Home>Home Maintenance>Where To Get Freon For An Air Conditioner


Home Maintenance
Where To Get Freon For An Air Conditioner
Modified: March 7, 2024
Looking for where to get freon for your air conditioner? Discover the best home maintenance solutions and find reliable suppliers near you.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
When it comes to air conditioning systems, Freon plays a crucial role in keeping your home cool and comfortable. But what exactly is Freon, and why is it needed for air conditioners? In this article, we will explore the importance of Freon and its role in the cooling process.
Key Takeaways:
- Freon is essential for air conditioners to cool your home by absorbing and releasing heat. It’s important to buy the right type of Freon and have it recharged by a professional to ensure optimal performance.
- Responsible disposal of old Freon is crucial to protect the environment. Look for recycling or reclamation options to minimize the impact of Freon on ozone depletion and climate change.
What is Freon?
Freon is a brand name for a class of refrigerants known as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) or hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs). These chemicals are commonly used as cooling agents in air conditioners and refrigeration systems. Freon works by absorbing heat from the surrounding air and releasing it outside, resulting in the cooling effect that we experience indoors.
Why is Freon needed for air conditioners?
Freon is essential for air conditioners to function effectively and efficiently. It is responsible for the heat transfer process that cools the air in your home. When the air conditioner’s compressor compresses the refrigerant (Freon), it turns into a high-pressure gas. This gas then moves through the evaporator coil, where it absorbs heat from the indoor air, causing it to cool down.
Once the heat is absorbed, the refrigerant, now in a gas state, is sent to the condenser coil located outside. Here, the compressor pressurizes the gas, causing it to release the absorbed heat into the outdoor air. As a result, the refrigerant condenses back into a liquid state and is ready to repeat the cooling cycle again.
Without Freon, the air conditioning system cannot effectively transfer heat and cool down the air in your home. It is a vital component in achieving the desired indoor temperature and maintaining a comfortable living environment.
However, it is important to note that due to their potential harm to the ozone layer, the production and importation of CFC-based refrigerants, including Freon, have been phased out in many countries. The HVAC industry has gradually transitioned to using more environmentally friendly refrigerants to minimize their impact on the environment.
Now that we understand the basics of Freon and its relevance to air conditioning systems, let’s dive deeper into the types of Freon available and consider the options when it comes to purchasing this essential refrigerant.
Understanding Freon
Now that we have a basic understanding of what Freon is, let’s explore its role in an air conditioner and how it helps to cool the air in your home.
What is the role of Freon in an air conditioner?
The primary role of Freon in an air conditioner is to facilitate the heat transfer process. As the refrigerant flows through the various components of the air conditioning system, it undergoes phase changes from a gas to a liquid and back to a gas, absorbing and releasing heat in the process.
When the air conditioner is turned on, the compressor compresses the refrigerant, causing it to become a high-pressure gas. This high-pressure gas is then sent to the condenser coil, where it releases heat to the outdoor environment. As the refrigerant loses heat, it condenses into a liquid.
The liquid refrigerant then moves to the expansion valve, which regulates its flow and reduces its pressure. This low-pressure liquid then enters the evaporator coil, where it expands and evaporates. As the liquid refrigerant evaporates, it absorbs heat from the surrounding air, cooling it down.
After absorbing the heat, the refrigerant, now in a gaseous state, is sent back to the compressor to continue the cycle. This continuous cycle of compression, condensation, expansion, and evaporation allows the air conditioner to cool the air in your home.
How does Freon help to cool the air?
Freon helps to cool the air by facilitating the transfer of heat from the indoor air to the outdoor environment. As the refrigerant flows through the evaporator coil, it absorbs heat from the indoor air, causing the air to cool down.
When warm air enters the evaporator coil, the low-pressure liquid refrigerant inside the coil absorbs the heat from the air, causing the refrigerant to evaporate and turn into a gas. This heat absorption process removes the heat from the air, effectively cooling it. The cooled air is then circulated back into your home through the ventilation system.
