

Articles
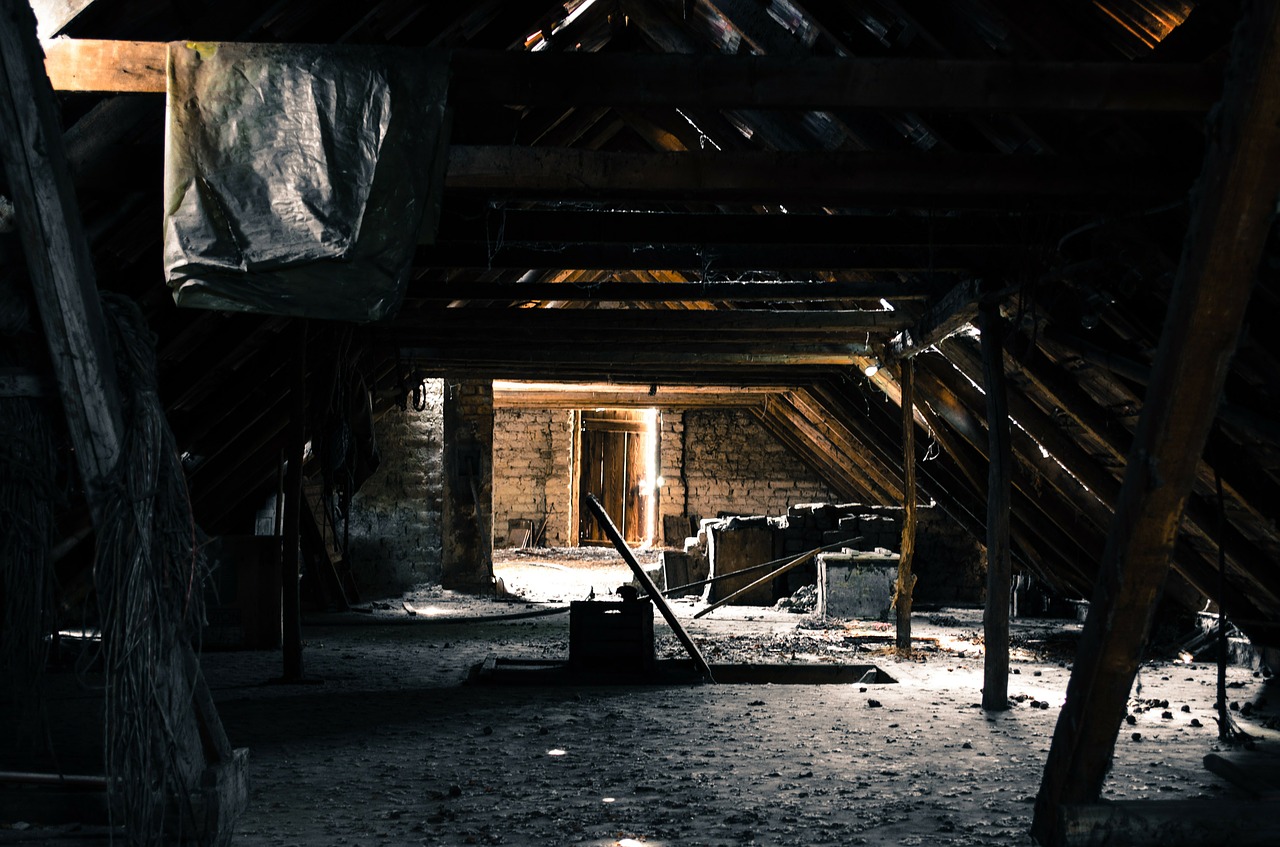
What Causes Mold In The Attic
Modified: October 19, 2024
Discover the main causes of mold in your attic and how to prevent it. Read our informative articles for expert tips and advice on mold prevention.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Mold is a common issue that homeowners face, and one area where it often thrives is in the attic. Mold growth in attics can be a significant problem, as it not only affects the health of the occupants but can also lead to structural damage if left untreated. Understanding the causes of mold in attics is essential to prevent its growth and mitigate the associated risks.
In this article, we will explore the common causes of mold in attics and discuss the potential effects it can have on both health and the integrity of your home. Additionally, we will provide some practical tips to help you prevent mold growth in your attic and maintain a healthy living environment.
Key Takeaways:
- Proper ventilation, regular roof inspections, and prompt leak repairs are crucial in preventing mold growth in attics. Proper insulation and bathroom exhaust fan usage also play key roles in maintaining a healthy living environment.
- Understanding the causes of mold growth in attics and implementing preventative measures are essential for homeowners to mitigate the risks associated with mold, promote a healthy living environment, and protect the structural integrity of their homes.
Read more: What Causes Mold In Toilet Bowl
Understanding Mold
Mold is a type of fungus that thrives in damp and humid environments. It reproduces by releasing spores into the air, which can then settle on various surfaces and start to grow and spread. While mold plays a vital role in nature by breaking down organic matter, its presence indoors can lead to numerous problems.
When it comes to attics, mold growth occurs when there is excess moisture present. This can be due to factors such as poor ventilation, roof leaks, condensation, insufficient insulation, or improper bathroom ventilation. Understanding these causes is crucial in effectively preventing mold growth and keeping your attic mold-free.
