Home>Home Appliances>Home Automation Appliances>What Voltage Does A Thermostat Use


Home Automation Appliances
What Voltage Does A Thermostat Use
Modified: January 9, 2024
Discover the ideal voltage for your thermostat in your home automation appliances. Learn about the voltage requirements for efficient temperature control.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Welcome to the world of home automation, where modern technology seamlessly integrates with everyday life to enhance comfort and convenience. In the realm of home automation, thermostats play a pivotal role in regulating indoor temperatures, ensuring energy efficiency, and optimizing overall comfort. However, when it comes to understanding the intricacies of thermostat voltage, confusion often arises. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the realm of thermostat voltage, shedding light on the different types of thermostats and their compatibility with various HVAC systems.
Whether you are a homeowner seeking to upgrade your thermostat or a curious enthusiast eager to explore the nuances of home automation appliances, this guide is designed to provide you with valuable insights. By the end of this journey, you will have a clear understanding of the voltage requirements for different types of thermostats and how they integrate with heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems.
So, let's embark on this enlightening exploration of thermostat voltage, unraveling the mysteries and demystifying the complexities associated with these essential devices. Whether you're a DIY enthusiast or a homeowner seeking to make informed decisions about your home's heating and cooling systems, this guide is tailored to equip you with the knowledge needed to navigate the world of thermostat voltage with confidence and clarity.
Key Takeaways:
- Thermostats come in low voltage and line voltage types, with low voltage being more versatile and energy-efficient for traditional HVAC systems, while line voltage is designed for specific applications like electric heating systems.
- Understanding thermostat voltage is crucial for selecting the right thermostat for your HVAC system, ensuring optimal performance, energy efficiency, and seamless integration with smart home platforms.
Read more: What Is A Low Voltage Thermostat
Understanding Thermostat Voltage
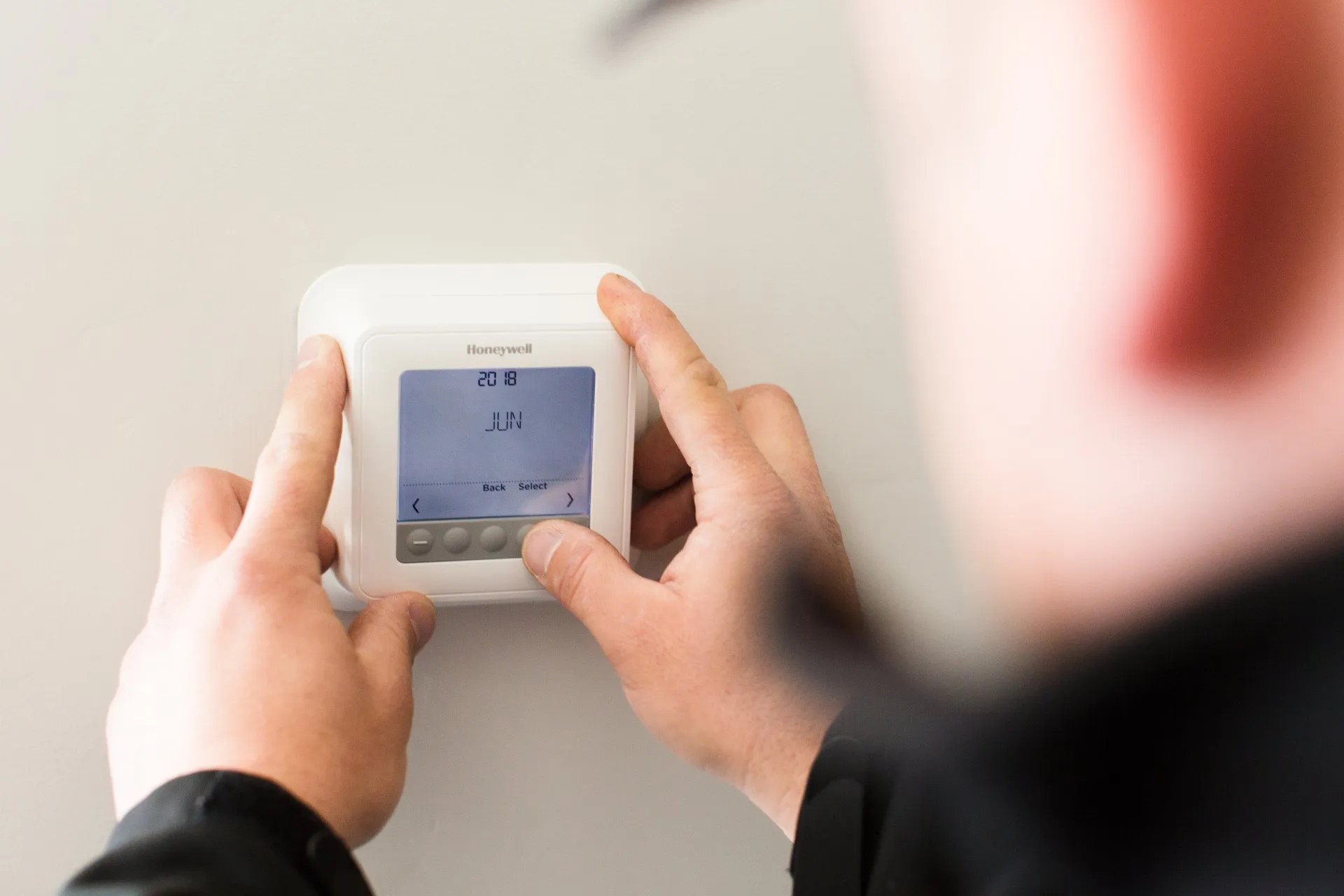
Before delving into the specifics of thermostat voltage, it’s crucial to grasp the fundamental concepts underlying the operation of these indispensable devices. At its core, a thermostat serves as the control center for regulating indoor temperatures, ensuring optimal comfort while maximizing energy efficiency. To achieve this, thermostats rely on voltage to power their operation and facilitate communication with heating, cooling, and ventilation systems.
