Home>diy>Building & Construction>What Does PPE Stand For In Construction


Building & Construction
What Does PPE Stand For In Construction
Modified: March 6, 2024
Discover the meaning of PPE in construction and its significance in building-construction. Learn how personal protective equipment is crucial for worker safety and compliance.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
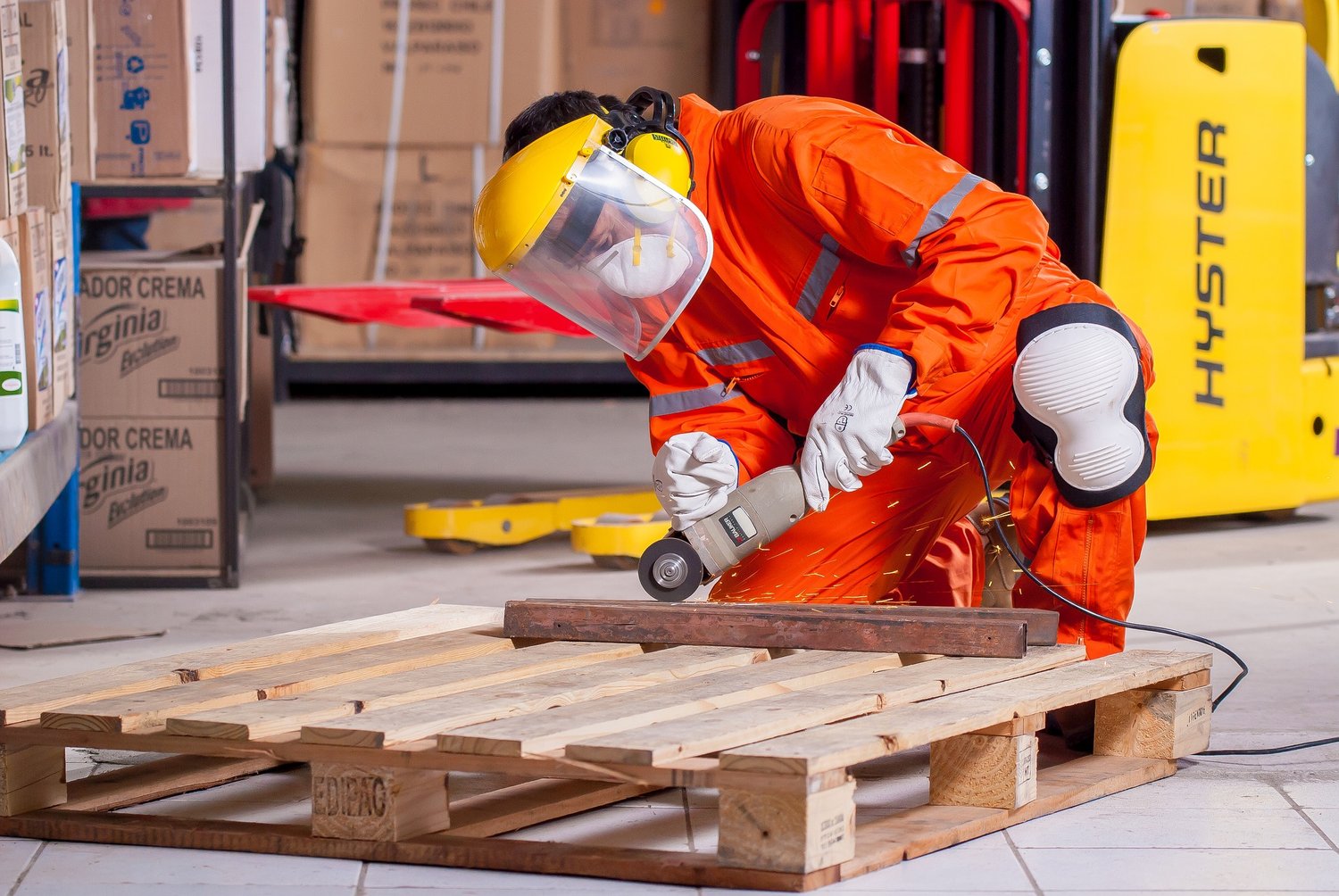
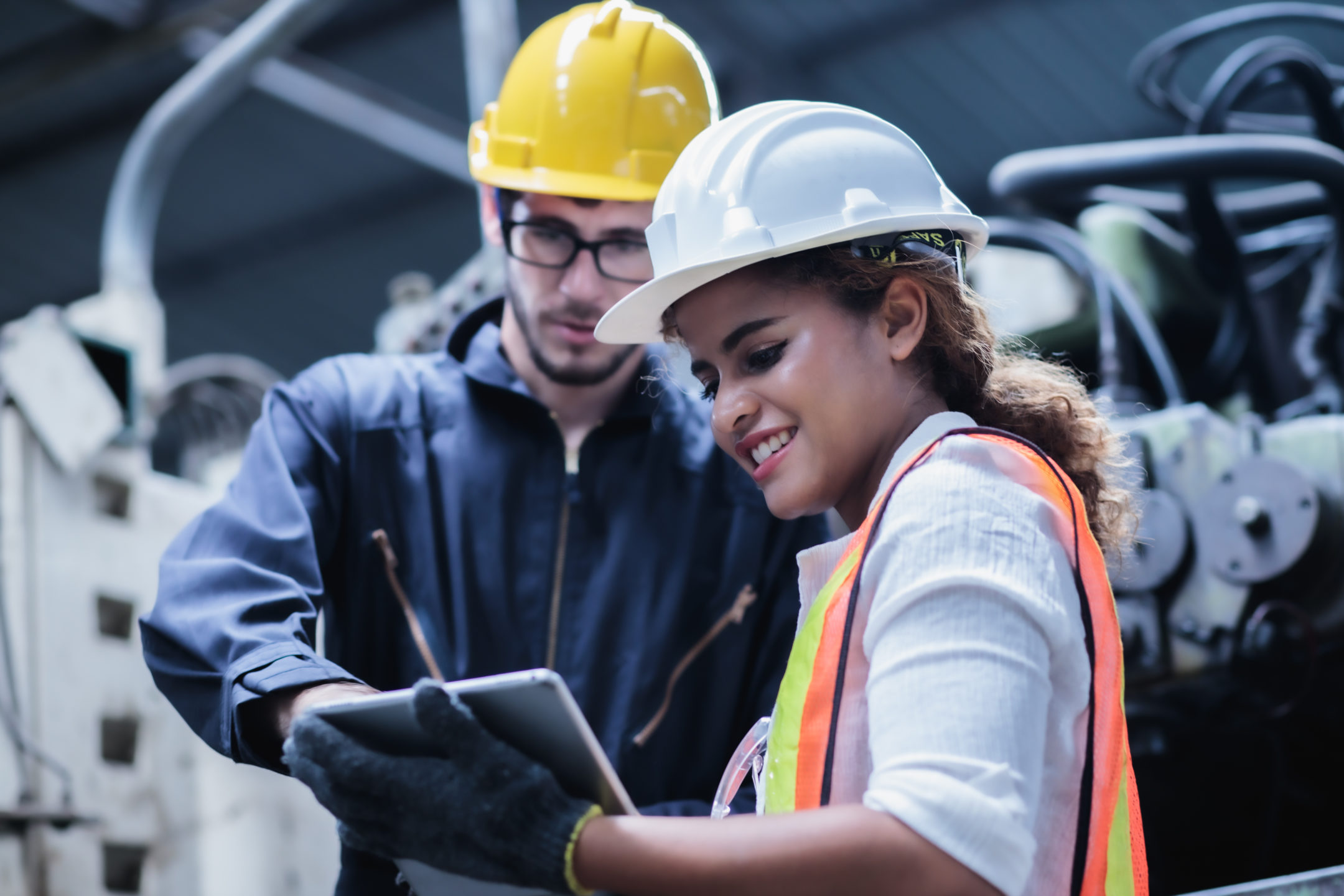
Welcome to the exciting world of construction! Construction sites are bustling hubs of activity, where skilled workers come together to create magnificent structures that shape our cities and communities. However, amidst the noise and movement, there’s an invisible force that silently protects and safeguards these workers – Personal Protective Equipment, commonly known as PPE.
PPE plays a crucial role in the construction industry, ensuring the safety and well-being of workers in hazardous environments. In this article, we will explore what PPE stands for, its importance in construction, and the types of PPE commonly used on construction sites.
So, let’s dive in and unravel the secrets behind this vital aspect of construction safety!
Key Takeaways:
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is crucial in construction for protecting workers from various hazards like falling objects, chemicals, and noise. Proper selection, use, and maintenance of PPE are essential for maximum effectiveness.
- Training and compliance with PPE requirements are vital for creating a safe working environment in construction. Workers need to be educated, trained, and regularly assessed to ensure they understand and follow PPE guidelines.
Read more: What Is PPE In Construction
Definition of PPE
Personal Protective Equipment, or PPE, refers to the specialized gear, equipment, and clothing designed to protect workers from potential hazards and risks in the workplace. In the construction industry, PPE acts as a barrier against various physical, chemical, and biological hazards that workers might encounter on the job.
PPE is a critical component of any construction site’s safety program. Its primary goal is to prevent or minimize injuries and illnesses by providing a layer of protection between the worker and the potential hazards in their environment. By wearing the appropriate PPE, workers can greatly reduce their risk of injury or illness, ensuring a safer and more productive work environment.
PPE can encompass a wide range of items, including helmets, goggles, gloves, safety shoes, high-visibility clothing, respiratory masks, and protective suits. These items are carefully designed and manufactured to meet stringent safety standards and provide maximum protection in specific work situations.
