Home>diy>Building & Construction>What Is The Difference Between BIM And VDC?

Building & Construction
What Is The Difference Between BIM And VDC?
Modified: December 7, 2023
Discover the key distinctions between BIM and VDC in the realm of building construction. Enhance your understanding of these essential components.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
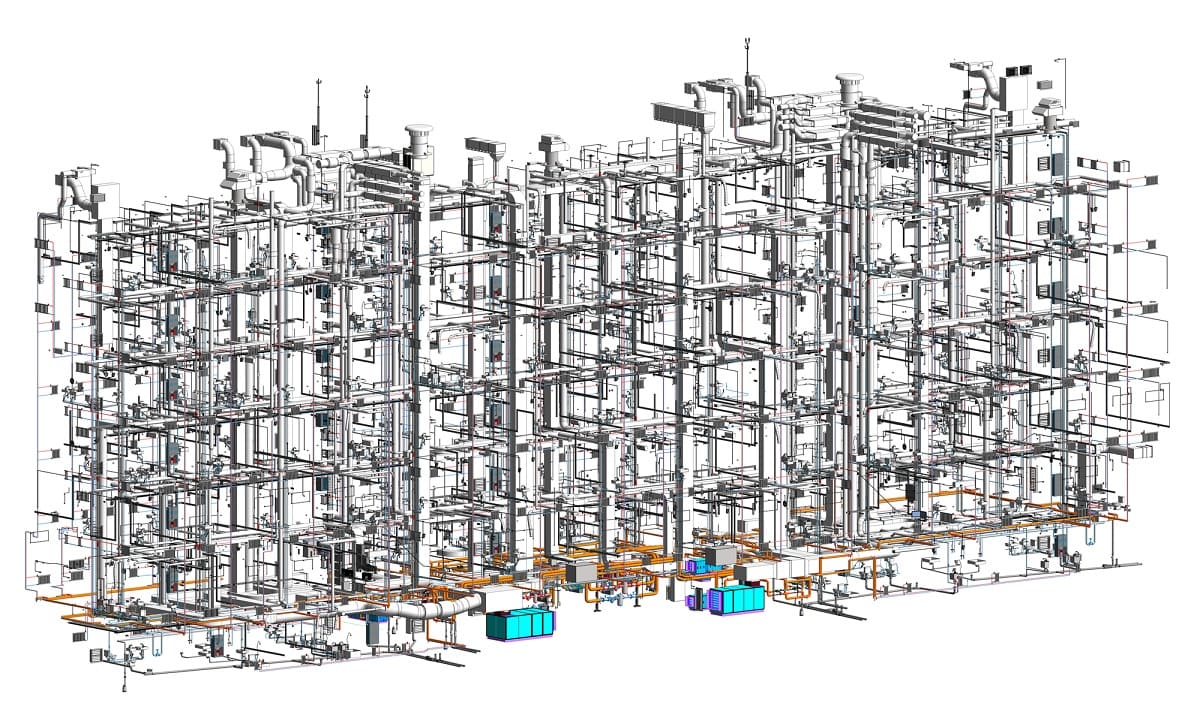
In today’s increasingly digital world, innovative technologies are transforming industries, and the construction sector is no exception. Two such technologies that have gained significant traction in recent years are Building Information Modeling (BIM) and Virtual Design and Construction (VDC). While both BIM and VDC are related to the construction industry, they serve distinct purposes and offer unique benefits.
BIM and VDC are revolutionizing the way construction projects are planned, designed, and executed. These technologies enable stakeholders to collaborate more effectively, streamline processes, reduce costs, and enhance the overall project outcomes. Understanding the difference between BIM and VDC is crucial for professionals in the construction industry to leverage the full potential of these tools.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of BIM and VDC, highlighting their key features, applications, benefits, and challenges. By the end, you will have a clear understanding of the differences between BIM and VDC and how they can be harnessed to drive success in the construction industry.
Key Takeaways:
- BIM and VDC are distinct technologies with unique focuses and benefits. BIM emphasizes collaborative design and data integration, while VDC centers around construction planning, coordination, and simulation. Both technologies offer significant potential to revolutionize the construction industry.
