Home>diy>Planning & Engineering>What Are PUD Zoning Definitions?


Planning & Engineering
What Are PUD Zoning Definitions?
Modified: December 7, 2023
Learn about PUD zoning definitions and their significance in planning and engineering. Gain insights into the regulations and implications for development projects.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
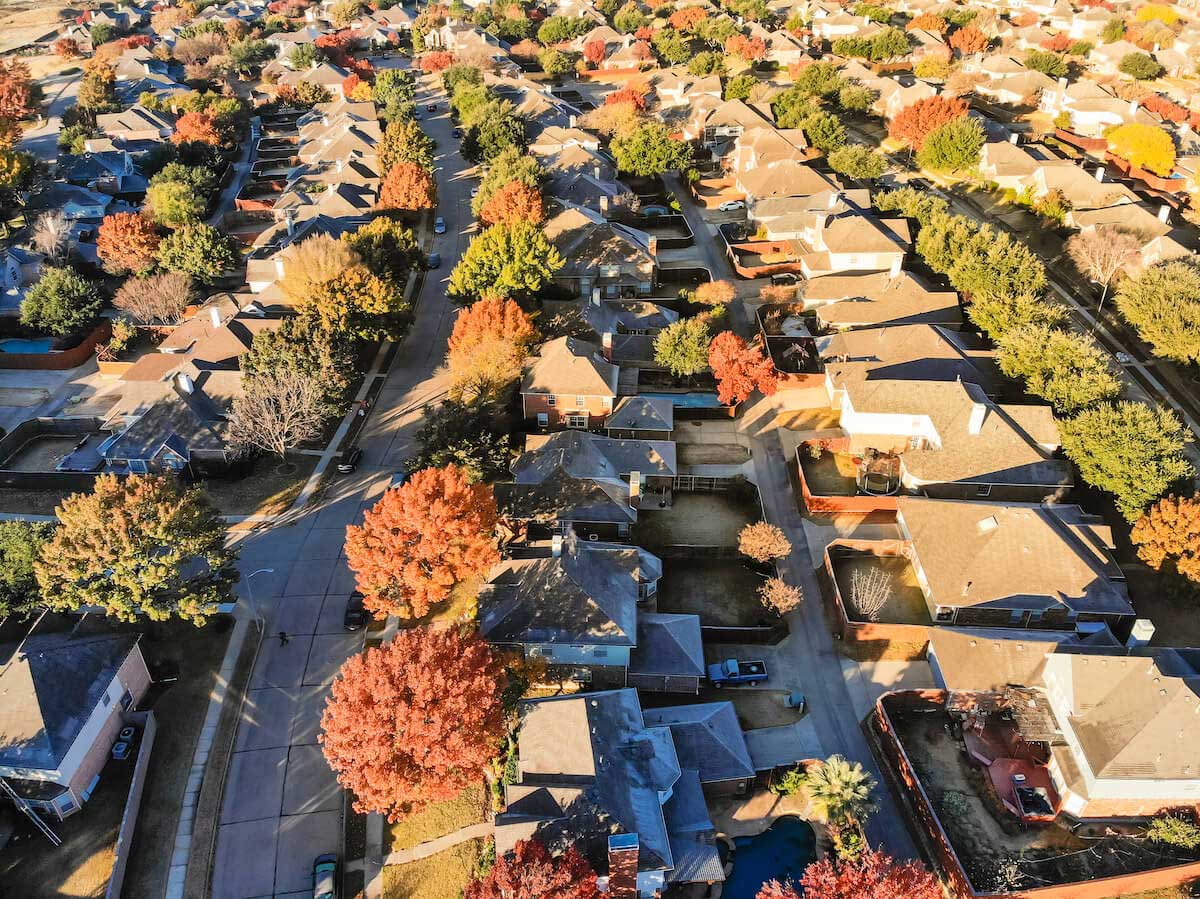
PUD (Planned Unit Development) zoning is a powerful tool used by municipalities to regulate land use and promote flexible and innovative development. In this article, we will explore the definition, purpose, benefits, process, requirements, and examples of PUD zoning.
When it comes to land development, traditional zoning laws often impose strict regulations that can limit creativity and hinder the ability to adapt to changing market conditions. This is where PUD zoning comes into play. PUD zoning offers developers and communities the opportunity to create unique, mixed-use developments that integrate various land uses, such as residential, commercial, and recreational, in a more flexible and inclusive manner.
