Home>diy>Building & Construction>What Is Infill Construction
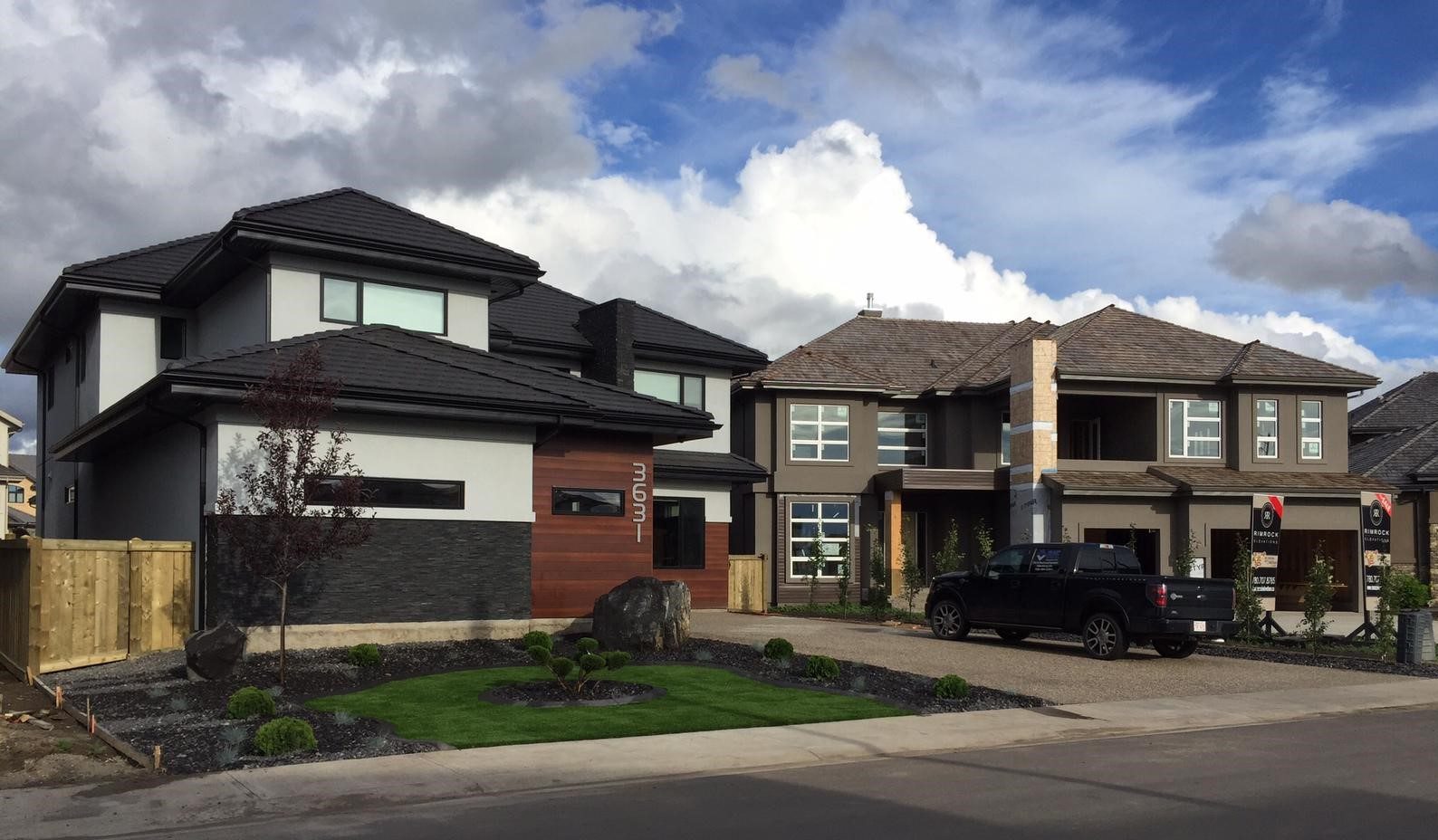


Building & Construction
What Is Infill Construction
Modified: December 7, 2023
Discover the benefits and process of infill construction in building construction. From maximizing land use to creating sustainable communities, infill construction is a game-changer in urban development.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Infill construction is a building practice that involves the development of vacant or underutilized spaces within existing urban areas. It is a strategic approach to maximizing land use and increasing the density of urban environments. Infill construction projects aim to fill in gaps between existing structures and can encompass anything from small-scale developments on individual lots to large-scale revitalization projects in declining neighborhoods.