- Implementing BIM and VDC comes with challenges such as technology adoption, collaboration, and change management. Overcoming these challenges requires a proactive and collaborative approach from all project stakeholders to fully leverage the benefits of these game-changing technologies.
Read more: What Is The Difference Between CAD And BIM?
Definition of BIM
Building Information Modeling, commonly known as BIM, is a digital representation of a construction project that encompasses the entire lifecycle – from design and construction to operation and maintenance. BIM utilizes advanced software tools to create a 3D virtual model that integrates various architectural, structural, and MEP (mechanical, electrical, plumbing) elements.
BIM goes beyond traditional 2D drawings by incorporating additional layers of information, such as material specifications, cost estimates, and project schedules. This rich and detailed model allows stakeholders, including architects, engineers, contractors, and facility managers, to collaborate and communicate more effectively throughout the project’s lifecycle.
With BIM, the construction industry moves away from fragmented and siloed processes to a more integrated approach. All project information is consolidated within the BIM model, ensuring that stakeholders have access to accurate and up-to-date data. This facilitates better decision-making, reduces the risk of errors and clashes, and improves overall project coordination.
BIM enables real-time visualization, simulation, and analysis of various aspects – such as structural integrity, energy efficiency, and constructability – before the actual construction begins. This allows for early detection of issues and the ability to address them in the planning stages, resulting in cost savings and improved project outcomes.
Furthermore, BIM offers the ability to generate detailed and accurate construction documentation, saving time on manual drafting and reducing the chances of misinterpretations. The model can also be used for clash detection, ensuring that different building systems, such as plumbing and electrical, are seamlessly integrated without conflicts.
In summary, BIM is a collaborative process that utilizes advanced software tools to create a virtual model of a construction project. It facilitates effective communication, improves coordination, reduces errors, and provides valuable insights for all stakeholders involved.
Definition of VDC
Virtual Design and Construction (VDC) is a technology-driven approach that utilizes 3D modeling, simulation, and collaboration tools to plan, coordinate, and manage construction projects. VDC focuses on integrating various project data, processes, and stakeholders to optimize the construction process from conception to completion.
VDC leverages advanced software platforms that enable stakeholders, including architects, engineers, contractors, and subcontractors, to collaborate in a virtual environment. By centralizing project information and integrating various disciplines, VDC enhances communication and coordination, resulting in improved project efficiency and reduced risks.
One of the key elements of VDC is the creation of a detailed 3D model, similar to BIM, that represents the physical aspects of the project. However, VDC goes beyond the 3D model by incorporating additional elements such as scheduling, cost estimation, and project management information.
Through VDC, stakeholders can visualize and analyze the construction process, identify potential clashes or conflicts, and make informed decisions before construction begins. This early detection of issues helps in minimizing delays, reducing rework, and managing costs effectively.
VDC also enables the simulation and analysis of construction activities, allowing stakeholders to evaluate different construction scenarios. This allows for better sequencing of activities, optimization of resources, and identification of potential problems, resulting in improved project scheduling and efficiency.
Furthermore, VDC supports the integration of data from various sources and platforms, including Building Information Models (BIM), construction schedules, cost estimates, and equipment specifications. This integration allows for better coordination between different disciplines and ensures that all stakeholders are working with the most up-to-date information.
By leveraging VDC, construction projects can benefit from improved collaboration, reduced rework, enhanced project control, and better overall project outcomes. It helps streamline processes, improve communication between stakeholders, and minimize errors and conflicts during the construction phase.
In summary, VDC is a technology-driven approach that utilizes 3D modeling, simulation, and collaboration tools to optimize the construction process. It focuses on integrating project data and stakeholders, allowing for better coordination, improved decision-making, and enhanced project efficiency.
Key Features of BIM
Building Information Modeling (BIM) offers several key features that enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of construction projects. These features provide stakeholders with valuable insights and streamline the collaborative process. Let’s explore some of the key features of BIM:
- Three-Dimensional (3D) Visualization: BIM allows stakeholders to create and visualize a three-dimensional digital representation of the construction project. This realistic and immersive visualization helps in better understanding the design intent, identifying design conflicts, and communicating ideas effectively.