Unlike conventional zoning ordinances, which dictate specific land use requirements for different zones within a community, PUD zoning allows for a customized approach to development. It encourages collaboration between developers and local authorities, fostering a more cooperative and mutually beneficial relationship.
Under PUD zoning, developers have the flexibility to propose plans that deviate from traditional zoning regulations, provided they meet certain guidelines and contribute to the overall enhancement of the community. This approach promotes a more comprehensive and integrated approach to development and can result in vibrant, sustainable, and aesthetically pleasing neighborhoods.
The purpose of PUD zoning is to promote innovative design, preserve natural resources, enhance the quality of life for residents, and create sustainable and resilient communities. By encouraging mixed-use development, PUD zoning can reduce traffic congestion, promote walkability and connectivity, and provide a diverse range of housing options to meet the needs of a growing population.
In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the various aspects of PUD zoning, including the benefits it offers, the process for implementing PUD zoning, the requirements for approval, and real-world examples that demonstrate its effectiveness.
Key Takeaways:
- PUD zoning fosters vibrant, sustainable communities by promoting mixed-use development, innovative design, and collaboration between developers and local authorities. It enhances residents’ quality of life and contributes to economic vitality.
- The PUD zoning process involves pre-application meetings, public hearings, and thorough evaluation. Developers must comply with zoning regulations, present a comprehensive development plan, and consider community benefits, environmental factors, and infrastructure considerations.
Read more: What Is The Definition Of Class A Glassware
Definition of PUD Zoning
PUD zoning, or Planned Unit Development zoning, is a land use regulation that allows for the creation of mixed-use developments that integrate various land uses, such as residential, commercial, and recreational, within a single planned development. Under PUD zoning, developers have the flexibility to deviate from traditional zoning regulations to create a more customized and innovative approach to development.
Unlike conventional zoning, which assigns specific land uses to different zones within a community, PUD zoning offers a more fluid and flexible framework. It allows developers to design a cohesive development plan that meets the unique needs and characteristics of the site and the surrounding community.
Under PUD zoning, developers typically submit a detailed development plan that outlines the proposed land uses, building types, densities, setbacks, open spaces, and other design guidelines. This plan is reviewed by the local planning authority to ensure that it aligns with the overall goals and objectives of the community.
One of the key features of PUD zoning is the ability to cluster buildings or allocate open spaces in a way that maximizes the efficient use of land. This can result in a more compact and walkable development with shared amenities and green spaces.
PUD zoning also encourages the use of innovative design principles and sustainability practices. Developers are encouraged to consider factors such as energy efficiency, water conservation, stormwater management, and the preservation of natural resources.
In summary, PUD zoning provides a framework that allows for the creation of unique and innovative mixed-use developments. It offers flexibility in land use, encourages creativity in design, and promotes the integration of various land uses to create vibrant and sustainable communities.
Purpose of PUD Zoning
The purpose of Planned Unit Development (PUD) zoning is to promote innovative and sustainable development while addressing the specific needs and characteristics of a particular site and community. It aims to create well-designed and cohesive neighborhoods that enhance residents’ quality of life, promote economic vitality, and contribute to the overall sustainability of the area.
One of the main objectives of PUD zoning is to encourage mixed-use development. By allowing for a combination of residential, commercial, and recreational uses within a single planned development, PUD zoning promotes walkability, reduces the need for long commutes, and provides convenient access to amenities and services for residents.
PUD zoning also fosters creativity and flexibility in design. Developers have the opportunity to innovate and implement alternative design strategies that deviate from conventional zoning regulations. This flexibility enables the integration of unique architectural styles, the preservation of natural features, and the creation of open spaces and recreational facilities that contribute to a sense of community and enhance the overall aesthetics of the development.
Furthermore, PUD zoning encourages environmentally responsible development practices. Developers are encouraged to incorporate sustainable features such as energy-efficient buildings, green infrastructure, and alternative transportation options. By considering environmental factors, PUD zoning can help mitigate the impact of development on natural resources, improve energy efficiency, and reduce carbon emissions.
