

Articles
How Many Watts Is An LED Bulb
Modified: January 8, 2024
Discover the answer to the question "How many watts is an LED bulb?" in this informative article. Learn about the energy efficiency of LED bulbs and their wattage equivalents.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
LED (Light Emitting Diode) bulbs are becoming increasingly popular as a lighting choice for homes and businesses. Their energy efficiency, durability, and variety of light output options make them a smart alternative to traditional incandescent and fluorescent bulbs. But how many watts is a LED bulb actually?
In this article, we will explore the world of LED bulbs, their wattage, and why it matters. We will discuss how LED bulbs work, compare their wattage to traditional bulbs, and delve into the factors that affect LED bulb wattage. Additionally, we will highlight the benefits of using LED bulbs and why they are a great investment for both monetary savings and environmental impact.
So, if you’re curious about understanding the wattage of LED bulbs and why it’s important, read on to discover more!
Key Takeaways:
- LED bulbs have lower wattage ratings than traditional bulbs but can produce the same or higher brightness levels while consuming significantly less energy, leading to cost savings and environmental benefits.
- Factors such as lumen output, color temperature, dimmability, and design impact the wattage of LED bulbs, allowing for customized lighting solutions that maximize energy efficiency and brightness.
Read more: How Many Watts In A Light Bulb
What is a LED bulb?
A LED bulb is a type of lighting source that utilizes a semiconductor device called a Light Emitting Diode (LED) to produce light. Unlike traditional incandescent bulbs that rely on a filament to generate light, LED bulbs work by passing an electric current through a microchip, which illuminates the LED and emits light.
LED bulbs are known for their energy efficiency and longevity. They consume significantly less energy compared to incandescent and fluorescent bulbs, making them an eco-friendly choice. Moreover, LED bulbs have a longer lifespan, typically lasting up to 25 times longer than incandescent bulbs.
LED bulbs are available in a range of shapes and sizes, making them suitable for various lighting applications. They can be found in standard screw-in bulbs, as well as specialized formats such as tube lights, floodlights, and decorative bulbs.
With advancements in technology, LED bulbs now offer a variety of color temperatures, allowing users to choose between warm white, cool white, and daylight tones. This versatility makes LED bulbs suitable for both ambient and task lighting.
LED bulbs also come with additional features, such as dimmable options and smart capabilities, allowing users to control brightness and color with ease. These features add to the convenience and customization possibilities of LED lighting.
In summary, LED bulbs are energy-efficient, long-lasting, and versatile lighting sources that utilize LED technology to produce light. Their numerous advantages over traditional bulbs make them a popular choice for both residential and commercial lighting needs.
How does a LED bulb work?
To understand how a LED bulb works, it’s important to grasp the basic principles of the LED technology. At the heart of an LED bulb is a semiconductor material, typically made of gallium arsenide, gallium nitride, or silicon carbide. This semiconductor material acts as a diode, allowing the current to flow in only one direction.
When an electric current is applied to the LED, the electrons in the semiconductor material gain energy and move to a higher energy level. As these electrons transition back to a lower energy level, they release energy in the form of photons, which produces light.
Unlike traditional bulbs, LED bulbs do not rely on heating a filament to produce light, which results in a significant reduction in energy consumption. The energy efficiency of LED bulbs can be attributed to the fact that they convert almost all of the electrical energy into light, rather than generating excess heat.
LED bulbs also have a different method of color generation compared to incandescent bulbs. In incandescent bulbs, the filament emits a broad spectrum of light, which then gets filtered to produce specific colors. LED bulbs, on the other hand, emit light in a narrow color range determined by the materials used in the semiconductor layers. By adjusting the composition of these layers, different colors can be achieved.
The size and composition of the semiconductor material also play a crucial role in determining the brightness and efficiency of an LED bulb. Larger semiconductor materials and higher-quality materials tend to produce brighter and more efficient bulbs.
In summary, LED bulbs work by using a semiconductor material to convert electrical energy into light. The movement of electrons within the semiconductor generates photons, resulting in the emission of light. The absence of a filament and the ability to control color output make LED bulbs highly efficient and versatile illumination sources.
Energy consumption of LED bulbs
One of the main advantages of LED bulbs is their energy efficiency. LED bulbs consume significantly less energy compared to traditional incandescent and fluorescent bulbs. This energy-saving characteristic is a result of the unique way LED bulbs produce light.