- Data Integration: BIM integrates various types of project data, including architectural, structural, and MEP (mechanical, electrical, plumbing) information. This integration ensures that all stakeholders have access to consistent and up-to-date data, facilitating improved decision-making and coordination.
- Parametric Modeling: BIM utilizes parametric modeling, where objects in the model are defined by their properties and relationships with other objects. This feature facilitates the automatic updating of the model when changes are made, ensuring that all elements remain consistent and coordinated throughout the project lifecycle.
- Collaboration and Coordination: BIM enables real-time collaboration and coordination among stakeholders. Multiple disciplines can work simultaneously on the same model, contributing their expertise and making informed decisions. This feature improves communication, reduces errors, and enhances overall project coordination.
- Clash Detection and Conflict Resolution: BIM incorporates clash detection tools that identify potential clashes or conflicts between different building elements, such as pipe clashes or structural clashes. This helps in identifying and resolving issues before construction begins, reducing rework and avoiding costly changes during the construction phase.
- Quantification and Cost Estimation: BIM includes the ability to extract quantities and generate accurate cost estimations directly from the model. This feature provides stakeholders with valuable cost insights throughout the project, enabling better budgeting and cost control.
- Facilities Management: BIM extends beyond the construction phase and supports facilities management. The BIM model can be utilized for tasks such as asset management, maintenance planning, and energy analysis, improving the efficiency of building operations and long-term maintenance.
The key features of BIM empower stakeholders to visualize the project, integrate data, collaborate efficiently, detect conflicts, and optimize construction processes. These features contribute to improved design quality, reduced costs, enhanced construction coordination, and better project outcomes.
Key Features of VDC
Virtual Design and Construction (VDC) offers a range of key features that enhance project planning, coordination, and management. These features leverage advanced technologies and collaboration tools to optimize construction processes. Let’s explore some of the key features of VDC:
- Integrated Project Information: VDC centralizes project information, including 3D models, schedules, cost estimates, and other relevant data, in a single platform. This integration ensures that all stakeholders have access to real-time and accurate information, fostering collaboration and informed decision-making.
- Collaborative Virtual Environment: VDC provides a virtual environment where stakeholders can collaborate, communicate, and share ideas effectively. This collaborative space enables simultaneous multi-disciplinary input, fostering better coordination and reducing conflicts.
- Visualization and Simulation: VDC allows for the visualization and simulation of construction activities and processes. Stakeholders can create virtual walkthroughs, conduct clash detection, and evaluate construction sequencing. This feature enables better project planning, identification of potential issues, and optimization of resources and schedules.
- Construction Coordination: VDC enhances coordination between different construction disciplines. It ensures that all stakeholders, including architects, engineers, and contractors, can work together seamlessly by integrating their inputs into the virtual model. This integration minimizes conflicts, reduces rework, and improves overall project efficiency.
- Clash Detection and Conflict Resolution: Similar to BIM, VDC incorporates clash detection tools to identify clashes or conflicts between different building elements. Through virtual simulations, potential clashes can be identified and resolved before construction begins, saving time and reducing costly changes during the construction phase.
- Real-Time Data Analysis: VDC enables real-time data analysis, allowing stakeholders to monitor project progress, identify potential bottlenecks, and track performance metrics. This feature provides valuable insights into project health, facilitating proactive decision-making and timely interventions.
- Cost and Schedule Control: VDC includes tools for cost estimation, resource allocation, and schedule optimization. Stakeholders can analyze the impact of design changes, evaluate alternative construction scenarios, and make informed decisions that help keep projects within budget and on schedule.
The key features of VDC enable stakeholders to collaborate effectively, visualize and simulate construction activities, detect clashes, monitor project progress, and control costs and schedules. By leveraging these features, construction projects can benefit from improved coordination, reduced conflicts and rework, enhanced decision-making, and ultimately, successful project delivery.
Read more: What Is The Difference Between CAD And Bim
Application in Construction Industry
Both Building Information Modeling (BIM) and Virtual Design and Construction (VDC) have numerous applications in the construction industry, revolutionizing traditional processes and improving project outcomes. Let’s explore some of the key applications of BIM and VDC:
BIM Applications:
- Design and Visualization: BIM enables architects and designers to create detailed 3D models that provide a realistic visualization of the project. This helps stakeholders to better understand the design intent, identify design flaws, and communicate ideas effectively.