Thermostats are available in two primary voltage categories: low voltage and line voltage. Understanding the distinction between these two categories is essential for selecting the appropriate thermostat for your specific HVAC system and ensuring seamless compatibility.
Low voltage thermostats typically operate on 24 volts of alternating current (VAC), making them compatible with a wide range of heating and cooling systems. These thermostats are commonly found in residential settings and are renowned for their energy efficiency and versatility. In contrast, line voltage thermostats are designed to handle higher voltage levels, typically 120 to 240 volts, and are often used in specific applications such as baseboard heaters and ductless mini-split systems.
As you navigate the realm of thermostat voltage, it’s important to consider the compatibility of your chosen thermostat with your HVAC system. Different systems require specific voltage levels to operate optimally, and selecting the wrong type of thermostat can lead to compatibility issues and potential malfunctions.
By gaining a deeper understanding of thermostat voltage and its implications for HVAC compatibility, you are empowered to make informed decisions when selecting, installing, and configuring thermostats in your home. This knowledge not only enhances the efficiency of your heating and cooling systems but also contributes to a more comfortable and harmonious indoor environment.
Now that we’ve laid the foundation for comprehending thermostat voltage, let’s explore the nuances of low voltage thermostats and line voltage thermostats, shedding light on their unique characteristics and applications.
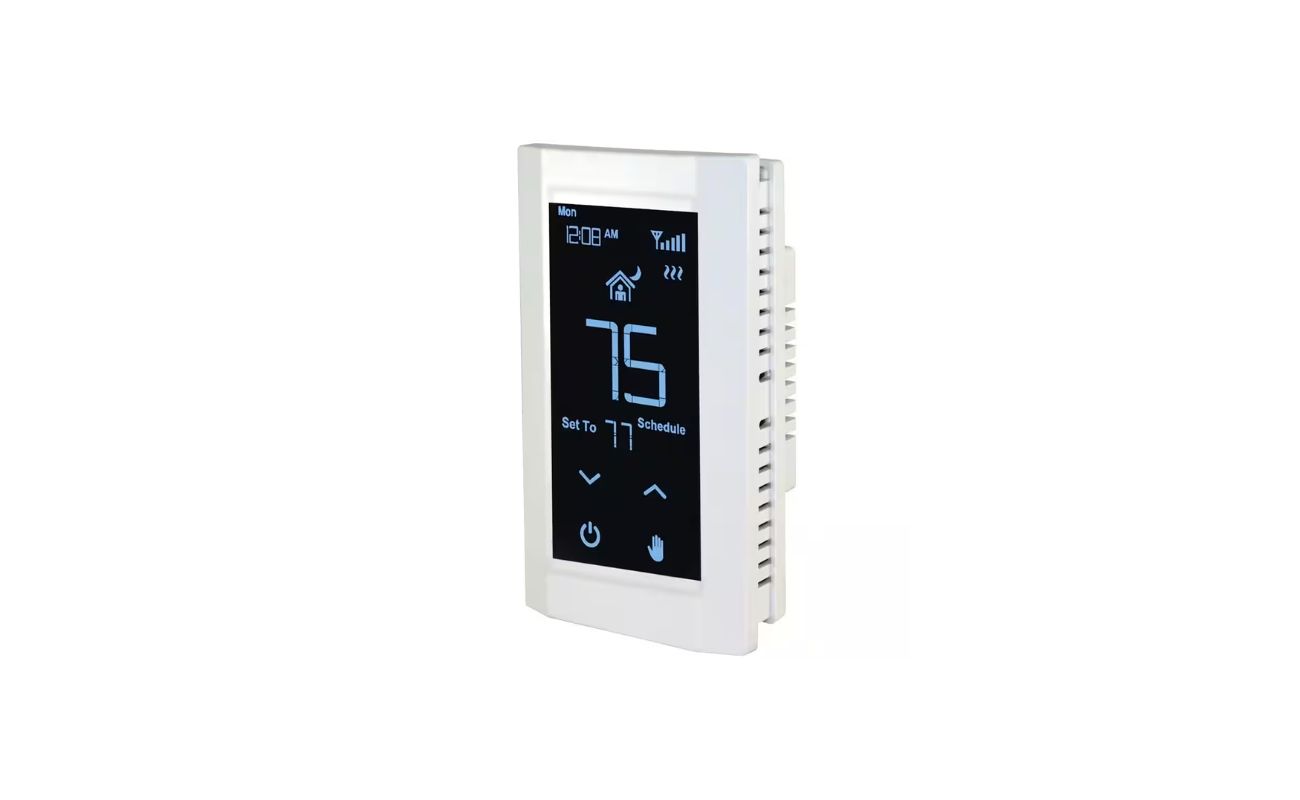
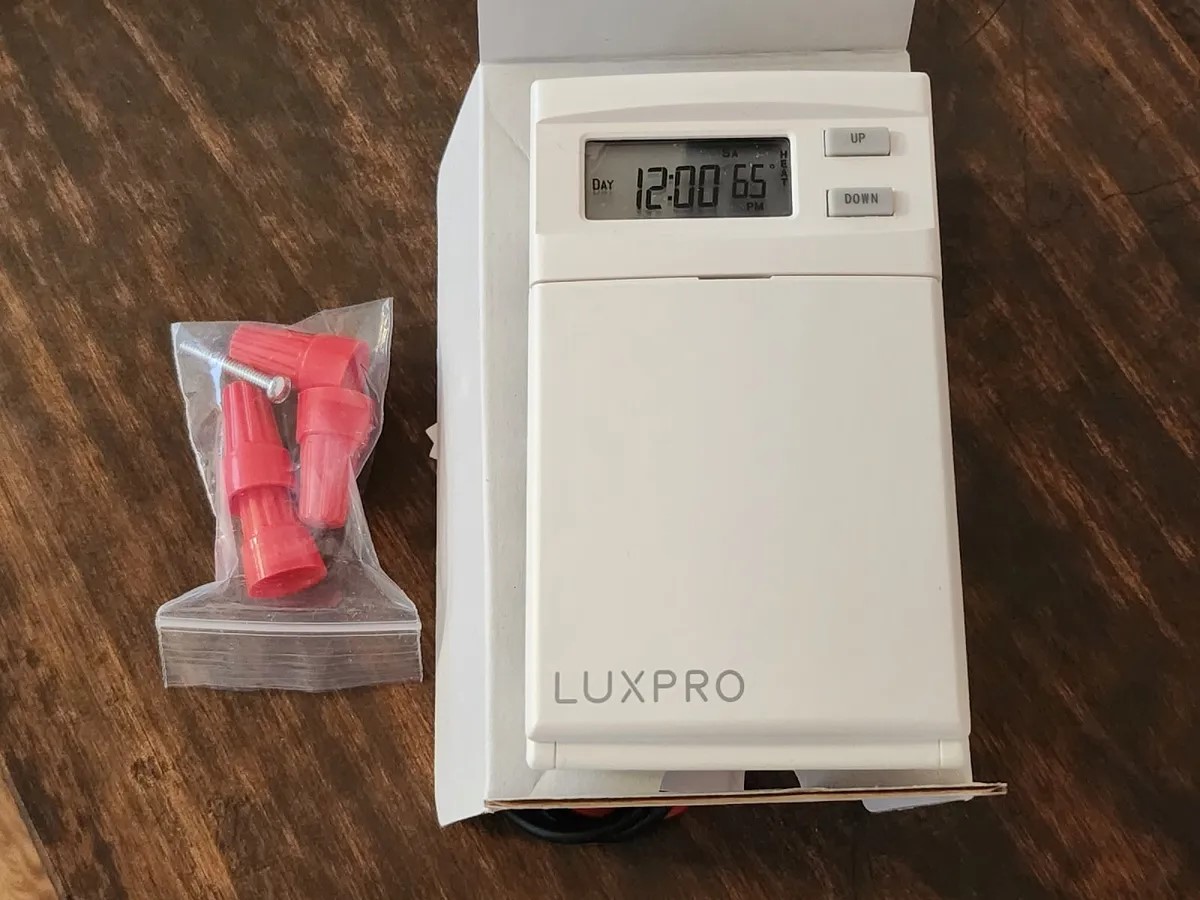
