Home>diy>Planning & Engineering>What Is A Zoning Overlay

Planning & Engineering
What Is A Zoning Overlay
Modified: January 9, 2024
Discover the importance of zoning overlays in planning-engineering and how they impact land use regulations and development projects.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Welcome to the world of zoning overlays! In the realm of urban planning and land use regulations, zoning overlays play a vital role in shaping the development of communities. These overlays provide an additional layer of restrictions and guidelines that work alongside traditional zoning regulations.
Imagine a zoning map as a canvas, painting a picture of how land can be used within a city or town. Zoning regulations establish the framework for allocating different types of land uses, such as residential, commercial, and industrial. But sometimes, a one-size-fits-all approach doesn’t work for every area or property.
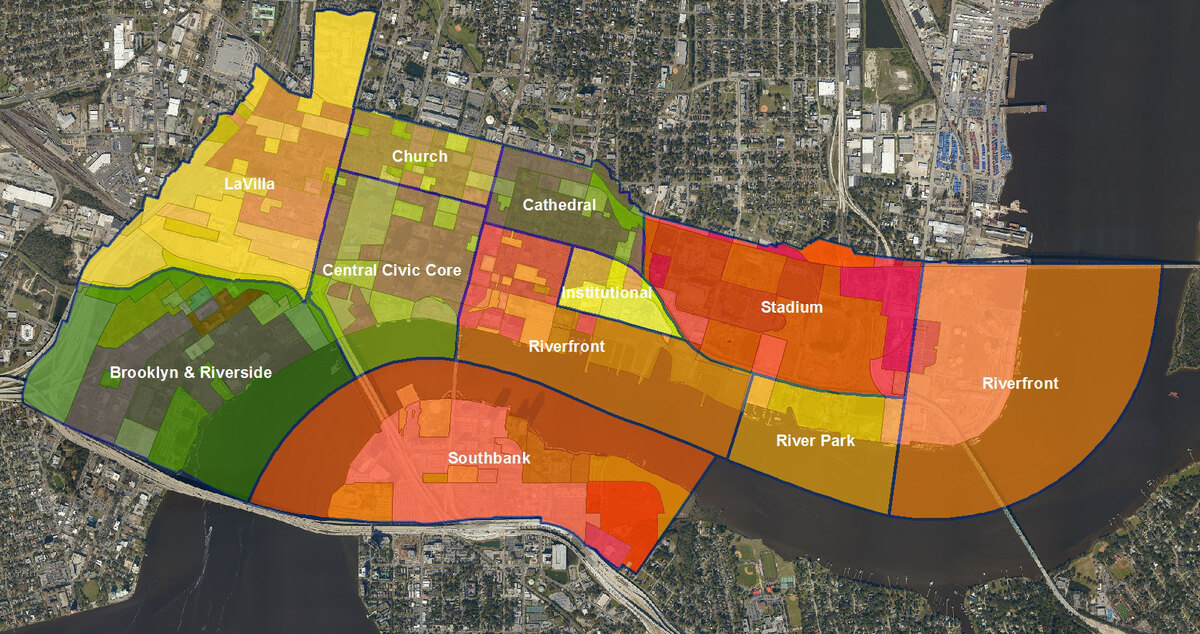
This is where a zoning overlay comes into play. A zoning overlay is a set of additional regulations that are applied to specific areas within a zoning district. These overlays act as a supplement to the existing zoning regulations, providing more specific guidelines and requirements tailored to address unique characteristics or concerns.
Let’s dive deeper into the world of zoning overlays and explore their purposes, types, examples, and the benefits and challenges they bring to the table.
Key Takeaways:
- Zoning overlays are tailored regulations that address specific concerns, enhance neighborhood character, and promote sustainable development, ensuring that development aligns with the unique needs and goals of each community.
- While zoning overlays offer benefits such as preservation of heritage and community engagement, they also present challenges like complexity, potential conflicts, and administrative burdens that require careful consideration and planning for successful implementation.