- Cost Estimation and Material Quantification: BIM allows for accurate cost estimation by associating cost data with building elements. It also facilitates efficient material quantification, making it easier to track and manage project costs.
- Clash Detection and Coordination: BIM identifies clashes and conflicts between different building systems, such as structural clashes or clashes between mechanical and electrical systems. This helps in resolving issues before construction, reducing rework and potential delays.
- Scheduling and Resource Planning: BIM supports construction scheduling and resource planning by providing a visual representation of the project timeline and resource allocation. This enables efficient sequencing of activities and optimization of resources.
- Facilities Management: BIM models can be utilized for facility management, allowing maintenance teams to access accurate information about the building’s systems and components. This helps in streamlining maintenance processes and improving operational efficiency.
VDC Applications:
- Collaborative Project Planning: VDC facilitates collaborative project planning by creating a virtual environment where stakeholders can work together on project design, sequencing, and coordination. This leads to better communication, increased transparency, and improved decision-making.
- Construction Simulation and Visualization: VDC allows stakeholders to visualize and simulate construction activities, enabling better understanding of the construction process and identifying potential issues or conflicts. This enhances project planning and minimizes risks.
- Better Project Control: VDC provides real-time data analysis, allowing stakeholders to monitor project progress, track key performance indicators, and make data-driven decisions. This helps in maintaining project control and ensuring timely completion.
- Improved Collaboration and Coordination: VDC fosters collaboration and coordination among different project participants by providing a centralized platform for exchanging information, resolving conflicts, and streamlining communication. This reduces misunderstandings and improves project efficiency.
- Lean Construction Practices: VDC supports lean construction practices by optimizing processes, minimizing waste, and maximizing efficiency. This results in cost savings, improved productivity, and enhanced project outcomes.
Overall, BIM and VDC find applications across various stages of the construction project lifecycle, from design and planning to construction and facility management. They significantly enhance collaboration, improve decision-making, and streamline processes, leading to more efficient and successful construction projects.
BIM (Building Information Modeling) focuses on creating a digital representation of a building, while VDC (Virtual Design and Construction) encompasses the entire process of using digital tools to plan, construct, and manage a project.
Benefits of BIM
Building Information Modeling (BIM) offers a wide range of benefits for stakeholders in the construction industry. These benefits revolutionize traditional construction processes and improve project outcomes. Let’s explore some of the key benefits of BIM:
- Improved Collaboration and Communication: BIM facilitates effective collaboration and communication among project stakeholders. Through the shared digital model, architects, engineers, contractors, and other team members can work together seamlessly, reducing errors and misunderstandings.
- Enhanced Visualization: BIM allows stakeholders to visualize the project in 3D, providing a more realistic representation of the final result. This visual clarity helps in better understanding the design intent, identifying potential issues, and making informed decisions.
- Early Clash Detection and Conflict Resolution: BIM’s clash detection capabilities enable the identification of conflicts or clashes between different building systems. This early detection helps in resolving issues before construction, minimizing rework, and avoiding costly delays.
- Better Construction Coordination: BIM improves construction coordination by enabling the integration of various building systems and disciplines. This integration ensures that different components work together seamlessly, maximizing efficiency and reducing errors during construction.
- Efficient Cost Estimation and Material Quantification: BIM associates cost data with building elements, allowing for accurate cost estimation. It also facilitates efficient material quantification, ensuring optimal procurement and reducing waste.
- Improved Project Scheduling and Planning: BIM supports project scheduling and planning by providing a visual representation of the construction timeline and sequencing. This allows for better coordination of construction activities and resource allocation.
- Enhanced Facilities Management: BIM models can be utilized for facility management, providing detailed information about building systems and components. This improves maintenance planning, reduces downtime, and enhances operational efficiency.
- Reduced Rework and Enhanced Quality: BIM’s comprehensive and accurate digital representation reduces the chances of errors and conflicts during construction. This minimizes rework, improves construction quality, and ultimately saves time and costs.