Another key purpose of PUD zoning is to foster collaboration between developers and local authorities. The PUD process typically involves extensive dialogue and cooperation between the developer, planning staff, and the community. This collaboration ensures that the development aligns with the goals and vision of the community while addressing any concerns or specific needs that may arise.
Overall, the purpose of PUD zoning is to create vibrant, sustainable, and cohesive communities. It promotes mixed-use development, encourages innovation and flexibility in design, incorporates environmental considerations, and fosters collaboration between developers and the local community. By achieving these objectives, PUD zoning can result in neighborhoods that are economically viable, socially connected, and environmentally sustainable.
Benefits of PUD Zoning
Planned Unit Development (PUD) zoning offers a range of benefits for developers, communities, and the overall urban landscape. By providing flexibility in land use and encouraging innovative design, PUD zoning can lead to the creation of vibrant and sustainable neighborhoods. Let’s explore some of the key benefits of PUD zoning:
- Mixed-Use Development: PUD zoning allows for the integration of various land uses, such as residential, commercial, and recreational, within a single development. This promotes walkability, reduces the need for long commutes, and creates a more dynamic and inclusive environment for residents.
- Creative and Innovative Design: PUD zoning encourages developers to think outside the box and implement alternative design strategies. This flexibility enables the creation of unique architectural styles, the preservation of natural features, and the development of open spaces and community amenities that enhance the overall aesthetics and functionality of the development.
- Sustainable Development: PUD zoning promotes environmentally responsible development practices. Developers are incentivized to incorporate energy-efficient building designs, green infrastructure, and sustainable transportation options. This can lead to reduced energy consumption, improved stormwater management, and a smaller carbon footprint for the development.
- Enhanced Quality of Life: The mix of land uses and the availability of amenities and services within a PUD development can greatly improve the quality of life for residents. They have convenient access to shopping, dining, recreational facilities, and public spaces, all within close proximity to their homes. This fosters a sense of community and provides opportunities for social interaction and engagement.
- Economic Benefits: PUD zoning can have positive economic impacts. Mixed-use developments create opportunities for job growth and economic diversification. By incorporating commercial spaces within the development, local businesses can thrive, attracting additional investment and revenue to the community.
- Community Input and Collaboration: PUD zoning typically involves extensive collaboration between developers, planning staff, and the community. This allows for the input and feedback of stakeholders, ensuring that the development aligns with the needs and aspirations of the community. This collaborative approach fosters a stronger sense of ownership and community pride.
- Adaptability and Flexibility: PUD zoning provides developers with the flexibility to adapt to changing market conditions and trends. The ability to modify land uses and design elements within the development plan allows for adjustments that meet the evolving needs and preferences of residents and the community.
Overall, PUD zoning offers a host of benefits that contribute to the creation of vibrant, sustainable, and socially inclusive neighborhoods. By encouraging mixed-use development, fostering creativity in design, and incorporating sustainable practices, PUD zoning can have a positive and long-lasting impact on communities and the individuals who call them home.
When researching PUD zoning definitions, be sure to review the specific regulations and guidelines set forth by the local planning department or zoning commission. These regulations will outline the specific requirements and allowances for PUD developments in that area.
Process for Implementing PUD Zoning
The process for implementing Planned Unit Development (PUD) zoning varies depending on the specific requirements and procedures of the municipality or local government. However, there are common steps involved in the PUD zoning process. Let’s take a closer look at each of these steps:
- Pre-application Phase: During this initial phase, developers and stakeholders meet with the planning department or relevant authorities to discuss the concept of the proposed development. This is an opportunity to gain a preliminary understanding of the PUD zoning requirements, potential challenges, and any community concerns that may need to be addressed.
- Application Submission: Once the pre-application phase is completed, developers will submit a formal application for PUD zoning. The application typically includes a detailed development plan that outlines the proposed land uses, building types, densities, setbacks, open spaces, and other design guidelines. Supporting documents, including environmental impact assessments, traffic studies, and financial analyses, may also be required.
- Public Hearings and Community Input: Public hearings are an essential part of the PUD zoning process. These hearings provide an opportunity for the community to learn about the proposed development, ask questions, and voice any concerns or support. Developers may be required to present their development plans to the community and address any issues raised by residents, advocacy groups, or other stakeholders.
