Home>Gardening & Outdoor>Plant Care & Gardening Tips>Why Is The Fire Pink Wildflower Becoming Extinct


Plant Care & Gardening Tips
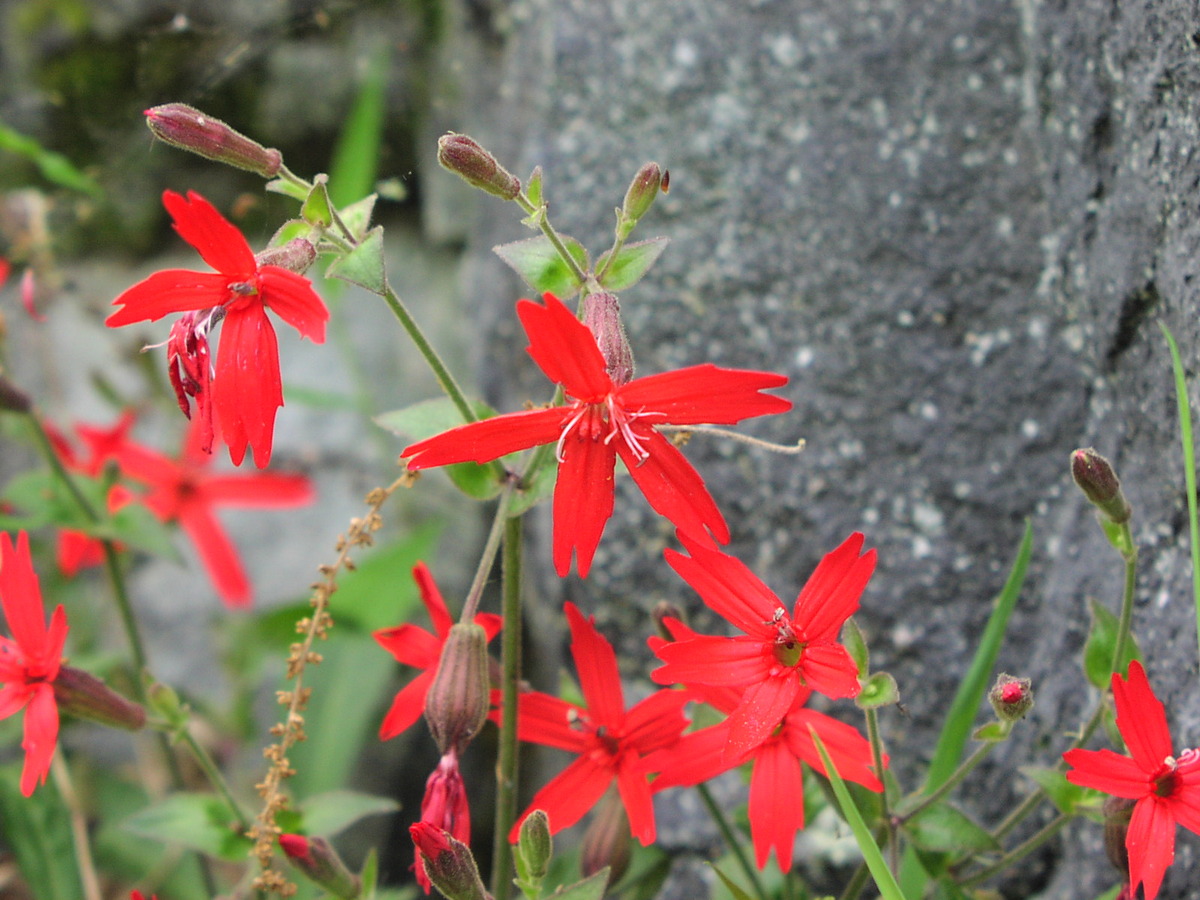
Why Is The Fire Pink Wildflower Becoming Extinct
Modified: January 3, 2024
Discover why the fire pink wildflower is facing extinction and learn plant care and gardening tips to help preserve this beautiful species. Explore ways to protect and nurture these delicate flowers in your garden.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
The fire pink wildflower, scientifically known as Silene virginica, is a stunning and vibrant native wildflower that has been captivating nature enthusiasts for generations. This delicate and striking plant is renowned for its vivid, star-shaped, deep pink flowers that adorn woodlands, meadows, and roadsides across North America. However, despite its ethereal beauty and ecological significance, the fire pink wildflower is facing the looming threat of extinction. In this article, we will delve into the various factors contributing to the decline of this iconic wildflower and explore the crucial conservation efforts aimed at preserving its existence for future generations to cherish.
The fire pink wildflower holds a special place in the hearts of nature lovers, as its presence signals the arrival of spring and the awakening of the natural world. Its bright blooms serve as a vital source of nectar for pollinators, including butterflies, bees, and hummingbirds, thus playing a pivotal role in maintaining the delicate balance of local ecosystems. Regrettably, the fire pink wildflower is grappling with a myriad of challenges that jeopardize its survival, ranging from habitat loss and climate change to the relentless encroachment of invasive species. As such, it is imperative to shed light on these pressing issues and explore actionable measures to safeguard the future of this enchanting wildflower.
