Home>diy>Building & Construction>Who Started The Construction Of The Colosseum


Building & Construction
Who Started The Construction Of The Colosseum
Modified: December 7, 2023
Discover who initiated the colossal building construction project of the iconic Colosseum, one of Rome's most renowned structures.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
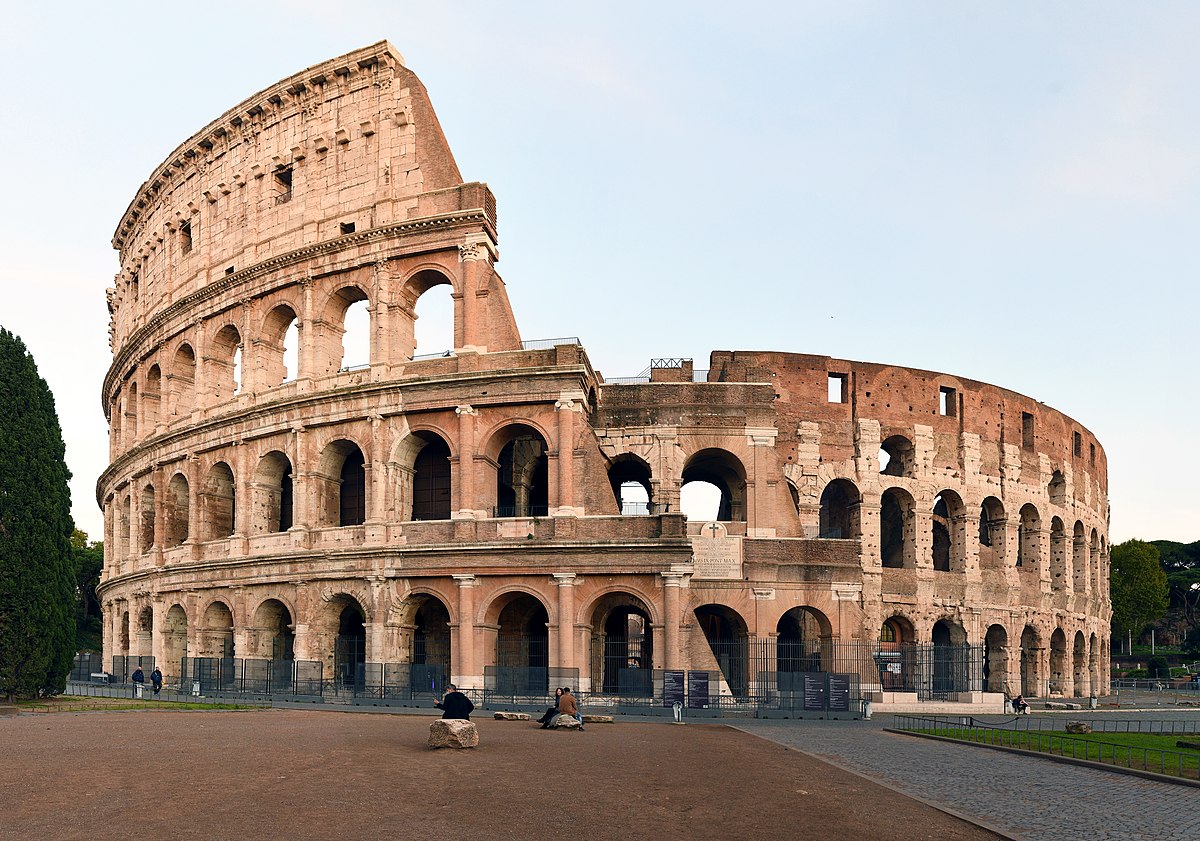
The Colosseum, also known as the Flavian Amphitheatre, is one of the most iconic and enduring symbols of ancient Rome. This grand structure, located in the heart of the city, stands as a testament to the ingenuity and architectural prowess of the Romans. Spanning nearly 2,000 years of history, the Colosseum has fascinated visitors from around the world with its grandeur and ancient glory.
