are two notable examples:
1. The High Line – New York City, USA
The High Line is a prime example of transforming an abandoned, elevated railway into a thriving urban park. Located in Manhattan, New York City, this iconic project revitalized a historic structure and transformed it into a unique green space that attracts millions of visitors each year.
The project involved the adaptive reuse of the elevated railway tracks, creating a linear park that spans 1.45 miles (2.33 kilometers) through the Chelsea neighborhood. The design incorporates lush landscaping, seating areas, art installations, and stunning views of the city skyline.
The High Line has had a transformative effect on the surrounding neighborhood, attracting new businesses, boosting property values, and fostering community engagement. The project successfully demonstrates how repurposing existing infrastructure can create vibrant public spaces that enhance the urban fabric and promote economic revitalization.
2. Kings Cross Central – London, UK
Kings Cross Central is a large-scale urban infill development project located in the heart of London. The project transformed an underutilized former industrial site into a vibrant, mixed-use neighborhood that seamlessly integrates residential, commercial, and public spaces.
The development consists of a master-planned community that spans 67 acres (27 hectares) and includes residential units, office spaces, retail establishments, educational facilities, and public squares. It prioritizes sustainability by incorporating energy-efficient buildings, green spaces, and a focus on active transportation.
Kings Cross Central has not only brought much-needed housing, job opportunities, and amenities to the area but has also preserved and repurposed heritage buildings, such as the iconic Granary Building. The project serves as a model for sustainable and inclusive urban development that successfully balances the preservation of historical character with modern, innovative design.
These case studies showcase the potential and benefits of urban infill development. They demonstrate how thoughtful planning, innovative design, community engagement, and adaptive reuse can transform underutilized spaces into vibrant, sustainable, and inclusive urban environments.
Read more: What Is Urban Garden
Conclusion
Urban infill development plays a crucial role in creating sustainable, vibrant, and thriving cities. By repurposing underutilized or vacant land within existing urban areas, infill projects maximize land use, preserve open spaces, and minimize the environmental impact associated with urban sprawl. These projects contribute to the economic revitalization of neighborhoods, increase housing options, and enhance community connectivity and walkability.
While urban infill development comes with its challenges, such as land availability, regulatory hurdles, and community resistance, these can be overcome through comprehensive planning, community engagement, and sustainable design practices. Engaging with stakeholders, collaborating with local authorities, and incorporating feedback from residents are essential to ensure that infill projects align with community needs and values.
Successful infill projects require careful consideration of factors such as location, site feasibility, sustainable design, infrastructure integration, and neighborhood compatibility. By embracing mixed-use development, preserving existing assets, and employing phased planning, developers can create projects that maximize the potential of underutilized urban spaces and meet the evolving needs of their communities.
Case studies like The High Line in New York City and Kings Cross Central in London demonstrate the transformative power of urban infill development. These projects have revitalized abandoned spaces, created vibrant public areas, and attracted economic investment, all while preserving the character and heritage of their respective neighborhoods.
As cities continue to grow and face the challenges of limited resources and sustainability, urban infill development will become increasingly important. By reimagining and repurposing existing urban spaces, infill projects contribute to creating more livable, sustainable, and inclusive cities. With careful planning, collaboration, and innovative design, urban infill development has the potential to shape the future of our urban landscapes and foster vibrant communities for generations to come.
References
- Sullivan, D., & Campanella, T. J. (2017). Urban Infill Development. Oxford Research Encyclopedia of American History.
- Pyrzycka, K., & Marinos-Kouris, D. (2016). Urban infill development: towards more sustainable cities. Sustainability, 8(3), 215.
- AlWaer, H. (2018). Urban infill: creating sustainable, inclusive and compact cities. Cities & Health, 2(1), 1-3.
- Burchell, R. W., & Poblete, M. D. (2014). The design and planning of urban infill developments: an international review. Journal of Urban Design, 19(1), 51-78.
- Wilkinson, S. (2019). Urban infill for sustainable growth. Springer International Publishing.
- Beasley, M., Burbidge, D., & Coates, P. (2013). Hidden densities, the value of infill development in established urban areas. Research Report No. 03-13, Australian Housing and Urban Research Institute Limited.
- Lott, B., & Haas, T. (2017). Urban infill as a catalyst for sustainable urban regeneration. Sustainable Cities and Society, 28, 322-334.
- Faludi, A. (Ed.). (2015). Sea Change: Proactive Urban Planning and Design for Resilient Waterfronts. IOS Press.
- García, E., & Estébanez, L. (2016). Retrofitting the world’s suburban business districts as innovative urban environments. Cities, 59, 40-53.
- Németh, J., Lang, T., & Fehér, B. (2017). Idea generation and screening methods for urban infill research and development. Procedia Engineering, 198, 22-30.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is Urban Infill Development
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.












0 thoughts on “What Is Urban Infill Development”