It is important to note that PPE should always be used in conjunction with other safety measures, such as engineering controls and safe work practices. While PPE acts as the last line of defense, it should never be considered a substitute for proper hazard control and risk mitigation.
Now that we understand the significance of PPE, let’s explore why it is essential in the construction industry.
Importance of PPE in Construction
The construction industry is inherently hazardous, with workers exposed to a wide range of risks and dangers on a daily basis. From falling objects and airborne debris to chemical exposures and loud noises, the potential hazards are numerous. This is where PPE plays a crucial role, ensuring the safety and well-being of construction workers. Here are some reasons why PPE is of utmost importance in construction:
1. Protection against head injuries: Construction sites are known for their elevated risk of head injuries due to falling objects, flying debris, or accidental falls. Wearing a sturdy helmet provides crucial protection to the head, reducing the risk of traumatic brain injuries.
2. Prevention of eye and face injuries: The eyes and face are susceptible to injuries from flying debris, dust particles, sparks, or chemical splashes. Properly fitted safety goggles and face shields shield the delicate eyes and face, preventing injuries that could lead to vision impairment or disfigurement.
3. Safeguarding hearing: Construction sites are noisy environments, with loud machinery, equipment, and tools constantly in operation. Prolonged exposure to high noise levels can lead to hearing loss. By wearing hearing protection devices, such as earplugs or earmuffs, construction workers can preserve their hearing health and prevent long-term damage.
4. Protection for hands and arms: Construction workers routinely handle sharp objects, heavy equipment, and hazardous materials. Gloves, arm sleeves, and gauntlets provide necessary protection against cuts, abrasions, burns, and chemical exposures, reducing the risk of hand and arm injuries.
5. Prevention of foot and leg injuries: Construction sites often involve working on uneven terrain, with the potential for slips, trips, and falls. Safety shoes with reinforced toe caps and puncture-resistant soles provide vital protection against falling objects, compression injuries, and puncture wounds.
6. Respiratory protection: Construction activities can expose workers to harmful airborne particles, dust, gases, and fumes. Respirators, such as masks or respirator cartridges, filter out these hazardous substances, ensuring clean air inhalation and preventing respiratory diseases.
7. Shielding the body: In some construction tasks, such as welding or handling hazardous chemicals, workers need full-body protection. Coveralls, aprons, and chemical-resistant suits shield the body from chemical splashes, burns, and other physical hazards.
By providing comprehensive protection against these risks, PPE serves as a vital defense mechanism, keeping construction workers safe and reducing the incidence of injuries and illnesses. However, it’s important to note that simply having PPE is not enough. Proper selection, use, and maintenance of PPE are equally essential to ensure its effectiveness. We will delve into these aspects further in the upcoming sections.
Types of PPE Used in Construction
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) in construction varies depending on the specific hazards workers may encounter on the job. By providing the right type of PPE, employers can ensure that workers are adequately protected. Here are the commonly used types of PPE in construction:
1. Head Protection: Hard hats, also known as safety helmets, are essential for protecting the head from falling objects, debris, and impacts. Hard hats are typically made of durable materials, such as high-density polyethylene, and equipped with suspension systems to absorb and distribute the force of an impact.
2. Eye and Face Protection: Safety goggles, face shields, and safety glasses protect the eyes and face from flying debris, sparks, chemicals, and harmful UV radiation. Goggles form a snug seal around the eyes, while face shields provide full-face coverage and can be worn over prescription glasses or safety glasses.
3. Hearing Protection: Noise-induced hearing loss is a significant risk in construction. Earplugs and earmuffs effectively minimize harmful noise levels and protect the ears from excessive noise exposure. Earplugs are inserted into the ear canal, while earmuffs provide a cushioned seal over the ears.
4. Hand and Arm Protection: Gloves are essential in construction to protect the hands and arms from cuts, punctures, burns, and chemical exposures. Different types of gloves are available depending on the nature of the work, such as leather gloves for general protection, cut-resistant gloves for handling sharp objects, and chemical-resistant gloves for working with hazardous materials.
5. Foot and Leg Protection: Safety shoes or boots with steel toes and puncture-resistant soles provide protection against falling objects, compression injuries, punctures, and electrical hazards. Some construction tasks may require specialized footwear, such as slip-resistant shoes or heat-resistant boots.
6. Respiratory Protection: Respirators protect the respiratory system from inhaling hazardous substances, such as dust, fumes, gases, and vapors. There are different types of respirators available, including filtering facepiece respirators (like N95 masks), half-face respirators, and powered air-purifying respirators (PAPRs).
7. Body Protection: Depending on the task, construction workers may require body protection in the form of coveralls, aprons, vests, or full-body suits. These garments protect against chemical splashes, flames, heat, excessive exposure to the sun, and other physical hazards.
Remember, the selection of PPE should be based on a thorough assessment of the hazards present at the construction site. It is crucial to ensure that the chosen PPE provides adequate protection against the identified risks and is properly fitted and maintained to ensure its effectiveness.