The construction of the Colosseum began in the first century AD during the reign of the Flavian Dynasty, specifically under the leadership of Emperor Vespasian. This monumental endeavor was not only a symbol of Roman power and dominance, but it also served as a venue for various forms of entertainment, including gladiatorial contests, animal hunts, and mock naval battles.
In this article, we will delve into the intriguing story behind the construction of the Colosseum, exploring the motivations, architectural design, and the individuals involved in bringing this magnificent structure to life.
Key Takeaways:
- The construction of the Colosseum was initiated by Emperor Vespasian during the first century AD, showcasing Rome’s power and commitment to public welfare through grand architectural projects.
- The completion and inauguration of the Colosseum under Emperor Titus marked a grand spectacle of entertainment, solidifying its status as an enduring symbol of Roman power and dominance.
Read more: How To Start A House Construction
The Flavian Dynasty
The Flavian Dynasty, also known as the Flavian Emperors, ruled the Roman Empire from 69 AD to 96 AD. It was founded by Vespasian, a military general who emerged victorious after the chaos and instability following the death of Emperor Nero.
Vespasian and his two sons, Titus and Domitian, formed a powerful dynasty that sought to restore stability and prosperity to Rome. Under their rule, the empire experienced a period of relative peace and economic growth, known as the Flavian era.
It was during this time that the Colosseum was conceived and constructed, solidifying the Flavian Dynasty’s legacy as great builders and patrons of the arts. The amphitheater would become an enduring symbol of their power and the greatness of Rome.
Vespasian’s Decision to Build the Colosseum
After ascending to the throne in 69 AD, Vespasian faced the daunting task of stabilizing a war-torn and financially drained empire. To restore the confidence and loyalty of the Roman people, he sought to undertake ambitious construction projects that would showcase the power and grandeur of Rome.
Vespasian’s decision to build the Colosseum was rooted in his desire to provide the citizens with awe-inspiring entertainment, demonstrate his commitment to public welfare, and create a lasting monument that would immortalize his reign.
The location chosen for the construction was significant – the site of Nero’s sprawling palace, the Domus Aurea. By repurposing the land of a despised and extravagant emperor, Vespasian was able to gain popular support and convey a message of rebirth and renewal.
Furthermore, the amphitheater would serve as a venue for various spectacles that were deeply ingrained in Roman culture. Gladiatorial contests, animal hunts, and theatrical productions were all commonplace forms of entertainment and represented an integral part of the Roman identity.
Vespasian’s decision to invest heavily in this project was not only a political move but also an economic one. The construction of the Colosseum provided employment for thousands of workers and stimulated the local economy, further bolstering Vespasian’s popularity among the people.
This monumental undertaking reflected Vespasian’s astute understanding of the importance of public works in maintaining the stability and prosperity of the empire. His vision and determination laid the foundation for the construction of one of the most magnificent structures in human history.
Architectural Design and Planning
The architectural design of the Colosseum was a remarkable feat of engineering that showcased the ingenuity and innovative spirit of the ancient Romans. The project was entrusted to skilled architects and engineers who meticulously planned and executed the construction.
The primary architect of the Colosseum was believed to be a man named Celer, while another architect named Severus may have also played a significant role. Their expertise and vision guided the design process, resulting in a structure that both captivated the eye and fulfilled the functional requirements of an amphitheater.
The Colosseum was designed as a massive elliptical building, with an impressive circumference of over 500 meters. It stood four stories tall, reaching a height of approximately 48 meters. The outer shell of the amphitheater was made of travertine stone, quarried from the nearby Tivoli region.
One of the defining features of the Colosseum was its complex system of seating. The amphitheater could accommodate an estimated 50,000 to 80,000 spectators, divided into different social classes. The seating arrangements were meticulously planned to ensure optimal viewing angles and ease of access.
The underground levels of the Colosseum were just as intricate as the visible structure above ground. A network of tunnels and chambers, known as the hypogeum, housed the gladiators, animals, and elaborate mechanisms for staged performances. Trapdoors, pulleys, and elevators allowed for dramatic entrances and grand spectacles.
