Home>diy>Planning & Engineering>What Is A Zoning Ordinance?

Planning & Engineering
What Is A Zoning Ordinance?
Modified: January 9, 2024
Learn about zoning ordinances and their role in planning-engineering. Understand how these regulations impact land use and development.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Welcome to the world of urban planning and development, where zoning ordinances play a crucial role in shaping the physical landscape of our cities and towns. If you’ve ever wondered what a zoning ordinance is and how it affects community planning, you’ve come to the right place.
In simple terms, a zoning ordinance is a set of regulations that govern the use of land within a particular jurisdiction. These regulations dictate what types of activities can take place in different areas, such as residential, commercial, industrial, or recreational. Zoning ordinances serve as a tool for local governments to manage and control the growth and development of their communities.
While zoning ordinances may seem like a dry topic, they have a significant impact on the way our neighborhoods are designed and function. From the location of homes and businesses to the preservation of open spaces and the creation of vibrant public spaces, zoning ordinances play a vital role in shaping the character and livability of our communities.
In this article, we will provide a comprehensive overview of zoning ordinances, exploring their definition, purpose, components, implementation, challenges, controversies, and benefits.
So, let’s dive into the world of zoning ordinances and discover how they shape our built environment.
Key Takeaways:
- Zoning ordinances are essential for managing land use, preserving community character, and promoting economic development, contributing to vibrant and sustainable neighborhoods.
- Despite challenges, zoning ordinances offer benefits such as orderly land use, environmental protection, and enhanced quality of life, shaping thriving and inclusive communities.
Definition of Zoning Ordinance
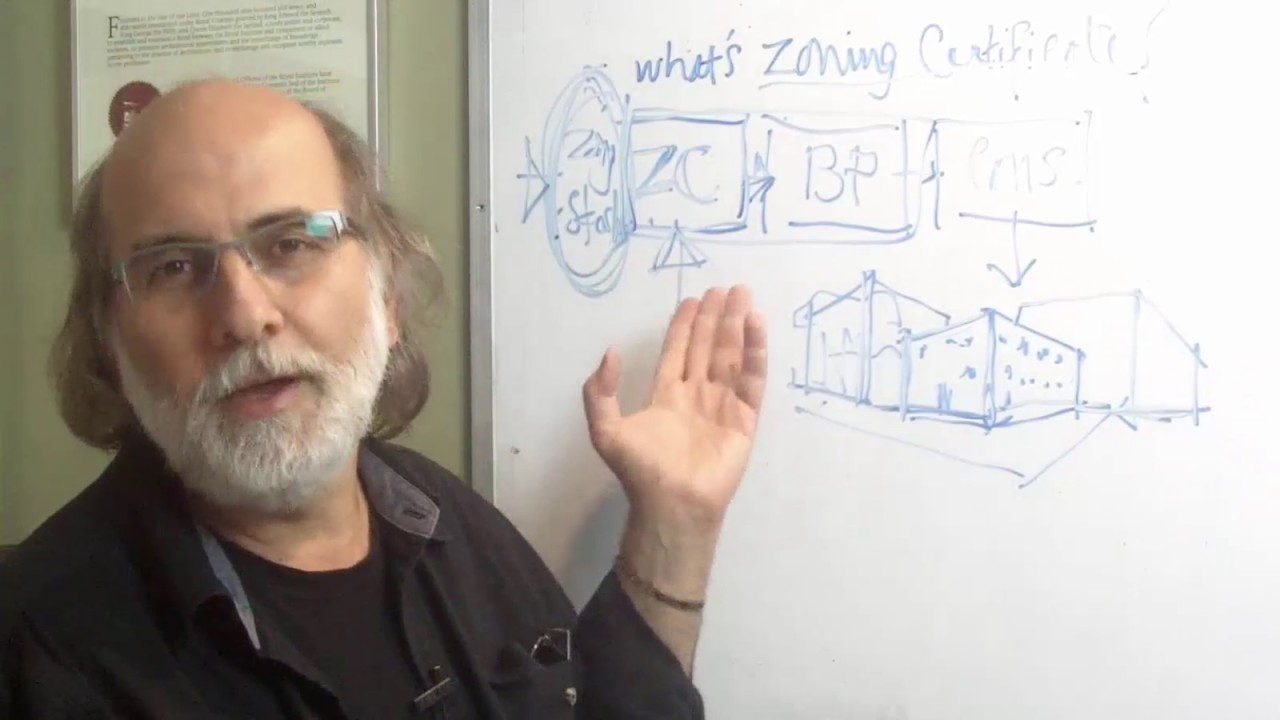
A zoning ordinance is a legal document that outlines the land-use regulations and restrictions for a specific geographic area. It is typically created and enforced by local governments, such as cities or counties, and serves as a guide for property owners, developers, and government officials regarding the permitted uses, density, setbacks, building heights, and other development standards within a given jurisdiction.
