Home>Garden Essentials>How Long For Mushroom Spores To Germinate


Garden Essentials
How Long For Mushroom Spores To Germinate
Modified: April 22, 2024
Discover how long it takes for mushroom spores to germinate in your garden. Learn the factors that affect germination time and optimize your gardening process for success.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Have you ever wondered how long it takes for mushroom spores to germinate? The process of mushroom spore germination can vary depending on several factors. Understanding these factors and knowing the ideal conditions for spore germination can help you cultivate healthy and productive mushrooms.
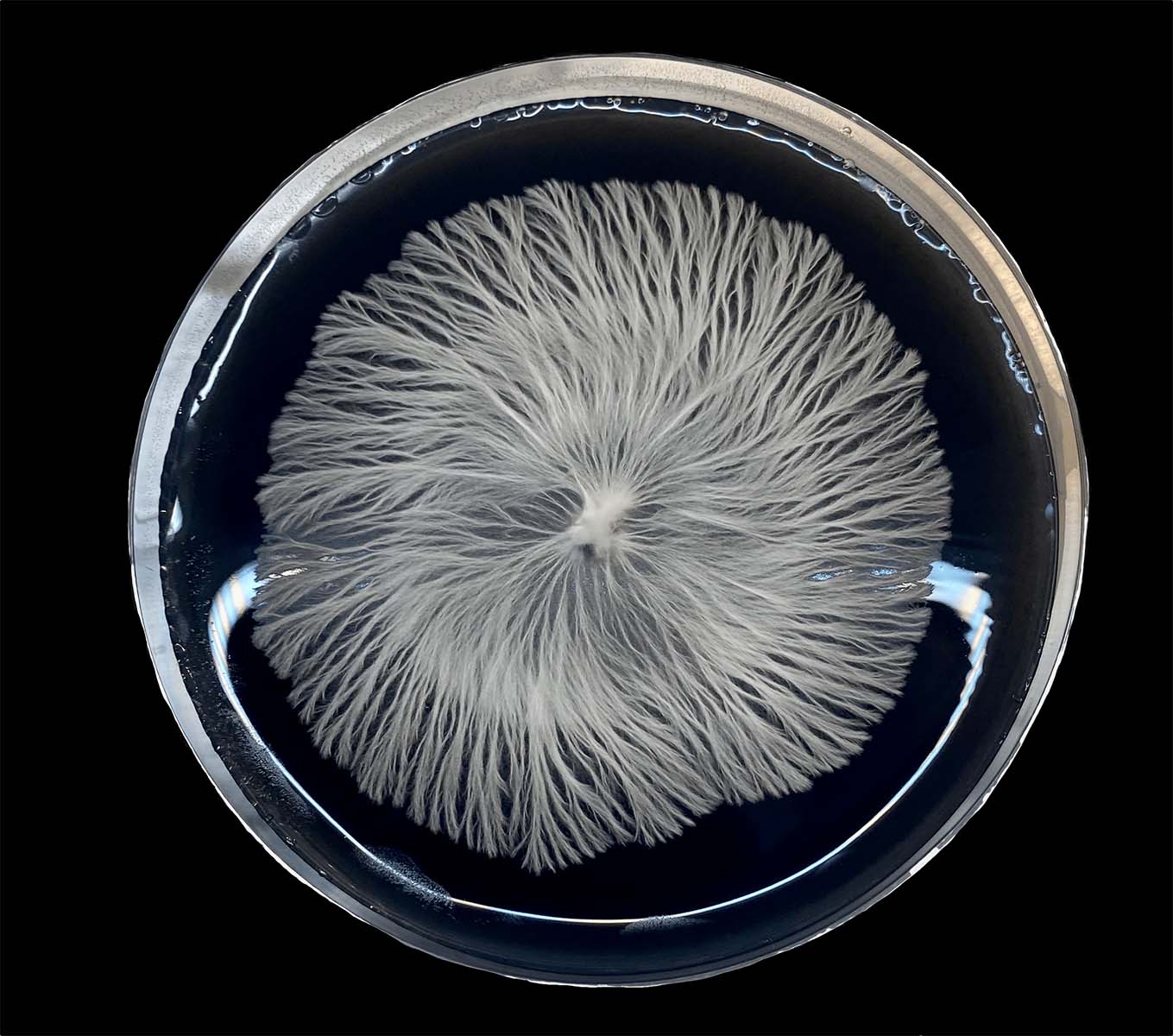
Mushrooms are fascinating organisms that play a crucial role in nature’s ecosystem. They belong to the fungi kingdom and reproduce through spores rather than seeds. These spores are tiny reproductive cells that are dispersed into the environment. When conditions are right, these spores can germinate and develop into mycelium, which is the vegetative part of the fungus.
