

Articles
How To Store Batteries When Not In Use
Modified: February 22, 2024
Learn how to properly store batteries when they are not in use with these helpful articles. Prevent corrosion and extend the lifespan of your batteries.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Batteries are an essential part of our daily lives. From powering our portable electronic devices to providing the necessary energy for our vehicles, batteries play a crucial role in our modern society. However, there are often instances when we find ourselves with unused batteries. Whether it’s a spare set of batteries or those that we remove from our devices due to low power, knowing how to store batteries when not in use is essential.
Improper storage of batteries can lead to reduced performance, leakage, or even explosions in extreme cases. Therefore, understanding the different types of batteries and their individual storage requirements is imperative to prolong their lifespan and ensure their safety.
In this article, we will explore the various types of batteries commonly used and provide valuable insights on how to store them correctly when they are not in use. We will delve into the specific storage conditions for alkaline batteries, lithium-ion batteries, nickel-based batteries, rechargeable batteries, button cell batteries, and car batteries.
By following the guidelines and best practices for battery storage, you can maximize their shelf life, prevent accidents, and ultimately save money by avoiding unnecessary replacements.
Key Takeaways:
- Proper storage of batteries is crucial for maintaining performance, preventing leakage, and ensuring safety. Follow specific guidelines for each battery type to maximize shelf life and avoid unnecessary replacements.
- Check expiry dates, store in a cool, dry place, and use individual containers to prevent contact between terminals. Regularly monitor charge levels and follow manufacturer recommendations for optimal battery storage.
Read more: How To Store Car Battery When Not In Use
Understanding Battery Types
Before diving into the specifics of storing batteries, it is essential to understand the different types of batteries and their characteristics. This knowledge will help us determine the appropriate storage conditions for each type.
1. Alkaline Batteries: Alkaline batteries are the most commonly used type of batteries. They are typically used in devices like remote controls, toys, and flashlights. Alkaline batteries are non-rechargeable and have a long shelf life if stored correctly.
2. Lithium-ion Batteries: Lithium-ion batteries are rechargeable and are commonly found in electronic devices such as laptops, smartphones, and cameras. They have a high energy density and can store a significant amount of power. However, they require special care when storing to prevent overheating or leakage.
3. Nickel-based Batteries: Nickel-based batteries include Nickel-Cadmium (Ni-Cd) and Nickel-Metal Hydride (Ni-MH) batteries. They are rechargeable batteries commonly used in portable electronics like cordless phones and power tools. Nickel-based batteries can suffer from memory effects if not properly managed.
4. Rechargeable Batteries: Rechargeable batteries come in various chemistries, including lithium-ion, nickel-based, and lead-acid. They are designed to be used repeatedly and are an eco-friendly alternative to disposable batteries. Proper storage is essential to maintain their performance and extend their lifespan.
5. Button Cell Batteries: Button cell batteries are small, round, and often used in devices such as watches, calculators, and hearing aids. They come in different chemistries, such as silver oxide and lithium, and should be stored properly to prevent leakage and damage to devices.
6. Car Batteries: Car batteries are lead-acid batteries specifically designed to provide the necessary power to start the engine and run various electrical components in vehicles. They require specific storage conditions to prevent sulfation and maintain their charge.
Understanding these different battery types is crucial for determining the appropriate storage methods for each type. By taking the specific characteristics of each battery into account, we can ensure their longevity, safety, and optimal performance when they are needed.
Proper Storage Conditions
Proper storage conditions play a vital role in maintaining the performance and extending the lifespan of batteries. Here are some general guidelines to follow when storing batteries:
- Temperature: Batteries should be stored in a cool, dry place at temperatures between 50°F (10°C) and 77°F (25°C). Avoid exposing batteries to extreme temperatures like freezing cold or excessive heat, as it can impact their performance and cause leakage.
- Avoid Moisture: Moisture can cause corrosion and damage to batteries. Store batteries in a dry environment and avoid exposing them to excessive humidity or water.
- Avoid Direct Sunlight: Sunlight can generate heat and adversely affect batteries. Keep batteries away from direct sunlight or other sources of heat, such as radiators or ovens.
- Avoid Vibration: Vibrations can cause internal damage to batteries. Store them in a stable location and avoid keeping them near machinery or appliances that produce vibrations.