- Improved Sustainability and Energy Efficiency: BIM allows for analysis and optimization of energy-related factors, such as daylighting, energy consumption, and HVAC systems. This helps in designing more sustainable and energy-efficient buildings.
- Long-Term Asset Management: BIM models serve as a valuable asset management tool, providing information about the building’s systems, components, and maintenance history. This facilitates efficient maintenance, reduces lifecycle costs, and extends the building’s lifespan.
The benefits of BIM are numerous and significantly impact the construction industry. They include improved collaboration, enhanced visualization, clash detection, cost estimation efficiency, better project coordination, reduced rework, improved sustainability, and long-term asset management. Embracing BIM can lead to more successful construction projects and increased competitiveness in the industry.
Benefits of VDC
Virtual Design and Construction (VDC) offers a range of benefits to stakeholders in the construction industry, revolutionizing project planning, coordination, and management. Let’s explore some of the key benefits of VDC:
- Improved Collaboration and Communication: VDC provides a collaborative virtual environment where stakeholders can work together seamlessly, facilitating effective communication and reducing misunderstandings. This enhances teamwork and improves project coordination.
- Enhanced Visualization and Simulation: VDC allows stakeholders to visualize and simulate construction activities, providing a better understanding of the construction process. This helps in identifying potential issues, optimizing resources, and making informed decisions.
- Better Project Control: VDC enables real-time data analysis, allowing stakeholders to monitor project progress, track key performance indicators, and make data-driven decisions. This improved project control helps in minimizing delays, controlling costs, and ensuring timely completion.
- Streamlined Collaboration and Coordination: VDC centralizes project information and facilitates collaboration between different disciplines and stakeholders. This streamlines communication, improves coordination, and reduces conflicts, contributing to more efficient project delivery.
- Cost and Schedule Optimization: VDC supports cost estimation, resource allocation, and construction scheduling. Stakeholders can simulate different construction scenarios, evaluate their impact, and optimize schedules and resources, leading to cost savings and improved project efficiency.
- Lean Construction Practices: VDC enables the implementation of lean construction principles by optimizing processes, minimizing waste, and maximizing value. This leads to improved productivity, reduced rework, and enhanced project outcomes.
- Early Issue Detection and Conflict Resolution: Through clash detection and simulation capabilities, VDC helps in identifying and resolving issues before construction begins. This minimizes rework, reduces delays, and ensures smoother project execution.
- Increased Safety: VDC allows for the visualization and evaluation of construction sequences, helping in identifying potential safety hazards. This proactive approach to safety management enhances on-site safety and reduces the risk of accidents.
- Improved Stakeholder Engagement: The visualization and simulation capabilities of VDC enhance stakeholder engagement by providing a realistic representation of the project. This facilitates effective communication, ensures alignment of expectations, and fosters stakeholder satisfaction.
- Efficient Facilities Management: VDC models can be utilized for facilities management, providing detailed information about the building’s components, systems, and maintenance history. This simplifies maintenance planning, improves operational efficiency, and reduces downtime.
The benefits of VDC transform construction processes, improving collaboration, visualization, project control, cost optimization, safety, and stakeholder engagement. By leveraging VDC, construction projects can benefit from enhanced efficiency, reduced risks, and improved project outcomes.
Challenges in Implementing BIM
While Building Information Modeling (BIM) offers numerous benefits, its successful implementation can come with certain challenges. Overcoming these challenges is essential for stakeholders to fully leverage the potential of BIM. Let’s explore some of the key challenges in implementing BIM:
- Technology Adoption: Implementing BIM requires the adoption of advanced software tools and technologies. This may involve a learning curve for stakeholders who are not familiar with BIM software or who may be resistant to change.
- Initial Investment: BIM implementation requires an initial investment in hardware, software, and training. This can be a significant upfront cost for organizations, especially small and medium-sized enterprises, which may pose financial challenges.
- Collaboration and Data Sharing: BIM relies heavily on collaboration among different project stakeholders. However, achieving effective collaboration can be challenging due to the need for data sharing, coordination, and mutual understanding of different disciplines and workflows.
- Standardization and Interoperability: Ensuring standardization and interoperability across different software platforms and disciplines can be a hurdle in the implementation of BIM. Interoperability issues may arise when sharing BIM models or data between different software programs or when collaborating with external project participants.