Definition of Zoning Overlay
A zoning overlay is a regulatory tool used in land use planning to apply additional requirements and restrictions to specific areas within a designated zoning district. It is essentially an extra layer of regulations that augment the existing zoning regulations.
While traditional zoning regulations define the allowable land uses and specifications for an entire zoning district, a zoning overlay narrows down the focus to address particular concerns or characteristics within that district. These concerns can include aspects such as architectural design, environmental preservation, historic preservation, density, and more.
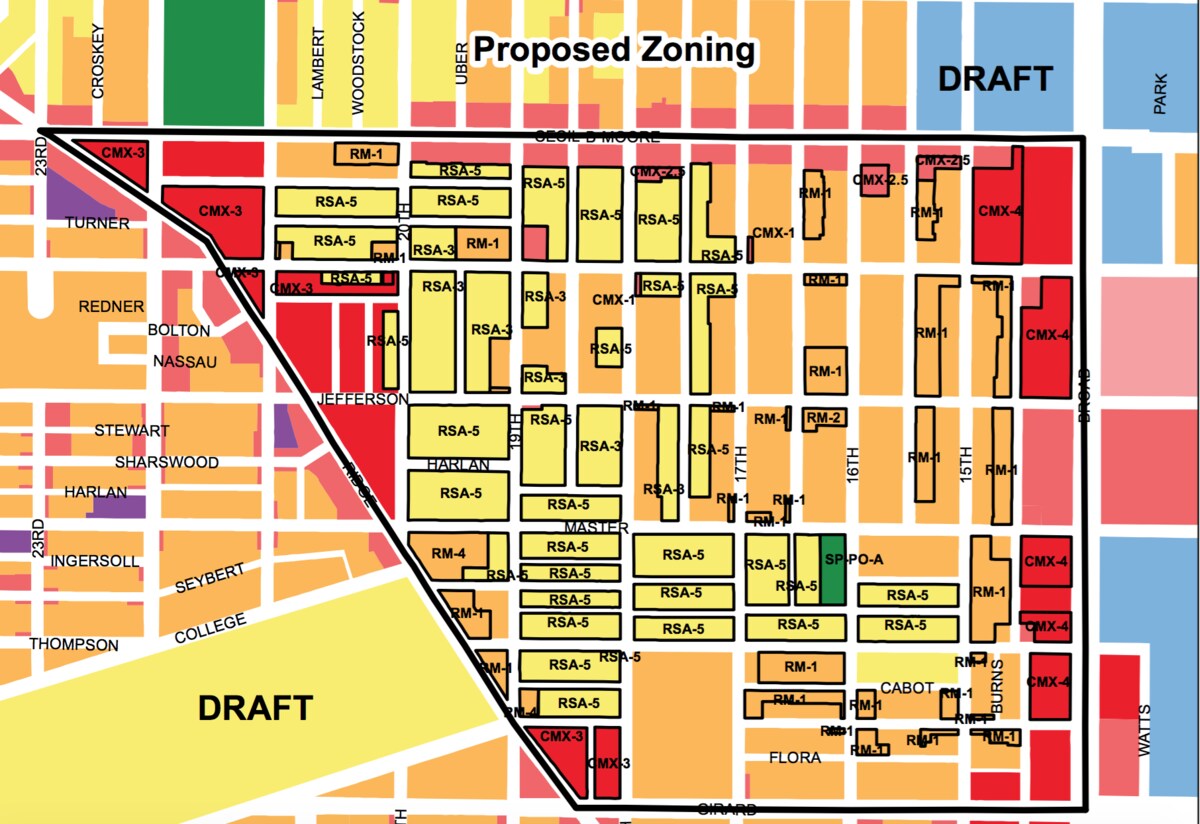
Implemented through zoning ordinances, overlays create a framework that adds an extra set of criteria that must be met in addition to the standard zoning guidelines. The regulations within a zoning overlay are typically more detailed and specific than the broader zoning regulations.