Once the refrigerant has absorbed the heat, it is then sent to the condenser coil located outside, where the compressor pressurizes the gas, causing it to release the absorbed heat to the outdoor environment. As the refrigerant releases heat, it condenses back into a liquid, ready to repeat the cooling cycle again.
Overall, Freon and its heat transfer properties play a fundamental role in cooling the air in your home. Without it, the air conditioner would not be able to efficiently remove heat from the indoor air, resulting in a less comfortable living environment.
Now that we have a solid understanding of the role of Freon in air conditioning systems, let’s explore the different types of Freon available and compare their pros and cons.
Types of Freon
When it comes to air conditioners, there are different types of Freon used as refrigerants. Each type has its own characteristics and properties that determine its suitability for specific air conditioning systems. In this section, we will explore the different types of Freon and compare the pros and cons of each.
Different types of Freon used in air conditioners
1. R-22 (Freon-22): R-22, also known as Freon-22, was one of the most commonly used refrigerants in air conditioners for many years. It is an HCFC refrigerant that has significantly contributed to ozone depletion. Due to its harmful environmental impact, the production and importation of R-22 have been phased out in many countries. It is being replaced by more environmentally friendly alternatives.
2. R-410A (Puron): R-410A, also known as Puron, is a more environmentally friendly alternative to R-22. It is an HFC refrigerant that does not contribute to ozone depletion. R-410A operates at higher pressures, requiring specific equipment designed for its use. It is commonly used in new air conditioning systems and is known for its excellent cooling efficiency.
3. R-134a: R-134a is another HFC refrigerant commonly used in automotive air conditioning systems. It is also used in some smaller residential air conditioning systems. While it has a lower global warming potential compared to R-22, R-134a still has some environmental impact.
4. R-407C: R-407C is a blend of HFC refrigerants that was developed as a replacement for R-22. It has similar cooling properties to R-22 and is compatible with the existing air conditioning equipment designed for R-22. However, like other HFC refrigerants, R-407C contributes to global warming.
Comparing the pros and cons of each type
1. R-22 (Freon-22):
– Pros: Known for its excellent cooling capacity; widely available until the phase-out; compatible with many existing air conditioning systems.
– Cons: Contributes to ozone depletion; restricted or banned in many countries; expensive due to limited supply.
2. R-410A (Puron):
– Pros: Environmentally friendly; operates at higher pressures, leading to better energy efficiency; widely used in new air conditioning systems.
– Cons: Requires specialized equipment for handling and installation; may not be compatible with older systems designed for R-22.
3. R-134a:
– Pros: Lower global warming potential compared to R-22; commonly used in automotive air conditioning systems.
– Cons: Still has some environmental impact; not as widely used in residential air conditioning systems.
4. R-407C:
– Pros: Designed as a drop-in replacement for R-22; similar cooling properties to R-22; compatible with existing equipment.
– Cons: Contributes to global warming; not as environmentally friendly as other alternatives.
When choosing the right Freon for your air conditioner, it is essential to consider the environmental impact, availability, compatibility with your system, and legal restrictions in your region. Consulting with a professional HVAC technician can help you make an informed decision based on your specific needs and circumstances.
Now that we have covered the different types of Freon, let’s explore where you can purchase Freon for your air conditioner and the factors to consider when making a purchase.
Purchasing Freon
When it comes to buying Freon for your air conditioner, there are a few important factors to consider. In this section, we will discuss where you can purchase Freon, the factors to consider when making a purchase, and how much Freon is typically needed for an air conditioner.
Where to buy Freon for an air conditioner
Freon can be purchased from various sources, including:
– HVAC supply stores: Local HVAC supply stores often carry a range of refrigerants, including Freon. These stores cater to both professionals and homeowners who need refrigerants for their air conditioning systems.
– Online retailers: There are numerous online retailers that specialize in HVAC supplies and refrigerants. These platforms provide convenient access to a wide selection of Freon products.