- Change Management: Implementing BIM involves a shift in traditional workflows and processes. Resistance to change from stakeholders, including designers, engineers, and contractors, can pose challenges to successful BIM adoption. Effective change management strategies and stakeholder engagement are crucial for overcoming this challenge.
- Training and Skill Development: BIM requires a certain level of expertise and skillset from stakeholders involved in the project. Providing adequate training and support to stakeholders to develop BIM-related skills can be demanding and time-consuming.
- Data Management and Quality Control: Managing large volumes of data in a BIM project can be complex. Ensuring data integrity, accuracy, and quality control is vital for the success of the project. Proper data management systems and protocols need to be established to address this challenge.
- Legal and Contractual Considerations: The legal and contractual framework in the construction industry may not always align with BIM implementation. This can create challenges related to intellectual property rights, liability, ownership, and obligations. Clear contractual agreements and legal frameworks need to be established to address these concerns.
- Industry Adoption and Collaboration: BIM’s success relies on widespread industry adoption and collaboration. If not all project participants embrace BIM or if there is a lack of communication and collaboration, the full potential of BIM may not be realized. Encouraging industry-wide adoption and fostering a culture of collaboration are essential for overcoming this challenge.
Addressing these challenges requires a proactive approach from all stakeholders involved. It involves effective change management strategies, continuous training and upskilling, improved collaboration and communication, overcoming interoperability issues, and establishing clear standards and protocols. By successfully navigating these challenges, stakeholders can fully harness the benefits of BIM and transform the construction industry.
Challenges in Implementing VDC
Implementing Virtual Design and Construction (VDC) in the construction industry comes with its own set of challenges. Overcoming these challenges is crucial for stakeholders to fully leverage the benefits of VDC. Let’s explore some of the key challenges in implementing VDC:
- Technology Adoption: Adopting VDC requires stakeholders to become familiar with new software tools and technologies. This may involve a learning curve and training to ensure proper utilization of VDC platforms.
- Data Integration and Management: VDC relies on integrating data from various sources and disciplines. Ensuring smooth data integration and management can be challenging, especially when dealing with different file formats and software platforms used by different project participants.
- Collaboration and Communication: Effective collaboration and communication among different project stakeholders can be a challenge in VDC implementation. Ensuring that all stakeholders actively participate, share information, and communicate effectively requires a culture of collaboration and clear communication protocols.
- Standardization and Interoperability: Standardization and interoperability between different software platforms is essential for seamless data exchange and collaboration. However, achieving standardization and interoperability across the industry can be a significant challenge due to proprietary file formats and varying software capabilities.
- Cost and Resource Allocation: Implementing VDC can involve initial costs for software licenses, hardware infrastructure, and training. Allocating the necessary resources and budget for VDC implementation can pose challenges, particularly for smaller organizations with limited financial capabilities.
- Change Management: Like any technology-driven change, implementing VDC requires stakeholder buy-in and effective change management strategies. Resistance to change from project participants, including designers and contractors, can hinder the successful implementation of VDC.
- Data Security and Confidentiality: VDC involves the sharing and exchange of sensitive project data. Ensuring data security, protection, and confidentiality can be a challenge in the implementation of VDC. Robust data security measures and clear policies need to be established to address these concerns.
- Training and Skill Development: VDC implementation requires stakeholders to develop new skills and competencies to effectively utilize the technology. Providing adequate training and support to stakeholders to enhance their VDC skills can be challenging, especially for organizations with limited resources.
- Perception and Resistance: Some stakeholders may have misconceptions or reservations about VDC, perceiving it as a threat to their traditional roles or methods. Overcoming resistance and fostering a mindset shift towards embracing VDC requires effective communication, education, and demonstration of the benefits VDC can bring to the project.
- Industry-wide Adoption: VDC’s success relies on industry-wide adoption and collaboration. Challenges can arise if not all project participants, including subcontractors and suppliers, are equipped with the necessary technology and skills to engage in VDC practices. Encouraging industry-wide adoption and collaboration is crucial for overcoming this challenge.
