

Articles
What Not To Plug Into A Power Strip
Modified: August 26, 2024
Avoid plugging certain articles into a power strip to prevent damage and potential fire hazards. Learn which items you should never connect to a power strip.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Welcome to the world of technology and convenience, where power strips have become a staple in every household and office. These compact devices offer a multitude of outlets, allowing us to plug in multiple appliances and devices simultaneously. However, it is essential to understand that not everything should be plugged into a power strip.
In this article, we will explore the importance of knowing what not to plug into a power strip. We will discuss the potential risks and hazards associated with improper use and highlight specific appliances and devices that should never be connected to a power strip. Additionally, we will provide guidelines for the safe and efficient use of power strips.
By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of the do’s and don’ts when it comes to using power strips. So let’s dive in and ensure that your electrical setup remains safe and hazard-free!
Key Takeaways:
- Avoid plugging high-wattage appliances like air conditioners and kitchen appliances into power strips to prevent overloading, overheating, and electrical fires. Use dedicated outlets for these devices to ensure safety.
- Follow safe usage guidelines for power strips, including regular inspection, proper cable management, and using surge protectors for sensitive devices. Educate others on safe usage to create a culture of electrical safety.
Why It’s Important to Know What Not to Plug into a Power Strip
Power strips are designed to provide convenience and flexibility when it comes to powering multiple devices. However, it is crucial to know what appliances and devices should not be connected to a power strip. Ignoring this can lead to various risks, including electrical fires, damage to devices, and even personal injuries. Let’s explore why it’s important to be aware of what not to plug into a power strip.
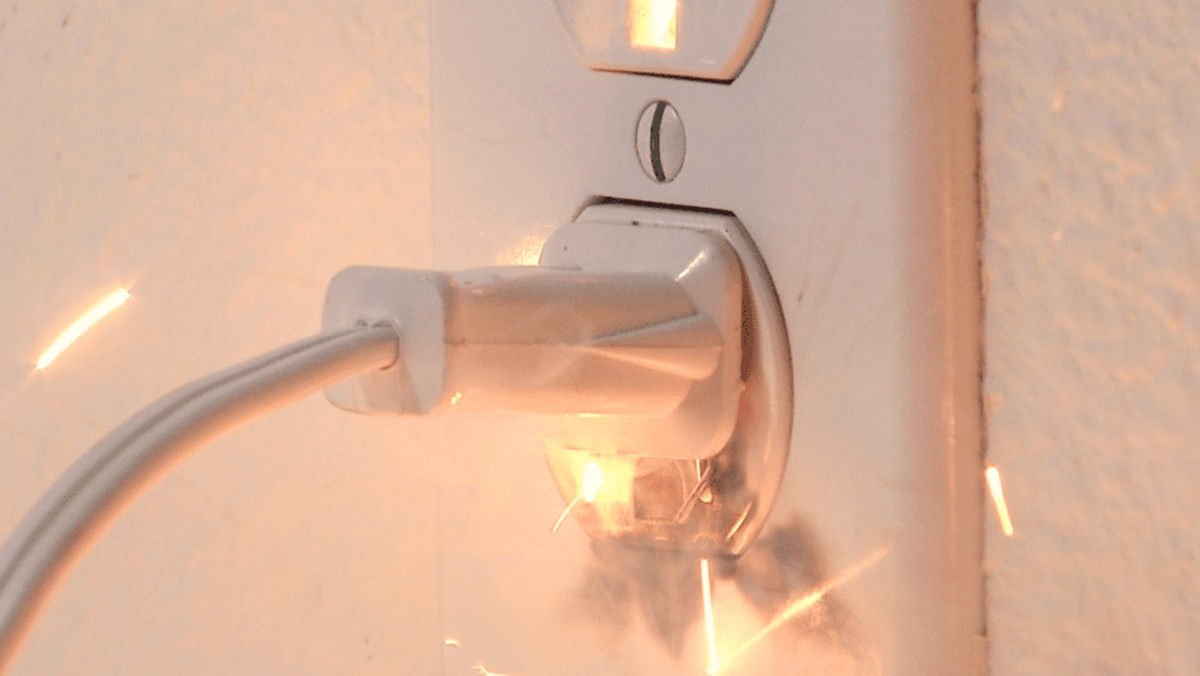
1. Overloading and Fire Hazards: Power strips have a maximum load capacity, usually measured in amps. Plugging in appliances that draw high wattage, such as space heaters, air conditioners, or large kitchen appliances, can overload the power strip. This can result in overheating, melting of components, and potentially even electrical fires. Knowing the power requirements of your devices and avoiding overloading is crucial to prevent these hazards.