- Evaluation and Review: The planning department or relevant authorities will evaluate and review the PUD application against established criteria, zoning regulations, and community goals. They may consider factors such as the compatibility of the proposed development with the surrounding area, the impact on public infrastructure and services, and any potential environmental or social implications. The evaluation may involve multiple rounds of review and feedback before a decision is made.
- Approval and Conditions: If the PUD application meets all the necessary requirements and passes the review process, the planning department or relevant authorities will grant approval for the project. However, approval may be subject to certain conditions or modifications that the developer must comply with. These conditions may include specific design elements, mitigation measures, or contributions to community infrastructure or amenities.
- Implementation and Construction: Once the PUD zoning has been approved, the developer can proceed with the implementation and construction of the project. This may involve obtaining additional permits, adhering to building codes, and coordinating with contractors, architects, and other professionals to bring the development to fruition.
- Monitoring and Compliance: After the completion of the development, the planning department or relevant authorities may conduct periodic inspections and monitoring to ensure compliance with the approved PUD zoning regulations. This helps ensure that the development continues to meet the intended objectives and remains in accordance with the original plan.
It is important to note that the specific steps and requirements for implementing PUD zoning can vary depending on the jurisdiction. Developers and stakeholders should consult with the local planning department or relevant authorities to understand the intricacies of the process and ensure compliance with all applicable regulations.
Read more: What Is The Definition Of A Green Space
Requirements for PUD Zoning Approval
Planned Unit Development (PUD) zoning approval is contingent upon meeting certain requirements set by the local municipality or governing body. These requirements ensure that the proposed development aligns with the community’s objectives, preserves the character of the area, and provides tangible benefits to the overall community. While specific requirements may vary depending on the jurisdiction, there are common elements that are typically considered in the PUD zoning approval process. Let’s explore these requirements:
- Compliance with Zoning Regulations: The PUD must comply with the existing zoning regulations and guidelines established by the local municipality. This includes adherence to height restrictions, setback requirements, density limits, parking standards, and other applicable land use regulations.
- Comprehensive Development Plan: A detailed development plan is essential for PUD zoning approval. The plan should include information such as proposed land uses, building types, densities, setbacks, open spaces, green areas, and community amenities. The plan should demonstrate how the development will integrate and enhance the surrounding area while providing a cohesive and functional design.
- Community Benefits: PUD zoning approval typically requires developers to provide specific community benefits in exchange for the flexibility granted by the zoning designation. This may include the provision of affordable housing units, public open spaces, recreational facilities, sustainable design features, infrastructure improvements, or other contributions that enhance the quality of life for the surrounding community.
- Environmental Considerations: PUD zoning applications must address how the proposed development will mitigate any potential environmental impacts. This may involve conducting environmental impact assessments, implementing stormwater management plans, preserving natural features, promoting energy efficiency, and using sustainable building practices.
- Public Input and Engagement: Input from the community and stakeholders is often a requirement for PUD zoning approval. Developers are generally expected to engage in open dialogues, public meetings, and workshops to gather feedback and address concerns raised by residents, advocacy groups, or other stakeholders.
- Traffic and Infrastructure Considerations: PUD zoning applications should demonstrate how the proposed development will address any potential impacts on local traffic and infrastructure. This may involve conducting traffic impact studies, proposing transportation improvements, or contributing to infrastructure upgrades to accommodate the anticipated increase in population or activity.
- Economic Feasibility: PUD zoning approval may require an analysis of the economic feasibility of the proposed development. Developers may need to present financial projections, market studies, or feasibility assessments to demonstrate the long-term viability and sustainability of the project.
It is crucial for developers and applicants to carefully review the specific requirements set forth by the local municipality or governing body responsible for PUD zoning. Engaging in proactive communication and seeking guidance from planning department staff or relevant authorities can help ensure compliance with all requirements and increase the likelihood of PUD zoning approval.
Examples of PUD Zoning in Practice
Planned Unit Development (PUD) zoning has been successfully implemented in various communities around the world, resulting in the creation of vibrant and sustainable neighborhoods. Let’s explore a few examples of PUD zoning in practice:
- The Quarry, San Antonio, Texas, USA: The Quarry is a prime example of a successful PUD development. This former limestone quarry was transformed into a mixed-use community that includes residential homes, commercial spaces, recreational amenities, and preserved natural landscapes. The development focuses on creating a pedestrian-friendly environment with walkable streets, communal gathering spaces, and public art installations. The Quarry showcases how PUD zoning can turn a vacant industrial site into a thriving and attractive community.
