Home>Garden Essentials>What Vegetables Need Light To Germinate


Garden Essentials
What Vegetables Need Light To Germinate
Modified: October 18, 2024
Discover which vegetables require light to germinate and ensure a successful garden with our comprehensive guide.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Welcome to the world of gardening! Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or just starting out, understanding the fundamentals of germination is crucial for successful plant growth. While many factors come into play for successful germination, one key element that often gets overlooked is light. In this article, we will explore the importance of light during the germination process and delve into which vegetables require light and which do not.
Light is a vital element for plant growth, and it plays a crucial role in the germination process. When a seed is exposed to light, it triggers a series of reactions within the seed that kickstarts the germination process. This process is known as photomorphogenesis, where plants sense and respond to light.
During germination, light provides energy to the seed, helping it to break dormancy and grow. It also influences the production of hormones within the seed, which regulate cell growth and development. Without proper light exposure, seeds may struggle to germinate or experience stunted growth.
Now let’s dive into the specific types of vegetables that require light for successful germination. Understanding which plants need light will help you optimize your gardening practices and set up the ideal environment for your seeds to thrive.
Key Takeaways:
- Light is crucial for the germination of certain vegetables like lettuce, spinach, carrots, parsley, and celery. Understanding which vegetables need light can help you create the ideal environment for successful germination.
- Providing the right amount of light, such as moderate intensity and balanced spectrum, is essential for healthy seedling growth. Remember to monitor and adjust the light conditions to support successful germination.
Read more: What Herbs Need Light To Germinate
Importance of Light for Germination
Light is an essential factor in the germination process as it impacts various aspects of seed development. Here are some key reasons why light plays a crucial role in the germination of plants:
Photosynthesis: Light is crucial for the process of photosynthesis, where plants convert sunlight into energy. During germination, young seedlings rely on the energy produced through photosynthesis to grow and develop. Without adequate light, the plants may become weak and fail to thrive.
Seedling Growth: Light promotes healthy seedling growth by stimulating the development of chlorophyll, the pigment responsible for absorbing light energy. Chlorophyll helps the seedlings in the production of carbohydrates, which are essential for providing energy for growth and development.
Regulation of Hormones: Light exposure influences the production of hormones, such as auxins and gibberellins, in seeds. These hormones play a vital role in initiating cell elongation, which is necessary for seedling emergence. Light also helps in the regulation of other hormones that control the direction of growth and the opening of cotyledons.
Dormancy Breakage: Some seeds have built-in mechanisms to remain dormant until favorable conditions are present. Light can act as a signal for these seeds to break dormancy and start the germination process. This is particularly important for some larger seeds that require light to penetrate and activate enzymes, allowing them to sprout.
Resilience: Exposure to light during germination helps plants develop resilience to factors such as wind and changes in environmental conditions. Seedlings that receive adequate light during germination tend to have stronger stems and better overall vigor, making them more capable of withstanding environmental stressors.
Understanding the importance of light during germination can help you create the optimal conditions for your plants. Now let’s explore which varieties of vegetables specifically require light to germinate.