Zoning ordinances divide a community into distinct zones or districts, each with its own set of regulations. These districts are often categorized based on the type of land use, such as residential, commercial, industrial, agricultural, or mixed-use. Within each zone, the ordinance specifies what types of activities are allowed, prohibited, or conditional, aiming to create a cohesive and harmonious development pattern.
The zoning ordinance provides a clear framework for land-use planning, ensuring that land is utilized efficiently and in a manner that aligns with the community’s objectives. By designating specific areas for different types of land use, zoning ordinances help prevent conflicts between incompatible activities, promote orderly growth, and protect the health, safety, and welfare of residents.
These regulations can cover a wide range of aspects, including the size and location of buildings, parking requirements, signage rules, setbacks from property lines, landscaping standards, noise regulations, and more. Zoning ordinances also address issues related to environmental protection, historic preservation, and other community-specific concerns.
It is important to note that zoning ordinances can vary significantly from one jurisdiction to another, reflecting the unique needs and priorities of each community. Some municipalities may have more flexible zoning regulations to encourage economic development, while others may prioritize preserving the character of the existing neighborhoods.
Overall, a zoning ordinance provides a legal framework that defines how land can be used and developed within a given area. By establishing clear guidelines and standards, zoning ordinances help maintain order, protect property values, and ensure that development aligns with community goals.
Purpose of Zoning Ordinances
Zoning ordinances serve several essential purposes in the realm of urban planning and development. Let’s explore these purposes in more detail:
- Land Use Management: One of the primary purposes of zoning ordinances is to manage and regulate land use. By designating different zones for residential, commercial, industrial, and other uses, zoning ordinances ensure that land is utilized in a way that is compatible with the surrounding areas. For instance, residential areas are typically separated from industrial zones to protect residents from noise, pollution, and other potential nuisances. By controlling the mix of land uses, zoning ordinances strive to create balanced and sustainable communities.
- Protection of Property Values: Zoning ordinances aim to protect the property values of residents and property owners by maintaining a consistent and predictable development pattern. These regulations provide a level of certainty to property owners about the types of land uses that will be allowed in their neighborhoods, minimizing the risk of incompatible or undesirable development that could diminish property values. By offering stability and assurance, zoning ordinances play a crucial role in real estate investment and homeownership.
- Preservation of Natural Resources and Open Spaces: Another significant purpose of zoning ordinances is to preserve natural resources, environmentally sensitive areas, and open spaces. By designating areas as conservation zones, greenbelts, or parks, zoning ordinances help protect valuable ecosystems, wildlife habitats, water bodies, and scenic landscapes. This preservation not only enhances the quality of life for residents but also contributes to environmental sustainability and biodiversity conservation.
- Promotion of Public Health and Safety: Zoning ordinances play a crucial role in ensuring public health and safety by establishing regulations related to building codes, setbacks, fire prevention measures, and other safety standards. These ordinances help ensure that buildings are constructed in a manner that meets safety requirements and that adequate infrastructure, such as roads, utilities, and emergency services, is provided to support the needs of the community.
- Creation of Vibrant and Livable Communities: Zoning ordinances are instrumental in creating vibrant and livable communities by encouraging well-designed and mixed-use developments, walkable neighborhoods, and access to essential services and amenities. These regulations may promote the development of neighborhood centers, encourage public transportation, establish requirements for parks and recreational facilities, and prioritize the creation of pedestrian-friendly streetscapes. By shaping the physical environment, zoning ordinances contribute to the social, economic, and cultural vitality of a community.