Low Voltage Thermostats
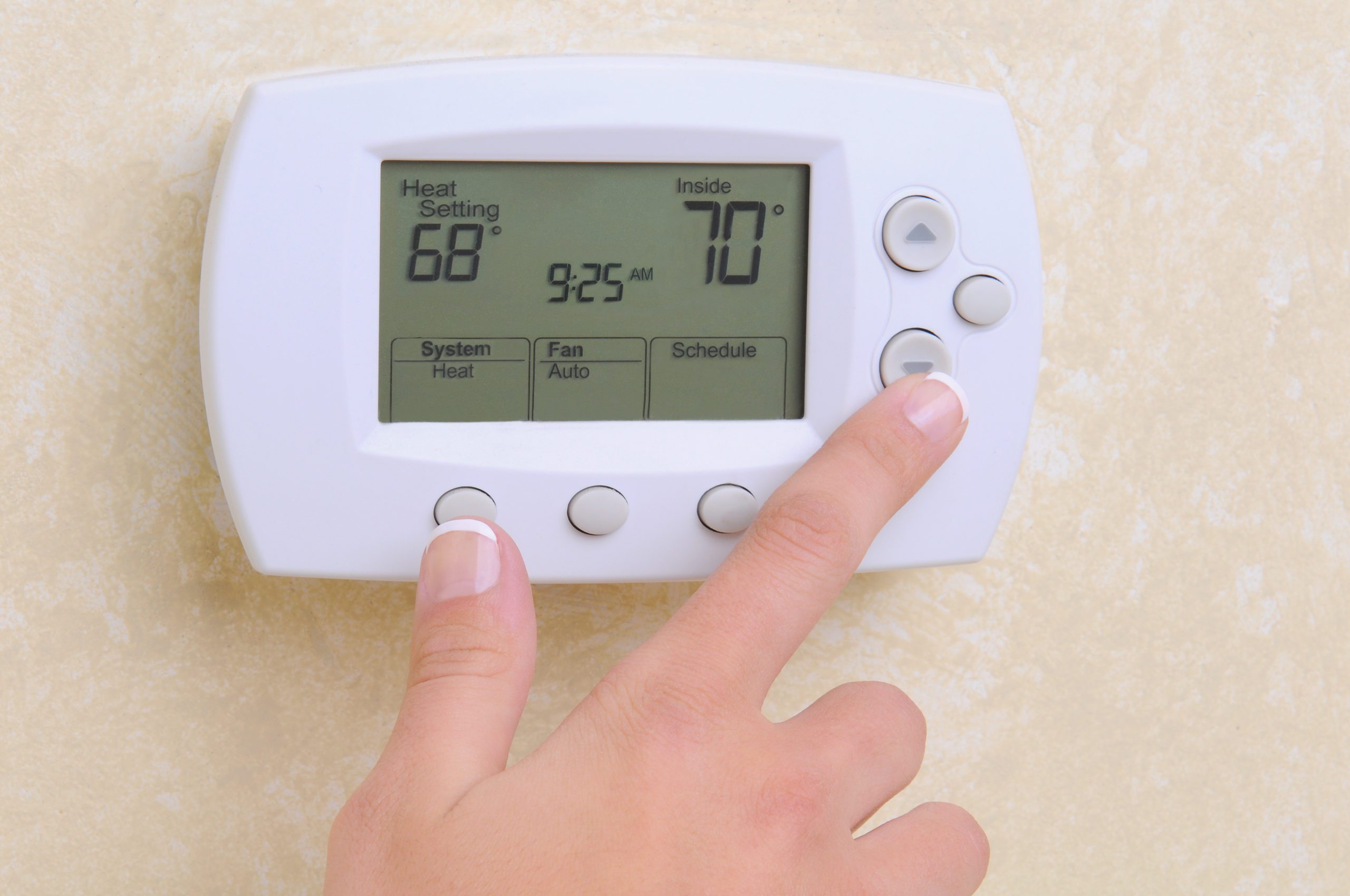
Low voltage thermostats are ubiquitous in residential heating and cooling systems, offering a versatile and energy-efficient solution for regulating indoor temperatures. Operating on 24 volts of alternating current (VAC), these thermostats are compatible with a wide array of HVAC systems, including furnaces, heat pumps, and central air conditioning units.
One of the key advantages of low voltage thermostats is their compatibility with modern HVAC systems, making them an ideal choice for homeowners seeking to upgrade their existing thermostats or integrate smart and programmable features into their heating and cooling controls. These thermostats leverage low voltage to power their internal circuitry, display screens, and communication interfaces, enabling seamless interaction with the HVAC system.
