

Articles
How To Store Mushroom Spores
Modified: February 29, 2024
Learn how to properly store mushroom spores with our informative articles. Find expert tips and techniques to ensure long-term preservation and viability.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on how to store mushroom spores. If you’re a mushroom enthusiast or a hobbyist looking to expand your collection, understanding how to properly store mushroom spores is crucial for their longevity and viability. Mushroom spores contain the genetic material needed to grow new mushrooms, making them a valuable asset for cultivators.
Properly storing mushroom spores ensures that you have a steady supply of high-quality spores on hand whenever you need them, whether you plan to use them for cultivation, research, or sharing with fellow mushroom enthusiasts.
In this article, we will walk you through the process of collecting, cleaning, drying, and storing mushroom spores. We will also provide you with best practices to help you maintain the viability and longevity of your spore collection. So let’s dive in and explore the fascinating world of mushroom spores!
Key Takeaways:
- Preserve the Viability: Understanding the biology of mushroom spores and following proper collection, cleaning, and storage techniques ensures a steady supply of high-quality spores for future cultivation and exploration.
- Best Practices for Longevity: Maintaining a sterile environment, avoiding moisture exposure, and creating backups are essential for safeguarding the viability and integrity of stored mushroom spores.
Read more: How To Store Mushroom Spore Syringes
Understanding Mushroom Spores
Before we delve into the specifics of storing mushroom spores, let’s take a moment to understand what mushroom spores actually are. Spores are the reproductive cells of fungi, including mushrooms. They are tiny, lightweight structures that are analogous to seeds in plants.
When a mushroom releases its spores, they are dispersed into the air or onto nearby surfaces. These spores contain the genetic information needed for the growth and development of new mushrooms. Under suitable conditions, spores can germinate and give rise to a network of thread-like structures called mycelium. The mycelium then forms the foundation for the mushroom’s growth.
Mushroom spores come in a variety of shapes, sizes, and colors, depending on the species. They can be cylindrical, spherical, elliptical, or even intricately sculpted. The color of the spores can range from white and cream to shades of brown, black, and even purple.
It’s important to note that mushroom spores are microscopic, making them nearly invisible to the naked eye. They are typically less than 10 micrometers in size, which is why specialized techniques and equipment are needed for their collection and storage.
Understanding the lifecycle and characteristics of mushroom spores is crucial for successful spore collection and storage. By maintaining the integrity and viability of spores, you can ensure their usefulness for future mushroom cultivation endeavors.
Preparing for Spore Collection
Before you can start collecting mushroom spores, it’s important to gather the necessary supplies and create a suitable environment for the process. Here are the steps to prepare for spore collection:
- Identify the mushroom species: The first step is to identify the mushroom species from which you want to collect spores. Different mushrooms have different spore characteristics, so it’s essential to be able to correctly identify the species.
- Gather sterilized equipment: Collect sterilized equipment such as sterile glass slides, petri dishes, or sterile aluminum foil. Sterilization is crucial to prevent contamination and ensure the purity of the spores.
- Create a sterile environment: Set up a clean and sterile workspace for spore collection. You can use a laminar flow hood or work in a sterilized glove box to maintain a sterile environment. Alternatively, you can clean and disinfect your work area thoroughly before starting.
- Prepare a spore collection surface: If you’re using glass slides or petri dishes, sterilize them and create a spore collection surface. You can do this by lightly coating the surface with a clean droplet of sterile water or sterilized agar media.
- Use proper sterile techniques: It’s crucial to practice proper sterile techniques during spore collection. Wear sterilized gloves, work with sterilized tools, and avoid any unnecessary contact with the surrounding area to prevent contamination.
- Select mature mushrooms: Choose mushrooms that are fully mature and have opened their caps to ensure the release of mature and viable spores. Immature mushrooms may not have developed fully formed spores, which can affect their viability.
- Time the collection: Timing is essential when collecting spores. The best time to collect spores is when the cap of the mushroom is fully opened, but before it starts to release its spores on its own. This ensures that you capture the largest quantity of viable spores.
- Handle mushrooms carefully: Handle mushrooms with care to avoid damaging the delicate spore-bearing structures. Use clean and sanitized tools to gently detach the cap from the stem, ensuring that the spores are undisturbed.