The length of time it takes for mushroom spores to germinate depends on various factors such as the type of mushroom, environmental conditions, and the quality of the spores. Some mushroom spores can germinate within a few days, while others may take several weeks.
Understanding and optimizing the conditions for mushroom spore germination is essential for successful mushroom cultivation. In this article, we will explore the factors that affect germination time, ideal conditions for spore germination, common types of mushrooms and their germination times, techniques to speed up germination, and the challenges often encountered in the germination process.
Key Takeaways:
- Mushroom spores can take days to weeks to germinate, depending on factors like species, spore quality, and environmental conditions. Understanding and optimizing these factors is crucial for successful cultivation.
- Techniques like proper spore preparation, pre-hydration, and agar cultures can speed up mushroom spore germination. However, challenges like contamination and inconsistent germination may arise and need to be addressed.
Read more: How To Store Mushroom Spores
Factors Affecting Germination Time
Several factors can influence the time it takes for mushroom spores to germinate. Understanding these factors can help you optimize the germination process and increase your chances of successful cultivation.
1. Mushroom Species: Different types of mushrooms have different germination times. Some mushroom species have spores that germinate quickly, while others may take longer. It’s important to research the specific mushroom species you are working with to understand their typical germination time.
2. Spore Quality: The quality of the spores can affect germination time. Fresh and viable spores have a higher chance of germinating quickly compared to old or poor-quality spores. It is recommended to obtain spores from reputable sources to ensure their quality and viability.
3. Environmental Conditions: The environmental conditions play a crucial role in mushroom spore germination. Factors such as temperature, humidity, and light can either promote or hinder the germination process. Each mushroom species has its preferred range of environmental conditions conducive to germination. Maintaining the ideal conditions can significantly impact germination time.
4. Nutrient Availability: Mushrooms require a suitable substrate to grow and thrive. The availability and quality of nutrients in the substrate can affect the germination time. Ensuring a nutrient-rich substrate can enhance spore germination and subsequent mycelium development.
5. Oxygen Levels: Adequate oxygen levels are essential for successful spore germination. Proper ventilation and airflow can facilitate oxygen exchange, promoting the germination process. Insufficient oxygen levels can impede germination and lead to poor results.
6. pH Level: The pH level of the substrate can impact spore germination. Different mushroom species have specific pH preferences for optimal growth and germination. It’s crucial to adjust the pH of the substrate to suit the requirements of the mushroom species you are cultivating.
By understanding and controlling these factors, you can significantly influence the time it takes for mushroom spores to germinate. Providing the optimal conditions for spore germination increases the chances of successful cultivation and enhances the overall mushroom growth process.
Ideal Conditions for Mushroom Spore Germination
Creating and maintaining the ideal conditions for mushroom spore germination is crucial for successful cultivation. By providing the optimal environment, you can promote quick and healthy spore germination. Here are the key factors to consider:
1. Temperature: Temperature plays a vital role in spore germination. Each mushroom species has its preferred temperature range for optimal germination. Generally, temperatures between 70-80°F (21-27°C) are suitable for many common mushroom species. However, some species may have specific temperature requirements, so it’s essential to research and adjust accordingly.
2. Humidity: Mushrooms thrive in moist environments. Maintaining a high humidity level promotes spore germination. A humidity range of 80-90% is generally recommended for successful germination. You can achieve this by misting the growing area regularly or using a humidity dome to create a humid microclimate.
3. Light: While light is not necessary for spore germination, it can influence the subsequent growth of mushrooms. Once the spores have germinated and developed into mycelium, exposing them to diffused light or low-level lighting can aid in the development of healthy mycelial growth.