Now that we are familiar with the types of PPE used in construction, let’s explore the specific details and considerations for each category of PPE in the upcoming sections.
Head Protection
Head protection is of utmost importance in the construction industry, as the head is vulnerable to several hazards, including falling objects, flying debris, and accidental falls. The primary form of head protection used in construction is the hard hat, also known as a safety helmet.
Hard Hats: Hard hats are designed to absorb and distribute the force of an impact, thereby reducing the risk of head injuries. They are typically made of high-density polyethylene (HDPE), a durable material that can withstand significant force. Hard hats consist of a hard outer shell and a suspension system composed of straps and cradle, which holds the helmet in place and provides a cushioning effect.
When selecting a hard hat, ensure that it meets the safety standards specific to construction, such as those set by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the United States. Look for hard hats with labels indicating compliance with ANSI Z89.1 standards, which ensure quality and performance.
Hard hats also come with additional features to enhance their functionality, such as:
- Accessory Slots: Many hard hats have slots on the sides or front to attach accessories like face shields, ear muffs, or headlamps. These slots add versatility to the hard hat and allow for customization based on specific job requirements.
- Color Coding: Hard hats are available in various colors, and different colors may indicate different roles or responsibilities on the construction site. For example, blue may be used for site visitors, while yellow or orange may indicate supervisors.
- Reflective Strips: Some hard hats come equipped with reflective strips, enhancing visibility in low-light conditions and helping to identify workers from a distance.
- Ventilation: Ventilated hard hats have small holes or vents that allow air circulation, keeping the head cool and comfortable during hot weather or physically demanding tasks.
It’s essential to inspect hard hats regularly for signs of damage, such as cracks, dents, or degradation. Any damaged hard hats should be replaced immediately, as they may compromise the protection provided. Additionally, hard hats should fit securely on the head and be properly adjusted using the suspension system to ensure a snug and comfortable fit.
Remember, wearing a hard hat alone is not sufficient. It should be combined with other necessary PPE, such as eye protection, hearing protection, and respiratory protection, as required by the specific hazards present on the construction site.
By prioritizing head protection and ensuring the proper use of hard hats, construction workers can significantly reduce the risk of head injuries and work confidently in their demanding environment.
Read more: What Does TV Stand For In Television
Eye and Face Protection
In the construction industry, workers are exposed to various hazards that can affect the eyes and face, including flying debris, dust particles, chemicals, sparks, and intense light. To protect against these hazards, the use of proper eye and face protection is imperative.
Safety Goggles: Safety goggles are a common form of eye protection in construction. They are designed to fit securely around the eyes and form a seal to prevent debris or particles from entering. Safety goggles have impact-resistant lenses that can withstand high-velocity objects, protecting the eyes from injuries. They also provide good coverage, protecting not only the eyes but also the surrounding areas.
Face Shields: Face shields are another form of eye and face protection commonly used in construction. They provide full-face coverage, protecting the eyes, face, and neck from hazards like flying particles, sparks, or chemical splashes. Face shields are typically made of clear, impact-resistant materials and are worn over safety glasses or goggles.
When choosing eye and face protection, it’s important to ensure that they comply with the safety standards established by organizations like the American National Standards Institute (ANSI). Look for products with ANSI Z87.1 certification, which ensures they meet the required level of impact resistance and optical clarity.
Factors to consider when selecting eye and face protection include:
- Fitting: Ensure that the eyewear fits comfortably and securely on the face without interfering with vision or causing discomfort. Adjustable features like elastic straps or nose pads can help achieve a proper fit.
- Visibility: Opt for clear lenses without distortions or obstructions to maintain clear vision. Some lenses may have anti-scratch or anti-fog coatings to enhance durability and visibility in different working conditions.
- Comfort: Consider features like cushioning pads, lightweight materials, and proper ventilation to ensure that the eye and face protection can be worn for extended periods without causing discomfort or fatigue.
- Compatibility: Eye and face protection should be compatible with other PPE, like hard hats or respiratory masks, so they can be worn together without interference.
It’s crucial to inspect eye and face protection regularly for any signs of damage, such as scratches, cracks, or loose straps. Damaged equipment should be replaced promptly to maintain optimal protection.
Remember, the use of eye and face protection should be mandatory in all situations where there is a risk to the eyes or face. By wearing the appropriate eye and face protection, construction workers can minimize the risk of eye injuries, chemical exposures, and other facial hazards, ensuring their safety on the job.
Hearing Protection
In the construction industry, workers are exposed to high levels of noise from heavy machinery, power tools, and other equipment. Prolonged exposure to loud noises can lead to permanent hearing damage and loss. Hearing protection is crucial in minimizing the risk of noise-induced hearing loss and maintaining the long-term auditory health of construction workers.
Earplugs: Earplugs are small, foam or silicone inserts that are inserted into the ear canal to reduce the amount of sound entering the ear. These plugs create a barrier that blocks out or decreases the intensity of loud noises. Earplugs come in various shapes and sizes, and they can be disposable, reusable, or custom-molded for a comfortable fit.