Mold growth in attics can be challenging to detect, as it often goes unnoticed until it becomes visible or creates a distinct musty odor. By the time the signs become apparent, the mold infestation may have already spread significantly.
It is important to note that different types of mold can be found in attics, such as Aspergillus, Penicillium, and Stachybotrys (also known as “black mold”). While some molds may be less harmful, others can pose serious health risks, especially for those with respiratory issues, allergies, or weakened immune systems.
To effectively prevent and address mold issues in your attic, it is crucial to understand the common causes of mold growth in this particular area of your home.
Common Causes of Mold in Attics
Mold growth in attics can occur due to a variety of factors. Understanding these causes will help you identify potential issues and take appropriate measures to prevent mold from developing in your attic. Here are some of the most common causes of mold growth:
Poor Ventilation
Inadequate ventilation is one of the primary causes of mold in attics. Without proper airflow, moisture becomes trapped, creating a favorable environment for mold to thrive. The lack of ventilation can be due to a variety of reasons, such as blocked soffit vents, improperly installed insulation, or a lack of exhaust fans.
Roof Leaks
A roof leak can introduce significant amounts of moisture into the attic. Whether it’s due to damaged shingles, flashing issues, or faulty roof installations, these leaks provide the ideal conditions for mold growth. Detecting and repairing roof leaks promptly is crucial in preventing mold from spreading.
Read more: How To Remove Mold From Attic
Condensation
Condensation occurs when warm, humid air comes into contact with cooler surfaces. In attics, condensation commonly forms on roof sheathing and other cold surfaces. If not properly managed, condensation can lead to high humidity levels, creating an environment where mold can flourish.
Insufficient Insulation
Insufficient insulation can contribute to mold growth. When warm air from the living spaces below rises into the attic, it can come into contact with colder surfaces, leading to condensation and increased moisture levels. Proper insulation helps maintain consistent temperatures and reduces the risk of mold development.
Improper Bathroom Ventilation
Bathrooms produce a significant amount of moisture through showers, baths, and other activities. If the bathroom exhaust fan is not properly installed or adequately sized, it may not effectively remove the moisture from the air. As a result, the excess moisture can migrate to the attic, promoting mold growth.
Understanding these common causes of mold growth in attics is the first step in preventing mold infestations. By addressing these issues and implementing appropriate preventative measures, you can maintain a mold-free attic and a healthy home environment.
Poor Ventilation
Poor ventilation is a significant culprit when it comes to mold growth in attics. Without proper airflow, moisture becomes trapped, creating a prime environment for mold to flourish. There are several factors that can contribute to poor ventilation in attics:
Read more: How To Remove Mold From Plywood In Attic
Blocked Soffit Vents
Soffit vents are essential for allowing fresh air to enter the attic while expelling stale air. However, these vents can become blocked over time due to debris, insulation, or even improper installation. When soffit vents are blocked, the airflow is restricted, and moisture can accumulate, leading to mold growth.
Inadequate Number or Size of Vents
If your attic does not have enough vents or the vents are not sized appropriately, proper airflow may not be achieved. Insufficient venting means that moisture-laden air cannot escape, creating a stagnant environment where mold can thrive. It’s important to ensure that your attic has an adequate number of properly sized vents to facilitate proper ventilation.
Inadequate Exhaust Fans
In addition to soffit vents, exhaust fans play a crucial role in attic ventilation. Exhaust fans are typically installed near the roof peak and work to expel warm, moist air from the attic. However, if the exhaust fan is not functioning optimally or if there are not enough fans installed, it can result in inadequate ventilation and the potential for mold growth.
Improperly Installed Insulation
Insulation is meant to help regulate temperature and moisture levels in the attic. However, if insulation is installed improperly, such as blocking airflow paths or covering vents, it can hinder ventilation and contribute to mold growth. It’s essential to ensure that insulation is installed correctly and does not impede proper airflow.
To address poor ventilation in your attic and prevent mold growth, consider taking the following steps:
- Clean and clear any debris or insulation that may be blocking soffit vents.
- Ensure that your attic has an adequate number of properly sized vents to facilitate proper airflow.
- Check the functionality of your exhaust fans and consider installing additional fans if needed.
- Ensure that insulation is properly installed and does not impede ventilation.
By improving ventilation in your attic, you can create an environment that is less conducive to mold growth and promote a healthier living space.
Read more: How Much Does Mold Removal Cost In Attic
Roof Leaks
Roof leaks are a common cause of mold growth in attics. When water enters the attic through a leaky roof, it introduces excess moisture that creates an ideal environment for mold to thrive. Several factors can contribute to roof leaks:
Damaged Shingles
Over time, shingles can become damaged due to age, severe weather conditions, or improper installation. Cracked, missing, or curling shingles can allow water to infiltrate your roof and seep into the attic, leading to mold growth if left unresolved.
Flashing Issues
Flashing is the material used to protect areas where the roof meets vertical surfaces, such as chimneys, vents, and skylights. When flashing becomes damaged or improperly installed, water can penetrate these vulnerable areas and find its way into the attic, causing moisture buildup and potential mold problems.