In summary, the purpose of zoning ordinances is multi-faceted, encompassing land use management, protection of property values, preservation of natural resources, promotion of public health and safety, and the creation of vibrant and livable communities. By fulfilling these purposes, zoning ordinances play a critical role in shaping the built environment and fostering sustainable and harmonious communities.
Components of a Zoning Ordinance
A zoning ordinance is a comprehensive document that consists of various components, each serving a specific purpose in regulating land use and development within a jurisdiction. Let’s explore the key components of a typical zoning ordinance:
- Zoning Districts: The zoning ordinance establishes different zoning districts or zones within the jurisdiction. These districts are designated for specific types of land use such as residential, commercial, industrial, agricultural, mixed-use, and more. Each district has its own set of regulations regarding permitted uses, density, setbacks, building heights, and other development standards.
- Use Regulations: Use regulations outline what types of activities are allowed or prohibited in each zoning district. For example, residential zones may allow single-family homes, duplexes, or apartment buildings, while commercial zones may permit retail stores, offices, or restaurants. Use regulations often include conditional uses, which are permitted under certain circumstances subject to specific conditions or requirements, such as obtaining a special permit or meeting specific design standards.
- Development Standards: Development standards specify the requirements for buildings and structures within each zoning district. This includes regulations related to building heights, lot sizes, setbacks from property lines, parking requirements, signage rules, landscaping standards, and more. These standards aim to ensure that the visual appeal, scale, and design of development are compatible with the character of the surrounding neighborhood.
- Overlay Districts: Some zoning ordinances include overlay districts, which are designed to address specific characteristics or concerns within a particular area. Overlay districts may address historic preservation, environmentally sensitive areas, flood zones, or design guidelines for certain districts. These additional regulations provide an extra layer of protection or requirements that apply to specific properties or areas on top of the base zoning district regulations.
- Administrative Procedures: The zoning ordinance typically outlines the administrative procedures for processing land-use applications, including zoning permits, variances, special exceptions, and rezoning requests. These procedures may include detailed instructions on application submission, public notification, review processes, and criteria for decision-making by local government bodies such as planning boards or zoning commissions.
- Enforcement and Penalties: Zoning ordinances include provisions for enforcement and penalties for violations. They designate the authority responsible for enforcement, such as a zoning administrator or code enforcement officer, and outline the potential penalties for non-compliance. This may include fines, permit revocation, or even legal action in extreme cases.
In addition to these key components, zoning ordinances may also include provisions related to affordable housing, environmental regulations, public utilities, impact fees, and other specific requirements or considerations applicable to the jurisdiction.
It is important to note that the components of a zoning ordinance can vary between jurisdictions, depending on the specific needs, priorities, and legal requirements of the community. However, these components generally form the framework for regulating land use, shaping the physical environment, and ensuring the orderly and sustainable development of a community.
A zoning ordinance is a set of regulations that dictate how land can be used in a specific area, such as residential, commercial, or industrial. It’s important to understand the zoning regulations in your area before purchasing or developing property.