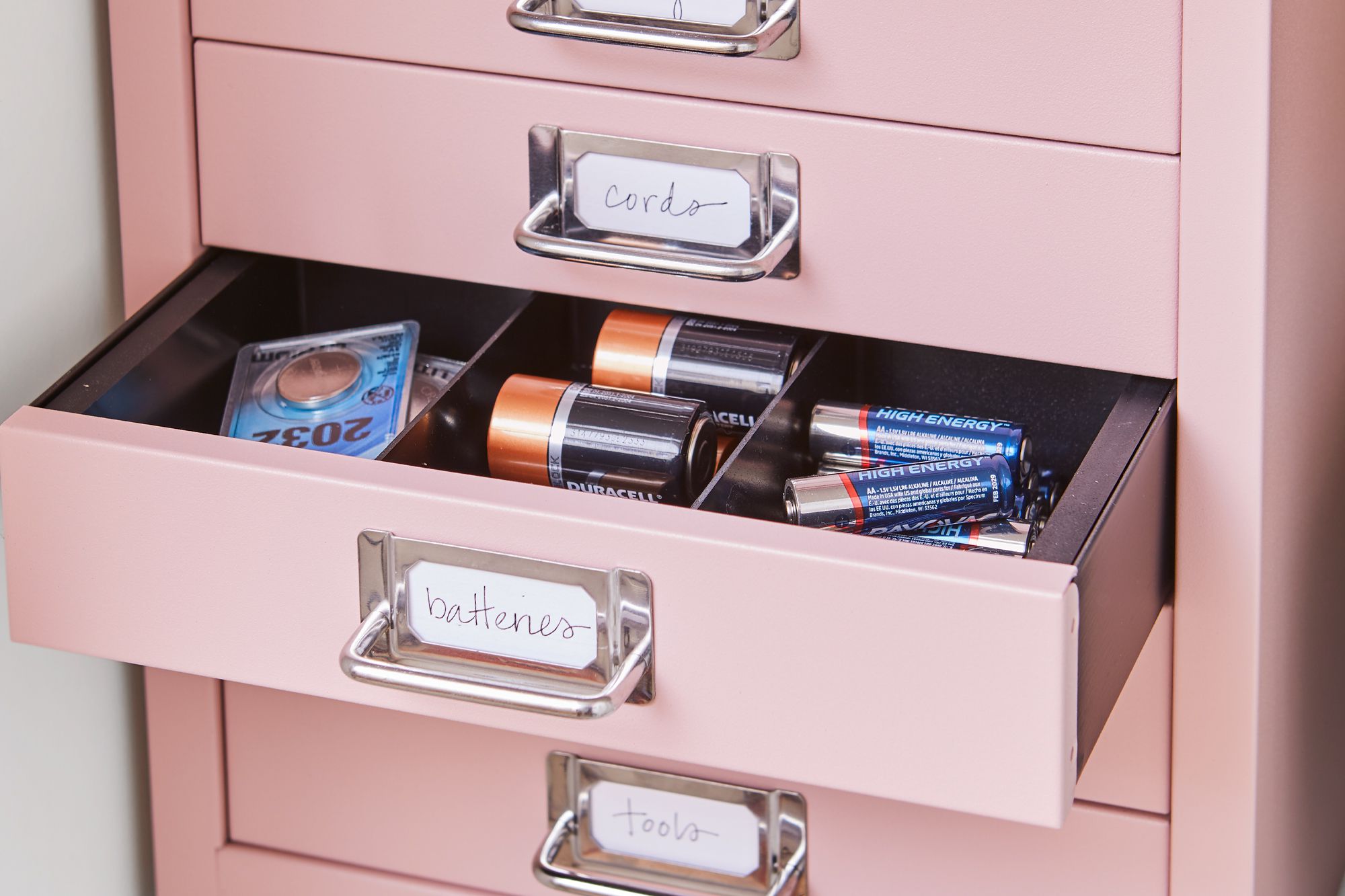
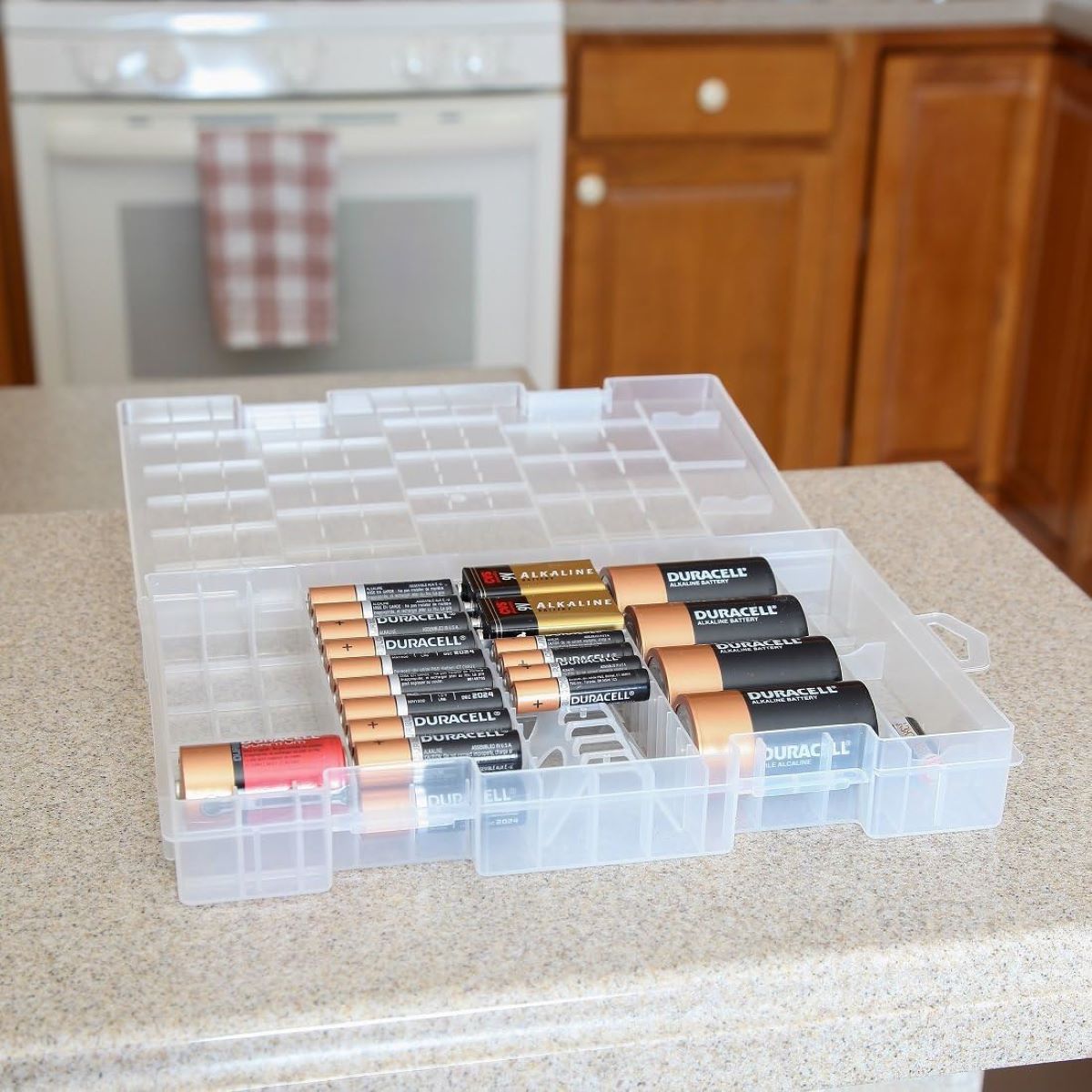
- Keep Separate: Store batteries individually or keep them separated using non-conductive materials such as plastic bags or containers. This prevents accidental short circuits caused by battery contact.
While these general guidelines apply to most types of batteries, it is important to note that specific battery types may have additional storage requirements. Let’s take a closer look at the storage recommendations for different battery types.
Storing Alkaline Batteries
Alkaline batteries are widely used in various household devices, and proper storage is essential to maintain their performance and prevent leakage. Here are some tips for storing alkaline batteries:
- Check Expiry Dates: Before storing alkaline batteries, check the expiry dates. Discard any batteries that have expired, as they may leak or not function properly.