In recent years, there has been a growing emphasis on infill construction as a sustainable and efficient solution for urban development. Instead of expanding into undeveloped land on the outskirts of cities, infill construction utilizes existing infrastructure and resources to create vibrant, walkable communities. This approach not only helps to preserve natural habitats and reduce the pressure on transportation networks, but it also contributes to the revitalization of urban centers and promotes a sense of community.
Additionally, infill construction plays a significant role in addressing the housing shortage in many urban areas. As populations continue to grow, demand for affordable housing has increased. Infill projects provide an opportunity to optimize land utilization and create housing options that are more accessible both in terms of location and cost. The creation of mixed-use developments, which combine residential and commercial spaces, further contributes to the vibrancy and livability of urban communities.
However, infill construction is not without its challenges. Redeveloping existing urban spaces can be complex and requires careful planning and coordination. The availability of suitable sites, potential environmental issues, and existing zoning regulations may pose obstacles to the successful implementation of infill projects. Additionally, the impact on existing communities and infrastructure needs to be carefully managed to ensure a harmonious integration.
In this article, we will explore the definition, benefits, challenges, and types of infill construction. We will also discuss the factors to consider when undertaking an infill construction project and highlight examples of successful projects. By the end, you will have a comprehensive understanding of infill construction and its significance in sustainable urban development.
Key Takeaways:
- Infill construction maximizes land use, promotes sustainability, and revitalizes urban areas by strategically developing vacant spaces, addressing housing needs, and preserving community character. It offers a sustainable solution for efficient urban development.
- Successful infill construction projects, such as The High Line in New York City and The Pearl District in Portland, demonstrate the positive impact of well-executed infill projects in creating vibrant, sustainable, and community-centric urban spaces.
Read more: What Is An Infill Speed
Definition of Infill Construction
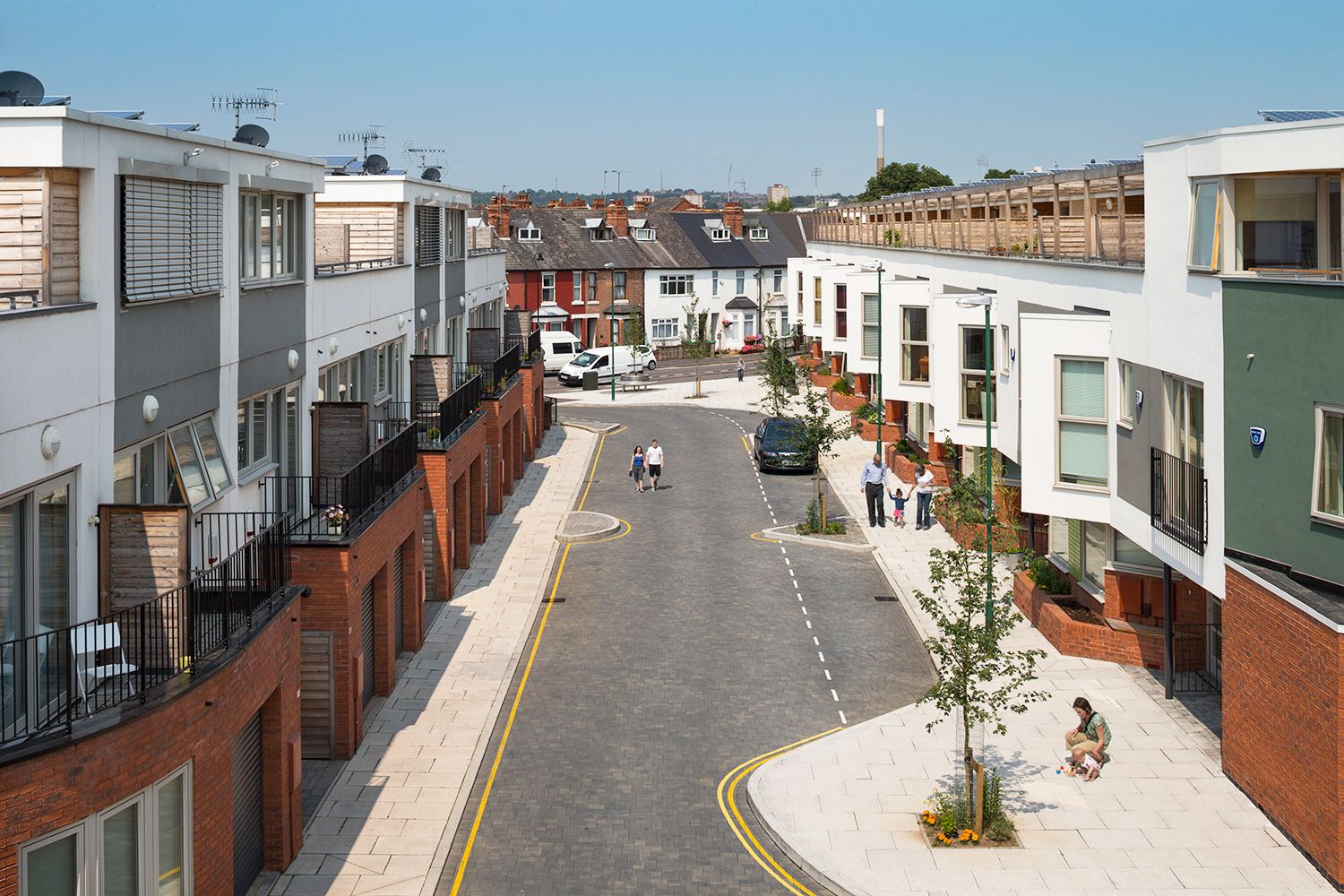
Infill construction refers to the development of new buildings or structures within existing urban areas, typically in spaces that are vacant, underutilized, or considered “gaps” between existing structures. Unlike traditional urban development that focuses on expanding into undeveloped areas on the outskirts of cities, infill construction maximizes the use of existing infrastructure and land to create vibrant, sustainable communities.
At its core, infill construction involves the intentional filling of vacant or underused spaces within already established urban environments. These spaces can range from empty lots, abandoned buildings, outdated parking areas, or even the redevelopment of existing structures. The goal is to utilize these spaces efficiently and create new opportunities for residential, commercial, or mixed-use development.