Furthermore, low voltage thermostats are renowned for their energy efficiency, consuming minimal power while delivering precise temperature control and programming capabilities. This efficiency not only contributes to reduced energy consumption but also aligns with sustainable and eco-friendly practices, making low voltage thermostats a compelling choice for environmentally conscious homeowners.
When considering low voltage thermostats, it’s essential to assess their compatibility with your specific HVAC system and any additional components, such as zoning controls, humidifiers, or dehumidifiers. Understanding the voltage requirements and communication protocols of these components is crucial for ensuring seamless integration and optimal performance.
In addition to their technical prowess, low voltage thermostats often boast user-friendly interfaces, intuitive programming features, and compatibility with smart home platforms, allowing homeowners to customize their heating and cooling schedules, monitor energy usage, and remotely control their HVAC systems via mobile applications or voice commands.
As you explore the realm of low voltage thermostats, it’s important to consider factors such as compatibility, energy efficiency, programmability, and integration with smart home ecosystems. By harnessing the power of low voltage technology, these thermostats offer a compelling blend of functionality, convenience, and energy savings, elevating the comfort and control of residential heating and cooling systems.
Now, let’s delve into the realm of line voltage thermostats, uncovering their unique characteristics and applications in specialized HVAC systems.
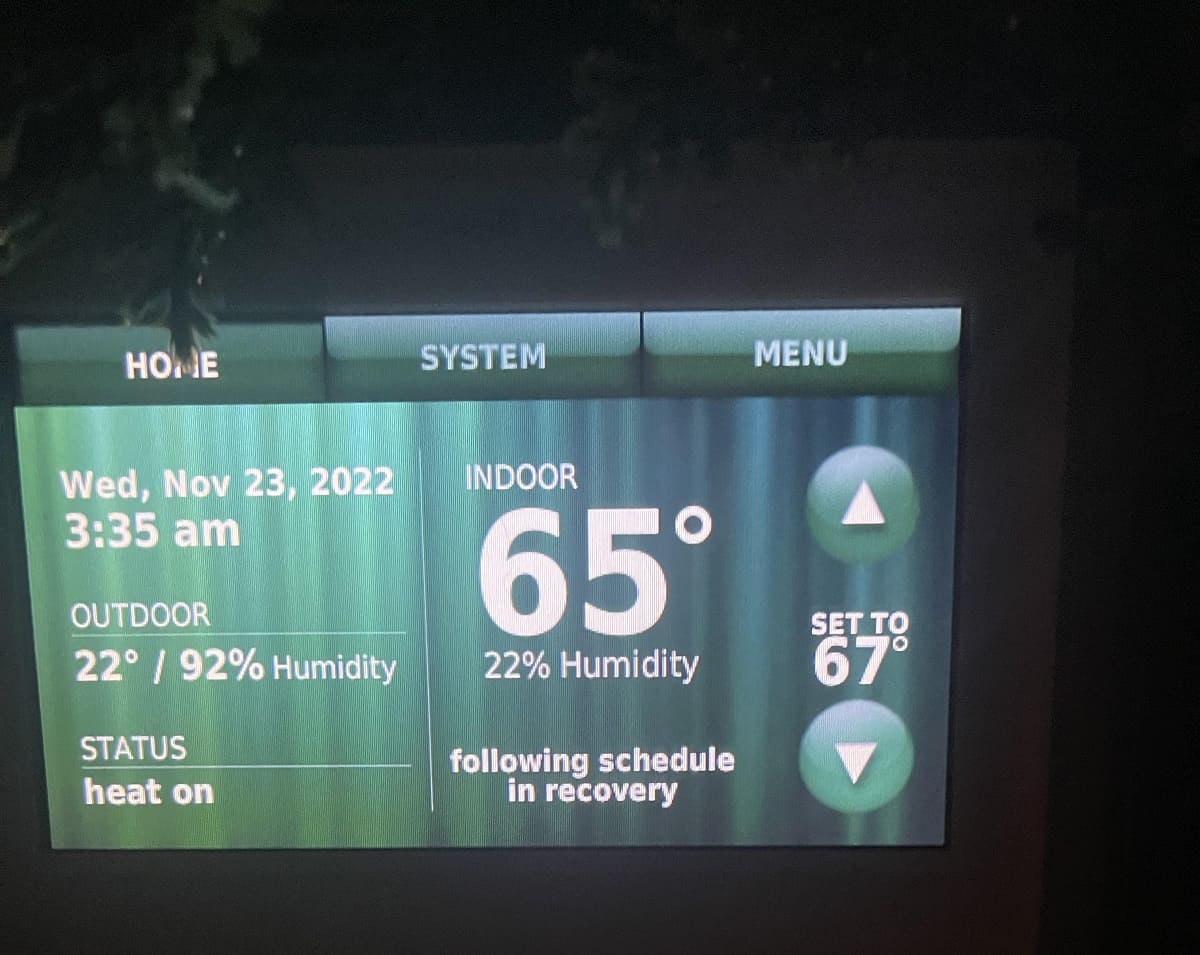
Most thermostats use a low voltage of 24 volts. It’s important to check the specific voltage requirements for your thermostat before installation.