– Licensed HVAC contractors: If you are not comfortable purchasing Freon yourself or have specific requirements, you can consult with a licensed HVAC contractor who can supply and install the refrigerant for you.
Factors to consider when purchasing Freon
When purchasing Freon for your air conditioner, several factors need to be considered:
– Type of Freon: Determine the specific type of Freon required for your air conditioning system. Refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines or consult with an HVAC professional to ensure compatibility and optimal performance.
– Environmental regulations: Familiarize yourself with local regulations regarding the use and disposal of certain types of Freon. Some refrigerants may be restricted or banned in your region due to their environmental impact.
– Brand reliability: Choose reputable brands that adhere to industry standards and have a track record of quality and performance.
– Authenticity: Be cautious of counterfeit or low-quality refrigerants. Purchase from trusted sources to ensure that you are buying genuine and reliable products.
– Quantity needed: Determine how much Freon is required for your air conditioner, which brings us to our next point.
How much Freon is needed for an air conditioner?
The amount of Freon needed for an air conditioner depends on various factors, including the size and capacity of the unit. HVAC professionals typically measure the refrigerant charge in pounds or ounces. It is crucial to follow the manufacturer’s specifications or consult with a qualified technician to ensure the correct amount of Freon is used.
Adding too little or too much refrigerant can negatively impact the performance and efficiency of the air conditioner. It can lead to inadequate cooling, increased energy consumption, or even damage to the system. Therefore, it is vital to have a trained professional assess and charge the system with the correct amount of Freon.
To determine the optimal refrigerant charge, the HVAC technician will consider factors such as the size of the air conditioner, the length of refrigerant lines, and potential leaks. They may also perform a pressure test to ensure the system is properly sealed and the refrigerant is accurately charged.
Purchasing Freon for your air conditioner requires careful consideration of the type, source, and quantity needed. By following these guidelines and consulting with professionals, you can ensure a smooth and efficient process when acquiring Freon for your air conditioning system.
Now that we have covered where to purchase Freon and the factors to consider when buying it, let’s explore alternative refrigerants that can be used as substitutes for Freon in air conditioners.
Freon Alternatives
As the environmental impact of traditional Freon refrigerants became more apparent, the need for alternative options for air conditioners arose. In this section, we will explore some of the alternative refrigerants available and discuss the benefits and drawbacks of using these options.
Exploring alternative refrigerants for air conditioners
1. R-32: R-32 is one of the most widely used alternative refrigerants for air conditioners. It is a hydrofluorocarbon (HFC) refrigerant with a lower global warming potential (GWP) than older Freon-based refrigerants. R-32 is known for its excellent energy efficiency and is commonly used in split air conditioning systems.
2. R-290 (Propane): R-290, or propane, is a hydrocarbon refrigerant with a very low GWP. It is highly efficient and has excellent thermodynamic properties. R-290 is used in some smaller residential air conditioning systems and offers a more environmentally friendly alternative to traditional refrigerants.
3. R-407A: R-407A is a blend of HFC refrigerants designed as a drop-in replacement for R-22. It has a lower GWP than R-22 but still contributes to global warming. R-407A is compatible with existing air conditioning systems designed for R-22, making it a convenient alternative without requiring extensive system modifications.
4. R-1234ze: R-1234ze is an HFO (hydrofluoroolefin) refrigerant that has a very low GWP and is non-flammable. It is considered a long-term alternative to Freon-based refrigerants. R-1234ze is used in some commercial and industrial air conditioning systems and offers excellent energy efficiency and environmental performance.
Benefits and drawbacks of using alternative options
Using alternative refrigerants in air conditioning systems offers several benefits, including:
– Environmental friendliness: Alternative refrigerants have significantly lower GWP compared to older Freon-based refrigerants, contributing less to climate change and ozone depletion.
– Energy efficiency: Many alternative refrigerants have improved energy efficiency, allowing for more sustainable and cost-effective cooling.