Earmuffs: Earmuffs consist of two ear cups connected by a headband. The ear cups are cushioned and seal around the ears to create a complete sound barrier. Earmuffs are adjustable and can fit different head sizes. They provide a higher level of noise reduction compared to earplugs and are ideal for environments with continuous or intermittent loud noise.
When choosing hearing protection, it is important to look for products with a Noise Reduction Rating (NRR) indicated on the label. The NRR represents the effectiveness of the hearing protection in reducing noise levels. The higher the NRR, the greater the level of noise reduction provided by the product.
Factors to consider when selecting hearing protection include:
- Comfort: Ensure that the earplugs or earmuffs fit properly and are comfortable to wear for extended periods. Adjustable features, like headbands or foam plugs with different sizes, can help achieve a secure and comfortable fit.
- Effectiveness: Check the NRR rating to determine the level of noise reduction offered by the hearing protection. It should be suitable for the noise levels present on the construction site.
- Convenience: Consider factors such as ease of use, maintenance requirements, and portability when selecting hearing protection. Some earmuffs may have folding features for easy storage, while disposable earplugs offer convenience in replacement.
It’s essential to use hearing protection consistently in noisy construction environments, even when the noise exposure is intermittent. Employers should provide education and training on the importance of wearing hearing protection and encourage workers to use it correctly.
Regular inspections of hearing protection equipment should be conducted to identify any damage or wear. Damaged or worn-out hearing protection should be replaced promptly to maintain its effectiveness.
By utilizing proper hearing protection, construction workers can safeguard their hearing and prevent long-term hearing loss. It’s crucial to prioritize hearing health and take proactive steps to protect the ears from excessive noise levels in the construction industry.
PPE stands for Personal Protective Equipment in construction. This includes gear like hard hats, gloves, safety glasses, and high-visibility clothing to keep workers safe on the job site.
Hand and Arm Protection
In the construction industry, workers often encounter various hazards that can pose risks to their hands and arms. These hazards include sharp objects, abrasive materials, chemicals, excessive heat or cold, and vibration. Proper hand and arm protection is essential to minimize the risk of injuries and ensure the safety of construction workers.
Gloves: Gloves are the primary form of hand and arm protection used in construction. They are available in a wide range of materials and designs, each suited for specific hazards and tasks. Some common types of gloves used in construction include:
- Leather Gloves: Leather gloves provide general protection from abrasions, cuts, and punctures. They are durable and offer good grip and dexterity, making them suitable for a variety of construction tasks.
- Cut-Resistant Gloves: Cut-resistant gloves are made with materials like Kevlar or high-performance polyethylene fibers. They provide excellent protection against sharp objects such as glass, metal, or sharp tools.
- Chemical-Resistant Gloves: Chemical-resistant gloves are designed to protect against exposure to hazardous chemicals. They are made from materials that resist permeation and degradation by various chemicals, ensuring worker safety when handling corrosive substances.
- Electrically Insulated Gloves: Electrically insulated gloves are used when working with electrical equipment or in environments with the risk of electrical shock. These gloves provide protection against electrical current and are designed to meet specific industry standards.
When selecting gloves, consider the following factors:
- Task-specific Protection: Choose gloves that provide the necessary protection for the specific hazards and tasks at hand. Identify the type of hazards workers may encounter, such as sharp objects, chemicals, or extreme temperatures, and select gloves that are designed to withstand those hazards.
- Fit and Comfort: Gloves should fit properly and allow for a comfortable grip and dexterity. Ill-fitting gloves can impede movement and decrease tactile sensitivity, potentially increasing the risk of accidents. Ensure that gloves have adjustable features, such as wrist closures, to achieve a secure fit.
- Durability: Look for gloves made from durable materials that can withstand the demands of construction work. Reinforced areas, double stitching, and high-quality materials can enhance the longevity of gloves.
It is crucial to regularly inspect gloves for wear, tears, or other damage. Damaged gloves should be replaced immediately to maintain optimal protection. Additionally, proper hand hygiene should be practiced, ensuring that gloves are cleaned and sanitized regularly to prevent the buildup of contaminants.
Remember, gloves are not a one-size-fits-all solution. The appropriate type of glove should be determined by the specific hazards present, and workers should be trained on the proper use and limitations of the gloves provided.
By wearing the appropriate hand and arm protection, construction workers can minimize the risk of injuries and ensure their safety when handling hazardous materials or performing tasks that pose a threat to their hands and arms.
Foot and Leg Protection
In the construction industry, workers often encounter hazards that pose risks to their feet and legs. These hazards may include falling objects, heavy equipment, sharp objects, slippery surfaces, electrical hazards, and uneven terrain. Proper foot and leg protection is vital to ensure the safety and well-being of construction workers.