Implementation of Zoning Ordinances
Once a zoning ordinance is established, the next crucial step is its implementation. The successful implementation of zoning ordinances requires coordination, communication, and enforcement efforts by various stakeholders, including government officials, planning departments, property owners, and the community at large. Let’s explore the key aspects of implementing a zoning ordinance:
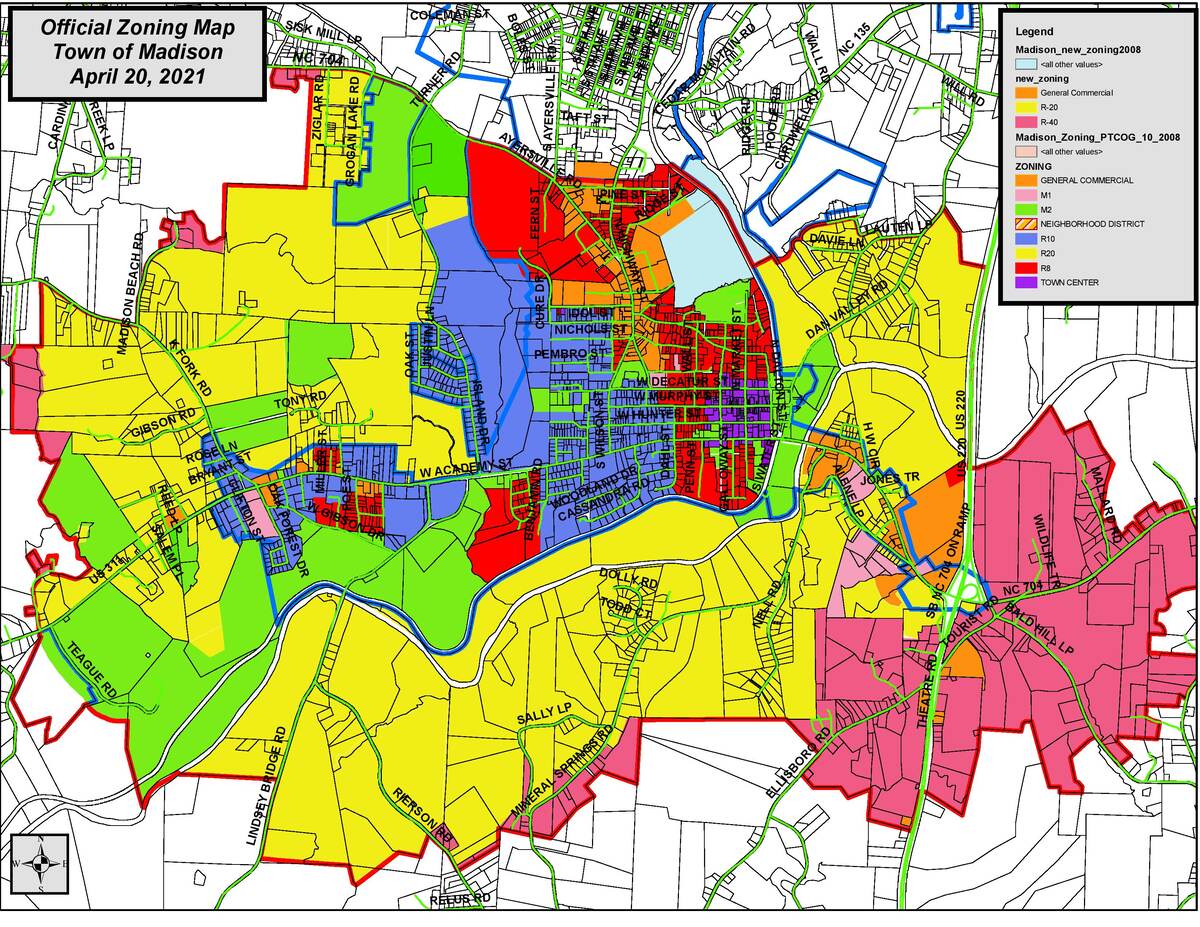
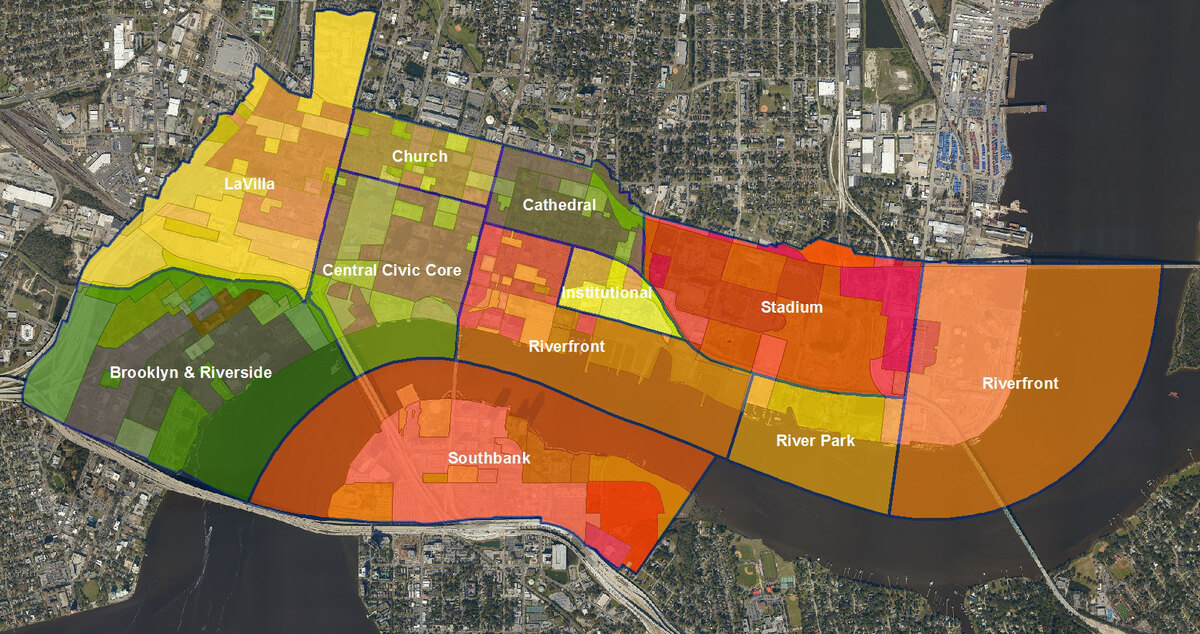
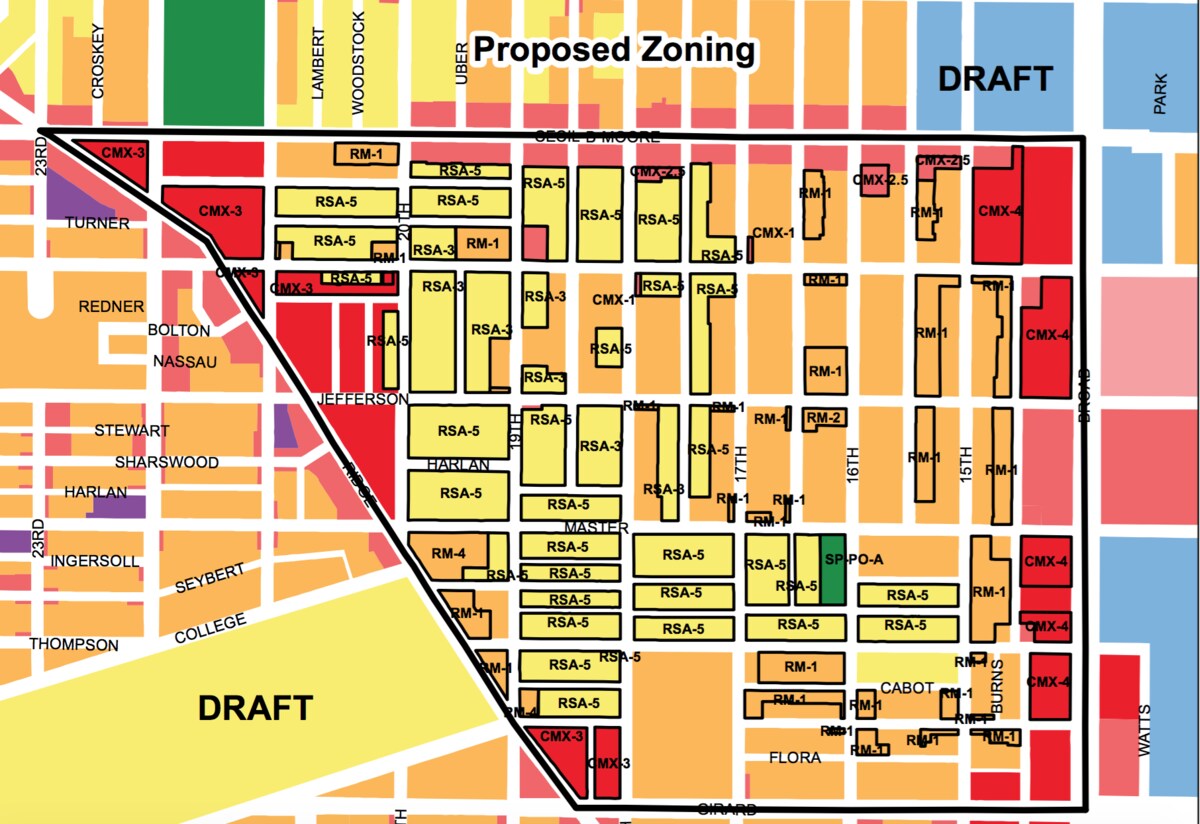