– Compliance with regulations: Switching to alternative refrigerants helps meet environmental regulations and phase-out requirements for older refrigerants.
However, there are a few drawbacks to be aware of:
– System compatibility: Some alternative refrigerants may require modifications to existing air conditioning systems or the use of specialized equipment designed for their specific properties.
– Cost considerations: The cost of alternative refrigerants may vary, and in some cases, they may be more expensive than traditional options.
– Availability: Depending on your location, the availability of certain alternative refrigerants may be limited. It is essential to consult with HVAC professionals or suppliers to ensure the availability of the desired refrigerant.
When considering alternative refrigerants, it is crucial to consult with HVAC professionals who have expertise in the specific refrigerant and its requirements. They can guide you in selecting the most suitable option based on your air conditioning system, cost considerations, and compliance with regulations.
Now that we have explored alternative refrigerants, let’s dive into the topic of recharging Freon in your air conditioner, including the signs that indicate a need for recharge and the options for getting it done.
Getting Freon Recharged
Over time, the Freon levels in your air conditioner may decrease due to leaks or natural evaporation. Recharging the Freon is necessary to ensure optimal cooling performance. In this section, we will discuss the signs that indicate your air conditioner needs a Freon recharge, how to recharge the Freon, and the considerations when deciding between hiring a professional or doing it yourself.
Read more: How To Remove Freon From An Air Conditioner
Signs that your air conditioner needs a Freon recharge
Several indications may suggest that your air conditioner requires a Freon recharge:
– Reduced cooling performance: If you notice that your air conditioner is not providing the same level of cooling as before, it could be a sign of low refrigerant levels.
– Longer cooling cycles: If your air conditioner is running for an extended period to achieve the desired temperature, it may be due to insufficient Freon.
– Warm air blowing: When warm air is coming out of the supply vents instead of cool air, it could be an indication of low Freon levels.
– Ice formation: If you observe ice forming on the evaporator coils, it could be a result of insufficient refrigerant.
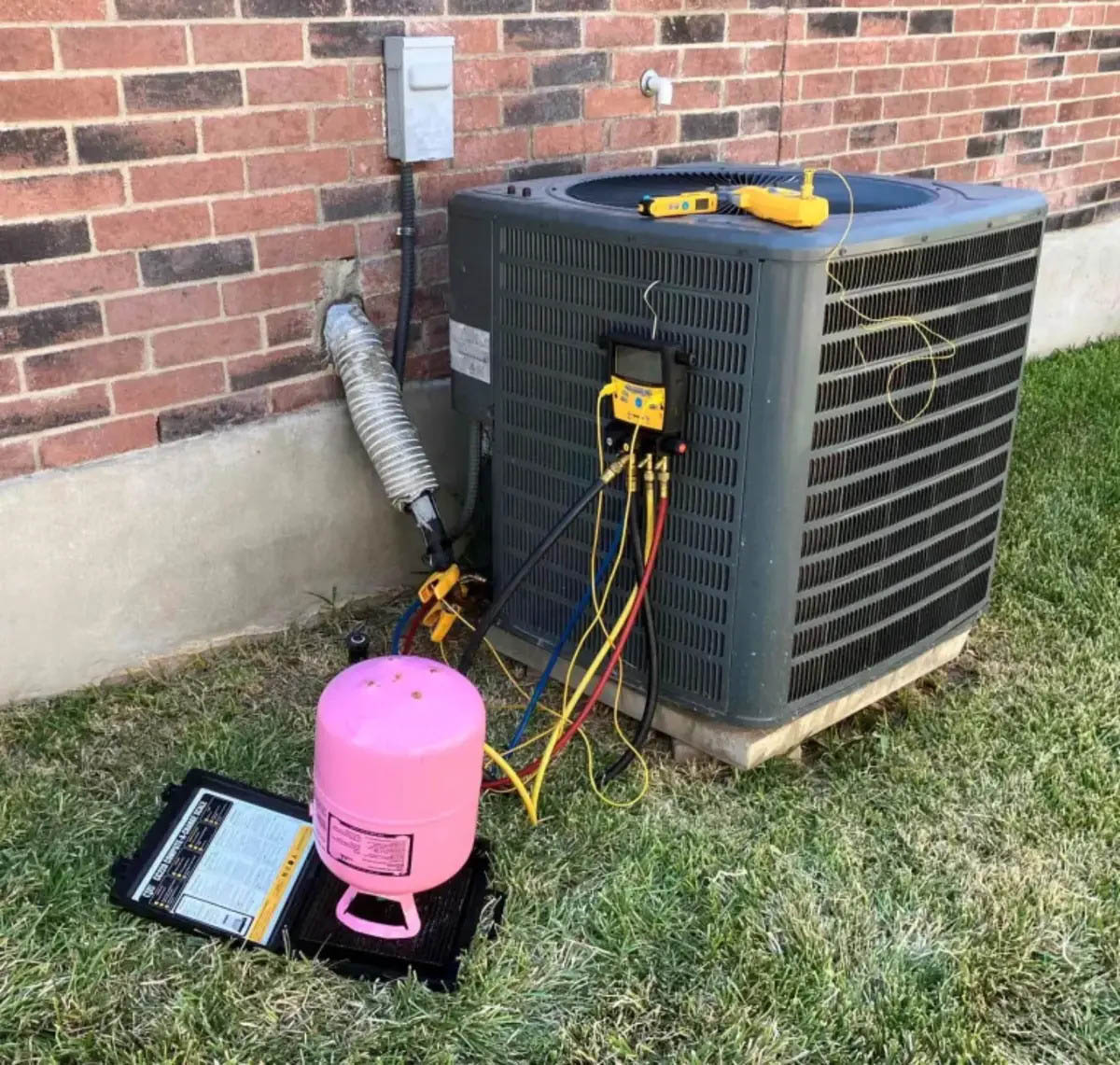
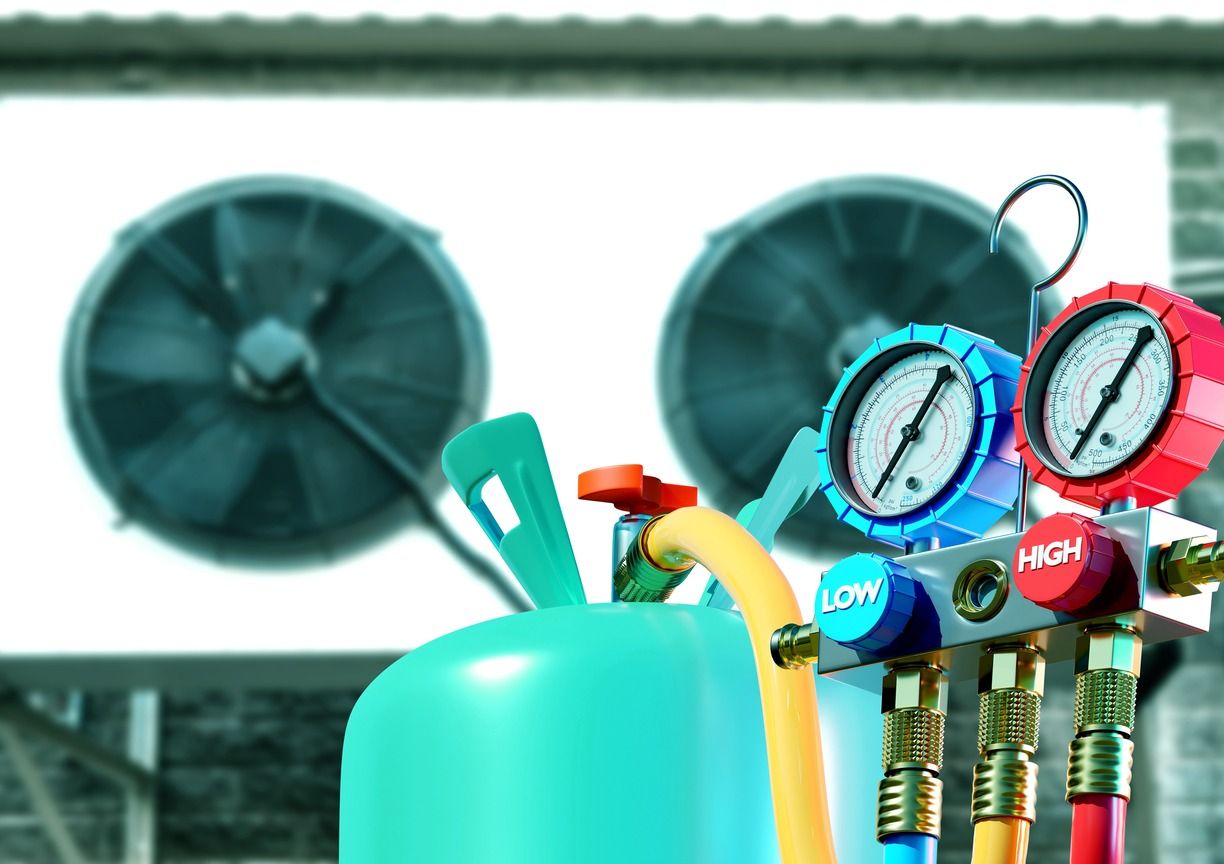
How to recharge the Freon in your air conditioner
Recharging the Freon in your air conditioner should be done by a qualified HVAC professional who has the necessary knowledge and equipment. The process typically involves these steps:
– Diagnosis: The technician will inspect your air conditioning system to determine if a Freon recharge is necessary. They will also check for any leaks that may be causing the refrigerant loss.
– Leak detection: If a leak is identified, the technician will locate and repair it before proceeding with the recharge. It is essential to fix leaks to prevent further refrigerant loss.
– Evacuation: Before adding new Freon, the technician will evacuate any remaining refrigerant from the system.
– Recharge: The technician will then introduce the correct amount of Freon into the system, based on the manufacturer’s specifications.
– Testing: Once the recharge is complete, the technician will test the system to ensure it is operating correctly and providing adequate cooling.
Hiring a professional versus DIY recharging
When it comes to recharging the Freon in your air conditioner, it is recommended to hire a professional for several reasons:
1. Safety: Handling refrigerants requires specialized knowledge and equipment to prevent harm to yourself and the environment. HVAC professionals are trained to handle refrigerants safely and follow proper disposal protocols.