Key Takeaways:
- The fire pink wildflower is at risk of extinction due to habitat loss, climate change, invasive species, and human activities. Conservation efforts are crucial to protect this iconic plant and its vital role in local ecosystems.
- Habitat restoration, public awareness, and protected areas are essential for preserving the fire pink wildflower. By addressing threats and promoting sustainable practices, we can ensure the continued existence of this stunning native plant.
Read more: What Is The Fire Pink Wildflower
Habitat Loss
Habitat loss stands as one of the primary threats to the fire pink wildflower’s existence. The encroachment of human development, including urban expansion, agricultural activities, and infrastructure projects, has led to the degradation and fragmentation of the natural landscapes that once provided a thriving habitat for this delicate wildflower. Woodlands and meadows, which were once adorned with the resplendent blooms of the fire pink, have succumbed to the relentless march of human progress, leaving the wildflower with dwindling spaces to call home.
Furthermore, the rampant clearing of land for various purposes, such as residential and commercial construction, has further exacerbated the loss of the fire pink wildflower’s natural habitat. As these vital ecosystems continue to diminish, the wildflower faces increased competition for resources and struggles to find suitable areas for germination and growth. The disruption of its habitat not only diminishes the wildflower’s population but also hampers the intricate web of interactions it sustains with other native flora and fauna.
Efforts to combat habitat loss and preserve the remaining natural areas where the fire pink wildflower thrives are of paramount importance. Conservation organizations and environmental advocates are tirelessly working to protect and restore these critical habitats, advocating for the establishment of nature reserves, wildlife corridors, and protected areas to provide safe havens for the wildflower and other imperiled species. By addressing the root causes of habitat loss and promoting sustainable land management practices, we can strive to ensure that the fire pink wildflower continues to grace our landscapes with its resplendent blooms for generations to come.
Climate Change
Climate change poses a formidable threat to the survival of the fire pink wildflower and numerous other plant species. The escalating impacts of global warming, including shifts in temperature, precipitation patterns, and extreme weather events, have profound implications for the delicate balance of ecosystems where the fire pink thrives. These changes can disrupt the wildflower’s life cycle, alter its flowering times, and affect the availability of essential resources, thereby impeding its ability to flourish in its native habitats.
Rising temperatures and erratic weather patterns can lead to prolonged droughts or unseasonable frosts, directly impacting the fire pink’s ability to germinate, grow, and reproduce. Additionally, alterations in precipitation levels can disturb the delicate hydrological balance of the wildflower’s habitats, potentially leading to soil erosion, habitat degradation, and diminished water availability, all of which can imperil the wildflower’s survival. Furthermore, changes in climate can also influence the interactions between the fire pink and its pollinators, potentially disrupting the intricate relationships that are vital for the wildflower’s reproduction.
As climate change continues to exert its influence on the natural world, it is imperative to implement strategies aimed at mitigating its impacts and bolstering the resilience of vulnerable plant species like the fire pink wildflower. Advocating for sustainable practices, reducing carbon emissions, and fostering conservation initiatives that prioritize the preservation of diverse habitats are crucial steps in safeguarding the wildflower against the adverse effects of a rapidly changing climate. By embracing these measures, we can strive to create a more hospitable environment for the fire pink and mitigate the existential threat posed by climate change.
Invasive Species
The proliferation of invasive species represents a significant threat to the fire pink wildflower and the delicate balance of native ecosystems. Invasive plants, often introduced unintentionally or through horticultural trade, can outcompete native flora, disrupt ecological processes, and alter the structure of natural habitats, posing a formidable challenge to the survival of indigenous plant species like the fire pink.
Invasive plants can aggressively colonize and dominate the landscapes where the fire pink wildflower once thrived, leading to the degradation and fragmentation of its habitats. The encroachment of invasive species not only diminishes the available resources and space for the wildflower but also hampers its ability to establish and perpetuate viable populations. Furthermore, the presence of invasive plants can disrupt the intricate web of interactions between the fire pink and native pollinators, potentially impeding its reproductive success.
Efforts to mitigate the impact of invasive species on the fire pink wildflower encompass a multifaceted approach, including early detection and rapid response initiatives, invasive species management programs, and public awareness campaigns. By identifying and addressing the presence of invasive plants in the wildflower’s habitats, conservationists and land managers can strive to curtail their spread and minimize their detrimental effects on the native flora, thereby fostering a more favorable environment for the fire pink to thrive.
One tip for helping to prevent the extinction of the fire pink wildflower is to support conservation efforts and initiatives that aim to protect its natural habitat and promote its growth. This can include volunteering with local conservation organizations, advocating for the preservation of wildflower habitats, and participating in community restoration projects.