One of the defining characteristics of infill construction is its focus on densification. By strategically infilling vacant spaces, developers aim to increase the population density of urban areas, creating more compact and walkable communities. Through careful planning and design, infill projects can help revitalize declining neighborhoods, improve connectivity, and promote a sense of place and identity.
Infill construction is often seen as an integral part of sustainable urban development. By reusing existing infrastructure and leveraging available resources, infill projects minimize the need for additional infrastructure expansion and reduce the pressure on natural landscapes. Additionally, infill construction supports the efficient use of energy and resources by capitalizing on existing utilities, transportation networks, and community amenities.
It is important to note that infill construction is not solely limited to residential development. While creating new housing options is a significant aspect, infill projects can also incorporate commercial spaces, parks, community centers, and other amenities that enhance the overall livability and functionality of the urban environment.
In summary, infill construction refers to the strategic development of new buildings within existing urban areas, utilizing vacant or underutilized spaces. It aims to increase population density, promote sustainability, and contribute to the revitalization of urban communities. By optimizing land use and leveraging existing infrastructure, infill construction offers an efficient and adaptive approach to urban development.
Benefits of Infill Construction
Infill construction offers numerous benefits that contribute to sustainable urban development and the overall well-being of communities. Let’s explore some of the key advantages of infill construction:
- Optimized Land Use: Infill construction maximizes the utilization of existing land within urban areas. By developing vacant or underutilized spaces, it helps avoid sprawl and minimizes the need for expanding into undeveloped areas. This approach allows for the efficient use of valuable urban land, making the most of limited resources.
- Sustainable Development: Infill construction is considered a more sustainable development practice compared to expanding into new areas. By leveraging existing infrastructure, utilities, and transportation networks, infill projects reduce the demand for additional resources and the environmental impact associated with developing new infrastructure. It also helps protect green spaces and preserves natural habitats by focusing on redevelopment rather than encroachment into undeveloped land.
- Enhanced Connectivity: Infill construction promotes connectivity by creating walkable neighborhoods and reducing reliance on private vehicles. By densifying urban areas, infill projects support the development of pedestrian-friendly streets and increase accessibility to public transportation, amenities, and services. This improves overall mobility, reduces traffic congestion, and enhances the quality of life for residents.