Vegetables that Require Light to Germinate
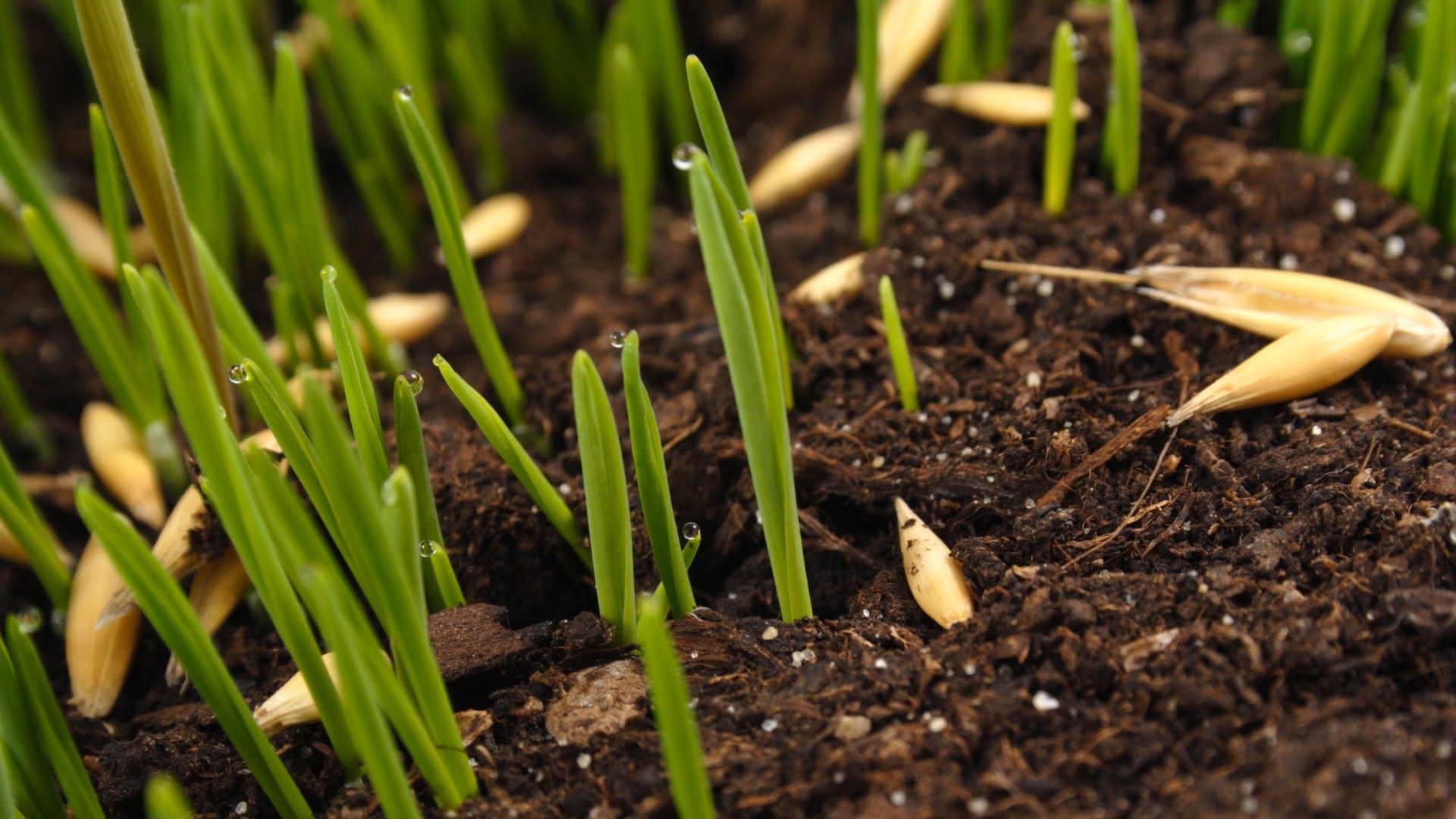
Not all vegetable seeds require light for germination, but there are certain varieties that rely on light to trigger the germination process. Here are some popular vegetables that need light to successfully sprout:
- Lettuce: Lettuce seeds are small and require light for germination. Scatter the seeds on the soil surface, lightly press them in, and keep them moist. Avoid covering them with soil as they need direct exposure to light for optimal germination.
- Spinach: Similar to lettuce, spinach seeds also need light to germinate. Sow the seeds directly on top of the soil and gently press them in. Keep the soil consistently moist until the seeds sprout.
- Carrots: Carrot seeds are relatively large and prefer exposure to light during germination. Place the seeds on the soil surface and lightly cover them with a thin layer of fine soil. Keep the soil consistently moist until the seeds germinate.