Faulty Roof Installations
If your roof was improperly installed or if shortcuts were taken during the installation process, it can lead to vulnerabilities that allow water to enter the attic. Poorly sealed or improperly fastened roofing materials can create openings for water intrusion and subsequent mold growth.
Read more: What Are Attic Baffles
Detrimental Effects of Roof Leaks
Mold growth resulting from roof leaks can have various detrimental effects:
Structural Damage
Excessive moisture from roof leaks can weaken the structural components of your attic, including the wooden framework and insulation. Over time, this can compromise the integrity of your entire roof system and potentially lead to costly repairs or replacement.
Health Risks
Mold spores released into the air can cause respiratory issues, allergies, and other health problems. Prolonged exposure to mold can exacerbate existing respiratory conditions and weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to illnesses.
Increased Energy Costs
Roof leaks can lead to increased energy costs as the moisture infiltrates insulation, reducing its effectiveness and causing air conditioning or heating systems to work harder. This results in higher energy consumption and expenses.
Therefore, it is crucial to address roof leaks promptly to prevent mold growth and minimize the potential damages. Regular roof inspections, prompt repair of any underlying issues, and maintaining a healthy roofing system are vital in preventing roof leaks and stopping mold from spreading into your attic.
Condensation
Condensation is a common cause of mold growth in attics. It occurs when warm, humid air comes into contact with cooler surfaces, causing the moisture in the air to condense into water droplets. Attics are particularly prone to condensation due to a combination of factors:
Poor Ventilation
If your attic is not adequately ventilated, stagnant air can trap moisture and contribute to condensation. Without proper airflow, the moist air has no means of escape, leading to higher humidity levels and an increased likelihood of condensation forming on cold surfaces.
Lack of Insulation
Insufficient insulation can exacerbate condensation issues in attics. When warm air from the living spaces below enters the attic, it can come in contact with cooler surfaces such as roof sheathing or metal structures. The temperature difference causes the warm air to cool rapidly, increasing the chances of moisture condensation.
Read more: What Causes Stucco Leaks
Inadequate Air Sealing
Air leaks in the attic can introduce warm, moist air from the living spaces below. If there are gaps or cracks around penetrations, such as plumbing vents or electrical wiring, it allows humid air to enter the attic and contribute to condensation problems.
The presence of condensation in your attic can lead to mold growth and a host of other issues. Mold thrives in damp environments, and the water droplets from condensation provide the perfect breeding ground. The effects of condensation and subsequent mold growth include:
Mold Infestation
Excessive condensation in the attic can create an environment conducive to mold growth. As mold spores settle on moist surfaces, they can quickly multiply and spread, leading to a full-blown mold infestation if left untreated.
Deterioration of Materials
Over time, the moisture from condensation can cause damage to the structural components of your attic. Wood rot, deterioration of insulation, and corrosion of metal structures are some of the potential consequences of prolonged moisture exposure.
Health Effects
Mold resulting from condensation can release spores into the air, which can trigger respiratory allergies and other health problems. Individuals with allergies, asthma, or weakened immune systems are particularly at risk of experiencing adverse health effects from mold exposure.
To prevent condensation and consequent mold growth in your attic, consider the following measures:
- Improve attic ventilation by ensuring proper exhaust vents and air intake.
- Properly insulate the attic to minimize temperature differences and reduce the potential for condensation.
- Seal any air leaks in the attic to prevent warm, humid air from entering.
- Manage indoor humidity levels by using dehumidifiers or air conditioners, especially during humid seasons.
By addressing condensation issues in your attic, you can significantly reduce the risk of mold growth and create a healthier living environment.
Insufficient Insulation
Insufficient insulation is a common cause of mold growth in attics. Inadequate insulation can lead to temperature differences and moisture buildup, creating an environment prime for mold development. Several factors contribute to insufficient insulation:
Lack of Proper Installation
If insulation is not installed correctly, such as leaving gaps or compressing the material, it can reduce its effectiveness. Improper installation can compromise the insulation’s ability to regulate temperature and prevent moisture buildup, increasing the likelihood of mold growth.
The thickness or R-value of insulation is crucial in maintaining proper thermal resistance. If the insulation is not thick enough for your specific climate zone, it may not provide sufficient protection against heat transfer or condensation. Insufficient insulation thickness can result in temperature differences that contribute to mold-friendly conditions in the attic.
Over time, insulation can settle or become damaged, losing its effectiveness. Settling occurs when the insulation material compresses under its weight or due to environmental factors. Damaged insulation, such as from water leaks or pest infestations, can also reduce its thermal resistance and increase the risk of moisture accumulation.
The consequences of insufficient insulation in the attic include:
Temperature Variations
Inadequate insulation allows heat to escape during colder months and infiltrate during warmer months. The resulting temperature variations create conditions that contribute to moisture buildup and condensation, fostering mold growth.
Increased Energy Consumption
Insufficient insulation means less effective thermal insulation, leading to increased reliance on heating or cooling systems to maintain a comfortable indoor temperature. This results in higher energy consumption and increased utility bills.
Mold Growth
Insufficient insulation can allow warm, moist air from the living spaces below to infiltrate the attic. When this air meets cooler surfaces, condensation can occur, leading to moisture accumulation and subsequent mold growth.