On average, LED bulbs consume around 80% less energy than incandescent bulbs for the same level of brightness. This drastic reduction in energy consumption leads to substantial cost savings on electricity bills and contributes to a greener environment.
The energy efficiency of LED bulbs can be attributed to several factors:
- Directional lighting: LED bulbs emit light in a specific direction, unlike traditional bulbs that emit light in all directions. This eliminates the need for reflectors or diffusers, reducing energy wastage.
- No heat wastage: LED bulbs generate minimal heat compared to incandescent bulbs. Incandescent bulbs waste a significant amount of energy by converting it into heat rather than light.
- Instantaneous lighting: LED bulbs light up instantly when switched on, without any warm-up period. This ensures that no energy is wasted while waiting for the bulb to reach full brightness.
Furthermore, LED bulbs have a longer lifespan, which also contributes to their energy efficiency. The extended lifespan means fewer replacements, resulting in reduced energy consumption during the manufacturing and disposal processes.
In terms of actual wattage consumption, LED bulbs vary depending on the brightness level or lumen output. Generally, LED bulbs range from 2 to 20 watts, with higher wattage bulbs producing more brightness. However, it’s important to note that wattage alone does not determine the brightness; the lumens output is a more accurate measure of a bulb’s brightness.
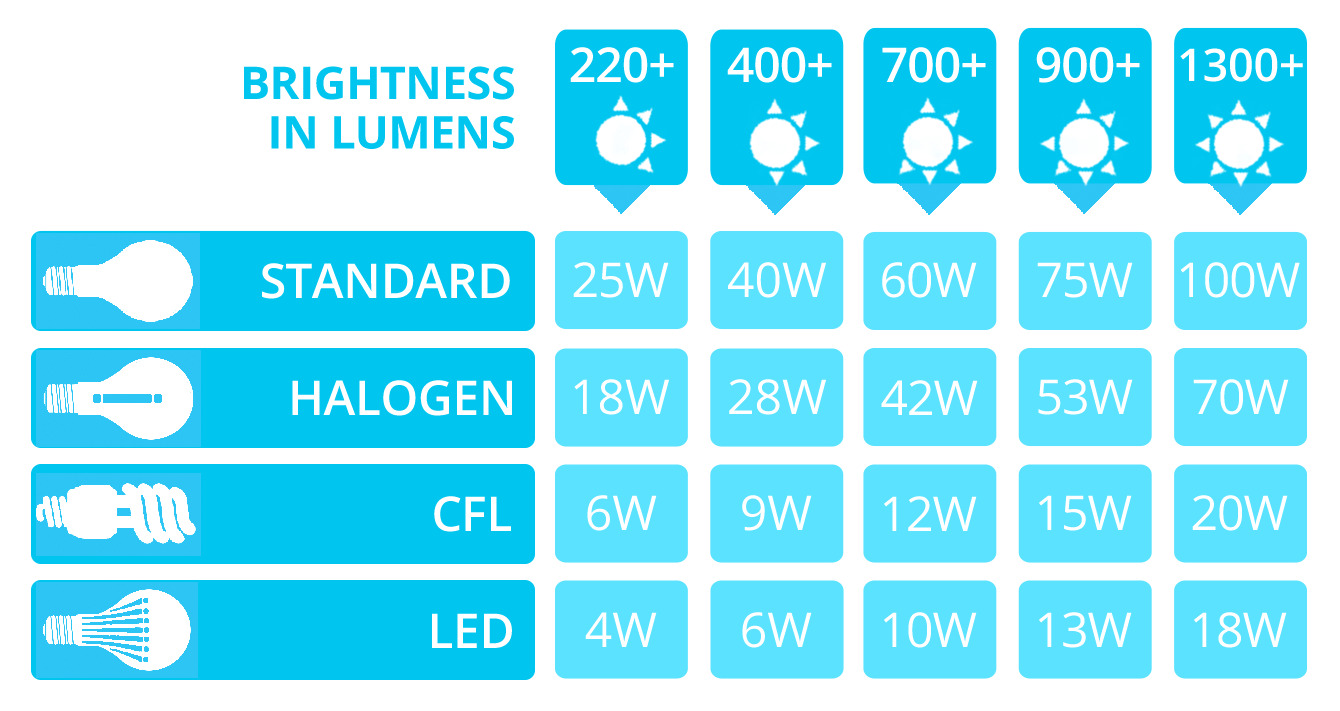
For example, a 10-watt LED bulb can provide the same amount of brightness as a 60-watt incandescent bulb, but at a fraction of the energy consumption. This is why it’s crucial to consider the lumens output when comparing the brightness of LED bulbs to traditional ones.