2. Voltage Surges: Power strips are not equipped with surge protection capabilities by default. Plugging in sensitive devices like computers, televisions, or gaming consoles directly into a power strip without surge protection exposes them to the risk of voltage spikes and surges. These power fluctuations can cause irreversible damage to electronic devices. It is recommended to use surge protectors specifically designed for sensitive equipment.
3. Inadequate Wiring and Current Capacity: Power strips are not designed to handle the high electrical currents required by heavy-duty appliances such as refrigerators, washers, or dryers. Attempting to plug in these devices into a power strip can strain the wiring and lead to overheating, which may result in electrical malfunctions or fire hazards.
4. Tangling and Overheating: Plugging multiple power strips into one another, also known as daisy-chaining, can cause tangled and messy wiring that increases the risk of overheating. Using extension cords and power strips together can also create a similar problem. These situations can potentially lead to damaged cables, short circuits, and fire hazards. It is essential to avoid these practices and ensure proper cable management.
5. Electrical Interference: Some appliances and devices, such as Wi-Fi routers, speakers, or audio visual equipment, can generate electrical interference that may affect the performance of other devices connected to the power strip. Plugging such devices directly into a wall outlet can help minimize interference and ensure optimal functionality.
By understanding the potential risks and hazards associated with improper use, you can make informed decisions about what not to plug into a power strip. This knowledge can help safeguard your devices, protect your property, and ensure the well-being of yourself and others.
Potential Risks and Hazards
Improper use of power strips can lead to a range of risks and hazards that pose a threat to your safety and the integrity of your electrical system. It is crucial to be aware of these potential dangers to ensure the responsible and safe use of power strips. Let’s explore some of the most common risks and hazards associated with power strip misuse.
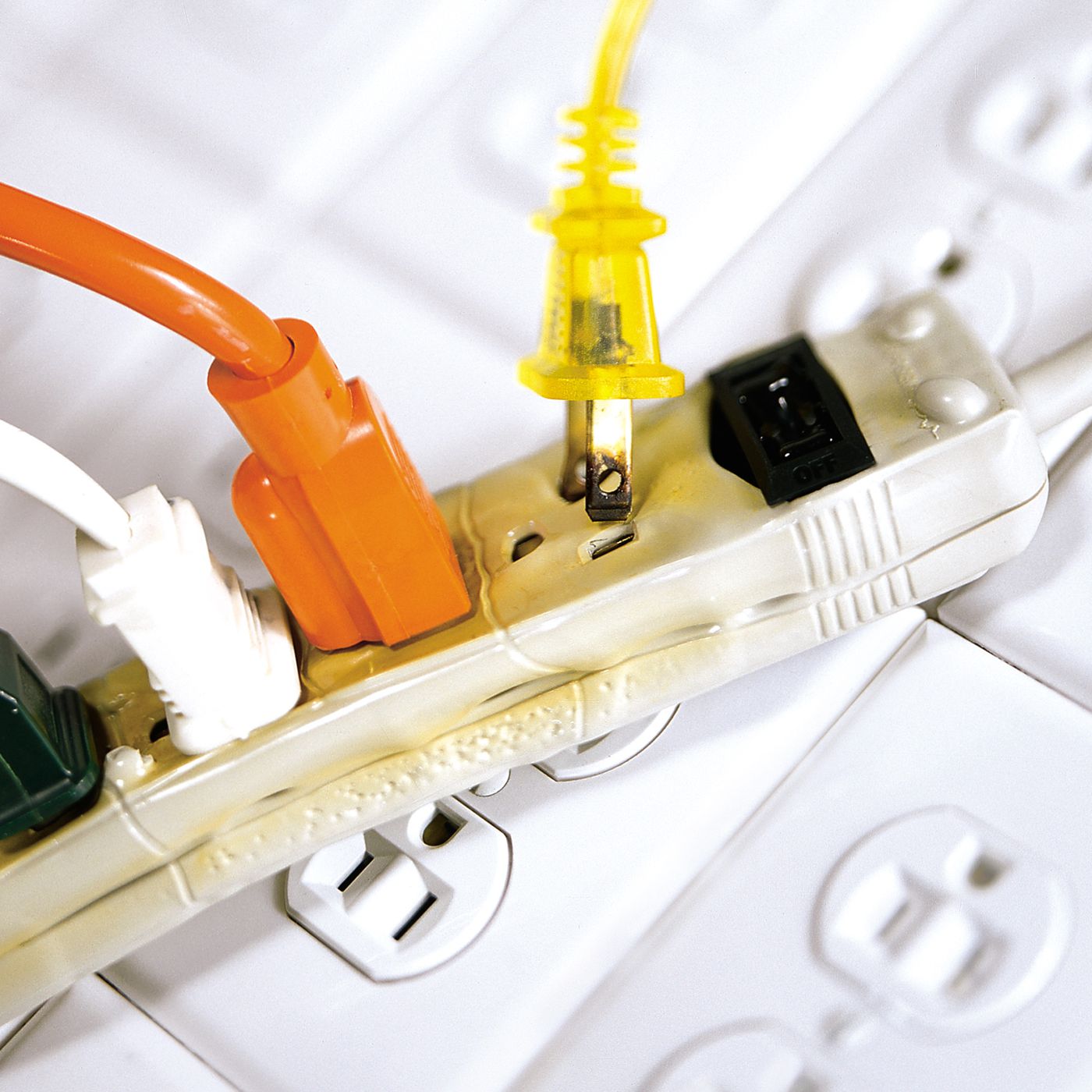
1. Electrical Fires: Overloading a power strip with high-wattage appliances or devices can cause excessive heat buildup, leading to melted wires, sparks, and in the worst-case scenario, electrical fires. The combination of overloaded circuits and flammable materials in close proximity can result in significant property damage and pose a danger to your well-being.