If you suspect that your attic has insufficient insulation, consider taking these steps:
- Consult with a professional to assess your insulation needs and determine if additional insulation is required.
- Ensure that insulation is properly installed, covering all areas of the attic and minimizing any air gaps.
- Regularly inspect and maintain insulation to ensure it remains in good condition and restore its thermal effectiveness.
By addressing insulation issues in your attic, you can improve energy efficiency, regulate temperature, and minimize the risk of mold growth.
Improper Bathroom Ventilation
Improper bathroom ventilation can contribute to mold growth in attics. Bathrooms produce a significant amount of moisture through activities such as showers, baths, and handwashing. Without proper ventilation, this excess moisture can accumulate and migrate to the attic, creating a favorable environment for mold to thrive. Several factors can contribute to improper bathroom ventilation:
Read more: What Causes Rust In Grass
Lack of Exhaust Fan
An exhaust fan is an essential component of proper bathroom ventilation. It helps remove moisture-laden air from the bathroom, preventing it from spreading through the rest of the house. If your bathroom does not have an exhaust fan or if it is not functioning properly, the moisture generated during bathroom activities can contribute to increased humidity levels in the attic.
If your bathroom has an exhaust fan, it is crucial to ensure that it is properly sized for the room and has sufficient airflow capacity. An undersized or inefficient fan may not effectively remove the moisture from the air, allowing excess humidity to escape into the attic. It is recommended to consult with a professional to determine the appropriate size and capacity for your bathroom exhaust fan.
The ductwork that connects the bathroom exhaust fan to the exterior of the house plays a critical role in ventilation. If the ductwork is inadequate or improperly installed, it can hinder the proper airflow necessary to remove moisture from the bathroom. This can lead to the migration of humid air to the attic, contributing to mold growth.
The consequences of improper bathroom ventilation and subsequent mold growth in the attic include:
Mold Infestation
The excess moisture from the bathroom can infiltrate the attic, creating an environment conducive to mold growth. Mold spores can settle on surfaces in the attic, leading to the formation of mold colonies if conditions are favorable.
Poor Air Quality
Mold spores released by attic mold can circulate through the air ducts, affecting indoor air quality and potentially causing health issues for occupants. Breathing in mold spores can trigger allergies, respiratory problems, and other health concerns.
To prevent improper bathroom ventilation and mitigate the risks associated with mold growth in the attic, consider these measures:
- Install an adequately sized and efficient exhaust fan in your bathroom to remove excess moisture.
- Ensure that the exhaust fan is properly installed and connected to ductwork that leads directly to the exterior of the house.
- Regularly clean and maintain the exhaust fan to ensure optimal performance.
- Consider utilizing a dehumidifier in the bathroom to help control moisture levels.
By promoting proper bathroom ventilation, you can minimize the risk of mold growth in your attic and maintain a healthy living environment.
Effects of Mold in Attics
Mold growth in attics can have several detrimental effects, both on the health of the occupants and the structural integrity of the home. Understanding these effects is crucial in recognizing the importance of addressing mold issues in attics promptly. Here are some of the primary effects of mold in attics:
Health Risks
Mold releases spores into the air, which can trigger allergies, respiratory issues, and other health problems. Individuals with pre-existing respiratory conditions, allergies, or weakened immune systems are particularly susceptible to the adverse effects of mold exposure. Symptoms may include coughing, wheezing, nasal congestion, throat irritation, and skin rashes. Prolonged exposure to mold can exacerbate these symptoms and lead to more severe health complications.
Structural Damage
Mold infestations in attics can cause significant damage to the structural components of the home. Mold can feed on organic materials such as wood, drywall, and insulation, deteriorating their integrity over time. Wooden frameworks may rot, leading to compromised structural stability. Additionally, mold can cause discoloration, warping, and decay of building materials, resulting in costly repairs and potential structural risks if left untreated.
Read more: What Causes An Endospore To Germinate?
Unpleasant Odors
Mold growth in attics often produces a distinct musty odor. This odor can permeate through the home, affecting indoor air quality and creating an unpleasant living environment. The persistent smell can be challenging to eliminate without addressing the underlying mold issue.
Reduced Property Value
A home with a history of mold problems, including mold in the attic, can significantly impact its market value. Potential homebuyers may be reluctant to purchase a property with a mold issue due to concerns about health risks and the costly remediation process. Mold can also create a negative perception of the overall condition and maintenance of the home.
Increased Energy Costs
Mold in attics can compromise the thermal effectiveness of insulation, leading to increased energy consumption. Insulation that has been infested by mold loses its ability to provide proper thermal resistance, resulting in heat loss during the winter and heat gain during the summer. As a result, homeowners may experience higher utility bills as heating and cooling systems work harder to maintain desired indoor temperatures.
It is essential to address mold issues in attics promptly to prevent these effects from worsening. A professional mold remediation company can safely remove the mold, treat the affected areas, and provide solutions to prevent future mold growth.