- Label and document: It’s important to label each spore collection with the corresponding mushroom species and any relevant information. Maintain a record of the collection date and any observations to track the viability and characteristics of the spores.
By following these preparation steps, you will create an optimal environment for spore collection and ensure the purity and viability of the collected spores. In the next section, we will explore the actual process of harvesting mushroom spores.
Harvesting Mushroom Spores
Now that you have prepared the necessary supplies and created a suitable environment, it’s time to harvest the mushroom spores. Follow these steps to ensure a successful spore collection:
- Place the mushroom cap: Take the detached mushroom cap and place it gill-side down on the prepared spore collection surface. The gills, located on the underside of the cap, are where the spores are produced and released.
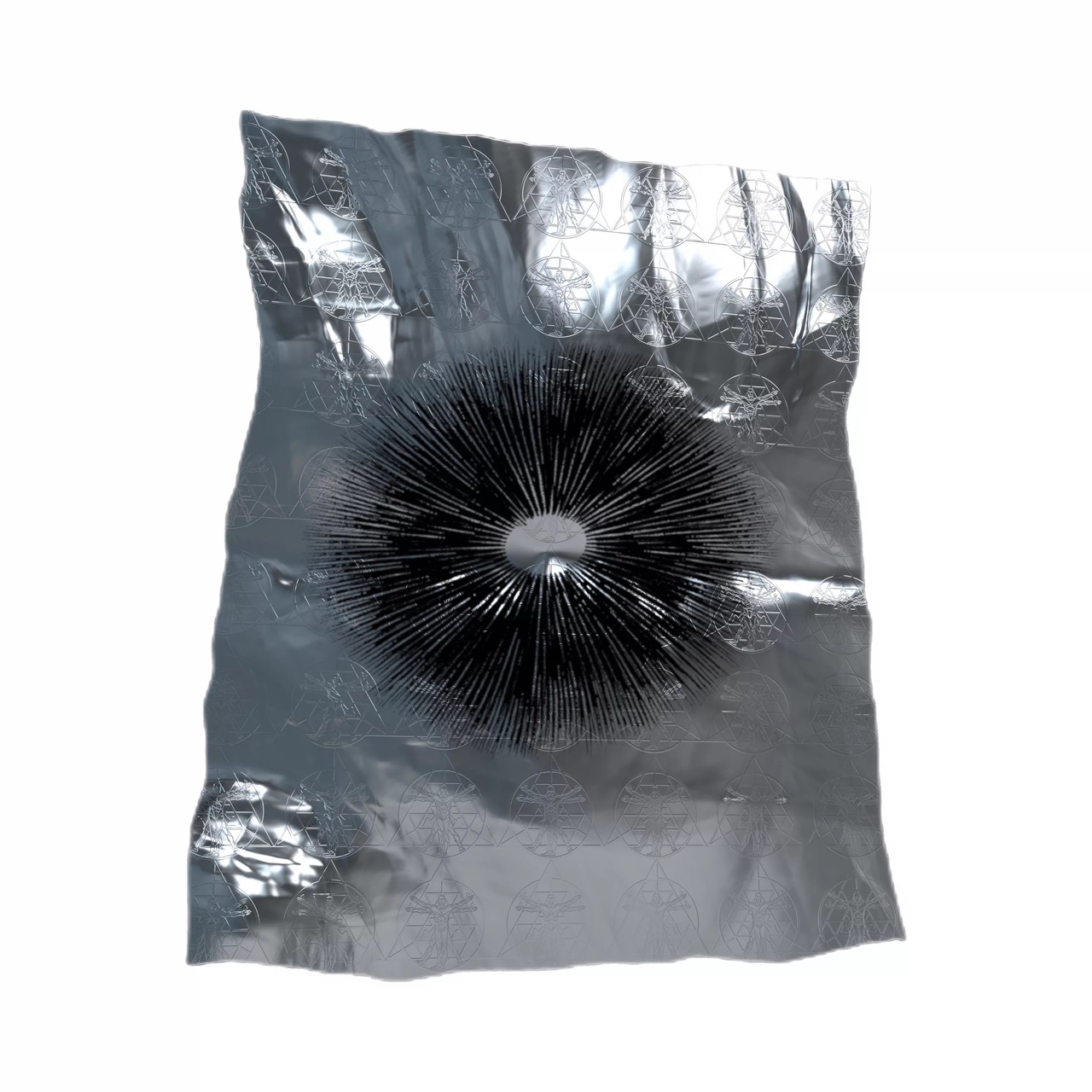
- Allow spore release: Place a clean, sterilized glass jar or other cover over the mushroom cap. This enclosure helps to create a controlled environment for spore release. Leave it undisturbed for several hours or overnight, allowing the cap to drop its spores onto the collection surface.
