Home>Home Appliances>Home Automation Appliances>What Breaker Controls Thermostat


Home Automation Appliances
What Breaker Controls Thermostat
Modified: January 6, 2024
Find out which breaker controls your thermostat for efficient home automation. Learn how to optimize your home automation appliances. Discover more tips now!
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
**
Introduction
**
Welcome to the world of home automation, where convenience and efficiency converge to simplify daily living. In this realm, the thermostat serves as a pivotal device, regulating indoor temperatures for optimal comfort. However, have you ever pondered over the mechanism that powers this essential component of your home? The breaker, an often overlooked yet crucial element of the electrical system, plays a vital role in controlling the thermostat and ensuring its seamless operation.
Delving into the intricacies of this relationship between the breaker and thermostat unveils a fascinating interplay of electrical components and home automation technology. Understanding the dynamics of this connection not only empowers homeowners to make informed decisions but also sheds light on the underlying mechanisms that govern the modern household.
In this comprehensive guide, we will navigate through the labyrinth of circuitry, explore the various types of breakers, elucidate their connection to the thermostat, and provide insights into selecting the right breaker for optimal performance. By the end of this journey, you will emerge with a deeper understanding of the breaker-thermostat nexus, equipped with the knowledge to make informed choices and optimize the functionality of your home automation system.
Key Takeaways:
- The breaker in your home’s electrical panel controls the power supply to your thermostat, ensuring it functions properly to regulate indoor temperatures for comfort and efficiency.
- Understanding the different types of breakers and selecting the right one for your thermostat circuit is crucial for maintaining electrical safety and optimizing the performance of your home automation system.
Read more: What Color Thermostat Wire Controls The Heat
Understanding the Circuit
Before delving into the specifics of the breaker that controls the thermostat, it is essential to grasp the fundamental workings of the electrical circuit in a home. The circuit serves as the circulatory system of the electrical network, facilitating the seamless flow of electricity to power various appliances and devices, including the thermostat.
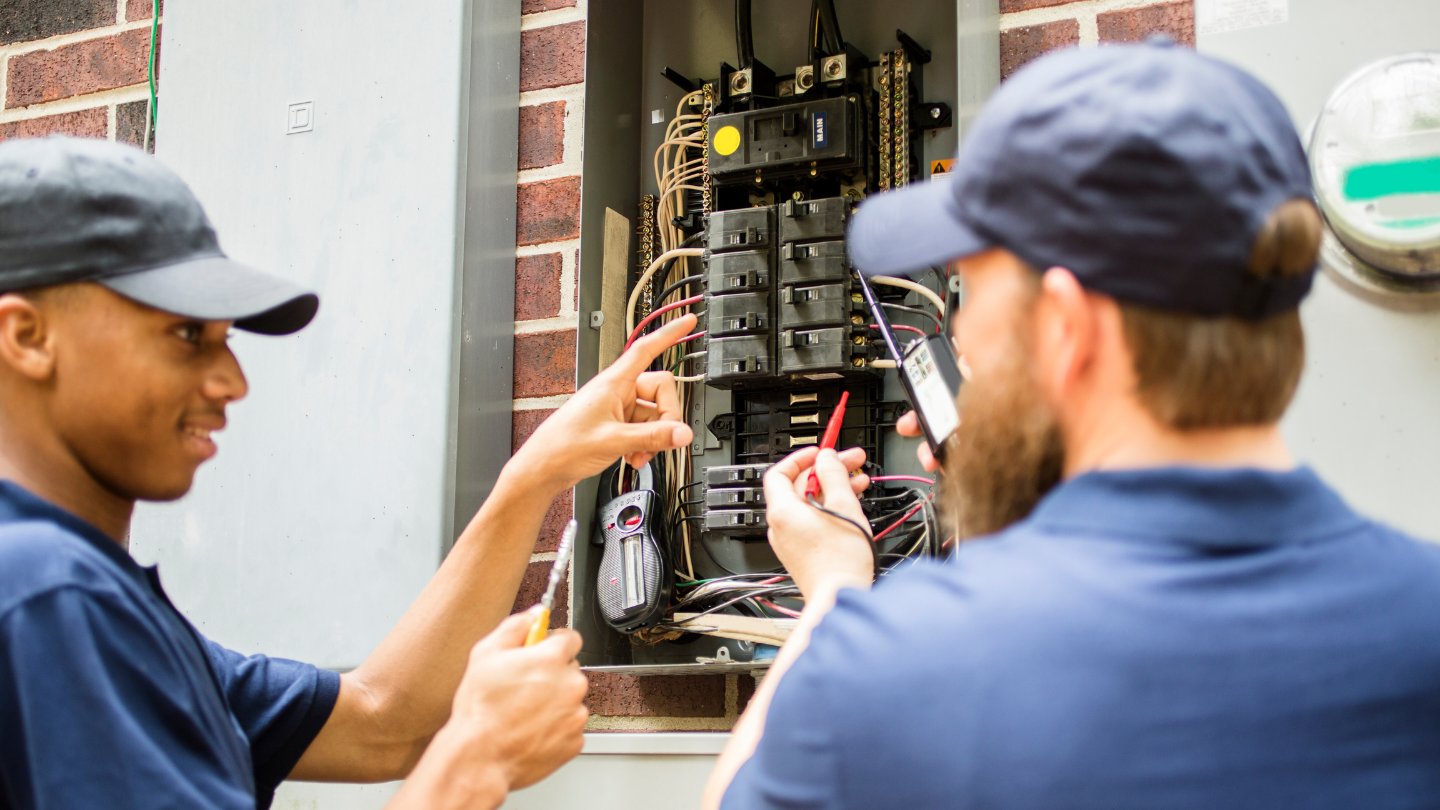
At the heart of this circuit lies the breaker panel, also known as the electrical panel or distribution board. This panel acts as the command center, receiving electrical power from the utility and distributing it to different circuits throughout the home. Each circuit is protected by a breaker, which serves as a safety mechanism to prevent electrical overloads and short circuits.