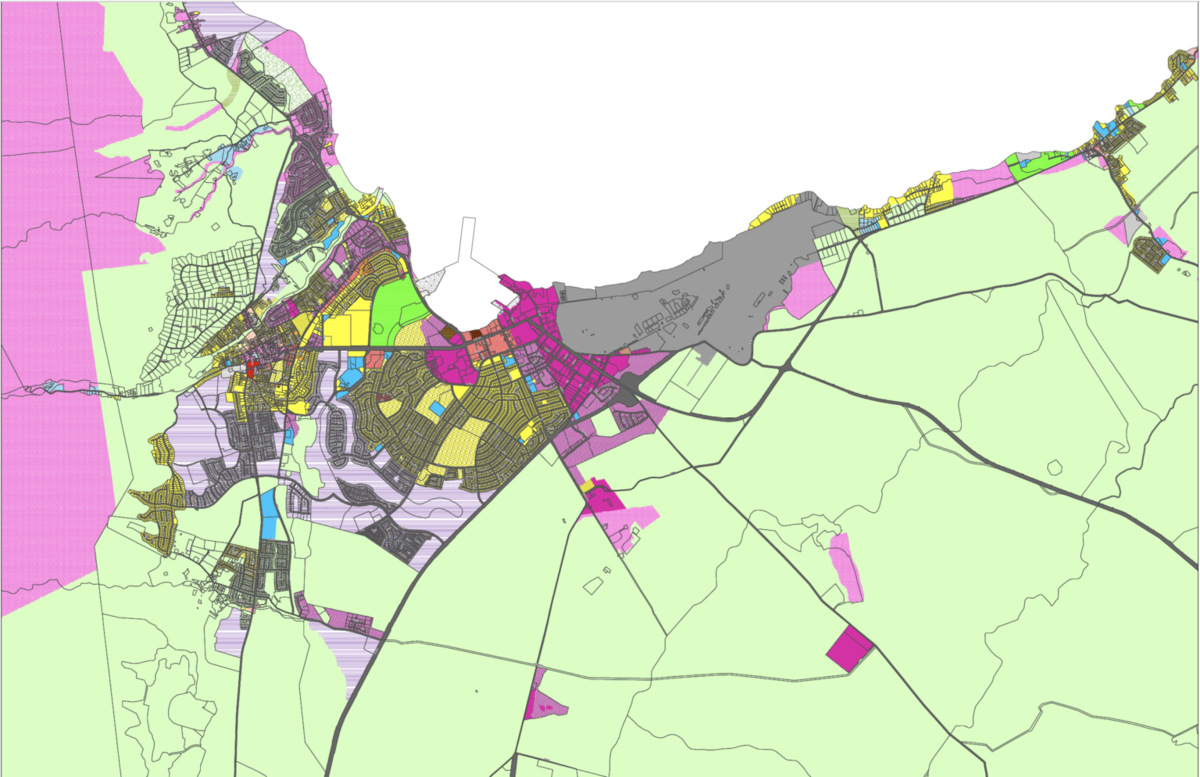
- Zoning Map: The zoning ordinance is accompanied by a zoning map, which visually represents the different zoning districts within the jurisdiction. The zoning map delineates the boundaries of each district and provides a clear understanding of the areas designated for different land uses. The accurate and up-to-date zoning map is essential for effectively implementing the zoning ordinance.
- Community Education and Outreach: To ensure understanding and compliance with the zoning ordinance, community education and outreach efforts are crucial. Government officials and planning departments should engage in public meetings, workshops, and informational sessions to inform and educate property owners and the general public about the zoning regulations, their implications, and how they impact the community’s long-term vision. Clear and accessible communication channels, such as websites, brochures, and newsletters, can also help disseminate information about the zoning ordinance to residents.