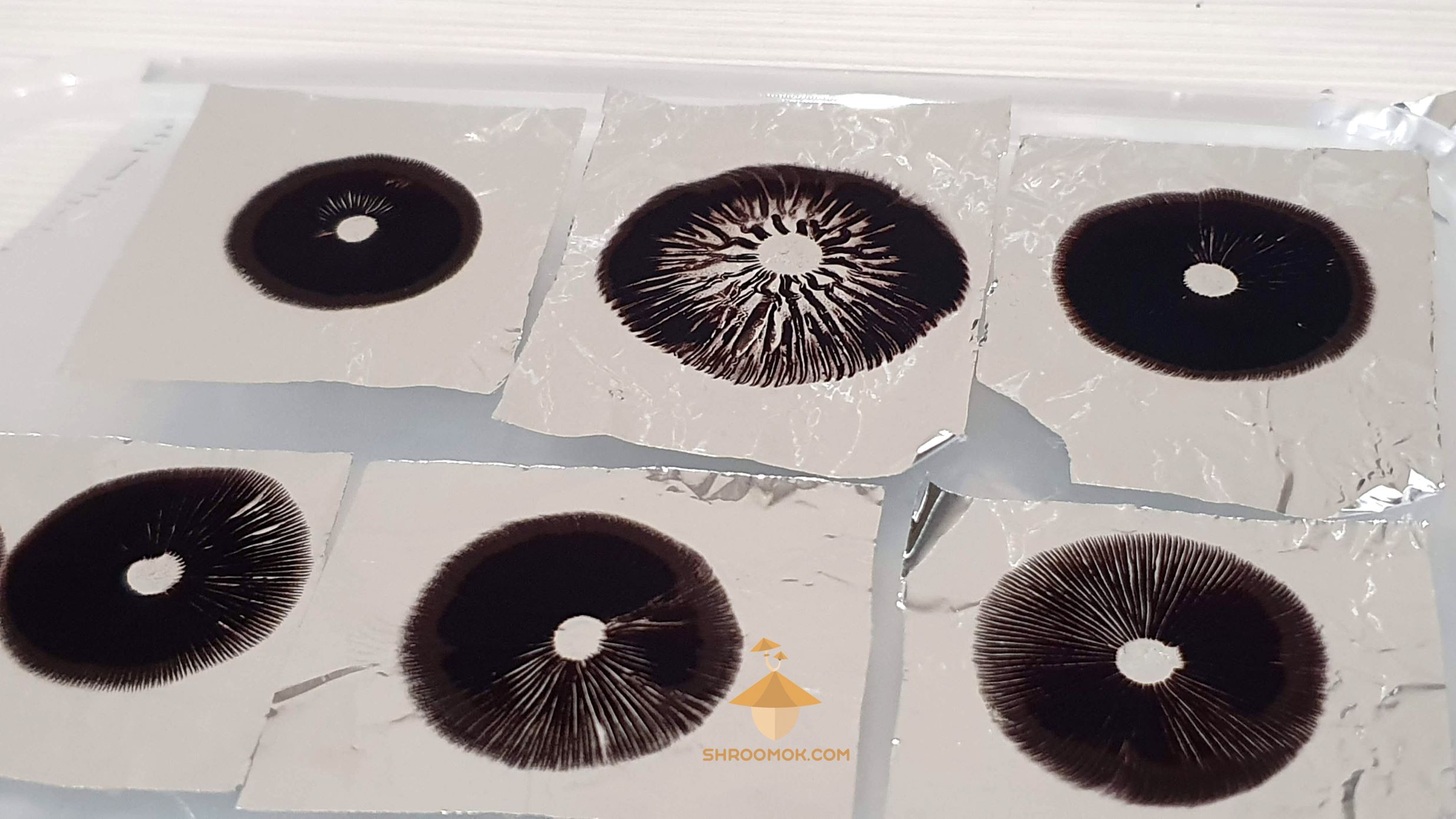
- Observe spore deposition: After the designated time, carefully remove the cover and observe the spore deposition. You will notice a fine layer of colored powder covering the collection surface. This powder consists of the mushroom spores.