- Parsley: Parsley seeds require light for germination as well. Sprinkle the seeds on top of the soil and press them in gently. Maintain moist soil conditions until germination occurs.
- Celery: Celery seeds also need light to sprout successfully. Plant them on the soil surface and press them gently into the soil. Maintain moisture in the soil until the seeds germinate.
These are just a few examples of vegetables that require light for germination. It’s important to read the specific instructions on seed packets or do some research to determine the light requirements of the vegetables you wish to grow. Providing the right amount of light will help your seeds sprout and develop into healthy seedlings.
Vegetables that Do Not Require Light to Germinate
While some vegetables rely on light for successful germination, there are others that do not necessarily need light during this stage. These vegetables can be sown deeper into the soil or covered with a thin layer of topsoil. Here are a few examples of vegetables that can germinate in the absence of light:
- Beans: Beans, including varieties like green beans and pole beans, don’t require light for germination. Plant the seeds about an inch or two deep in the soil, ensuring good soil moisture for sprouting.
- Peas: Peas are another vegetable that can germinate without direct exposure to light. Plant the pea seeds about an inch deep in the soil and keep the soil consistently moist until germination occurs.
- Radishes: Radish seeds are relatively small and can be sown directly into the soil. Plant them about half an inch to an inch deep and keep the soil moist for successful germination.
- Beets: Beets can germinate in darkness as well. Sow the beet seeds about half an inch deep in the soil and maintain moist soil conditions for optimal sprouting.
- Onions: Onion seeds can germinate without light, but they require slightly warmer soil temperatures. Plant the seeds about half an inch deep in the soil and keep the soil consistently moist until germination occurs.
These vegetables have adapted to different types of germination environments, and their seeds can sprout even when light is not readily available. Just be sure to provide the right soil moisture levels and temperature conditions to support their germination process.
While some vegetables require light and others don’t, it’s important to remember that all plants need light once they have germinated. Light is crucial for photosynthesis and overall plant growth. So, once your vegetable seeds have sprouted, be sure to provide them with adequate light to promote healthy and vigorous growth.
Most vegetable seeds need light to germinate, so it’s important to plant them at the right depth. Check the seed packet for specific instructions on how deep to plant each type of vegetable seed.
Optimal Light Conditions for Germination
When it comes to providing light for germinating seeds, understanding the optimal conditions can greatly enhance the success rate of germination. Here are some key factors to consider:
Light Intensity: In the early stages of germination, seeds need a moderate level of light intensity. Too much direct sunlight can be overwhelming and may cause the soil to dry out quickly. Placing the seeds near a sunny window or providing them with 12-16 hours of fluorescent light per day is generally sufficient.
Light Duration: Most vegetable seeds require a minimum of 8-12 hours of light each day. Plants use light as an energy source for photosynthesis, so providing them with enough light ensures healthy growth and development. You can use a timer or keep track of the light exposure manually to maintain consistent light duration.
Light Spectrum: Different wavelengths of light have varying effects on seed germination. The blue spectrum of light promotes stem and leaf growth, making it ideal for early seedling development. Grow lights with a balanced blue and red spectrum are commonly used to provide optimal light conditions for germination.
Distance from Light Source: The distance between the light source and the seeds should be carefully considered. If the light source is too close, it may generate excessive heat and damage the tender seedlings. On the other hand, if it’s too far away, the seedlings may become leggy and weak. Finding the right balance is crucial for optimal growth.
Light vs. Darkness: Remember that some vegetables require light for germination, while others can sprout in darkness. It’s important to provide the appropriate light conditions based on the specific requirements of the vegetable you are growing. Always check the instructions on the seed packet or do some research to determine the light requirements of the particular variety.
By considering these factors and providing the optimal light conditions, you can ensure successful germination and set your seeds up for healthy growth. Monitor the seedlings closely as they emerge and adjust the lighting conditions as needed to support their development.