Furthermore, the design of the Colosseum incorporated advanced engineering techniques to ensure the safety and stability of the structure. The use of arches, columns, and concrete made from a combination of volcanic ash and lime created a strong and durable framework that has withstood the test of time.
Overall, the architectural design and planning of the Colosseum exemplified the Romans’ advanced understanding of engineering and their ability to create monumental structures that seamlessly merged functionality and aesthetic beauty.
The construction of the Colosseum in Rome was started by the Emperor Vespasian in 70-72 AD.
Execution of the Construction
The execution of the construction of the Colosseum was a massive undertaking that required the coordination of thousands of workers, engineers, and craftsmen. The construction process spanned several years and involved a combination of skilled labor and innovative engineering techniques.
The first step in the construction process was to clear the site and lay the foundation. The construction team had to excavate the area, remove the remnants of Nero’s palace, and level the ground to create a stable base for the amphitheater. Large quantities of stone and concrete were brought in to form the foundation and support structures.
Once the foundation was in place, the construction of the Colosseum’s exterior walls began. The outer shell was made using large blocks of travertine stone, which were carefully fitted together without the use of mortar. This technique, known as “opus quadratum,” provided strength and stability to the structure.
Simultaneously, the interior seating stands were constructed using a combination of brick and concrete. The stands were divided into different sections based on social classes, with the upper levels reserved for the lower classes and the highest levels reserved for women and the poorest citizens.
The construction process also involved the installation of an elaborate system of corridors, ramps, and staircases to facilitate the movement of spectators throughout the amphitheater. The architects and engineers paid meticulous attention to crowd control and ease of access to ensure a seamless spectator experience.
As the construction progressed, the innovative hypogeum, or underground area, was developed. This intricate network included passages, cages, and elevators to transport gladiators, wild animals, and props to the main arena. The hypogeum also had mechanisms for simulated battles, such as the flooding of the arena for naval reenactments.
The execution of the construction was not without its challenges. The sheer scale of the project, along with the intricate design elements, required careful planning and exceptional craftsmanship. However, the skilled labor force, including stonemasons, carpenters, and specialized craftsmen, worked tirelessly to bring Vespasian’s vision to life.
Ultimately, the successful execution of the construction was a testament to the expertise and determination of the Roman builders, resulting in one of the most impressive and enduring architectural achievements in history.
Read more: Who Is A Foreman In Construction
The Role of Emperor Titus
Emperor Titus, the eldest son of Vespasian, played a crucial role in the construction and completion of the Colosseum. Shortly after his father’s death in 79 AD, Titus ascended to the throne and took on the responsibility of overseeing the final stages of the construction.
One of the significant contributions of Emperor Titus was his financial support for the project. Despite the immense cost of building the Colosseum, Titus continued his father’s commitment to public welfare and invested substantial resources to ensure its completion. His dedication to the project further solidified his image as a benevolent and generous ruler.
Titus also demonstrated his passion for grand spectacles and theatrical events by organizing elaborate inaugural games to commemorate the opening of the Colosseum. These games lasted for 100 days and included gladiatorial contests, mock battles, and extravagant performances, all of which enthralled the Roman citizens and cemented the Colosseum’s place as the premier venue for entertainment in ancient Rome.
Emperor Titus’s involvement didn’t end with the completion of the construction. He established a tradition of hosting lavish games and public events at the Colosseum, solidifying its reputation as a symbol of imperial power and entertainment. These spectacles served to maintain the loyalty and support of the people, as well as to showcase the empire’s military strength and wealth.
Furthermore, Titus enacted legislation to regulate the use of the Colosseum and ensure the safety and well-being of the spectators. These laws focused on crowd control, fire prevention, and ethical treatment of the gladiators and wild animals used in the games. His efforts to establish guidelines for the proper management of the amphitheater demonstrated his commitment to the welfare of the Roman people.