4. Substrate Quality: The substrate you provide for the spores to germinate on is crucial for their development. Using a nutrient-rich and well-prepared substrate can enhance spore germination. Common substrates include compost, sawdust, straw, or a mix of these materials. Ensure that the substrate is sterilized and has the necessary nutrients for mycelium development.
5. Ventilation: Proper ventilation is important to prevent the buildup of carbon dioxide and to provide fresh oxygen for spore germination. Good airflow promotes healthy mycelium growth and prevents the growth of unwanted contaminants. Ensure proper ventilation in the growing area by using fans or natural airflow.
6. pH Level: The pH level of the substrate plays a crucial role in spore germination. Different mushroom species have different pH preferences, so it’s important to adjust the pH accordingly. Most mushrooms prefer a slightly acidic to neutral pH level, ranging from 5.5 to 7.0. Testing and adjusting the pH of the substrate can optimize spore germination.
By creating an environment that meets these ideal conditions, you can significantly enhance the germination process and increase your chances of successful mushroom cultivation. Remember to research the specific requirements of the mushroom species you are working with to ensure the best results.
Common Types of Mushrooms and Their Germination Times
Mushrooms come in a wide variety of species, each with its own unique characteristics and germination times. Here are some common types of mushrooms and their typical germination times:
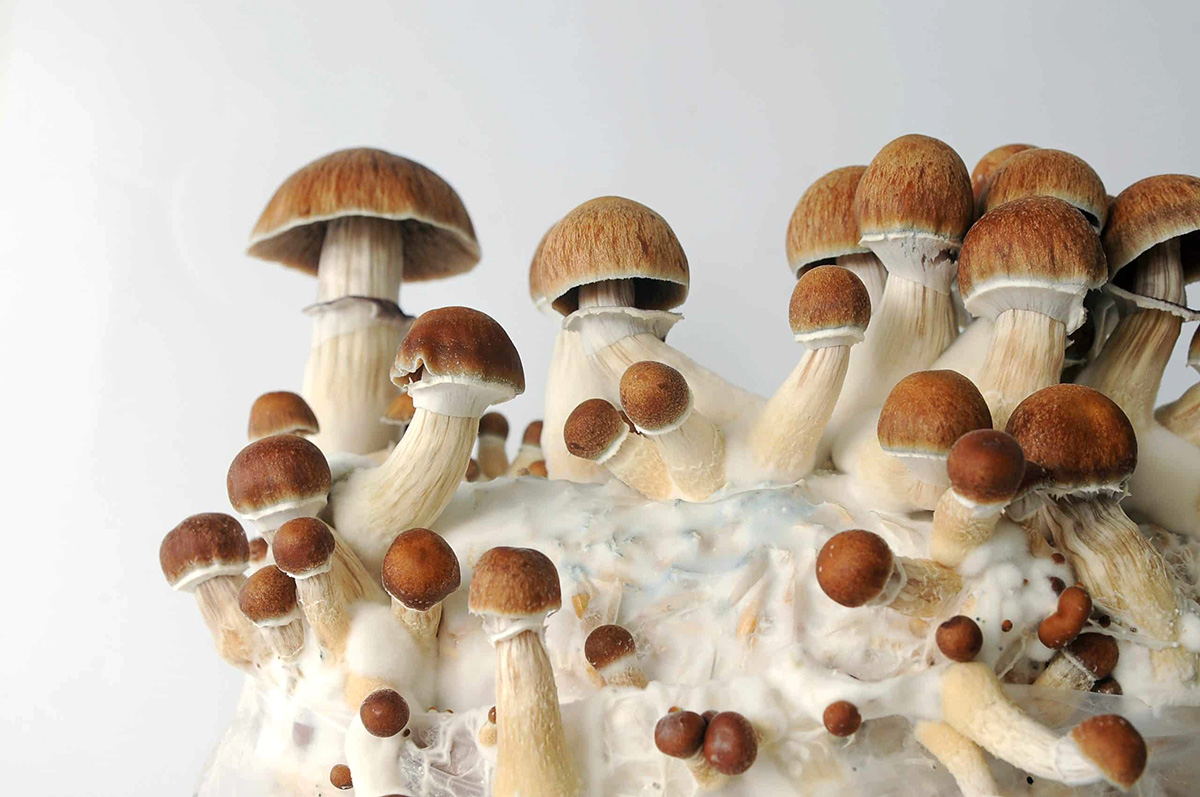
1. White Button Mushrooms (Agaricus bisporus): White button mushrooms are one of the most widely cultivated mushroom species. They are known for their mild flavor and versatile culinary uses. The spores of white button mushrooms typically germinate within 7-14 days under favorable conditions, and mycelium formation occurs shortly after.