- Economic Revitalization: Infill construction plays a vital role in revitalizing declining neighborhoods and urban centers. By redeveloping vacant spaces and attracting new businesses and residents, infill projects can spark economic growth and job creation. It helps breathe new life into areas that may have suffered from disinvestment and neglect, contributing to increased property values and economic prosperity.
- Preservation of Community Character: Infill construction allows for the preservation and enhancement of the existing community fabric. By reusing or adapting existing structures, infill projects can maintain the architectural heritage and character of a neighborhood. This helps preserve the sense of place, history, and cultural identity, fostering a stronger community spirit and pride.
- Addressing Housing Needs: Infill construction provides an opportunity to address the growing need for housing in urban areas. By creating new residential units within existing neighborhoods, infill projects contribute to the diversification of housing options, including affordable housing. This helps increase housing affordability and accessibility for a range of income levels, promoting inclusivity and reducing urban sprawl.
In summary, infill construction offers a range of benefits, including optimized land use, sustainable development, enhanced connectivity, economic revitalization, preservation of community character, and addressing housing needs. By capitalizing on existing resources and infilling vacant spaces, infill projects contribute to the creation of vibrant, livable, and resilient urban communities.
Challenges of Infill Construction
While infill construction brings many benefits to urban development, it also presents a set of unique challenges that need to be addressed. Let’s explore some of the key challenges associated with infill construction:
- Site Availability: Finding suitable sites for infill construction can be a significant challenge. In built-up urban areas, available vacant spaces may be limited, and identifying suitable sites that meet the project’s requirements and align with local regulations can be a complex task. The scarcity of available land can drive up costs and pose barriers to implementing infill projects.
- Environmental Considerations: Infill construction often involves the redevelopment or repurposing of existing sites, which may have environmental contamination or face unique ecological challenges. These sites may require remediation efforts or careful management to mitigate potential risks to the environment and health of residents. Environmental assessments and compliance with regulations are crucial aspects of infill construction.
- Zoning and Regulatory Constraints: Existing zoning regulations and land use designations can present legal and regulatory challenges for infill projects. It is essential to navigate through zoning codes, building restrictions, setback requirements, and other regulatory factors that govern land use. Sometimes, outdated regulations or conflicting policies may hinder the implementation of infill projects, requiring collaboration with local authorities and stakeholders for creative solutions.
- Infrastructure Upgrades: Infill construction may require upgrades or expansions to existing infrastructure such as roads, utilities, and public facilities. Integrating new development into established neighborhoods can strain the existing infrastructure, and the local community may resist changes that may disrupt services or increase congestion. Coordinating infrastructure improvements and ensuring their capacity to support the increased population density is a critical challenge in infill construction.
- Community Impact: Infill construction has the potential to significantly impact existing communities. The construction process can lead to disruptions, noise, and inconvenience for residents, businesses, and local stakeholders. It is crucial to engage and communicate with the community throughout the project, addressing concerns, and implementing mitigation measures to minimize any negative impact on the quality of life during and after construction.
- Historic Preservation: Infill construction in areas with historical significance requires balancing the preservation of heritage structures with the need for new development. The integration of new buildings into historic neighborhoods must be done thoughtfully, respecting the architectural character and preserving the cultural value of the area. Finding a balance between preserving history and meeting contemporary design and functional requirements can be a complex challenge.
In summary, infill construction brings various challenges, including site availability, environmental considerations, zoning and regulatory constraints, infrastructure upgrades, community impact, and historic preservation. Understanding and effectively addressing these challenges is crucial for successful infill construction projects that contribute positively to urban development.
When planning an infill construction project, consider the existing infrastructure and utilities in the area to avoid potential conflicts and ensure a smooth construction process.
Types of Infill Construction
Infill construction encompasses a variety of approaches and strategies to maximize land use within existing urban areas. Let’s explore some common types of infill construction:
- Single Lot Infill: This type of infill construction involves the development of a single vacant or underutilized lot within an existing urban area. It could be the construction of a single-family home, a townhouse, or a small commercial building on a vacant plot of land.