Safety Shoes or Boots: Safety shoes or boots are the primary form of foot and leg protection used in construction. They are designed to provide durable and protective footwear that can withstand the demands of a construction site. Some features of safety footwear include:
- Steel Toe Caps: Safety shoes or boots often have steel or composite toe caps that protect against impact from falling objects or compression hazards. These toe caps can withstand a significant amount of force, minimizing the risk of foot injuries.
- Puncture-Resistant Soles: Construction sites can have hazards such as nails, sharps objects, or debris that can penetrate the soles of ordinary shoes. Safety footwear with puncture-resistant soles provide an additional layer of protection against such objects.
- Slip-Resistant Soles: Construction sites can have slippery surfaces, especially in wet or oily conditions. Slip-resistant soles enhance traction and reduce the risk of slips, trips, and falls.
- Electrical Hazard Protection: Some safety shoes or boots are specifically designed with electrically insulated soles to protect against electrical hazards. This feature is crucial when working around live wires or in environments with electrical risks.
- Waterproof or Insulated Options: Depending on the working environment, construction workers may require safety footwear that is waterproof or insulated to protect against wet conditions or extreme temperatures.
When selecting safety footwear, consider the following factors:
- Proper Fit: Safety shoes or boots should fit properly to ensure comfort and stability. Ill-fitting footwear can cause discomfort and increase the risk of falls or foot-related injuries. Look for adjustable features like laces or straps to achieve a secure and comfortable fit.
- Durability: Construction sites can be harsh environments, so it is essential to choose safety footwear made from durable materials that can withstand wear and tear. Look for reinforced stitching, high-quality materials, and strong construction.
- Compliance with Safety Standards: Ensure that the safety footwear meets the relevant safety standards established by organizations like ASTM International or the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA). Look for labels or markings indicating compliance with safety standards.
Regular inspections of safety footwear should be conducted to identify signs of wear or damage. Worn-out or damaged footwear should be replaced promptly to maintain maximum protection. Additionally, employees should practice good foot hygiene and wear appropriate socks to prevent moisture buildup or friction-related issues.
It is important to note that safety footwear does not guarantee protection against all construction site hazards. Other necessary personal protective equipment, such as hard hats, eye protection, and hand protection, should be selected and worn in conjunction with safety footwear to provide comprehensive protection.
By wearing the appropriate foot and leg protection, construction workers can minimize the risk of foot and leg injuries, maintain stability and comfort, and confidently navigate the diverse and often challenging terrains of construction sites.
Read more: What Does TCL TV Stand For
Respiratory Protection
In the construction industry, workers can be exposed to various airborne hazards, including dust, fumes, gases, and hazardous particles. Inhalation of these substances can lead to respiratory problems or long-term health issues. That is why proper respiratory protection is essential to safeguard the health and well-being of construction workers.
Respirators: Respirators are devices designed to protect the respiratory system by filtering out harmful airborne particles and contaminants. There are different types of respirators used in construction:
- Filtering Facepiece Respirators (FFRs): Also known as disposable masks, FFRs cover the nose and mouth and provide protection against solid and liquid particles. N95 respirators are one commonly used type of FFR that can filter out at least 95% of airborne particles.
- Half-Face Respirators: Half-face respirators cover the nose and mouth and have replaceable cartridges or filters. They provide stronger protection against airborne contaminants, including gases and vapors.
- Powered Air-Purifying Respirators (PAPRs): PAPRs consist of a mask or hood connected to a powered unit that filters and delivers clean air to the wearer. PAPRs are suitable for environments with high concentrations of contaminants or where prolonged use is required.
When selecting the appropriate respiratory protection, it is crucial to assess the specific hazards present at the construction site. Factors to consider include:
- Hazard Type: Identify the types of hazards present, such as dust, fumes, gases, or vapors. Choose a respirator that is specifically designed to filter out or reduce exposure to those hazards.
- Protection Level: Ensure that the chosen respirator provides the necessary level of protection. Look for respirators labeled with assigned protection factor (APF) ratings, indicating the level of protection and the maximum concentration of contaminants they can filter out.
- Fit and Comfort: Respirators should fit properly to provide an effective seal and prevent the entry of contaminants. Look for adjustable straps and nose clips to achieve a secure and comfortable fit.
- Appropriate Maintenance: Follow manufacturer guidelines for maintenance, storage, and replacement of filters, cartridges, or other components to ensure the optimal performance of the respirator.
Proper training on the use, fitting, and maintenance of respiratory protection is crucial for construction workers. It is also important to perform fit tests to ensure that the respirator provides an adequate seal and proper protection.
It’s important to note that respiratory protection should not be viewed as a substitute for other safety measures, such as controlling hazards at the source or implementing engineering controls. Respiratory protection should be used in conjunction with other necessary personal protective equipment to provide comprehensive protection on construction sites.
By wearing appropriate respiratory protection, construction workers can minimize their exposure to airborne hazards and protect their respiratory health, ensuring they can work safely and confidently in potentially hazardous environments.