Health Risks
Mold growth in attics can pose significant health risks to the occupants of a home. Exposure to mold spores and the byproducts of mold growth can have various negative effects on respiratory health, allergies, and overall well-being. Here are some primary health risks associated with mold in attics:
Read more: What Causes Seized Calipers
Allergic Reactions
For individuals with allergies, mold spores can trigger allergic reactions. Common symptoms include sneezing, coughing, wheezing, runny or stuffy nose, itchy eyes, and throat irritation. These reactions occur when the immune system overreacts to the presence of mold spores in the air. Prolonged exposure to mold can exacerbate existing allergies and lead to more severe symptoms.
Asthma Exacerbation
Mold can be a significant trigger for individuals with asthma. Breathing in mold spores can cause asthma symptoms to worsen, resulting in coughing, wheezing, shortness of breath, and chest tightness. For those with asthma, mold exposure can lead to increased frequency and severity of asthma attacks.
Respiratory Issues
Mold spores and the mycotoxins produced by some types of mold can irritate the respiratory system, even in individuals without pre-existing allergies or asthma. Inhalation of these particles can cause respiratory symptoms such as coughing, throat irritation, chest discomfort, and difficulty breathing. Prolonged exposure to mold in attics can lead to chronic respiratory issues and respiratory infections.
Weakened Immune System
Prolonged exposure to mold can weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to respiratory infections, viruses, and other illnesses. Mold can produce volatile organic compounds (VOCs), which can further compromise the immune system and overall health when inhaled.
Read more: What Causes Grass Tetany
Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis
Hypersensitivity pneumonitis is a lung disease that can be caused by exposure to mold in some individuals. It is characterized by inflammation of the lung tissue, leading to flu-like symptoms such as fever, chills, cough, and shortness of breath. If left untreated, it can result in long-term lung damage.
It is important to note that the severity of health risks associated with mold exposure can vary depending on factors such as the type of mold, the extent of the infestation, and individual susceptibility. Some people may be more sensitive to mold and its effects than others.
To mitigate health risks associated with mold in attics, it is essential to address the mold issue promptly. This may involve hiring professional mold remediation services to safely remove the mold and improve the air quality within the home. Additionally, taking steps to prevent future mold growth, such as ensuring proper ventilation and controlling moisture levels, can help safeguard the health of the occupants.
Structural Damage
Mold growth in attics can lead to significant structural damage to a home. Mold colonies can compromise the integrity of the structural components, potentially causing costly repairs and compromising the safety of the building. Here are some of the primary ways in which mold can damage the structure of an attic:
One of the most common types of mold found in attics is wood-decaying mold. As the name suggests, this type of mold feeds on organic material, such as wooden beams or sheathing. Over time, the mold can cause the wood to decay and weaken, compromising the structural integrity of the attic. This can lead to sagging roofs, weakened supports, and even structural collapses in severe cases.
Mold growth can also affect the insulation in the attic. Insulation provides thermal resistance and helps regulate temperature in the home. However, when mold infests insulation, it can lead to its degradation and reduced effectiveness. Moisture from the mold can cause insulation to clump together, lose its insulating properties, and allow heat transfer between the attic and the living spaces below. This can result in energy inefficiency and increased utility bills.
In some cases, mold in attics can create a humid environment that promotes the corrosion of metal structures. This can include HVAC ducts, electrical wiring, and metal roof components. The presence of moisture from mold growth can accelerate the corrosion process, leading to weakened and potentially hazardous metal structures within the attic.
Mold can also damage other building materials found in attics, such as drywall or ceiling tiles. As mold spreads across these surfaces, it can cause discoloration, stains, warping, and deterioration. Not only does this affect the appearance of the attic, but it can also compromise the integrity of these materials, potentially requiring their replacement.
The consequences of structural damage due to mold growth in attics include:
Mold-induced deterioration of wooden structures can weaken the attic’s overall structural stability. This can create safety hazards and potentially compromise the safety of the entire building. It is crucial to address structural damage promptly to mitigate the risk of collapses or other structural failures.
Repairing and restoring the structural damage caused by mold growth in attics can be costly. It may involve replacing damaged wooden beams, repairing or replacing insulation, and addressing any corroded or compromised metal structures. The extent of the repairs depends on the severity of the mold infestation and the level of damage incurred.
To minimize structural damage caused by mold in attics, it is essential to address mold issues as soon as they are detected. Hiring a professional mold remediation company is recommended to safely remove the mold, treat the affected areas, and provide preventative measures to avoid future mold growth. Regular inspections and maintenance of attic spaces can also help identify and address any structural issues before they worsen.
How to Prevent Mold Growth in Attics
Preventing mold growth in attics is crucial for maintaining a healthy living environment and preserving the structural integrity of your home. By implementing the following preventative measures, you can significantly reduce the risk of mold infestation in your attic:
Proper Ventilation
Ensure that your attic has proper ventilation to promote airflow and prevent moisture buildup. This includes having well-placed soffit vents to allow fresh air to enter and exhaust vents near the roof peak to expel stale air. Adequate ventilation helps regulate temperature and humidity levels, reducing the chances of mold growth.
Read more: What Causes Moss On Lawns
Regular Roof Inspections
Schedule regular roof inspections to identify any potential sources of water intrusion. Look for signs of damage, such as cracked or missing shingles, damaged flashing, or inadequate seals around vents and chimneys. Promptly address any issues to prevent water from entering the attic and creating a conducive environment for mold growth.