When it comes to the thermostat, it is typically connected to a dedicated circuit within the breaker panel. This circuit ensures that the thermostat receives a consistent and regulated supply of electricity to function effectively. Understanding the layout and organization of the breaker panel is instrumental in identifying the specific breaker that controls the thermostat.
Furthermore, comprehending the flow of electricity within the circuit and the role of the breaker in regulating this flow is crucial. Breakers are designed to automatically interrupt the electrical current in the event of an overload or short circuit, thereby safeguarding the connected devices and preventing potential hazards. This pivotal function underscores the significance of the breaker in maintaining the safety and efficiency of the electrical system.
By gaining a comprehensive understanding of the circuitry and the pivotal role of the breaker panel, homeowners can navigate the intricacies of the electrical system with confidence. This knowledge forms the foundation for deciphering the connection between the breaker and the thermostat, paving the way for informed decision-making and proactive maintenance of the home automation infrastructure.
Types of Breakers
Breakers come in various types, each tailored to meet specific electrical requirements and safety standards. Understanding the distinctions between these breaker types is essential for homeowners seeking to optimize the functionality of their electrical systems and ensure the seamless operation of connected devices such as thermostats.
1. Standard Circuit Breakers: These are the most common type of breakers found in residential electrical panels. They are designed to protect standard household circuits and are available in different current ratings to accommodate varying electrical loads. Standard circuit breakers are characterized by their versatility and widespread applicability in powering a wide range of home appliances and devices, including thermostats.
2. AFCI (Arc-Fault Circuit Interrupter) Breakers: AFCI breakers are engineered to detect and mitigate the risk of electrical arcing, a potential fire hazard caused by damaged wiring or malfunctioning electrical devices. These breakers provide an added layer of protection against arc faults, enhancing the safety of the electrical system and reducing the likelihood of electrical fires. Given the critical role of thermostats in regulating heating and cooling systems, integrating AFCI breakers can bolster the overall safety of the home automation infrastructure.
3. GFCI (Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter) Breakers: GFCI breakers are specifically designed to safeguard against ground faults, which occur when electrical current inadvertently flows through a ground path, potentially leading to electric shocks and other safety hazards. These breakers are commonly employed in areas with heightened exposure to moisture, such as bathrooms, kitchens, and outdoor spaces. While thermostats may not directly necessitate GFCI protection, understanding the broader application of these breakers is vital for ensuring comprehensive electrical safety within the home.
4. Dual-Function Circuit Breakers: Combining the functionalities of AFCI and GFCI protection, dual-function circuit breakers offer a comprehensive solution for mitigating both arc faults and ground faults within the electrical system. This integrated approach enhances the overall safety and reliability of the circuitry, providing homeowners with a versatile and robust solution for protecting critical devices, including thermostats.
By familiarizing themselves with the diverse array of breaker types, homeowners can make informed decisions regarding the selection and integration of breakers tailored to the specific needs of their electrical systems, thereby fortifying the foundation on which their home automation infrastructure operates.
The breaker that controls the thermostat is usually labeled on the electrical panel. Look for a label that says “HVAC” or “Thermostat” to find the correct breaker to control the thermostat.
Connection to Thermostat
The connection between the breaker and the thermostat is a pivotal link in the intricate web of the home’s electrical infrastructure. Understanding how these components interface with each other is essential for ensuring the seamless operation of the thermostat and optimizing its performance within the broader context of home automation.
At the core of this connection lies the dedicated circuit that supplies power to the thermostat. This circuit, protected by a specific breaker within the electrical panel, serves as the conduit through which electricity is channeled to the thermostat, enabling it to regulate the heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) system. The breaker acts as a safeguard, ensuring that the electrical supply to the thermostat remains stable and protected from potential overloads or short circuits.
When installing or troubleshooting the thermostat, it is imperative to identify the corresponding breaker within the electrical panel to facilitate safe and efficient maintenance. This entails locating the circuit that powers the thermostat and verifying that it is appropriately protected by the designated breaker, thus ensuring compliance with electrical codes and safety standards.