- Rowhouse or Townhouse Development: Rowhouses or townhouses are a popular form of infill construction, especially in densely populated urban areas. They involve the construction of a series of housing units that share a common wall and are typically situated on narrow lots. This type of infill development helps optimize land use while providing multiple housing options within a limited space.
- Mixed-Use Development: Mixed-use development combines residential, commercial, and sometimes even industrial spaces within a single project. These developments can include a combination of retail shops, office spaces, residential units, and public amenities. By integrating different land uses, mixed-use developments promote walkability, reduce commuting distances, and create vibrant urban environments.
- Adaptive Reuse: Adaptive reuse involves repurposing or renovating existing buildings for new uses. This type of infill construction focuses on breathing new life into underutilized or abandoned structures, such as old warehouses, factories, or schools, by transforming them into residential, commercial, or cultural spaces.
- Brownfield Redevelopment: Brownfield redevelopment refers to the transformation of previously contaminated or environmentally compromised sites. These sites may have previously housed industrial or commercial facilities that require remediation efforts before they can be redeveloped. Brownfield infill projects help revive underutilized areas, restore contaminated land, and create new opportunities for sustainable development.
- Vertical Infill: Vertical infill involves the construction of new floors, additions, or extensions to existing buildings. This approach is commonly used in urban areas where land availability is limited, and building upwards is a practical solution to maximize space utilization. Vertical infill can be seen in the form of additional floors or rooftop extensions on existing structures.
These are just a few examples of the types of infill construction that can be implemented in urban areas. Each type offers unique opportunities and challenges, and the choice of infill construction approach depends on factors such as site characteristics, local zoning regulations, market demand, and community needs.
In summary, infill construction encompasses various types, including single lot infill, rowhouse or townhouse development, mixed-use development, adaptive reuse, brownfield redevelopment, and vertical infill. Each type contributes to maximizing land use and creating vibrant, sustainable, and well-connected urban communities.
Read more: What Is An Infill
Factors to Consider in Infill Construction
Infill construction requires careful consideration of various factors to ensure successful project implementation. Here are some key factors to consider when undertaking infill construction:
- Site Selection: Choosing the right site for infill construction is crucial. Factors to consider include site access, size, topography, environmental conditions, and proximity to amenities and transportation networks. It is essential to assess the site’s feasibility and ensure it aligns with the project’s goals and requirements.
- Community Engagement: Engaging with the local community and stakeholders is vital in infill construction. Open and transparent communication allows for the exchange of ideas, addressing concerns, and gaining community support. Working closely with residents, businesses, neighborhood associations, and local authorities helps create a sense of ownership and fosters a collaborative approach to development.
- Sustainability and Green Design: Incorporating sustainable practices and green design principles in infill construction is crucial for minimizing environmental impacts. This can include features like energy-efficient buildings, stormwater management systems, use of recycled materials, and green spaces. Implementing sustainable strategies not only benefits the environment but also enhances the overall livability and long-term value of the development.
- Infrastructure and Services: Ensuring that the existing infrastructure and services can support the increased population density is vital. It involves assessing the capacity of roads, utilities, schools, healthcare facilities, and other public services to accommodate the new development. If necessary, infrastructure upgrades and expansions may be required to meet the needs of the community. Coordination with local authorities and utility providers should be a priority.
- Design and Architecture: Thoughtful design and architecture play a significant role in the success of an infill construction project. The design should consider the surrounding context, maintain the character of the neighborhood, and respond to the needs and preferences of the community. Integrating green spaces, promoting walkability, and creating appealing streetscapes and public spaces contribute to a vibrant and cohesive development.
- Zoning and Regulatory Compliance: Understanding and complying with local zoning regulations and building codes is crucial in infill projects. It is necessary to ensure the proposed development aligns with the area’s zoning designation, setbacks, parking requirements, and other land use regulations. This may involve obtaining permits, variances, or exemptions as needed.
- Construction Considerations: The construction process should be carefully planned to minimize disruption to the community. This includes managing noise, dust, traffic, and construction waste. Implementing proper construction management practices, adhering to safety standards, and maintaining good communication with the community are essential for a successful construction phase.
- Affordability and Inclusivity: Infill construction provides an opportunity to address housing affordability and inclusivity. Consideration should be given to providing a range of housing options, including affordable housing units, to ensure that the development caters to diverse income levels. This promotes social equity and creates mixed-income communities.