2. Shiitake Mushrooms (Lentinula edodes): Shiitake mushrooms are highly prized for their rich, savory flavor and health benefits. They are commonly used in Asian cuisine. Shiitake spores have a germination time of around 10-14 days. After germination, mycelium growth occurs, and the mushrooms can be harvested within a few weeks to months, depending on the desired size.
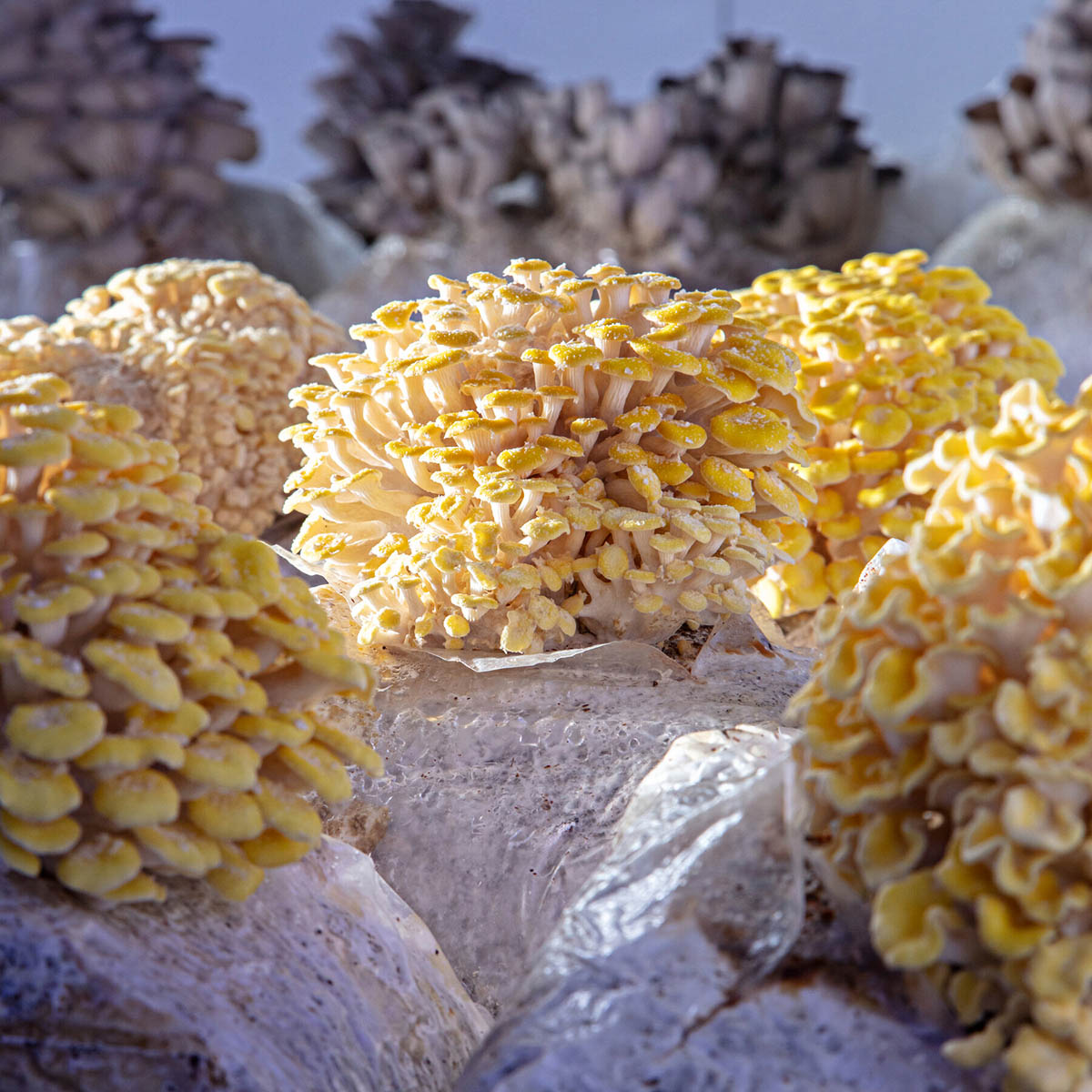
3. Oyster Mushrooms (Pleurotus ostreatus): Oyster mushrooms are popular for their delicate taste and unique appearance. They have a relatively rapid germination time, with spores typically germinating within 3-7 days. Mycelium growth follows, and the mushrooms can be harvested within a few weeks.