- Remove Batteries from Devices: If you’re not planning to use a device for an extended period, remove the alkaline batteries. This helps prevent corrosion and potential leakage if the batteries were to degrade over time.
- Store in a Cool, Dry Place: Keep alkaline batteries in a cool, dry place. Avoid areas with extreme temperature fluctuations, as it can impact battery performance. Ideal storage temperatures for alkaline batteries range between 50°F (10°C) and 77°F (25°C).
- Avoid High Humidity: Moisture can cause alkaline batteries to corrode and leak. Store them in a dry environment, away from humid areas like bathrooms or basements.
- Store in an Upright Position: To further prevent any potential leakage, store alkaline batteries in an upright position. This helps keep the electrolyte inside the battery and reduces the risk of contact between terminals.
- Keep Separate from Metal Objects: When storing alkaline batteries, avoid placing them near metal objects or other batteries. Metal objects can create a short circuit if they come into contact with battery terminals, which can lead to leakage or damage.
By following these guidelines, you can prolong the shelf life of your alkaline batteries and ensure they are ready for use when you need them. Remember to always dispose of expired or damaged alkaline batteries properly and responsibly.
Storing Lithium-ion Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries are commonly used in smartphones, laptops, and other electronic devices. Proper storage is crucial to maintain their performance, prevent degradation, and ensure safety. Follow these tips when storing lithium-ion batteries:
- Charge to Optimal Level: Before storage, charge the lithium-ion battery to around 50% capacity. This level helps to minimize degradation during storage, as fully charged or discharged batteries can be more prone to degradation.
- Store in a Cool Environment: Lithium-ion batteries should be stored in a cool environment with temperatures ranging from 50°F (10°C) to 77°F (25°C). Avoid storing them in extremely hot or cold locations, as it can affect battery performance and shorten their lifespan.
- Avoid Direct Sunlight: Keep lithium-ion batteries away from direct sunlight or sources of heat. Exposure to high temperatures can lead to internal damage or even thermal runaway, posing safety risks.
- Use Suitable Storage Containers: When storing lithium-ion batteries, use non-conductive containers or individual battery cases to prevent contact between terminals and other objects. This reduces the risk of short circuits and potential accidents.
- Disconnect Devices: If you’re storing a device with a non-removable lithium-ion battery, ensure the device is powered off or in a shutdown state. This helps minimize any potential power drain on the battery during storage.
- Regularly Check Charge Level: Periodically check the charge level of stored lithium-ion batteries. If you notice a significant drop below 50% capacity, consider giving them a brief charge to bring them back to the optimal storage level.
- Avoid Long-Term Storage: Lithium-ion batteries perform best when they are used regularly. If you plan to store lithium-ion batteries for an extended period, it is advisable to use them and recharge them at least once every six months to maintain their health.
Following these storage guidelines will help extend the lifespan and maintain the performance of lithium-ion batteries. Always ensure that lithium-ion batteries are recycled or disposed of properly if they are damaged or no longer functional.
Store batteries in a cool, dry place at room temperature. Avoid storing them in extreme temperatures or humid environments, as this can reduce their performance and lifespan.
Storing Nickel-based Batteries
Nickel-based batteries, such as Nickel-Cadmium (Ni-Cd) and Nickel-Metal Hydride (Ni-MH) batteries, are rechargeable and commonly used in portable electronics and power tools. To ensure their longevity and performance, proper storage is important. Follow these tips when storing nickel-based batteries:
- Charge to Full Capacity: Before storing nickel-based batteries, charge them to their full capacity. This helps prevent the development of a memory effect, which can reduce the overall capacity of the battery over time.
- Store at Cool Temperatures: Nickel-based batteries should be stored in a cool environment with temperatures below 77°F (25°C). Avoid exposing them to extreme heat or cold, as it can impact their performance and overall lifespan.
- Use Individual Battery Cases: When storing nickel-based batteries, it is recommended to store them individually in plastic battery cases or separate compartments. This prevents terminals from coming into contact with each other or with other metal objects, reducing the risk of a short circuit.
- Avoid High Humidity: Moisture can cause corrosion and damage to nickel-based batteries. Store them in a dry environment or use silica gel packs to absorb moisture and maintain optimal conditions.