Human Activities
Human activities have significantly contributed to the decline of the fire pink wildflower and continue to pose a substantial threat to its survival. The expansion of urban areas, agricultural practices, and land development has led to the widespread alteration and degradation of the wildflower’s natural habitats, resulting in habitat loss, fragmentation, and degradation. Additionally, activities such as indiscriminate land clearing, deforestation, and the disruption of natural ecosystems have further exacerbated the challenges faced by the fire pink.
Furthermore, the proliferation of pollutants and the introduction of non-native species through human activities have had detrimental impacts on the delicate balance of ecosystems where the fire pink thrives. Pollution from industrial and agricultural sources can degrade soil and water quality, potentially impeding the wildflower’s growth and reproductive success. The introduction of non-native species, whether intentionally or inadvertently, can outcompete native flora, disrupt ecological processes, and alter the structure of natural habitats, posing a formidable challenge to the survival of indigenous plant species like the fire pink.
Conservation efforts aimed at addressing the impact of human activities on the fire pink wildflower encompass a range of strategies, including sustainable land management practices, habitat restoration initiatives, and public education and outreach programs. By promoting responsible land stewardship, advocating for the preservation of natural habitats, and raising awareness about the importance of conserving native plant species, we can strive to mitigate the adverse effects of human activities and create a more hospitable environment for the fire pink to thrive.
Conservation Efforts
Amid the myriad challenges facing the fire pink wildflower, dedicated conservation efforts are underway to safeguard its existence and restore the habitats essential for its survival. Conservation organizations, environmental advocates, and governmental agencies are working tirelessly to implement a diverse array of initiatives aimed at addressing the threats confronting the wildflower and preserving its ecological significance.
Habitat restoration projects play a pivotal role in conservation efforts, focusing on the rehabilitation and preservation of the natural landscapes where the fire pink thrives. These initiatives encompass the restoration of woodlands, meadows, and other critical habitats, aiming to create conducive environments for the wildflower to flourish. By restoring vital ecosystems and enhancing the availability of suitable habitats, these efforts strive to bolster the resilience of the fire pink and support the diverse array of flora and fauna that rely on these habitats.
Furthermore, public awareness campaigns and educational programs are instrumental in fostering a deeper understanding of the importance of conserving native plant species like the fire pink. By engaging communities, schools, and stakeholders, these initiatives seek to instill a sense of stewardship for the natural world and promote sustainable practices that benefit the wildflower and its habitats. Empowering individuals with the knowledge and tools to actively participate in conservation endeavors is crucial for creating a collective commitment to preserving the fire pink and the ecosystems it inhabits.
In addition to habitat restoration and public outreach, the establishment of protected areas and nature reserves serves as a cornerstone of conservation efforts aimed at safeguarding the fire pink wildflower. These designated areas provide crucial refuges for the wildflower and other imperiled species, offering sanctuary from the pressures of habitat loss, invasive species, and human activities. By designating and managing protected areas, conservationists strive to create havens where the fire pink can thrive, perpetuate its populations, and contribute to the richness of natural biodiversity.
Through these multifaceted conservation endeavors, we can collectively strive to ensure the continued existence of the fire pink wildflower, preserving its beauty and ecological importance for generations to come.
Conclusion
The plight of the fire pink wildflower serves as a poignant reminder of the intricate challenges faced by native plant species in the wake of habitat loss, climate change, invasive species, and human activities. As we bear witness to the dwindling populations of this iconic wildflower, it becomes imperative to recognize the urgency of conservation efforts aimed at safeguarding its existence and the delicate ecosystems it inhabits.
While the threats to the fire pink wildflower are formidable, there exists a beacon of hope in the form of dedicated conservation initiatives and the unwavering commitment of passionate individuals and organizations. By addressing the root causes of habitat loss, advocating for sustainable land management practices, and fostering public awareness, we can strive to create a more hospitable environment for the fire pink to thrive.
Furthermore, the restoration and preservation of critical habitats, the management of invasive species, and the establishment of protected areas are indispensable components of comprehensive conservation strategies. These efforts not only serve to benefit the fire pink wildflower but also contribute to the resilience and vitality of diverse ecosystems, fostering a harmonious coexistence between native flora and fauna.
As we navigate the complexities of conserving imperiled plant species like the fire pink, it is essential to recognize the intrinsic value of these natural treasures and the profound interconnectedness they embody within the web of life. The preservation of the fire pink wildflower transcends the realm of conservation; it is a testament to our collective responsibility to cherish and protect the wondrous diversity of the natural world.
In the spirit of stewardship and reverence for nature, let us endeavor to champion the conservation of the fire pink wildflower, ensuring that its resplendent blooms continue to grace our landscapes, inspiring awe and nurturing the intricate tapestry of life for generations to come.
Frequently Asked Questions about Why Is The Fire Pink Wildflower Becoming Extinct
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.














0 thoughts on “Why Is The Fire Pink Wildflower Becoming Extinct”