Read more: What Does Grass Seed Need To Germinate
Tips for Providing Light during Germination
When it comes to providing light during the germination process, there are a few tips and techniques that can help you ensure optimal conditions for your seeds. Here are some useful tips to consider:
- Choose the Right Light Source: Select a light source that provides the appropriate light spectrum for seed germination. LED grow lights or fluorescent lights with a balanced blue and red spectrum are commonly used for indoor gardening. These lights are energy-efficient and produce minimal heat, making them ideal for seedlings.
- Position the Lights Correctly: Consider the distance between the light source and the seedlings. Start with the light positioned about 12-18 inches above the seeds and adjust as needed. As the seedlings grow, raise the light to maintain the right distance and prevent them from becoming leggy.
- Set up a Lighting Schedule: Establish a consistent lighting schedule for your seedlings. Most vegetable seeds require 8-12 hours of light each day. Use a timer to automate the light schedule or manually turn the lights on and off at the same time each day.
- Monitor Light Intensity: Keep an eye on the intensity of the light, especially if using natural sunlight. Direct sunlight can be too intense for delicate seedlings, so consider using sheer curtains or shade cloth to filter the light or moving the seedlings to a partially shaded area.
- Rotate Seed Trays: To ensure even growth, rotate the seed trays every couple of days. This helps prevent seedlings from leaning towards the light source and encourages them to grow straight and strong.
- Avoid Overwatering: Excessive moisture around the seedlings can lead to dampness and increased risk of fungal diseases. To prevent this, water the soil thoroughly but allow it to dry out slightly between waterings. Proper drainage is essential for healthy germination and growth.
- Consider Supplementary Lighting: If natural light is limited or inadequate, consider using supplementary lighting to provide consistent and sufficient light for your seedlings. Supplemental grow lights can help ensure that your seedlings receive the necessary light intensity and spectrum for healthy growth.
- Observe and Adjust: Regularly observe your seedlings and assess their response to the light conditions. Look for signs of healthy growth, such as sturdy stems, vibrant leaves, and overall vigor. If the seedlings appear stretched or pale, it may indicate a lack of light, and adjustments should be made accordingly.
By following these tips and providing the right light conditions, you can support successful germination and set your seedlings on the path to thriving. Remember to consider the specific light requirements of the vegetable you are growing and make adjustments as needed to ensure the best possible lighting environment.
Conclusion
Understanding the role of light in the germination process is essential for successful gardening. While some vegetables require light to sprout and thrive, others can germinate in the absence of light. Providing the optimal light conditions for your seeds can significantly improve their chances of successful germination and healthy growth.
Light serves as an energy source for seedlings through photosynthesis, aids in hormone production, and promotes strong stem and leaf development. It also plays a role in breaking seed dormancy and preparing the seedlings for the challenges of the environment.
When it comes to germination, it’s important to know which vegetables require light and which do not. Lettuce, spinach, carrots, parsley, and celery are examples of vegetables that need light for germination, while beans, peas, radishes, beets, and onions can sprout without direct light exposure.
To provide optimal light during germination, consider factors such as light intensity, duration, spectrum, distance from the light source, and the specific light requirements of the vegetables you are growing. Utilize proper lighting sources, set up a consistent lighting schedule, and monitor the seedlings to ensure they receive the right amount of light for healthy growth.
Remember that light is just one component of germination, and other factors such as proper watering, temperature, and soil quality also play vital roles. By understanding the needs of your seeds and providing them with the ideal germination conditions, you can set them up for success and enjoy a bountiful garden.
So, whether you’re starting a new garden or expanding your existing one, pay attention to the light requirements of your vegetables and create an environment that supports their germination. With a little knowledge and careful attention, you’ll be able to nurture your seeds into strong and productive plants.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Vegetables Need Light To Germinate
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.














0 thoughts on “What Vegetables Need Light To Germinate”