- Do Not Fully Discharge: Unlike some other battery types, nickel-based batteries should not be fully discharged before storage. It is recommended to store them with a charge level between 40% and 70% to maintain their health.
- Monitor Charge Periodically: Check the charge level of stored nickel-based batteries periodically. If the charge drops significantly below the recommended range, consider giving them a partial recharge to bring them back to the desired level.
- Avoid Long-Term Storage: Nickel-based batteries perform best when they are used regularly. If you plan to store them for an extended period, it is advisable to use and recharge them at least every three months to prevent capacity loss and maintain their optimal performance.
By following these guidelines, you can ensure that your nickel-based batteries remain in good condition and provide reliable power when you need them. Remember to always recycle or dispose of nickel-based batteries responsibly if they are no longer functional or damaged.
Storing Rechargeable Batteries
Rechargeable batteries come in various chemistries, including lithium-ion, nickel-based, and lead-acid. To maintain their performance and extend their lifespan, proper storage is essential. Here are some tips for storing rechargeable batteries:
- Charge to the Optimal Level: Before storage, ensure that rechargeable batteries are adequately charged. For lithium-ion batteries, store them at around 50% capacity, while nickel-based batteries should be fully charged. Lead-acid batteries should also be fully charged to prevent sulfation.
- Choose a Cool, Dry Location: Rechargeable batteries should be stored in a cool, dry place with temperatures between 50°F (10°C) and 77°F (25°C). Avoid exposing them to extreme temperatures, as it can affect their performance and lifespan.
- Use Individual Battery Cases: When storing rechargeable batteries, it is recommended to keep them in their original battery cases or store them individually. This prevents terminal contact and reduces the risk of short circuits or damage.
- Avoid High Humidity: Moisture can damage rechargeable batteries, so it’s essential to store them in a dry environment. If necessary, use desiccant packs or silica gel to absorb excess moisture and maintain optimal storage conditions.
- Regularly Check Charge Levels: Periodically check the charge levels of stored rechargeable batteries. If the charge drops significantly, consider giving them a brief charge to bring them back to their optimal storage level.
- Avoid Long-Term Storage Without Use: Rechargeable batteries perform best when used regularly. If you plan to store them for an extended period without use, it is recommended to recharge them every few months to prevent capacity loss and maintain their health.
- Follow Manufacturer Recommendations: Different rechargeable battery chemistries may have specific storage instructions. Always refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines for the specific type of rechargeable battery you are storing.
By following these guidelines, you can ensure that your rechargeable batteries remain in good condition and provide reliable power when needed. Proper storage will help maintain their performance, extend their lifespan, and maximize their value for your electronic devices or other applications.
Storing Button Cell Batteries
Button cell batteries are small, round batteries commonly used in devices like watches, calculators, and hearing aids. Although they may seem less powerful than other battery types, proper storage is still important to maintain their performance and prevent any potential issues. Here are some tips for storing button cell batteries:
- Check Expiry Dates: Before storing button cell batteries, check the expiry dates on the packaging or battery itself. Discard any batteries that have expired, as they may not function properly and could leak.
- Store in a Cool, Dry Place: Button cell batteries should be stored in a cool, dry place with temperatures between 50°F (10°C) and 77°F (25°C). Avoid exposing them to extreme temperature fluctuations or high heat.
- Use Individual Compartments or Containers: When storing button cell batteries, it is recommended to keep them separated using individual compartments or non-conductive containers. This prevents accidental contact between battery terminals and reduces the risk of short circuits.
- Avoid High Humidity: Moisture can cause button cell batteries to corrode and leak. Store them in a dry environment and consider using silica gel packs to absorb excess moisture and maintain optimal storage conditions.
- Keep away from Metal Objects: To prevent accidental short circuits, store button cell batteries away from other metal objects. Metal objects can create a connection between the battery terminals, which could lead to leakage or damage.
- Avoid Mixing Different Battery Types: If storing multiple button cell batteries, avoid mixing different chemistries or mixing new and used batteries. Mixing different battery types may cause irregular discharge rates and affect overall performance.