- King’s Cross Development, London, United Kingdom: The King’s Cross Development is a prominent PUD project in London. It has transformed a previously underutilized industrial area into a vibrant mixed-use neighborhood. The development incorporates a blend of residential, commercial, and cultural spaces, including office buildings, retail shops, restaurants, public parks, and waterfront promenades. The King’s Cross Development demonstrates how PUD zoning can revitalize urban areas and create a sustainable and inclusive community.
- Reston, Virginia, USA: Reston, located just outside Washington, D.C., is a renowned example of a planned community that implemented PUD zoning principles. Designed by architect Robert E. Simon in the 1960s, Reston incorporates a variety of land uses, such as residential, commercial, recreational, and cultural facilities, within a well-thought-out framework. The community is known for its interconnected network of walkable paths, extensive green spaces, and accessibility to amenities. Reston showcases the long-term success and enduring appeal of PUD zoning.
- One Pearl Bank, Singapore: One Pearl Bank is a contemporary PUD development in Singapore that demonstrates innovative design and sustainable features. The development comprises two curved towers joined by a sky bridge, offering residential units, rooftop gardens, and recreational facilities. One Pearl Bank incorporates lush greenery and vertical gardens, maximizing the use of open spaces in a dense urban environment. This unique project highlights how PUD zoning can integrate high-density living with sustainable design.
- King Street West, Toronto, Canada: King Street West is a PUD development that has revitalized a historic district in Toronto. It combines heritage preservation with modern urban design. The development has a mix of residential, commercial, and retail spaces, with a focus on preserving the architectural heritage and character of the area. King Street West demonstrates how PUD zoning can balance modern development needs with the preservation of cultural identity and historical significance.
These examples illustrate the diverse applications of PUD zoning and its ability to transform underutilized areas into vibrant and thriving communities. Each project showcases the benefits of mixed-use development, innovative design, environmental sustainability, and community engagement that PUD zoning can bring to a neighborhood.
Conclusion
Planned Unit Development (PUD) zoning provides a flexible and innovative approach to land use regulation, allowing for the creation of mixed-use developments that enhance communities and promote sustainable growth. Throughout this article, we have explored the definition, purpose, benefits, process, requirements, and real-world examples of PUD zoning.
PUD zoning offers developers the opportunity to create unique and vibrant communities that integrate residential, commercial, and recreational spaces within a single planned development. By deviating from traditional zoning regulations, PUD zoning encourages creativity in design, fosters collaboration between developers and local authorities, and allows for the incorporation of sustainable and environmentally friendly practices.
The benefits of PUD zoning are far-reaching. It promotes walkability, reduces traffic congestion, and creates inclusive neighborhoods that enhance residents’ quality of life. Mixed-use developments foster economic vitality, provide diverse housing options, and contribute to the overall sustainability of the community. PUD zoning also encourages community engagement and input, ensuring that the development aligns with the needs and aspirations of the local residents.
The process for implementing PUD zoning involves pre-application meetings, formal application submission, public hearings, evaluation and review, and approval with possible conditions. Developers must demonstrate compliance with zoning regulations, present a comprehensive development plan, provide community benefits, and consider environmental and infrastructure factors.
Real-world examples of successful PUD zoning projects, such as The Quarry in San Antonio and the King’s Cross Development in London, showcase the transformative power of PUD zoning. These projects have revitalized underutilized areas, creating vibrant, sustainable, and socially inclusive neighborhoods. Other examples, like Reston in Virginia and One Pearl Bank in Singapore, emphasize the long-term success and enduring appeal of PUD zoning, highlighting its ability to balance modern development needs with the preservation of cultural identity and historical significance.
In conclusion, Planned Unit Development zoning is a valuable tool for creating dynamic and sustainable communities. It promotes creativity in design, fosters collaboration, enhances quality of life, and contributes to the overall well-being of residents. By adopting PUD zoning principles, municipalities can create thriving neighborhoods that reflect the diverse needs and aspirations of their communities, both now and in the future.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Are PUD Zoning Definitions?
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.










0 thoughts on “What Are PUD Zoning Definitions?”