- Remove the mushroom cap: Gently lift the mushroom cap from the collection surface, being careful not to disturb the spores. Make sure to handle the cap with clean, sterilized tools to avoid contamination.
- Inspect spore quality: Examine the collected spores to ensure their quality and viability. They should appear as a fine, uniform layer on the collection surface. Any visible signs of mold or discoloration may indicate contamination and can affect the viability of the spores.
- Collect spores: Use a sterilized scalpel or needle to carefully scrape the spores from the collection surface. Transfer the spores into a clean, sterilized container for further processing and storage.
- Repeat the process (optional): If you have multiple mushrooms or want to collect spores from different individuals, repeat the process with each mushroom cap, ensuring proper labeling and documentation for each collection.
Harvesting mushroom spores requires patience and precision to ensure the highest quality and viability. By following these steps, you can successfully collect spores from your desired mushroom species. In the next section, we will learn about cleaning and drying the spores for long-term storage.
Store mushroom spores in a clean, airtight container with a desiccant packet to absorb moisture. Keep the container in a cool, dark place to maintain spore viability.
Cleaning and Drying Spores
After harvesting mushroom spores, it’s important to clean and dry them before storing. Cleaning and drying the spores remove any impurities or moisture, ensuring their longevity and viability. Follow these steps to clean and dry your mushroom spores:
- Transfer spores to a clean container: Take the container with the collected spores and transfer them to a fresh, clean container. This helps separate the spores from any debris or residual matter.
- Remove debris: Carefully inspect the spores and remove any visible debris or contaminants. Use a sterilized scalpel or needle to gently pick out any foreign particles that may have collected with the spores.
- Optional: Sterilize spores (for long-term storage): If you plan to store the spores for an extended period, you can further sterilize them to minimize the risk of contamination. This can be done by subjecting the spores to a brief and controlled heat treatment using a sterilization device or hot air.
- Spread out the spores to dry: Once the spores are cleaned, spread them out in a thin, even layer on a sterile surface. This can be a glass slide, petri dish, or any other suitable clean and sterile surface.
- Avoid direct sunlight: Place the spores in a well-ventilated area away from direct sunlight. Exposure to sunlight can degrade the spores’ viability and color pigments.
- Allow sufficient drying time: Let the spores air dry naturally for a period of 24 to 48 hours. This duration may vary depending on the humidity levels in your environment. Ensure the spores are completely dry before proceeding to the next step.
- Check for complete dryness: To check if the spores are dry, gently touch them with a clean, dry finger or sterile tool. If there is no moisture or stickiness, the spores are ready for storage.
Cleaning and drying the mushroom spores is an essential step in maintaining their viability and reducing the risk of contamination during storage. Properly dried spores can be stored for extended periods while retaining their genetic integrity. In the next section, we will explore the best practices for storing mushroom spores.
Read more: How To Store Mushroom Spore Prints
Storing Mushroom Spores
Proper storage of mushroom spores is crucial for maintaining their viability and longevity. By following the right techniques, you can ensure that your spore collection remains viable for future use. Here are the steps to store mushroom spores:
- Choose a suitable storage container: Select a clean and sterile container for storing the spores. Glass vials or small airtight containers are ideal choices as they provide a stable and secure environment for the spores.
- Add desiccant: Place a small amount of desiccant, such as silica gel or a drying agent, at the bottom of the container. The desiccant helps absorb any remaining moisture and prevents fungal growth that can compromise the spores’ longevity.
- Transfer spores to the storage container: Gently transfer the dried spores into the storage container. Take care not to touch the spores directly with your hands or any non-sterile surfaces to avoid contamination.
- Label and seal the container: Label the container with the mushroom species, collection date, and any other relevant information. This ensures proper identification and tracking of the stored spores. Seal the container tightly to prevent any moisture or contaminants from entering.