2. Diagnosis: An HVAC professional can accurately diagnose the cause of the refrigerant loss and address any underlying issues that may be affecting your air conditioner’s performance.
3. Expertise: HVAC professionals have the expertise to recharge the Freon correctly, ensuring the right amount is added and the system is operating optimally.
4. Warranty considerations: DIY recharging may void the warranty on your air conditioning system. Hiring a professional ensures that the work is performed in compliance with warranty requirements.
While there are DIY recharge kits available on the market, it is strongly advised against attempting to recharge the Freon yourself. Mishandling refrigerants can be dangerous and may cause further damage to your system.
Now that you understand the process of recharging Freon, let’s discuss the importance of recycling and proper disposal of old or unused Freon.
Recycling and Disposing of Freon
Proper disposal of old or unused Freon is crucial to minimize its environmental impact and comply with regulations. In this section, we will discuss the proper methods for disposing of Freon, the environmental impact of Freon, and responsible disposal options.
Proper methods for disposing of old or unused Freon
1. Recycling: Recycling Freon is the preferred method of disposal as it allows for the purification and reuse of the refrigerant. This process involves removing any impurities from the Freon so that it can be safely reintroduced into air conditioning systems. Contact your local HVAC supply store or recycling centers to inquire about Freon recycling programs.
2. Reclamation: Reclamation refers to the process of recovering and purifying Freon from air conditioning systems that are being decommissioned. HVAC professionals who specialize in refrigerant reclamation can safely remove and clean the refrigerant for reuse or proper disposal.