Overall, the energy efficiency of LED bulbs makes them a cost-effective and environmentally friendly lighting solution. With lower energy consumption and longer lifespans, LED bulbs not only save money but also reduce greenhouse gas emissions and contribute to a more sustainable future.
When choosing an LED bulb, look for the wattage equivalent rather than actual wattage. For example, a 10-watt LED bulb may be equivalent to a 60-watt incandescent bulb.
Comparing LED bulb wattage to traditional bulbs
When it comes to comparing LED bulb wattage with traditional bulbs, it’s important to consider both the brightness output and energy consumption. While LED bulbs typically have lower wattage ratings than traditional bulbs, they can still produce the same level of brightness or even higher.
LED bulbs are designed to be highly efficient, converting a higher percentage of electrical energy into light rather than heat. This means that they can achieve the same level of brightness as traditional bulbs while consuming significantly less energy.
For example, a traditional incandescent bulb may require 60 watts to produce a certain level of brightness. In contrast, an LED bulb with a wattage rating of 10 watts can provide the same amount of brightness. This discrepancy in wattage highlights the energy efficiency of LED bulbs, which can result in substantial energy savings over time.
It’s important to note that the brightness of a bulb is measured in lumens rather than wattage. Lumens indicate the amount of light output, while wattage refers to the electrical power consumed. LED bulbs can achieve a higher lumen output per watt compared to traditional bulbs, making them more energy-efficient and cost-effective.
Additionally, LED bulbs offer a wider range of options when it comes to brightness levels. They are available in various wattage ratings and color temperatures, allowing users to customize their lighting experience. This versatility gives users greater control over the ambiance and functionality of their lighting setups.
Another benefit of LED bulbs is their long lifespan, which significantly surpasses that of traditional bulbs. While traditional incandescent bulbs may last around 1,000 hours, LED bulbs can last up to 25,000 hours or more. This extended lifespan not only saves money on bulb replacements but also reduces environmental impact by reducing waste.
In summary, LED bulbs can produce the same level of brightness as traditional bulbs while consuming significantly less energy. The lower wattage ratings of LED bulbs are a testament to their efficiency, allowing users to achieve the desired brightness while reducing energy costs and environmental impact.
Read more: How Many Lumens Is A 200-Watt LED Bulb
Factors affecting the wattage of LED bulbs
The wattage of LED bulbs can be influenced by several factors that affect their energy consumption and light output. Understanding these factors can help users make informed decisions when selecting LED bulbs for their lighting needs.
- Lumen output: The lumen output measures the brightness or amount of light emitted by a bulb. LED bulbs with higher lumen outputs usually have higher wattage ratings to accommodate the increased light output. However, advancements in LED technology have allowed for more efficient luminous efficacy, which means that higher lumen outputs can be achieved with lower wattage consumption.
- Color temperature: LED bulbs are available in different color temperatures, ranging from warm white to cool white. The color temperature affects the appearance of the light, with lower color temperatures appearing warmer and higher color temperatures appearing cooler. While the color temperature does not directly affect the wattage rating, different color temperature options may have different wattage ratings available.
- Dimmability: Some LED bulbs offer dimmable capabilities, allowing users to adjust the brightness according to their preferences. Dimmable LED bulbs may have different wattage ratings to accommodate the dimming feature. It’s important to check the compatibility of dimmable LED bulbs with dimmer switches to ensure proper functionality.
- Design and construction: The design and construction of LED bulbs can also impact their wattage ratings. Higher-quality LED bulbs may have more advanced components and better heat dissipation mechanisms, resulting in higher efficiency and potentially lower wattage ratings for the same light output.
- Efficiency of the driver: LED bulbs require a driver to regulate the electrical current supplied to the LED. The efficiency of the driver can affect the overall energy consumption of the bulb. Higher-quality drivers can provide better power conversion efficiency, resulting in lower wattage consumption for the same light output.