4. Lions Mane Mushrooms (Hericium erinaceus): Lions Mane mushrooms have a distinct appearance with their long, cascading white spines. They have gained popularity for their unique flavor and potential health benefits. The germination time for Lions Mane spores is typically around 7-14 days. Mycelium growth occurs after germination, and the mushrooms develop over several weeks.
5. Portobello Mushrooms (Agaricus bisporus): Portobello mushrooms are matured white button mushrooms with a meaty texture and robust flavor. They have a slightly longer germination time compared to white button mushrooms, typically taking around 14-21 days for spores to germinate. Mycelium growth follows, and the mushrooms can be harvested at a mature stage.
6. Morel Mushrooms (Morchella spp.): Morel mushrooms are highly sought after for their unique appearance and earthy flavor. They are a bit more challenging to cultivate compared to other mushrooms. Morel spores can take longer to germinate, typically between 2-8 weeks. However, the resulting mushrooms are well worth the wait.
It’s important to note that these are general guidelines, and the germination times can vary depending on various factors such as temperature, humidity, and spore quality. Additionally, different varieties within each mushroom species may have slightly different germination times. It’s recommended to research and obtain specific information about the mushroom varieties you are working with to optimize the germination process.
Mushroom spores can take anywhere from 3 days to 3 weeks to germinate, depending on the species and environmental conditions. Keep the growing medium moist and at the right temperature for best results.
Techniques to Speed Up Mushroom Spore Germination
If you’re eager to see quick results in mushroom spore germination, there are several techniques you can employ to speed up the process. These techniques aim to create optimal conditions for spore germination and promote faster mycelium growth. Here are some effective techniques to consider:
1. Proper Spore Preparation: Before attempting to germinate mushroom spores, it’s important to ensure their viability. Using fresh and high-quality spores increases the chances of quick germination. Make sure to store spores in a cool, dry place, protected from light and moisture. It’s also a good idea to clean the spores before germination to remove any potential contaminants.
2. Soaking or Pre-Hydration: Some mushroom species benefit from pre-hydration before germination. Soaking the spores in sterile water or a nutrient broth for a short period can encourage faster germination. This technique provides the spores with the necessary hydration to kickstart the germination process.
3. Agar Cultures: Using agar plates or agar cultures can speed up spore germination. Agar provides a nutrient-rich medium for the spores to grow on. By transferring spores onto agar plates, you can create a controlled environment that promotes quicker germination and mycelium growth. Agar cultures can also help isolate and propagate desired mushroom strains.
4. Heat Shock Treatment: Some mushroom species respond well to a heat shock treatment, which involves subjecting the spores to a short period of elevated temperature. This process mimics natural conditions after forest fires and can stimulate spore germination. However, it’s essential to research and understand the specific temperature and duration requirements for each mushroom species before attempting this technique.
5. Increase Oxygen Levels: Proper oxygenation is crucial for spore germination. Increasing oxygen levels around the spores can speed up the germination process. You can achieve this by increasing airflow in the growing area, using fans, or providing adequate ventilation. Avoid stagnant air and ensure fresh oxygen reaches the spores.
6. Optimize Growing Conditions: Creating and maintaining the ideal environmental conditions for mushroom cultivation can enhance spore germination. Keeping the temperature within the specified range, maintaining high humidity levels, and providing diffused light can all contribute to faster germination and mycelial growth.
It’s important to note that while these techniques can speed up spore germination, each mushroom species may respond differently. It’s crucial to research the specific requirements and preferences of the mushroom species you are working with and tailor your techniques accordingly.
By employing these techniques, you can increase the chances of faster spore germination, allowing you to enjoy the results of your mushroom cultivation endeavors more quickly.