- Zoning Permits and Approvals: Property owners and developers must obtain zoning permits and approvals before initiating any development activity. The zoning ordinance outlines the application process, including the submission of necessary documents, plans, and payment of fees. Planning departments review these applications to ensure compliance with the zoning regulations and the overall goals of the community. The permit issuance or approval process may involve inspections, public hearings, and decisions made by local government bodies.
- Code Enforcement: Effective code enforcement is critical for the successful implementation of zoning ordinances. Zoning administrators or code enforcement officers play a key role in monitoring developments, conducting inspections, and addressing potential violations. They are responsible for investigating complaints, issuing violation notices, and initiating appropriate actions or penalties to ensure compliance with the zoning regulations. Regular monitoring and enforcement activities help maintain the integrity of the zoning ordinance and protect the interests of the community.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: Regular monitoring and evaluation of the zoning ordinance’s effectiveness are essential to identify any shortcomings or needed updates. Planning departments should analyze the impacts of the zoning regulations on the community’s development patterns, assess whether goals are being achieved, and make any necessary adjustments or amendments to the ordinance. Monitoring can also involve gathering feedback from stakeholders, tracking compliance rates, and reviewing the overall effectiveness and efficiency of the implementation process.
Implementing a zoning ordinance requires a collaborative effort between government officials, planning departments, property owners, and the community to ensure its successful execution. Effective communication, education, and code enforcement are essential to achieving the desired outcomes of the zoning regulations while balancing the needs and aspirations of the community.
Read more: What Is A-1 Zoning
Challenges and Controversies Surrounding Zoning Ordinances
While zoning ordinances play a crucial role in guiding land use and development, they are not without challenges and controversies. The complexities and potential conflicts associated with zoning regulations have led to various debates and issues. Let’s explore some of the common challenges and controversies surrounding zoning ordinances:
- Equity and Social Justice: Zoning ordinances have been criticized for perpetuating social and economic inequalities. Some argue that exclusionary zoning practices can lead to the concentration of certain socioeconomic groups in specific areas, creating unequal access to quality housing, amenities, and opportunities. Addressing equity concerns in zoning ordinances requires a comprehensive approach that aims to promote affordable housing, encourage mixed-income neighborhoods, and provide equitable access to services and amenities.
- Lack of Flexibility: Zoning ordinances that are overly rigid and restrictive may hinder innovation and adaptability. One-size-fits-all zoning regulations may not accommodate evolving trends or changing community needs. Striking a balance between preserving neighborhood character and allowing for growth and flexibility can be a challenge for planners and policymakers.
- Political and NIMBY Opposition: Zoning decisions can become highly politicized, leading to opposition from community members who may resist changes or new developments in their neighborhoods. This opposition is often driven by concerns about increased traffic, congestion, noise, or changes to the neighborhood’s character. The “Not-In-My-Backyard” (NIMBY) attitude can complicate the implementation of zoning ordinances, as it may hinder the approval of projects that are in the best interest of the broader community.
- Zoning Conflict with Other Goals: Zoning regulations sometimes clash with other community goals, such as affordable housing, sustainability, or economic development. For example, strict zoning limitations on building heights or density may impede efforts to accommodate a growing population or create affordable housing options. Balancing these competing objectives can be a challenge for planners and decision-makers.
- Unintended Consequences: Zoning ordinances can have unintended consequences, such as unintended segregation, displacement, or the stifling of small-scale entrepreneurship. For instance, exclusionary zoning practices may inadvertently contribute to the socioeconomic isolation of certain communities. It is crucial for planners to carefully consider the potential impacts of zoning regulations and take steps to mitigate any unintended negative outcomes.
- Complexity and Lack of Understanding: Zoning ordinances can be complex and technical documents, making it challenging for the general public to understand their implications. Lack of awareness and understanding can lead to misinterpretation, confusion, and frustration among property owners and community members. Transparent communication, effective community engagement, and simplified zoning regulations can help address these challenges.
Addressing these challenges and controversies requires a thoughtful and inclusive approach to zoning. It involves balancing the needs and desires of the community with broader goals of equity, sustainability, and economic development. Regular review and updates of zoning ordinances can help ensure their effectiveness, relevance, and alignment with evolving community values and aspirations.