Emperor Titus’s involvement in the construction and subsequent promotion of the Colosseum left an indelible mark on its history. His support, financial investment, and grand inaugural games elevated the status of the amphitheater and solidified it as an iconic symbol of Roman power and entertainment.
The Inauguration of the Colosseum
The inauguration of the Colosseum in 80 AD was a momentous event that marked the official opening of this magnificent amphitheater. The grand spectacle organized by Emperor Titus to commemorate the completion of the construction captivated the entire city of Rome and beyond.
The inaugural games, known as “Ludi,” lasted for 100 days and were attended by thousands of spectators from all walks of life. The festivities included gladiatorial contests, wild animal hunts, and theatrical performances, all designed to showcase the splendor and grandeur of the Colosseum.
On the first day of the games, Emperor Titus himself presided over the ceremonies, clad in the regal attire of a Roman Emperor. He offered prayers to the gods for the success of the games and the prosperity of Rome. The ceremonies were accompanied by extravagant processions, music, and fireworks, creating a spectacle that the Romans had never witnessed before.
The gladiatorial contests held during the inauguration were particularly captivating. Skilled gladiators from around the empire were pitted against each other, displaying their combat skills and bravery. These brutal battles were accompanied by roaring crowds and cheers, as the spectators were enthralled by the intense and often deadly fights.
The wild animal hunts, known as “venationes,” featured exotic animals brought from various corners of the Roman Empire. Lions, tigers, elephants, and other fearsome creatures were unleashed into the arena, providing a thrilling spectacle of man versus beast. The sheer magnitude of these hunts, combined with the intricate staging and lifelike sets, left the audience in awe.
The theatrical performances added a touch of dramatic flair to the games. Elaborate sets and costumes were used to bring ancient myths and legends to life, transporting the spectators to a world of fantasy and wonder. These performances showcased the Roman love for both entertainment and the arts.
The inauguration of the Colosseum not only provided unparalleled entertainment but also served as a powerful symbol of Roman power and dominance. The sheer scale of the event, the architectural brilliance of the Colosseum, and the meticulous planning and execution involved all contributed to an unforgettable experience for the spectators.
Emperor Titus’s vision and commitment to grand spectacles were fully realized during the inaugural games, leaving a lasting legacy in the history of the Colosseum as a center of entertainment and a symbol of imperial might.
Conclusion
The construction of the Colosseum stands as a testament to the remarkable engineering skills and grand vision of the Romans. From its inception during the reign of Vespasian to its completion and inauguration under Emperor Titus, the Colosseum has captured the imagination of people for centuries.
The monumental endeavor to build the Colosseum not only showcased the power and dominance of Rome but also provided entertainment and inspiration for its citizens. The architectural design, meticulous planning, and innovative construction techniques came together to create a structure that has stood the test of time.
Throughout its history, the Colosseum has witnessed countless gladiatorial contests, wild animal hunts, and theatrical performances, leaving indelible memories in the minds of those who were fortunate enough to witness these spectacles. The Colosseum was not just a symbol of entertainment but also a reflection of the lavish lifestyle and grandeur of the Roman Empire.
Today, the Colosseum is recognized as one of the most iconic structures in the world and continues to draw millions of visitors each year. It serves as a powerful reminder of the grand achievements of ancient Rome and the lasting impact of its architectural prowess.
The Colosseum is not merely a historic structure; it is a testament to human ingenuity and the enduring power of great civilizations. It is a reminder of the importance of preserving and appreciating our cultural heritage.
As we gaze upon the majestic ruins of the Colosseum, we are transported back in time, marveling at the incredible feats of construction and engineering. The legacy of the Colosseum serves as both an inspiration and a reminder of the greatness that humankind is capable of achieving.
In conclusion, the Colosseum stands as a magnificent symbol of ancient Rome’s power, entertainment, and architectural brilliance. It continues to captivate the world with its grandeur and serves as a timeless reminder of our shared human history.
Frequently Asked Questions about Who Started The Construction Of The Colosseum
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.














0 thoughts on “Who Started The Construction Of The Colosseum”