Addressing and Repairing Leaks Promptly
If a roof leak or any other water intrusion is detected in the attic, it is essential to address and repair it promptly. Mold can begin to grow within 24-48 hours in moist environments. The longer water is allowed to accumulate, the greater the risk of mold infestation. Engage the services of a professional to fix leaks and ensure proper repairs are made to prevent future moisture issues.
Installing Proper Insulation
Install and maintain insulation properly in your attic to regulate temperature and prevent condensation. Use insulation materials with the appropriate R-value for your climate zone. Ensure that insulation is installed uniformly and does not block ventilation areas, such as soffit vents or exhaust fans.
Using Bathroom Exhaust Fans
Ensure that your bathrooms are equipped with properly sized and efficient exhaust fans. Use these fans during and after bathing or showering to expel excess moisture from the bathroom. This helps prevent humid air from migrating to the attic and contributing to mold growth. Consider keeping the fans running for a period of time after bathroom use to ensure adequate ventilation.
Read more: What Causes Moths In The Pantry
Controlling Humidity Levels
Monitor and control the humidity levels in your home, as high humidity can lead to mold growth. Use dehumidifiers in areas prone to excess moisture, such as basements or crawl spaces. Keep indoor humidity levels between 30-50% to discourage mold growth throughout the home, including the attic.
Regularly inspecting your attic and addressing any signs of dampness or mold growth is also essential. If you notice any musty odors, discoloration, or visible mold, it is important to take immediate action and seek professional assistance for mold remediation.
By implementing these preventative measures, you can significantly reduce the risk of mold growth in your attic. Maintaining a dry and well-ventilated attic will help create a healthy environment and preserve the integrity of your home for years to come.
Proper Ventilation
Proper ventilation in the attic is essential to prevent mold growth and maintain a healthy living environment. Good ventilation helps regulate the temperature, humidity, and airflow, reducing the risk of excess moisture buildup. Here are some key aspects of proper ventilation in the attic:
Soffit Vents
Installing soffit vents is crucial for allowing fresh air to enter the attic. Soffit vents are typically located along the eaves of the roof, allowing outside air to flow into the attic space. These vents promote air circulation, preventing stagnant air and reducing the chances of moisture buildup. It is essential to ensure that soffit vents are not blocked by insulation or debris to allow for adequate airflow.
Exhaust Vents
Exhaust vents, such as ridge vents or roof vents, are responsible for expelling stale air from the attic. They are typically installed near the roof peak. These vents work in conjunction with soffit vents to create a natural flow of air, allowing warm, humid air to escape from the attic. Properly placed and sized exhaust vents help remove unwanted moisture, reducing the risk of mold growth.
Proper ventilation in the attic offers several benefits:
Moisture Control
Good ventilation helps control moisture levels in the attic by allowing fresh air to circulate and expelling humid air. This prevents condensation from forming on surfaces, reducing the risk of mold growth. By minimizing moisture, proper ventilation helps maintain a dry environment in the attic.
Temperature Regulation
Proper airflow in the attic helps regulate temperatures, preventing extreme heat buildup during warmer months and minimizing heat loss during colder months. This temperature regulation contributes to energy efficiency and reduces the potential for moisture condensation that can lead to mold growth.
Improved Air Quality
Effective ventilation in the attic ensures the circulation of fresh air throughout the home. This helps remove any stale or musty odors associated with mold growth. Improved air quality contributes to a healthy living environment for occupants.
Extended Roof Lifespan
Proper ventilation in the attic can extend the lifespan of your roof. By reducing excessive heat and moisture, ventilation helps prevent the deterioration of roofing materials, such as shingles, by minimizing thermal stress and potential moisture damage.
To ensure proper ventilation in your attic:
- Inspect and clean soffit vents regularly to prevent blockage.
- Ensure that exhaust vents are properly installed and in good working condition.
- Consider consulting with a professional to conduct a thorough assessment of your attic ventilation and make recommendations for improvements if needed.
- Ensure that insulation does not block airflow around vents and soffits.
By maintaining proper ventilation in the attic, you can create a healthier living space, prevent moisture-related problems, and reduce the risk of mold growth. Regular maintenance and inspection of ventilation systems will help ensure their effectiveness in preserving the overall health and integrity of your home.
Read more: What Causes Pink Grass
Regular Roof Inspections
Regular roof inspections are essential for maintaining a healthy and mold-free attic. Inspecting the roof at least once or twice a year can help identify potential issues before they worsen and contribute to mold growth. Here are the key benefits and steps involved in regular roof inspections:
Benefits of Regular Roof Inspections
Early Detection of Issues
Regular inspections allow for the early detection of any problems that may compromise the integrity of the roof. By identifying issues promptly, you can take immediate action to address them before they escalate and lead to more significant damage, such as leaks and subsequent mold growth.
Prolonged Roof Lifespan
Regular maintenance and inspections can extend the lifespan of your roof. Identifying and addressing minor issues, such as damaged shingles or flashing, helps prevent further deterioration and potential water intrusion. This proactive approach to roof care can save you money by avoiding premature roof replacements.