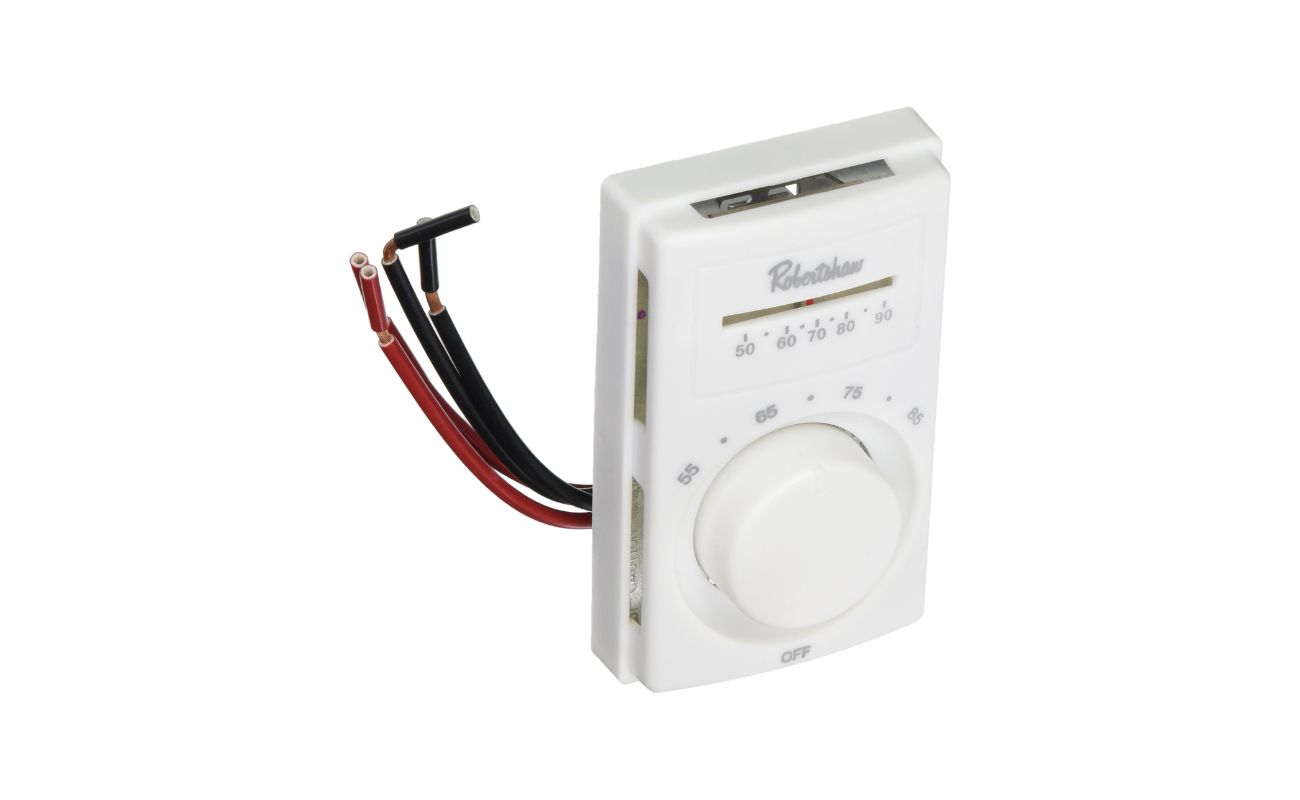
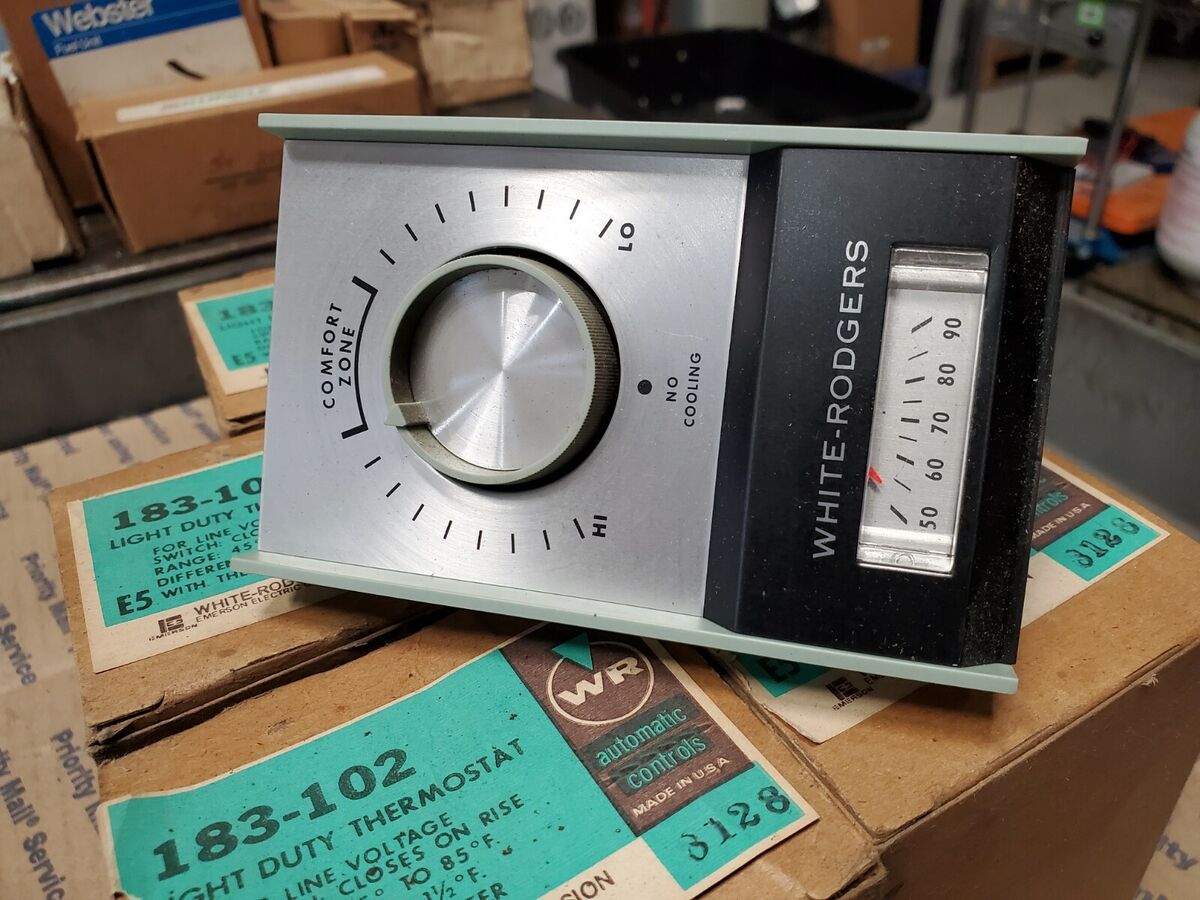
Line Voltage Thermostats
Line voltage thermostats cater to specific heating and cooling applications that require higher voltage levels, typically ranging from 120 to 240 volts. Unlike their low voltage counterparts, line voltage thermostats are designed to directly control electric heating systems, such as baseboard heaters, radiant floor heating, and ductless mini-split units.
These thermostats are engineered to handle the elevated voltage levels associated with electric heating systems, providing precise temperature regulation and control capabilities tailored to these specialized applications. By interfacing directly with the electrical circuits powering the heating elements, line voltage thermostats play a crucial role in maintaining consistent and comfortable indoor temperatures in spaces where electric heating is the primary source of warmth.
One of the distinguishing features of line voltage thermostats is their robust construction and electrical compatibility, ensuring safe and reliable operation in conjunction with electric heating systems. These thermostats are equipped to handle the unique demands of electric heating, offering durability and performance tailored to the specific requirements of these applications.
When considering line voltage thermostats, it’s essential to evaluate their compatibility with the electrical specifications of your heating system, ensuring that the thermostat can effectively regulate the flow of electricity to the heating elements. Additionally, understanding the wiring and installation requirements for line voltage thermostats is crucial for seamless integration and optimal performance.
While line voltage thermostats are primarily associated with electric heating systems, they may also find application in certain cooling scenarios, such as controlling the operation of electric fan-forced cooling units. Their ability to manage higher voltage levels and interface directly with electrically powered heating and cooling equipment positions line voltage thermostats as essential components in specialized HVAC setups.
As you navigate the realm of line voltage thermostats, it’s important to recognize their role in providing precise temperature control and regulation for electric heating systems, contributing to the comfort and efficiency of residential and commercial spaces where these systems are prevalent.