2. Device Damage: Power strips that lack surge protection can expose connected devices to voltage spikes or surges. Surges can cause irreversible damage to sensitive electronics, such as computers, televisions, or gaming consoles. The cost of replacing or repairing these devices can be substantial, so it is essential to use surge protectors appropriately.
3. Electrical Shock: Malfunctioning or damaged power strips increase the risk of electrical shock. Frayed wires, loose connections, or exposed components can lead to direct contact with live electrical currents. This can result in severe injuries or even prove to be fatal. Regular inspection and replacement of power strips are necessary to mitigate this risk.
4. Overheating: Overloading a power strip or daisy-chaining multiple strips together can strain the internal wiring, leading to overheating. This can cause the insulation around the wires to deteriorate, increase the risk of short circuits, and potentially start a fire. Consistently monitoring the load capacity and avoiding excessive use can help prevent overheating issues.
5. Trip and Fall Hazards: Improper cable management and excessive use of power strips can lead to tangled cords and cluttered spaces. This creates a tripping hazard, especially in high-traffic areas where people may not notice the cords on the floor. Trips and falls can cause injuries, ranging from minor bruises to more severe fractures or head injuries.
6. Damage to Power Strips: Connecting heavy-duty appliances directly to a power strip not designed for their load can damage the strip itself. Overheating, melting of components, or even internal wiring damage can occur, rendering the power strip ineffective or dangerous. It is essential to understand the power requirements of devices and use appropriate outlets or extension cords for heavy-duty appliances.
By being aware of these potential risks and hazards, you can take the necessary precautions to ensure the safe and responsible use of power strips. Regular inspection, proper load management, and avoiding any misuse can significantly minimize the likelihood of accidents and protect both yourself and your electrical system.
Never plug a power strip into another power strip, as this can overload the circuit and create a fire hazard. Only plug directly into a wall outlet.
Appliances and Devices to Avoid Plugging into a Power Strip
While power strips offer convenience and flexibility, it’s important to know which appliances and devices should never be plugged into them. Certain devices draw high wattage or have specialized power requirements that are not suitable for power strips. Here are some appliances and devices to avoid plugging into a power strip:
1. Large Kitchen Appliances: Appliances such as refrigerators, dishwashers, ovens, and microwaves should always be directly connected to a dedicated electrical outlet. These appliances have high power demands and can easily overload a power strip, leading to overheating and potential damage to the device or power strip.
2. Air Conditioners and Space Heaters: Air conditioners and space heaters consume a significant amount of energy and can quickly overwhelm a power strip. Plugging these devices into a power strip not only poses a fire hazard but also increases the risk of damaging both the device and the power strip.
3. Washer and Dryer: Similar to kitchen appliances, washers and dryers draw a substantial amount of power and should always be plugged directly into a dedicated outlet. These machines require a higher voltage and amperage than what a standard power strip can handle.
4. Power Tools: Power tools such as table saws, drills, and sanders require a significant amount of power to operate. It is important to plug these tools directly into a grounded outlet to ensure their safe and efficient use. Using a power strip may not be able to handle the power requirements, leading to malfunctions or even damaging the tool.
5. Medical Equipment: Medical devices like oxygen concentrators, CPAP machines, or dialysis machines often have specific power requirements and should be plugged directly into an outlet. Using a power strip can introduce unnecessary risks and potentially disrupt the proper functioning of vital medical equipment.
6. High-End Audio/Visual Equipment: Devices like high-end speakers, amplifiers, or home theatre systems require clean and uninterrupted power for optimal performance. Plugging these devices into a power strip can introduce electrical interference and degrade the quality of audio or video signals.
7. Electric Vehicle Charging Stations: Electric vehicle (EV) charging stations require high amperage to charge the vehicle’s battery. Utilizing a power strip to connect the charger is inappropriate and may lead to overheating, damaging the charger or the power strip itself. Always use a dedicated circuit for EV charging.