Body Protection
In the construction industry, workers may be exposed to various physical and chemical hazards that can potentially harm the body. To mitigate these risks, proper body protection is necessary to ensure the safety and well-being of construction workers.
Coveralls and Aprons: Coveralls and aprons are commonly used forms of body protection in construction. They are designed to provide full-body coverage and protection against physical hazards, such as splashes from chemicals or materials, sparks, flames, or rough surfaces. Coveralls are typically one-piece garments that cover the body from the neck to the ankles, while aprons cover the front of the body. These protective garments are usually made from durable materials that are resistant to tearing, punctures, and chemical contact.
High-Visibility Clothing: High-visibility clothing is essential in construction, especially for workers who need to be visible to others, such as flaggers or equipment operators. These garments are typically brightly colored, with fluorescent materials and reflective strips that increase visibility in low-light or high-traffic conditions. High-visibility clothing helps prevent accidents and ensures that workers are easily noticed by their colleagues and others in the vicinity.
Chemical-Resistant Suits: Chemical-resistant suits provide full-body protection against hazardous chemicals or substances. These coveralls are made from specialized materials that can resist penetration or absorption of chemicals, reducing the risk of skin contact and chemical burns. Chemical-resistant suits typically have a sealed or lined construction with a hood, gloves, and boots to provide complete coverage and protection.
When selecting body protection, consider the following factors:
- Hazard Analysis: Identify the specific hazards present at the construction site and select body protection that is appropriate for those hazards. Consider the type of chemicals, materials, or physical risks workers may encounter.
- Proper Sizing and Fit: Ensure that the body protection garments fit properly and allow for comfortable movement. Workers should be able to perform their tasks without restriction and discomfort.
- Durability: The chosen body protection should be made from durable materials that can withstand the demands of construction work. Reinforced stitching, secure closures, and tear-resistant fabrics are essential for durability.
- Compliance with Safety Standards: Look for body protection items that meet relevant safety standards, such as those set by organizations like ASTM International or regulatory bodies like OSHA. Compliance indicates that the garment has undergone testing and meets specified performance criteria.
Regular inspections of body protection should be conducted to identify any signs of wear or damage. Damaged garments should be replaced promptly to maintain optimal protection. Proper training on the use, care, and maintenance of body protection is necessary to ensure that workers understand how to properly wear and clean their protective garments.
It’s important to note that body protection should be used in conjunction with other necessary personal protective equipment, such as gloves, safety eyewear, and respiratory protection, to provide comprehensive protection on construction sites.
By wearing the appropriate body protection, construction workers can minimize their exposure to physical and chemical hazards, reduce the risk of injuries or illnesses, and confidently perform their tasks in a safer work environment.
Proper Selection and Use of PPE in Construction
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) plays a vital role in ensuring the safety and well-being of construction workers. However, it is important to understand that simply having PPE is not enough. Proper selection, use, and maintenance of PPE are crucial to maximize its effectiveness. Here are some key considerations for the proper selection and use of PPE in construction:
1. Conduct a Hazard Assessment: Before selecting PPE, it is essential to conduct a thorough hazard assessment of the construction site. Identify the potential hazards present, including physical, chemical, biological, and environmental risks. This assessment will help determine the specific PPE needed for each task or work area.
2. Select the Appropriate PPE: Based on the hazard assessment, choose the appropriate PPE to mitigate the identified risks. Ensure that the selected PPE provides adequate protection against the specific hazards encountered. Consider factors such as the type of PPE, the level of protection required, compatibility with other equipment, and compliance with safety standards.
3. Proper Fit and Sizing: PPE should fit correctly and be comfortable to wear, allowing for freedom of movement and not hindering the worker’s ability to perform tasks. Ill-fitting PPE can compromise its effectiveness and lead to discomfort, reduced dexterity, or even accidents. Ensure that PPE is available in various sizes and adjustable for individual workers.
4. Training and Education: Provide comprehensive training to workers on the proper use, limitations, and maintenance of PPE. Train workers on how to properly wear, adjust, and remove PPE, as well as how to recognize signs of wear or damage. Workers should also be educated on the hazards PPE can protect against and the importance of consistent PPE use.
5. Regular Inspection and Maintenance: PPE should be regularly inspected to ensure it is in good working condition. Inspect for signs of wear, damage, or deterioration and promptly replace any damaged or expired equipment. Follow manufacturer guidelines for cleaning, storage, and maintenance of PPE to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
6. Encourage Compliance: Achieving a culture of PPE compliance is crucial. Emphasize the importance of using PPE consistently and lead by example. Promote a supportive environment where workers feel comfortable reporting PPE issues or seeking clarification on proper PPE use.
7. Regular Reassessment: Hazards in the construction industry can change over time, so it is essential to regularly reassess the need for PPE. Conduct periodic reviews of the hazard assessment to ensure that the selected PPE is still appropriate and effective. Stay informed about new PPE technologies, regulations, and best practices to continually enhance safety measures.