Addressing these challenges requires a proactive and collaborative approach from all project stakeholders. It involves investing in training and skill development, standardizing processes and protocols, addressing interoperability issues, ensuring data security, promoting a culture of collaboration, and effective change management. By overcoming these challenges, stakeholders can successfully implement VDC and harness its full potential to transform the construction industry.
Comparison of BIM and VDC
While Building Information Modeling (BIM) and Virtual Design and Construction (VDC) are related concepts in the construction industry, they serve distinct purposes and offer unique benefits. Let’s compare BIM and VDC across various aspects:
Definition:
BIM is a digital representation of a construction project that encompasses the entire lifecycle, integrating architectural, structural, and MEP elements. It focuses on collaborative design and data integration.
VDC, on the other hand, is a technology-driven approach that utilizes 3D modeling, simulation, and collaboration tools to plan, coordinate, and manage construction projects. It focuses on virtual coordination and optimization of construction processes.
Key Focus:
BIM’s key focus is on collaboration, data integration, and visualization. It enables stakeholders to work together, share information, and create a comprehensive virtual model of the project.
VDC’s key focus is on construction planning, coordination, and simulation. It aims to optimize the construction process through the use of technology tools, reducing conflicts and improving project efficiency.
Applications:
BIM finds applications in various project stages, including design, cost estimation, clash detection, scheduling, and facilities management. It is widely used for coordination and collaboration among different stakeholders.
VDC primarily focuses on project planning, construction sequencing, clash detection, and resource optimization. It is utilized for simulating and visualizing construction activities and ensuring efficient construction coordination.
Benefits:
The benefits of BIM include improved collaboration, enhanced visualization, clash detection, efficient cost estimation, better coordination, reduced rework, and improved facilities management.
The benefits of VDC include enhanced collaboration, visualization, project control, cost optimization, safety management, stakeholder engagement, and efficient facilities management.
Challenges:
Challenges in implementing BIM include technology adoption, initial investment, collaboration, standardization, change management, training and skill development, data management, and legal considerations.
Challenges in implementing VDC include technology adoption, data integration and management, collaboration, standardization, cost and resource allocation, change management, data security, training and skill development, perception and resistance, and industry-wide adoption.
Coexistence:
BIM and VDC are complementary to each other, with overlapping functionalities. BIM provides a robust platform for collaboration and data integration, while VDC focuses on virtual coordination and simulation. They can be used together to enhance project outcomes and drive efficiency in the construction industry.
In summary, while BIM and VDC share some similarities, they have distinct focuses, applications, and benefits. Both technologies have the potential to revolutionize the construction industry by improving collaboration, visualization, coordination, and overall project efficiency.
Conclusion
Building Information Modeling (BIM) and Virtual Design and Construction (VDC) have emerged as game-changing technologies in the construction industry. These technologies offer significant benefits, revolutionizing traditional construction processes and improving project outcomes.
BIM focuses on collaborative design, data integration, and visualization. It enables stakeholders to work together seamlessly, share information, and create a comprehensive digital model of the project. BIM finds applications in design, cost estimation, clash detection, scheduling, and facilities management.
VDC, on the other hand, centers around construction planning, coordination, and simulation. It utilizes 3D modeling, simulation, and collaboration tools to optimize the construction process. VDC is valuable for project sequencing, clash detection, resource optimization, and improving construction efficiency.
Implementing BIM and VDC can come with its own set of challenges, including technology adoption, collaboration, data management, standardization, and change management. Overcoming these challenges requires a proactive and collaborative approach from all project stakeholders.
In conclusion, BIM and VDC offer unique benefits and have transformed the construction industry. They enhance collaboration, improve coordination, reduce conflicts, optimize resources, and improve project outcomes. While different in focus and application, they can be used together to maximize their potential and achieve greater construction efficiency.
By embracing BIM and VDC, stakeholders in the construction industry can not only adapt to the digital era but also gain a competitive edge in delivering successful projects. As technology continues to advance, the evolution of BIM and VDC will undoubtedly continue, shaping the future of construction and propelling the industry towards even greater heights of innovation and efficiency.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is The Difference Between BIM And VDC?
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.














0 thoughts on “What Is The Difference Between BIM And VDC?”