When in doubt, refer to the manufacturer’s instructions or consult a qualified electrician to determine the appropriate power source for specific appliances or devices. By avoiding the use of power strips for high-wattage or specialized devices, you can minimize the risk of electrical hazards, prolong the lifespan of your appliances, and ensure their safe operation.
Guidelines for Safe Use of Power Strips
While it’s important to understand what not to plug into a power strip, it is equally crucial to follow guidelines for safe usage. By adhering to these guidelines, you can minimize the risks associated with power strips and ensure the safety of your devices and electrical system. Here are some essential guidelines to follow:
1. Choose the Right Power Strip: Select a power strip that is suitable for your needs. Consider the number of outlets required and opt for a strip with surge protection if you plan to connect sensitive devices. Ensure the power strip is UL-listed and meets safety standards to guarantee reliability.
2. Avoid Overloading: Be mindful of the power strip’s maximum load capacity, which is typically measured in amps. Avoid plugging in appliances or devices that draw high wattage or exceed the power strip’s capacity. Distribute the load evenly across multiple power strips or outlets when necessary.
3. Inspect Regularly: Routinely check the power strip for any signs of damage, such as frayed wires, loose connections, or worn-out components. If any issues are detected, discontinue use and replace the power strip immediately. Regular inspection ensures the safety and reliability of your power strip.
4. Cable Management: Proper cable management is essential to prevent tripping hazards and maintain the integrity of the power strip. Keep cords organized and avoid routing them where they can be pinched, twisted, or damaged. Consider using cable ties or cord management systems to keep cables neat and secure.
5. Avoid Daisy-Chaining: It is best practice to avoid daisy-chaining or cascading power strips, which involves plugging one power strip into another. This practice can overload the circuit, cause overheating, and increase the risk of electrical fires. Instead, use separate power strips or consider installing additional outlets.
6. Surge Protection: If you are connecting sensitive electronic devices such as computers, televisions, or gaming consoles, consider using power strips with built-in surge protection. Surge protectors help safeguard your devices against voltage spikes and surges caused by power fluctuations.
7. Unplug when Not in Use: When not in use, it is recommended to unplug the power strip to minimize the risk of electrical hazards. This also helps save energy and reduces standby power consumption, which can contribute to lower electricity bills. Make it a habit to unplug unused power strips regularly.
8. Use Grounded Outlets: Always plug the power strip into a grounded outlet to ensure proper grounding and reduce the risk of electrical shocks. Avoid using adapters or removing the grounding prong from the power strip or the wall outlet.
9. Follow Manufacturer’s Instructions: Read and follow the manufacturer’s instructions and safety guidelines that come with the power strip. This will provide specific recommendations and precautions for your particular power strip model.
10. Educate Others: Share these guidelines with family members, colleagues, or roommates who may use the power strips in your space. Raising awareness about safe power strip usage helps create a culture of safety and protects everyone from potential electrical hazards.
By following these guidelines, you can ensure the safe and responsible use of power strips. Remember that safety should always be a top priority when dealing with electrical devices, and maintaining a well-maintained and properly used power strip can help mitigate the risks associated with electrical hazards.
Read also: 15 Best Power Strip With Flat Plug for 2025
Conclusion
Power strips have become an essential part of our lives, allowing us to conveniently connect multiple devices and appliances. However, it is vital to be aware of what not to plug into a power strip to ensure the safety of your devices, property, and well-being. This article has outlined the importance of knowing what not to plug into a power strip and the potential risks and hazards associated with improper use.
By avoiding the connection of high-wattage appliances, such as large kitchen appliances, air conditioners, or space heaters, to power strips, you reduce the risk of overloading, overheating, and electrical fires. It is also essential to be cautious with sensitive devices that require surge protection, like computers or home theater systems, and plug them directly into dedicated outlets or use power strips with built-in surge protectors.
Following guidelines for the safe use of power strips, such as choosing the right power strip, regularly inspecting for damage, practicing proper cable management, and avoiding daisy-chaining, is crucial in maintaining a safe electrical environment. Additionally, being aware of the importance of grounding, unplugging when not in use, and following the manufacturer’s instructions ensures the responsible and efficient use of power strips.
Remember, safety should always be a priority when it comes to electrical devices. By understanding and implementing the guidelines provided in this article, you can minimize the risks, protect your devices, and create a safer environment for yourself and those around you.
So, next time you reach for a power strip, make sure you plug in your devices responsibly and follow the guidelines to enjoy the convenience and flexibility it offers without compromising safety.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Not To Plug Into A Power Strip
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.














0 thoughts on “What Not To Plug Into A Power Strip”