Read more: How To Store Mushroom Spore Prints
Challenges in Mushroom Spore Germination
While mushroom spore germination is an exciting process, it comes with its fair share of challenges. Understanding and addressing these challenges can help improve the success rate of spore germination. Here are some common challenges you may encounter:
1. Contamination: Contamination is a significant challenge during the germination process. Spores are vulnerable to competition from other microorganisms such as bacteria or mold. These contaminants can inhibit spore germination or overtake the growing substrate. Maintaining a sterile environment, using proper sterilization techniques, and working in a clean, controlled space can help minimize the risk of contamination.
2. Slow or Delayed Germination: Some mushroom species have naturally slow germination times. It can be frustrating to wait weeks or even months for spores to germinate. Additionally, low-quality or old spores may have lower viability and longer germination times. Ensuring the freshness and quality of spores and maintaining optimal growing conditions can help overcome slow or delayed germination.
3. Inconsistent Germination: Achieving consistent germination across all spores can be challenging. Different spores within the same batch may germinate at varying rates, leading to uneven mycelial growth. This can result in patchy or incomplete colonization. Ensuring consistent spore distribution and providing consistent growing conditions can help promote more even germination.
4. Environmental Factors: Environmental factors play a crucial role in spore germination. Factors such as temperature, humidity, light, and airflow need to be carefully controlled. Fluctuations or deviations from the optimal conditions can hinder or delay germination. Regular monitoring and adjustment of these factors can help ensure a stable and conducive environment for spore germination.
5. Insufficient Nutrients: Mushrooms rely on a nutrient-rich substrate for growth and development. Using a substrate with insufficient nutrients or improper composition can impede spore germination. It’s important to create or select a substrate that provides the necessary nutrients for mycelium development. Adding supplements or adjusting the substrate composition can help overcome nutrient deficiencies.
6. Genetic Variability: Some mushroom species have inherent genetic variability, which can affect the germination process. This variability can result in differences in germination time, mycelial growth rate, and overall performance. It’s important to understand the genetic traits of the mushroom species you are working with and account for potential variations in germination outcomes.
Overcoming these challenges requires careful attention to detail, patience, and constant monitoring. By addressing these challenges head-on and implementing appropriate solutions, you can increase the success rate of mushroom spore germination and ultimately achieve a more productive and rewarding cultivation process.
Conclusion
Understanding the process of mushroom spore germination is essential for successful mushroom cultivation. By considering the various factors that affect germination time, providing ideal conditions, and implementing techniques to speed up the process, you can increase your chances of successful spore germination and subsequent mycelium growth.
Factors such as the mushroom species, spore quality, environmental conditions, nutrient availability, oxygen levels, and pH level all play a crucial role in spore germination. By controlling and optimizing these factors, you can create an environment that promotes quick and healthy germination.
It’s important to research and understand the specific requirements of the mushroom species you are working with, as germination times can vary. Different mushrooms, such as white button mushrooms, shiitake mushrooms, oyster mushrooms, lions mane mushrooms, portobello mushrooms, and morel mushrooms, have different germination times that you should be aware of.
Implementing techniques such as proper spore preparation, pre-hydration, agar cultures, heat shock treatment, increasing oxygen levels, and optimizing growing conditions can help speed up the germination process. These techniques create favorable conditions for spore germination and mycelium development.
However, challenges such as contamination, slow or delayed germination, inconsistent germination, environmental factors, insufficient nutrients, and genetic variability can arise during the germination process. It’s important to address these challenges through proper sterilization, maintaining optimal conditions, providing a nutrient-rich substrate, and understanding the genetic traits of the mushroom species being cultivated.
In conclusion, successful mushroom spore germination requires knowledge, attention to detail, and perseverance. By understanding the factors that affect germination time, providing ideal conditions, implementing techniques to speed up germination, and addressing the challenges that may arise, you can increase your chances of cultivating healthy, productive mushrooms.
Remember to continuously monitor and adjust the growing environment as needed, and always research and stay informed about the specific requirements of the mushroom species you are working with. With patience and dedication, you can achieve satisfying results in your mushroom cultivation endeavors.
Frequently Asked Questions about How Long For Mushroom Spores To Germinate
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.












0 thoughts on “How Long For Mushroom Spores To Germinate”