By identifying and repairing any areas of the roof that may allow water intrusion, you can significantly reduce the risk of mold growth in the attic. Promptly addressing leaks and other vulnerabilities helps maintain a dry and mold-free environment.
Start by visually inspecting the roof from the ground or by climbing up a ladder. Look for signs of damage, such as cracked or missing shingles, curling edges, or any areas where the roofing material appears to be lifting or deteriorating. Pay attention to the condition of the flashing around chimneys, vents, skylights, and any other roof penetrations.
Inspect the gutters and downspouts for any signs of debris buildup or blockage. Clogged gutters can prevent water from properly draining off the roof, leading to potential water backup and roof leaks.
If possible, access the attic and inspect it for any signs of water intrusion or mold growth. Look for dampness, discoloration on the walls or ceiling, and any musty odors. If you notice any of these signs, it may indicate a roof leak or other potential issues that need addressing.
For a more comprehensive inspection, consider hiring a professional roofing contractor. They have the expertise and knowledge to spot potential issues that may not be visible to the untrained eye. A professional inspection is particularly beneficial if your roof is aging, if you’ve experienced persistent leaks, or if you have concerns about its overall condition.
If you notice any issues during the roof inspection, take prompt action to address them. Have damaged shingles replaced, repair flashing, and address any signs of water intrusion. It is crucial to address potential problem areas promptly to prevent further damage and reduce the risk of mold growth.
By conducting regular roof inspections and addressing any issues promptly, you can minimize the risk of mold growth in your attic. Regular maintenance and vigilance will help ensure your roof remains in good condition, protecting your home and maintaining a healthy living environment.
Addressing and Repairing Leaks Promptly
Addressing and repairing roof leaks promptly is crucial for preventing water damage and mold growth in your attic. Persistent leaks provide an ideal environment for mold to thrive, so it is essential to take immediate action when signs of water intrusion occur. Here are the key steps to effectively address and repair roof leaks:
The first step in addressing a roof leak is identifying its source. Start by inspecting the interior of your home, looking for signs of water stains, discoloration, or dripping water. Trace the path of the water to find the approximate location of the leak. Remember that the place where water is entering your home may not necessarily be directly beneath the source of the leak on the roof.
If you notice an active leak, it is important to take immediate action to minimize water damage while you arrange for professional repairs. Place buckets or containers to collect any dripping water, and use towels or tarps to protect any furniture or belongings that may be at risk of water damage. Remember, these are temporary measures, and proper repairs should follow as soon as possible.
To effectively repair roof leaks and ensure the long-term integrity of your roof, it is advisable to hire a professional roofer. Roofers have the experience, knowledge, and tools to accurately assess the problem and address it appropriately. They can identify any underlying issues that may have caused the leak and provide the necessary repairs to prevent future water intrusion.
If the leak is caused by damaged or missing shingles, the roofer will inspect those areas and determine the extent of repairs needed. Damaged shingles will be replaced or repaired, ensuring that there are no gaps or vulnerabilities where water can infiltrate the roof system.
Flashing is used to seal the areas where the roof meets vertical surfaces, such as chimneys, skylights, and vents. If the flashing becomes damaged or improperly installed, it can allow water to enter the attic. The roofer will inspect and repair or replace the flashing, ensuring it provides a watertight seal to prevent further leaks.
After addressing a roof leak, it is crucial to maintain regular roof maintenance to prevent future leaks and minimize the risk of mold growth. Keep the roof clean from debris that can cause water pooling or damage. Regularly inspect the roof and gutters to identify and address any potential issues before they become significant problems.
Maintaining a watertight roof and addressing leaks promptly is vital to prevent water damage and mold growth in your attic. By hiring professional roofers and conducting regular roof maintenance, you can ensure the long-term integrity of your roof and the safety of your home.
Installing Proper Insulation
Installing proper insulation in your attic is essential for maintaining a comfortable and energy-efficient home while reducing the risk of mold growth. Proper insulation helps regulate temperature, prevent condensation, and minimize heat transfer between the attic and the living spaces below. Here are key considerations for installing proper insulation:
Selecting the appropriate insulation material is crucial for effective thermal resistance. Common types of insulation used in attics include fiberglass batts, blown-in cellulose, and spray foam insulation. Consider factors such as R-value (the measure of insulation’s thermal resistance), moisture resistance, and compatibility with your attic’s structure and ventilation requirements.
The R-value represents the insulation material’s thermal resistance, indicating how effectively it resists heat transfer. The R-value required for your attic depends on your climate zone. Consult local building codes or seek advice from professionals to identify the recommended R-value for your area. Properly installed insulation with the right R-value helps prevent temperature variations and condensation in the attic.
To maximize the effectiveness of insulation, ensure it is uniformly distributed throughout the attic. Gaps, compressed areas, or insufficient coverage can lead to thermal bridging and create areas prone to condensation and mold growth. Proper installation with even distribution helps maintain consistent insulation performance and reduce the risk of moisture-related issues.
When installing insulation, it is crucial to maintain adequate clearance around vents, soffit vents, and eaves. Blocking these areas with insulation can hinder proper airflow and ventilation, leading to moisture buildup. Use baffles or chutes to create a clear pathway for air to flow from the soffit vents to exhaust vents, allowing proper ventilation and preventing condensation in the attic.