3. Certified disposal: If recycling or reclamation is not possible, certified disposal facilities can safely handle the proper destruction of Freon. These facilities have the necessary equipment and expertise to ensure the refrigerant is safely neutralized or destroyed so that it doesn’t harm the environment.
Environmental impact of Freon and responsible disposal options
Freon and other chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) have been identified as significant contributors to ozone depletion and global warming. These substances have been phased out or restricted due to their harmful effects on the environment and human health.
By properly disposing of Freon, you can help reduce its environmental impact. Improperly discarding Freon, such as releasing it into the atmosphere or pouring it down the drain, can have severe consequences. Freon can deplete the ozone layer and contribute to climate change when it reacts with sunlight in the upper atmosphere.
It is essential to take responsibility for the proper disposal of Freon by following these guidelines:
– Avoid venting: Never release Freon into the atmosphere as it contributes to ozone depletion and global warming. Venting refrigerants is illegal in most jurisdictions due to environmental regulations.
– Partner with professionals: When decommissioning old air conditioning systems or disposing of unused refrigerants, work with HVAC professionals who are trained in proper refrigerant handling and disposal techniques.
– Follow local regulations: Familiarize yourself with local regulations regarding the disposal of refrigerants. Contact your local HVAC or environmental authorities to understand the specific guidelines and requirements in your area.
– Educate others: Spread awareness about the importance of responsible Freon disposal among friends, family, and the community. Encourage others to take proper measures to protect the environment by disposing of refrigerants responsibly.
By taking these responsible actions, you can contribute to preserving the environment and mitigating the impact of Freon on ozone depletion and global warming.
Now that we understand the importance of proper Freon disposal, let’s conclude with some final thoughts on where to get Freon for your air conditioner and future trends in refrigerant alternatives.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding Freon and its role in air conditioning systems is crucial for ensuring effective cooling in our homes. We have explored the importance of Freon, its function in the cooling process, and the different types of Freon used in air conditioners.
When it comes to purchasing Freon, you have various options, including HVAC supply stores, online retailers, and licensed HVAC contractors. Factors to consider when buying Freon include the type of refrigerant, environmental regulations, brand reliability, authenticity, and the quantity needed for your specific air conditioner.
Additionally, we have explored alternative refrigerants that serve as substitutes for Freon. These alternatives offer benefits such as lower environmental impact, improved energy efficiency, and compliance with regulations. R-32, R-290 (Propane), R-407A, and R-1234ze are some examples of alternative refrigerants that are being used in air conditioning systems.
Recharging the Freon in your air conditioner is a task best left to professionals. Signs that your air conditioner needs a Freon recharge include reduced cooling performance, longer cooling cycles, warm air blowing, and ice formation. To properly recharge the Freon, a qualified HVAC technician will diagnose the system, detect any leaks, evacuate the remaining refrigerant, recharge the correct amount of Freon, and perform testing to ensure optimal performance.
When it comes to disposing of old or unused Freon, recycling and reclamation are preferred methods. These options allow for the purification and reuse of the refrigerant, or its safe destruction. By responsibly disposing of Freon, we can minimize its environmental impact, prevent ozone depletion, and reduce contributions to climate change.
Looking ahead, the HVAC industry continues to evolve, with a focus on more environmentally friendly refrigerant alternatives. The future trends in refrigerant alternatives for air conditioners are centered around developing refrigerants with even lower global warming potential and improved energy efficiency. As technology advances and regulations become stricter, we can expect to see further advancements in refrigerant options that prioritize sustainability and performance.
Ultimately, when it comes to handling Freon and maintaining our air conditioning systems, prioritizing environmental responsibility and seeking professional expertise are essential. By staying informed, making conscious choices, and working with qualified professionals, we can ensure the comfort of our homes while safeguarding the environment.
Frequently Asked Questions about Where To Get Freon For An Air Conditioner
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.