- Regularly Check Charge Levels: Check the charge levels of stored button cell batteries periodically. If the battery voltage drops significantly, it may be an indication of self-discharge or battery degradation. Replace batteries with low voltage to ensure optimal performance.
By following these storage guidelines, you can prolong the shelf life of your button cell batteries and ensure they are ready for use when you need them. Remember to always dispose of used or damaged button cell batteries responsibly and in accordance with local regulations.
Storing Car Batteries
Car batteries are crucial for starting the engine and powering various electrical components in vehicles. Proper storage is essential to ensure the longevity and optimal performance of car batteries, especially when they are not in use for an extended period. Here are some tips for storing car batteries:
- Charge the Battery: Before storage, it is recommended to fully charge the car battery. A fully charged battery is less likely to freeze and will be better equipped to handle the storage period.
- Disconnect the Battery: If your vehicle will not be used for an extended period, disconnect the battery cables. This prevents any power drain from the vehicle’s electrical system and extends the battery’s life.
- Store in a Cool, Dry Place: Car batteries should be stored in a cool, dry place. Avoid exposure to direct sunlight and extreme temperatures, as excessive heat can accelerate battery degradation and freezing temperatures can damage the battery’s internal components.
- Avoid Corrosive or Flammable Substances: Keep car batteries away from corrosive substances such as cleaning agents or solvents. These chemicals can damage the battery casing and terminals. Additionally, avoid storing batteries near flammable substances that could pose a fire hazard.
- Check Voltage Periodically: Check the voltage of the stored car battery periodically using a multimeter. If the voltage drops significantly, consider giving it a charge to maintain the optimal charge level.
- Keep Battery Upright: Ensure that the car battery is stored in an upright position to prevent leakage. This also helps to maintain the correct distribution of electrolyte within the battery.
- Avoid Excessive Vibration: Choose a storage location that minimizes vibrations. Excessive vibration can potentially damage the internal components of the battery.
- Follow Manufacturer’s Guidelines: It’s essential to follow the specific storage recommendations provided by the car battery manufacturer. These guidelines may vary depending on the battery’s chemistry and other factors unique to the specific model.
- Regular Maintenance: Even during storage, it is beneficial to perform periodic maintenance tasks such as cleaning the battery terminals and checking the electrolyte levels (for non-sealed batteries) as recommended by the manufacturer.
By following these guidelines, you can ensure that your car battery remains in good condition during storage and is ready to start your vehicle when you need it. Always handle car batteries with caution and dispose of old or damaged batteries responsibly in accordance with local regulations.
Read more: How To Store A Car Battery When Not In Use
Conclusion
Proper storage of batteries is essential to maintain their performance, prolong their lifespan, and ensure their safety. Whether you’re storing alkaline batteries, lithium-ion batteries, nickel-based batteries, rechargeable batteries, button cell batteries, or car batteries, following the appropriate storage guidelines will help preserve their quality and prevent any potential issues.
Remember to check the expiry dates of batteries before storing them and discard any expired ones. Keep batteries in a cool, dry place, away from extreme temperatures, direct sunlight, and excessive humidity. Use individual battery cases or containers to prevent contact between terminals and avoid short circuits. Regularly monitor the charge levels of stored batteries and recharge them if necessary to maintain their optimal storage voltage.
Each battery type has its specific storage requirements, so it’s crucial to familiarize yourself with the recommendations provided by the manufacturer. Additionally, consider the unique characteristics of each battery and take necessary precautions to prevent leakage, damage, or accidents.
By implementing these storage practices, you can maximize the shelf life of your batteries, avoid the inconvenience of unexpected power failures, and save money by reducing the need for frequent replacements. Furthermore, responsible disposal and recycling of batteries at the end of their life cycle is crucial to protect the environment.
Remember, while proper storage is important, it is also vital to use and maintain batteries regularly. Batteries, especially rechargeable ones, perform best when they are used and recharged periodically. So, make sure to find a balance between storage and usage to optimize battery performance and longevity.
By following these guidelines and best practices, you can ensure that your batteries are ready to power your devices whenever you need them, while also promoting safety and environmental responsibility.
Frequently Asked Questions about How To Store Batteries When Not In Use
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.













0 thoughts on “How To Store Batteries When Not In Use”