These factors are crucial in guiding the planning, design, and implementation of an infill construction project. By considering these aspects, developers can create sustainable, community-centric, and well-integrated infill developments that contribute positively to the urban fabric.
Examples of Successful Infill Construction Projects
There are numerous examples of successful infill construction projects that have revitalized urban areas and created vibrant, sustainable communities. Here are a few notable examples:
- The High Line, New York City: The High Line is a prime example of successful infill construction. It transformed a disused elevated railway track on Manhattan’s West Side into a beautiful public park. This innovative project revitalized the surrounding neighborhood, attracting visitors and businesses while preserving the historic character of the railway structure.
- The Pearl District, Portland: The Pearl District in Portland, Oregon, is a prime example of adaptive reuse in infill construction. Formerly an industrial area, it has been transformed into a mixed-use neighborhood featuring reclaimed warehouses and industrial buildings converted into residential lofts, art galleries, restaurants, and shops. This successful revitalization project has become a vibrant and trendy neighborhood known for its unique character and community-centric design.
- The Battery Atlanta, Atlanta: The Battery Atlanta is a mixed-use development built adjacent to the Truist Park baseball stadium, home of the Atlanta Braves. This infill project includes residential units, office spaces, retail shops, restaurants, and entertainment venues. By integrating the development with the stadium, the Battery Atlanta has created a lively and dynamic destination that enhances the overall fan experience and stimulates economic growth in the area.
- The Central Market District, San Francisco: The Central Market District in San Francisco underwent a successful infill construction initiative to revitalize this historic area. The project involved the renovation and adaptive reuse of several existing buildings, including theaters and storefronts, as well as the construction of new residential and commercial spaces. This transformation has contributed to the rejuvenation of the neighborhood, attracting new businesses, and creating a thriving community hub.
- Pacaembu Stadium Neighborhood, São Paulo: In São Paulo, Brazil, the Pacaembu Stadium neighborhood underwent a successful infill construction project that revitalized an underutilized area. The project involved the construction of residential buildings, commercial spaces, and public amenities, transforming the neighborhood into a vibrant, pedestrian-friendly district with a mix of housing options and community services.
These examples highlight the diverse approaches and successful outcomes of infill construction projects. They have not only contributed to the economic growth and revitalization of urban areas but have also created sustainable and livable communities by leveraging existing resources and incorporating community engagement and sustainable design principles.
Each successful infill construction project is unique and tailored to its specific context and community needs. By studying and learning from these examples, developers, architects, and urban planners can gain valuable insights and inspiration for their own infill construction endeavors.
Conclusion
Infill construction is a strategic approach to urban development that maximizes land use within existing urban areas. It offers numerous benefits, including optimized land use, sustainable development, enhanced connectivity, economic revitalization, preservation of community character, and addressing housing needs. By utilizing vacant or underutilized spaces, infill construction creates vibrant, walkable communities and reduces the pressure on natural landscapes.
However, infill construction is not without its challenges. Site availability, environmental considerations, zoning constraints, infrastructure upgrades, community impact, and historic preservation are all factors that need to be carefully navigated. Successful infill projects require thoughtful planning, community engagement, and compliance with regulations to ensure their integration and compatibility with the surrounding neighborhood.
There are various types of infill construction, ranging from single lot development to mixed-use projects, adaptive reuse, and brownfield redevelopment. Each type offers unique opportunities and can be tailored to the specific context and needs of the community. Factors to consider in infill construction include site selection, community engagement, sustainability, infrastructure planning, design and architecture, zoning compliance, construction management, and affordability.
Examples of successful infill construction projects, such as The High Line in New York City, The Pearl District in Portland, The Battery Atlanta, The Central Market District in San Francisco, and the Pacaembu Stadium Neighborhood in São Paulo, showcase the positive impact that well-executed infill construction can have on urban areas. These projects have revitalized neighborhoods, created vibrant spaces, preserved historic character, and stimulated economic growth.
In conclusion, infill construction offers a sustainable and efficient solution for urban development, optimizing land use, creating vibrant communities, and addressing housing needs. By considering the factors discussed and drawing inspiration from successful projects, developers, architects, and urban planners can contribute to the creation of livable, connected, and sustainable cities for the future.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is Infill Construction
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.












0 thoughts on “What Is Infill Construction”