Before insulating your attic, seal any air leaks in the attic floor or ductwork to prevent warm, moist air from infiltrating the space. Use caulk, weatherstripping, or spray foam insulation to seal gaps or cracks around windows, doors, electrical outlets, and any other potential areas for air leakage. This helps maintain the desired temperature in the living spaces and prevents excess moisture from reaching the attic.
If you are unsure about the proper installation of insulation or need advice on the materials and processes, it is recommended to work with insulation professionals. They have the expertise and knowledge to assess your attic’s specific needs and install insulation correctly, ensuring maximum efficiency and minimizing the risk of moisture-related problems.
Installing proper insulation in your attic is crucial for maintaining a comfortable and energy-efficient home while reducing the risk of mold growth. By selecting the right materials, achieving the required R-value, maintaining clearance around vents, sealing air leaks, and working with professionals, you can help create a well-insulated attic space that promotes a healthy and mold-free environment.
Read more: What Causes Washer Not To Spin
Using Bathroom Exhaust Fans
Using bathroom exhaust fans is a crucial step in preventing moisture buildup and mold growth in your home. Bathrooms generate a significant amount of moisture through activities such as showers and baths, and without proper ventilation, this excess humidity can cause problems. Here are some key considerations for using bathroom exhaust fans effectively:
Ensure that your bathroom is equipped with a properly sized and well-installed exhaust fan. It should be installed near the shower or bathtub to effectively capture moisture at the source. The fan should be vented to the outside of the home and not simply into the attic or crawl space, as this can lead to moisture problems elsewhere in the house.
Turn on the bathroom exhaust fan before running water in the shower or bath and keep it running during the entire duration of the activity. This will help immediately capture moisture from the air and prevent it from spreading throughout the house. After using the shower or bath, continue to run the fan for an additional 10-15 minutes to ensure that all excess moisture is expelled.
Regularly clean and maintain your bathroom exhaust fan to ensure optimal performance. Dust and debris can accumulate on the fan blades, reducing its efficiency. Cleaning the fan periodically will help it function effectively in removing moisture from the air. Refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines for cleaning and maintenance instructions specific to your exhaust fan model.
Make sure that your exhaust fan is appropriately sized for the bathroom space. The fan’s capacity should be sufficient to effectively remove the moisture produced during showers or baths. Consult a professional if you are unsure about the fan’s capacity or if you find that the fan is not adequately removing moisture from the room.
In shared bathrooms with no windows or inadequate natural ventilation, it is especially important to use exhaust fans to control moisture. Encourage all occupants to use the fan and educate them about its proper operation to maintain a dry and mold-free environment.
Even in bathrooms with windows or good natural ventilation, it is still advisable to use the exhaust fan. Natural ventilation alone may not be sufficient to remove all moisture from the air, especially during periods of high humidity. The exhaust fan can provide an extra layer of protection by effectively removing excess moisture and preventing mold growth.
By using bathroom exhaust fans properly, you can effectively control moisture levels and reduce the risk of mold growth in your home. Remember to turn on the fan before running water, keep it running during and after showers or baths, and regularly maintain and clean the fan for optimal performance. These simple steps can help create a healthier and mold-free environment in your bathroom.
Conclusion
Mold growth in attics can have significant consequences for both the health of the occupants and the structural integrity of the home. Understanding the common causes of mold growth in attics, such as poor ventilation, roof leaks, condensation, insufficient insulation, and improper bathroom ventilation, is crucial in preventing such issues.
Proper ventilation is essential in maintaining a healthy attic environment. Adequate airflow through soffit vents and exhaust vents helps prevent moisture buildup and reduces the risk of mold growth. Regular roof inspections are also necessary to identify and address potential sources of water intrusion, such as damaged shingles or faulty flashing, before they lead to mold growth. Condensation can be a significant contributor to mold growth in attics. Proper insulation helps regulate temperature and prevent condensation by reducing temperature differences. It is essential to ensure insulation is installed correctly and uniformly to avoid thermal bridging and moisture-related problems. Addressing roof leaks promptly is crucial in preventing water damage and mold growth. Identifying the source of the leak, taking temporary measures to minimize damage, and hiring a professional roofer to address the issue are all essential steps to prevent further water intrusion. Proper bathroom ventilation plays a significant role in preventing excess moisture from reaching the attic. Using exhaust fans during and after baths or showers helps remove humid air and minimize the risk of moisture buildup. Regularly maintaining the bathroom exhaust fan ensures its optimal functioning and effectiveness. Preventing mold growth in attics requires a proactive approach. Regularly inspecting the attic, addressing any signs of moisture or mold promptly, and implementing preventative measures, such as proper ventilation, insulation, and bathroom exhaust fan usage, can help maintain a healthy living environment. In conclusion, by understanding the causes of mold growth in attics and implementing preventative measures, homeowners can mitigate the risks associated with mold, promote a healthy living environment, and protect the structural integrity of their homes. Regular maintenance, prompt repairs, and proper ventilation are key in preventing mold growth and ensuring a safe and mold-free attic space.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Causes Mold In The Attic
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.


0 thoughts on “What Causes Mold In The Attic”