Remember, PPE is just one component of a comprehensive safety program. It should always be used in conjunction with other engineering controls, administrative measures, and safe work practices to create a safe working environment for construction workers.
By properly selecting, using, and maintaining PPE, construction workers can work more safely and confidently, ensuring a reduction in the occurrence of injuries and illnesses on construction sites.
Training and Compliance with PPE Requirements
Training and compliance with Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) requirements are crucial components of a comprehensive safety program in the construction industry. Proper education and the establishment of a strong culture of compliance are essential to ensure the effective use of PPE and the protection of construction workers. Here are key considerations for training and achieving compliance with PPE requirements:
1. Comprehensive Training Programs: Develop and implement comprehensive training programs that cover the selection, use, limitations, maintenance, and inspection of PPE. Training should be tailored to the specific hazards present at the construction site and provide practical guidelines on how to properly wear, adjust, and remove PPE.
2. Hands-on Demonstrations: Include hands-on demonstrations during training sessions to ensure that workers understand how to correctly use and fit PPE. Allow workers to practice donning and doffing various types of PPE to reinforce proper techniques.
3. Hazard Awareness: Educate workers on the hazards they may encounter on the job and how PPE can mitigate those risks. Increase awareness about the importance of using PPE consistently and the potential consequences of non-compliance.
4. Supervisor and Management Involvement: Encourage supervisors and management to actively participate in and support PPE training programs. Their visible commitment to safety and adherence to PPE requirements will reinforce the importance of compliance among workers.
5. Communication and Feedback: Establish open lines of communication to allow workers to provide feedback or ask questions related to PPE. Encourage workers to report any issues or concerns they may have, and address them promptly to maintain a positive safety culture.
6. Regular Assessments and Audits: Conduct regular assessments and audits to evaluate the effectiveness of PPE training and the level of compliance. This includes reviewing PPE usage, identifying areas for improvement or additional training, and ensuring that PPE fits properly and is being worn correctly.
7. Reinforcement and Recognition: Reinforce the importance of compliance with PPE requirements through ongoing communication, reminders, and positive reinforcement. Recognize and acknowledge individuals or teams that consistently comply with PPE guidelines to foster a sense of accomplishment and encourage continued adherence.
8. Updated Policies and Procedures: Regularly review and update PPE policies and procedures to ensure they align with current safety regulations and best practices. Communicate any changes effectively and provide training on updated requirements to ensure ongoing compliance.
9. Lead by Example: Leaders and supervisors should set a positive example by consistently wearing PPE themselves. When workers see their superiors prioritizing safety and complying with PPE requirements, it reinforces the importance of compliance throughout the organization.
Remember, training and compliance are ongoing processes. Continuously monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of training programs and adjust them as needed. Regularly reinforce the importance of PPE compliance to create a culture of safety where using PPE becomes second nature to every worker on the construction site.
By emphasizing training and achieving high levels of compliance with PPE requirements, construction companies can significantly reduce workplace incidents, protect worker health, and create a safer working environment for all.
Read more: What Does HVAC Mean In Construction
Conclusion
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is a critical component of ensuring the safety and well-being of construction workers. It acts as a vital line of defense against a wide range of hazards present in the construction industry, including falling objects, flying debris, chemicals, noise, and more. Each piece of PPE plays a specific role in protecting different parts of the body, such as the head, eyes, ears, hands, feet, respiratory system, and overall body.
Proper selection, use, and maintenance of PPE are essential for maximum effectiveness. Conducting a thorough hazard assessment, selecting the appropriate PPE, ensuring proper fit, providing comprehensive training, and regular inspections are key considerations to achieve optimal protection. Additionally, creating a culture of compliance by involving supervisors and management, fostering communication and feedback, and reinforcing the importance of PPE usage contributes to a safer working environment.
Construction companies must prioritize the training and compliance with PPE requirements. Investing in comprehensive training programs, providing hands-on demonstrations, and increasing hazard awareness empower workers with the knowledge and skills they need to protect themselves. Regular assessments and audits, along with updated policies and procedures, help evaluate and improve the effectiveness of PPE programs over time.
By prioritizing safety through the proper selection and use of PPE, construction workers can perform their tasks with confidence, knowing that their health and well-being are protected. The usage of PPE not only reduces the risk of injuries and illnesses but also enhances productivity and ensures legal compliance.
Remember, using PPE is not a substitute for implementing other safety measures, such as engineering controls and safe work practices. It should be used in conjunction with other safety measures to provide comprehensive protection. The commitment to workplace safety, combined with the proper use of PPE, creates a culture where construction workers can thrive and build a brighter future.
Together, let us strive for a construction industry where the proper use of PPE is ingrained in every worker’s mindset, where safety is paramount, and where accidents and injuries become a thing of the past. Through education, training, and compliance, we can achieve safer construction sites and protect the most valuable asset of any construction project – our workers.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Does PPE Stand For In Construction
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.












0 thoughts on “What Does PPE Stand For In Construction”