Furthermore, the connection between the breaker and the thermostat underscores the symbiotic relationship between electrical safety and device functionality. By integrating the appropriate breaker and establishing a robust electrical connection, homeowners can mitigate the risk of electrical hazards while optimizing the reliability and performance of the thermostat within the broader spectrum of home automation.
Moreover, advancements in smart home technology have ushered in a new era of connectivity, enabling thermostats to interface with home automation systems and smart devices. This integration underscores the evolving role of the breaker in facilitating not only the electrical supply to the thermostat but also its seamless integration within the interconnected ecosystem of smart home solutions.
Understanding the nuances of the connection between the breaker and the thermostat empowers homeowners to proactively manage their home automation infrastructure, ensuring the efficient and reliable operation of the thermostat while upholding the highest standards of electrical safety and compliance.
Selecting the Right Breaker
Choosing the appropriate breaker for the thermostat circuit is a critical decision that directly impacts the safety, efficiency, and reliability of the home’s electrical infrastructure. Several factors should be considered when selecting the right breaker to safeguard the thermostat’s dedicated circuit and ensure its seamless operation within the broader context of home automation.
1. Current Rating: The current rating of the breaker should align with the electrical requirements of the thermostat and its associated HVAC system. It is imperative to ascertain the specific amperage needed to power the thermostat and select a breaker with a corresponding current rating to ensure optimal performance and safety.
2. Type of Protection: Depending on the unique electrical characteristics of the home and the desired level of safety, homeowners may opt for standard circuit breakers, AFCI breakers, GFCI breakers, or dual-function circuit breakers. Evaluating the specific protective features required for the thermostat circuit is essential in choosing the most suitable breaker type.
3. Compatibility with Smart Home Systems: For homeowners integrating smart home solutions and advanced automation technologies, selecting a breaker that aligns with the compatibility requirements of smart thermostats and interconnected home automation systems is crucial. This ensures seamless integration and optimized performance within the broader smart home ecosystem.
4. Compliance and Safety Standards: Adhering to electrical codes and safety standards is paramount when selecting a breaker for the thermostat circuit. Ensuring that the chosen breaker complies with relevant regulations and industry standards is essential for upholding the safety and integrity of the electrical system.
5. Future Expansion and Flexibility: Anticipating potential upgrades or expansions to the home automation infrastructure, including the thermostat and HVAC system, is integral to selecting a breaker that accommodates future growth and adaptability. Choosing a breaker with scalability and flexibility in mind can mitigate the need for frequent modifications as the home automation ecosystem evolves.
By meticulously evaluating these considerations and consulting with qualified electrical professionals, homeowners can make informed decisions when selecting the right breaker for the thermostat circuit. This proactive approach not only ensures the safety and reliability of the electrical system but also lays the groundwork for seamless integration within the broader landscape of home automation and smart home technologies.
Read more: How To Work Thermostat Controls
Conclusion
Embarking on a journey to unravel the intricacies of the breaker-thermostat relationship has illuminated the pivotal role of electrical components in the realm of home automation. From the fundamental workings of the circuit to the diverse array of breaker types and their connection to the thermostat, this exploration has unveiled the interconnected web of electrical infrastructure that underpins modern households.
Understanding the circuit as the lifeline of the electrical system, with the breaker panel at its helm, provides homeowners with a foundational comprehension of the electrical network that powers their homes. This knowledge empowers them to navigate the complexities of the breaker-thermostat nexus, facilitating informed decision-making and proactive maintenance of the home automation infrastructure.
Moreover, the exploration of breaker types has underscored the importance of tailoring the selection to meet the specific requirements of the thermostat circuit. Whether it entails standard circuit breakers, AFCI breakers, GFCI breakers, or dual-function circuit breakers, the choice of the right breaker is instrumental in fortifying the safety and efficiency of the electrical system while accommodating the evolving landscape of home automation technologies.
The connection between the breaker and the thermostat serves as a conduit through which electrical stability and device functionality converge. By recognizing the symbiotic relationship between electrical safety and device performance, homeowners can proactively manage their home automation infrastructure, ensuring the reliable operation of the thermostat within the broader spectrum of smart home solutions.
Ultimately, the process of selecting the right breaker for the thermostat circuit encapsulates a strategic approach to fortifying the electrical foundation of the home. By considering factors such as current rating, type of protection, compatibility with smart home systems, compliance with safety standards, and future expansion, homeowners can lay the groundwork for a resilient and adaptable electrical infrastructure that seamlessly integrates with evolving home automation technologies.
As we conclude this comprehensive guide, armed with a deeper understanding of the breaker that controls the thermostat, homeowners are poised to navigate the realm of home automation with confidence and foresight. By leveraging this knowledge, they can optimize the functionality of their thermostats while upholding the highest standards of electrical safety and compliance, thus embracing the seamless convergence of technology and convenience within the modern home.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Breaker Controls Thermostat
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.













0 thoughts on “What Breaker Controls Thermostat”