It’s important to consider these factors when selecting LED bulbs to ensure that the wattage rating aligns with the desired brightness and energy efficiency requirements. Users should also refer to the manufacturer’s specifications and recommendations for optimal performance and compatibility.
In summary, the wattage of LED bulbs can be influenced by various factors such as lumen output, color temperature, dimmability, design, and the efficiency of the driver. Understanding these factors allows users to choose LED bulbs that meet their specific lighting needs while maximizing energy efficiency.
Benefits of using LED bulbs
Switching to LED (Light Emitting Diode) bulbs offers numerous benefits compared to traditional incandescent and fluorescent bulbs. From energy savings to environmental impact, LED bulbs provide a host of advantages that make them a smart choice for both homes and businesses.
- Energy efficiency: LED bulbs are highly energy-efficient, consuming significantly less electricity compared to traditional bulbs. On average, LED bulbs use around 80% less energy, which translates to substantial savings on electricity bills. Their efficiency is due to the technology’s ability to convert a higher percentage of electrical energy into light rather than heat.
- Long lifespan: LED bulbs have an impressively long lifespan compared to traditional bulbs. While incandescent bulbs typically last around 1,000 hours, LED bulbs can last up to 25,000 hours or more. This means fewer replacements, reduced maintenance costs, and less environmental waste.
- Cost savings: Although LED bulbs may have a higher upfront cost compared to traditional bulbs, they offer long-term cost savings. The combination of energy efficiency and extended lifespan results in lower energy bills and reduced replacement expenses. Over time, the cost of LED bulbs is offset by the significant savings they provide.
- Environmentally friendly: LED bulbs are more environmentally friendly than traditional bulbs. Thanks to their energy efficiency, they help reduce greenhouse gas emissions associated with electricity generation. LED bulbs also contain no mercury or other harmful substances, making them safe for disposal and minimizing environmental impact.
- Durability: LED bulbs are built to be durable and resistant to shock, vibration, and temperature changes. Unlike traditional bulbs, which are fragile and prone to breaking, LED bulbs can withstand rough handling and are less likely to fail due to external factors. This makes them ideal for various applications, including outdoor lighting.
- Instant and flicker-free lighting: LED bulbs provide instant illumination without any warm-up time. They turn on at full brightness immediately, making them suitable for areas where instant lighting is required. LED bulbs also do not produce the noticeable flickering associated with some traditional bulbs, creating a more pleasant and comfortable lighting experience.
- Design flexibility: LED technology allows for design flexibility, as LED bulbs are available in various shapes, sizes, and colors. This versatility makes them suitable for different lighting applications, from decorative lighting to task lighting, allowing users to create the desired ambiance and functionality in any space.
By utilizing LED bulbs, users can enjoy the benefits of energy efficiency, cost savings, durability, and environmental responsibility. These advantages, combined with the versatility and aesthetic options of LED lighting, make it an excellent choice for both residential and commercial lighting needs.
Conclusion
LED bulbs have revolutionized the lighting industry with their energy efficiency, longevity, and versatility. Understanding the wattage of LED bulbs is essential in determining their energy consumption and brightness levels. While LED bulbs typically have lower wattage ratings compared to traditional bulbs, they can produce the same or even higher levels of brightness while consuming significantly less energy.
LED bulbs work by utilizing semiconductor technology to convert electrical energy into light, resulting in reduced energy wastage and heat generation. They offer various color temperatures, dimmable options, and design flexibility, allowing users to customize their lighting experience to suit their preferences and needs.
LED bulbs provide numerous benefits, making them a smart investment for lighting needs. They are highly energy-efficient, contributing to cost savings on electricity bills and reducing environmental impact. LED bulbs also have a long lifespan, minimizing the need for frequent replacements and reducing waste. Additionally, LED bulbs are durable, instant, flicker-free, and environmentally friendly.
In conclusion, LED bulbs offer a more sustainable, cost-effective, and technologically advanced lighting solution compared to traditional bulbs. Their energy efficiency, lifespan, and range of customizable options make them an appealing choice for residential and commercial applications. By switching to LED bulbs, individuals and businesses can enjoy the benefits of efficient, high-quality lighting while making a positive impact on both their finances and the environment.
Frequently Asked Questions about How Many Watts Is An LED Bulb
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.














0 thoughts on “How Many Watts Is An LED Bulb”