- Store in a cool and dark place: Find a cool, dark, and dry location to store the spores. Excessive heat, moisture, and light can degrade the spores’ viability. A refrigerator or a cool, dark cabinet is a suitable choice for long-term storage.
- Monitor the storage condition: Regularly check the storage conditions to ensure they remain optimal. If you notice any signs of moisture or contamination, take the necessary steps to address the issue immediately.
- Consider multiple backups: To safeguard your spore collection, it’s advisable to make multiple backups. This can involve creating duplicate containers or storing spores in different locations in case of any unforeseen events or accidents.
- Keep documentation: Maintain detailed documentation of your spore collection, including the mushroom species, collection date, storage location, and any observations. This information will help you keep track of the viability and characteristics of your stored spores.
By following these storage guidelines, you can ensure the longevity and viability of your mushroom spore collection. Regularly check and maintain the storage conditions, and handle the spores with care to avoid contamination. With proper storage, your spores will be ready for future cultivation, research, or sharing with fellow mushroom enthusiasts.
Best Practices for Spore Storage
To maximize the viability and longevity of your stored mushroom spores, it’s important to follow some best practices for spore storage. These practices will help ensure the optimal condition and integrity of your spore collection:
- Maintain a sterile environment: When handling spores or accessing your storage containers, always work in a clean and sterile environment. Use sterilized tools, wear sterilized gloves, and avoid unnecessary contact with non-sterile surfaces to minimize the risk of contamination.
- Avoid moisture exposure: Moisture is the enemy of spore storage. Always ensure that the spores are completely dry before storing them. Use desiccants in your storage containers to absorb any moisture and prevent fungal growth.
- Keep the storage containers sealed: It’s crucial to keep your spore storage containers tightly sealed to prevent the entry of moisture, air, or contaminants. Check the containers periodically to ensure that the seals are intact and reseal them if necessary.
- Store in a cool and dark place: Heat and light can degrade the viability of spores. Find a cool, dark, and dry location for the storage of your spores. A refrigerator or a cool, dark cabinet are suitable options for long-term storage.
- Monitor the storage conditions: Regularly check on your stored spores to ensure that the storage conditions remain optimal. If you notice any signs of moisture, contamination, or changes in color or texture of the spores, take immediate action to address the issue.
- Create backups: To protect your spore collection, it’s wise to create multiple backups. Make duplicate containers of your spores or store them in different locations. This will mitigate the risk of losing your entire collection due to unforeseen circumstances or accidents.
- Rotate your spores: If you plan to store spores for an extended period, consider periodically rotating your collection. Use the older spores first and replenish your collection with fresh spores regularly to ensure you always have a reliable supply.
- Document and track your spore collection: Keep detailed records of your spore collection, including the species, collection date, storage location, and any observations. This will help you track the viability and characteristics of your stored spores and make informed decisions about their use.
By adhering to these best practices, you can maintain the quality and viability of your mushroom spore collection for an extended period. Proper care and attention to storage conditions will ensure that your spores are ready for successful cultivation and exploration of the fascinating world of mushrooms.
Conclusion
Congratulations! You have now learned the essential steps for storing mushroom spores. By understanding the biology of spores, preparing for collection, and following best practices for cleaning, drying, and storing, you can preserve the viability of your spore collection for future use.
Mushroom spores are the building blocks of fungal growth, containing the genetic material necessary to cultivate new mushrooms. With proper storage techniques, you can ensure a steady supply of high-quality spores for research, cultivation, or sharing with fellow mushroom enthusiasts.
Remember to create a sterile environment when working with spores, using sterilized equipment and practicing proper techniques. Take the time to identify the mushroom species, select mature caps for spore collection, and provide the optimal conditions for spore release.
After collection, thoroughly clean and dry the spores to remove impurities and moisture. Choose suitable storage containers, add desiccants, and seal the containers tightly to prevent contamination and maintain a dry environment. Store the spores in a cool, dark place, and regularly monitor the storage conditions to ensure their longevity.
By implementing these best practices, you can safeguard the viability of your spores and expand your mushroom cultivation endeavors. Enjoy the fascinating journey of exploring the diversity and beauty of mushroom spores, and may your spore collection thrive for years to come!
Frequently Asked Questions about How To Store Mushroom Spores
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.













0 thoughts on “How To Store Mushroom Spores”