Now that we’ve explored the unique characteristics and applications of line voltage thermostats, let’s delve into the crucial aspect of compatibility with various HVAC systems, ensuring that thermostats align seamlessly with the operational requirements of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning setups.
Compatibility with HVAC Systems
When it comes to selecting thermostats for your heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, ensuring compatibility is paramount to achieving optimal performance and functionality. Whether you are considering low voltage thermostats for traditional HVAC setups or exploring line voltage thermostats for specialized applications, understanding their compatibility with specific HVAC systems is crucial for seamless integration and efficient operation.
Low voltage thermostats are widely compatible with a diverse range of HVAC systems, including furnaces, heat pumps, central air conditioning units, and multi-stage heating and cooling setups. Their 24-volt operating voltage aligns with the standard requirements of modern HVAC equipment, allowing for seamless communication and control over the heating and cooling processes.
When evaluating the compatibility of low voltage thermostats with HVAC systems, it’s essential to consider factors such as the number of heating and cooling stages, compatibility with auxiliary devices such as humidifiers or dehumidifiers, and support for advanced features like zoning controls and programmable schedules. By ensuring that the selected thermostat aligns with the specific requirements of your HVAC setup, you can optimize energy efficiency, comfort, and control within your living spaces.
On the other hand, line voltage thermostats cater to specialized HVAC applications that rely on electric heating systems, such as baseboard heaters, radiant floor heating, and ductless mini-split units. Their compatibility is closely tied to the electrical specifications of the heating system, ensuring that the thermostat can effectively regulate the flow of electricity to maintain desired temperatures.
When assessing the compatibility of line voltage thermostats with HVAC systems, it’s essential to consider the voltage requirements, electrical load capacity, and wiring configurations of the electric heating equipment. By ensuring that the thermostat is compatible with the specific electrical attributes of the heating system, you can guarantee reliable and precise temperature control tailored to the unique demands of electric heating applications.
As the landscape of home automation and HVAC technology continues to evolve, compatibility between thermostats and HVAC systems extends beyond basic functionality, encompassing integration with smart home platforms, wireless connectivity, and energy management capabilities. By selecting thermostats that harmonize with your HVAC system and align with your technological preferences, you can elevate the comfort, efficiency, and convenience of your indoor environment.
Now that we’ve explored the critical aspect of compatibility with HVAC systems, let’s conclude our journey through the realm of thermostat voltage, summarizing the key insights and empowering you to make informed decisions when selecting and integrating thermostats into your home automation ecosystem.
Read more: What Voltage Does A Hot Tub Use
Conclusion
As we conclude our exploration of thermostat voltage, we’ve unraveled the essential nuances of low voltage and line voltage thermostats, delving into their unique characteristics, applications, and compatibility with heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems. By gaining a deeper understanding of thermostat voltage, you are empowered to make informed decisions when selecting, installing, and integrating thermostats into your home automation ecosystem.
Low voltage thermostats, operating on 24 volts of alternating current (VAC), offer versatile and energy-efficient solutions for regulating indoor temperatures in traditional HVAC setups. Their compatibility with a wide array of heating and cooling systems, coupled with advanced features such as programmability and smart home integration, positions them as indispensable components in modern home automation environments.
On the other hand, line voltage thermostats cater to specialized applications that rely on higher voltage levels, providing precise temperature control for electric heating systems such as baseboard heaters and radiant floor heating. Their robust construction and electrical compatibility ensure reliable operation in these unique HVAC scenarios, contributing to the comfort and efficiency of residential and commercial spaces where electric heating is prevalent.
When selecting thermostats for your HVAC systems, compatibility is paramount to achieving optimal performance and functionality. Whether you opt for low voltage thermostats for traditional setups or line voltage thermostats for specialized applications, ensuring seamless integration with your specific heating and cooling equipment is essential for maximizing energy efficiency, comfort, and control within your living spaces.
As technology continues to advance, the integration of thermostats with smart home platforms, wireless connectivity, and energy management capabilities further enhances the potential for optimizing indoor comfort and energy efficiency. By harnessing the power of thermostat voltage and its implications for HVAC compatibility, you can embark on a journey toward a more comfortable, efficient, and intelligent home environment.
So, whether you’re a homeowner seeking to upgrade your thermostat, a DIY enthusiast exploring the realm of home automation, or a curious individual eager to delve into the intricacies of thermostat voltage, this guide has equipped you with the knowledge needed to navigate this essential aspect of modern living with confidence and clarity.
As you embark on your home automation journey, armed with a deeper understanding of thermostat voltage, may your living spaces be imbued with optimal comfort, energy efficiency, and the seamless integration of intelligent heating and cooling solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Voltage Does A Thermostat Use
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.













0 thoughts on “What Voltage Does A Thermostat Use”