Benefits of Zoning Ordinances
Zoning ordinances, despite the challenges and controversies surrounding them, offer several significant benefits to communities. These regulations play a crucial role in guiding land use and development, shaping the physical environment, and fostering sustainable and harmonious communities. Let’s explore some of the key benefits of zoning ordinances:
- Orderly Land Use: Zoning ordinances provide a structured framework for land use management, ensuring that different types of activities are appropriately located within a community. By designating zones for specific uses, such as residential, commercial, and industrial, zoning ordinances help maintain order and prevent conflicting land uses that could disrupt the functionality and livability of a neighborhood.
- Preservation of Community Character: Zoning ordinances are instrumental in preserving the unique character and identity of neighborhoods. These regulations help ensure that new developments align with the existing context, architectural styles, and scale of the community. By guiding design standards and protecting historic structures or areas, zoning ordinances contribute to the preservation of a community’s heritage and sense of place.
- Environmental Protection: Zoning ordinances play a vital role in protecting natural resources and the environment. By designating conservation areas, greenbelts, or open spaces, zoning ordinances help preserve sensitive ecosystems, protect water bodies, and maintain biodiversity. Additionally, zoning regulations can promote sustainable practices such as green building standards, energy-efficient infrastructure, and stormwater management, contributing to environmental sustainability.
- Enhanced Quality of Life: Zoning ordinances help create livable and vibrant communities. By incorporating amenities such as parks, recreational areas, and pedestrian-friendly spaces, zoning regulations contribute to the well-being and quality of life of residents. These regulations can encourage the development of walkable neighborhoods, access to essential services, and aesthetically pleasing surroundings, promoting a higher quality of life for community members.
- Protection of Property Values: Zoning ordinances provide property owners with a level of certainty and protection for their investments. By establishing clear guidelines and standards for development, zoning regulations help maintain property values by ensuring that incompatible or undesirable development does not occur in a neighborhood. Property owners can have confidence in the predictability of their surroundings and the maintenance of the character of their community.
- Economic Development: Zoning ordinances can foster economic development by attracting and facilitating diverse business activities. By designating areas for commercial or industrial uses, zoning regulations support the development of business districts and employment opportunities within a community. Well-planned zoning can also encourage mixed-use developments that combine residential and commercial uses, creating vibrant and economically thriving neighborhoods.
In summary, zoning ordinances offer a range of benefits to communities, including orderly land use, preservation of community character, environmental protection, enhanced quality of life, protection of property values, and support for economic development. By striking a balance between efficient land use and community needs, zoning regulations help create sustainable, livable, and attractive environments for residents, businesses, and visitors alike.
Conclusion
Zoning ordinances are a fundamental aspect of urban planning and development, serving as a blueprint for how land is utilized within a community. These regulations provide a framework for managing land use, promoting orderly growth, and shaping the physical environment of our cities and towns.
Throughout this article, we have explored the various aspects of zoning ordinances, including their definition, purpose, components, implementation, challenges, controversies, and benefits. We have seen how these regulations help maintain the integrity of neighborhoods, protect property values, preserve natural resources, and enhance the quality of life for residents.
However, it is important to recognize that zoning ordinances are not without challenges and controversies. Striking a balance between the needs of the community, equitable development, and economic growth can be a complex task. Issues such as social equity, flexibility, political opposition, and unintended consequences require careful consideration and ongoing evaluation to ensure that zoning ordinances meet the evolving needs and aspirations of the community.
Despite these challenges, the benefits of zoning ordinances far outweigh the drawbacks. By providing structure, order, and predictability, zoning regulations contribute to the creation of vibrant and sustainable communities. They safeguard the character and heritage of neighborhoods, protect the environment, and support economic development.
As communities continue to grow and evolve, it is essential to regularly review and update zoning ordinances to ensure their effectiveness and alignment with the changing needs and priorities of the community. Transparent communication, community engagement, and robust enforcement mechanisms are crucial for successful implementation and compliance.
In conclusion, zoning ordinances play a vital role in shaping our built environment and fostering thriving and inclusive communities. By striking a balance between various factors, including land use, development standards, and community goals, zoning regulations help create places where people can live, work, and thrive in harmony with their surroundings.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is A Zoning Ordinance?
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.










0 thoughts on “What Is A Zoning Ordinance?”