For example, imagine a zoning district that primarily allows residential use but has concerns about the preservation of historic buildings. The city may establish a zoning overlay specifically for that area, which would have more stringent regulations regarding the preservation, renovation, or demolition of historical structures within the district.
It is important to note that zoning overlays are tailored to specific geographic areas based on their unique needs and goals. They are not blanket regulations applied to an entire city or town, but rather selectively to areas where the additional requirements are deemed necessary.
In summary, a zoning overlay is an additional layer of regulations that supplements traditional zoning regulations. It focuses on specific areas within a zoning district and addresses particular concerns, aiming to achieve specific planning objectives and enhance the quality and character of a community.
Purpose of Zoning Overlay
The purpose of a zoning overlay is to provide more targeted and tailored regulations within specific areas of a zoning district. By implementing overlays, city planners and officials can address unique concerns and achieve specific goals that may not be fully addressed by the broad zoning regulations.
1. Addressing Special Conditions: Zoning overlays allow for the consideration of special conditions or unique characteristics within a particular area. These conditions could include factors such as environmental sensitivity, historical significance, or the need for architectural preservation. By implementing an overlay, specific guidelines can be put in place to ensure these special conditions are respected and protected.
2. Encouraging Design Standards: Zoning overlays often focus on promoting high-quality design and architectural standards within a designated area. These standards can include guidelines for building materials, façade treatments, landscaping, and more. By incorporating design standards, overlays help create more aesthetically appealing and cohesive communities.
3. Controlling Density and Scale: Zoning overlays can be used as a tool to regulate the density and scale of development within a particular area. For instance, an overlay may require setbacks, height restrictions, or building footprints to ensure that new construction aligns with the desired character of the neighborhood or preserves the natural landscape.
4. Protecting Historic or Cultural Resources: Historic preservation overlays are a common type of zoning overlay that aims to protect and preserve buildings and sites of historical or cultural significance. These overlays typically have stricter regulations around renovation or demolition to ensure the preservation of the area’s heritage.
5. Promoting Sustainable Development: Zoning overlays can also be used to encourage sustainable development practices. For example, an overlay may include requirements for energy-efficient building design, stormwater management, or the incorporation of green spaces. These measures help reduce the environmental impact of development and promote sustainable growth.
6. Enhancing Neighborhood Character: Zoning overlays can contribute to the preservation or enhancement of a neighborhood’s unique character. By establishing guidelines for architectural styles or building materials, overlays help maintain the distinct identity of a community or promote a specific aesthetic vision.
In summary, the purpose of zoning overlays is to address specific concerns, achieve specific goals, and enhance the quality and character of a community. They allow for more targeted regulations that go beyond the broader zoning regulations to address unique conditions, design standards, density, historic preservation, sustainability, and neighborhood character.
Types of Zoning Overlays
Zoning overlays come in various types, each serving a specific purpose and addressing different aspects of land use and development. Here are some common types of zoning overlays:
1. Historic Preservation Overlay: This type of overlay aims to protect and preserve historically significant buildings, districts, or sites. It typically includes regulations and guidelines for architectural design, renovation, and demolition to ensure the preservation of the area’s historical and cultural heritage.
2. Architectural Design Overlay: An architectural design overlay focuses on promoting specific design standards within a designated area. It may include requirements for building materials, façade treatments, roof styles, or even color palettes to enhance the visual cohesiveness of a neighborhood or district.
3. Environmental Protection Overlay: This overlay is designed to protect environmentally sensitive areas such as wetlands, floodplains, or wildlife habitats. It includes regulations to minimize the impact of development on the natural environment, ensuring the preservation of ecological systems and promoting sustainability.
4. Form-Based Code Overlay: A form-based code overlay emphasizes the physical form and character of development rather than specific land uses. It incorporates design guidelines for building placement, setbacks, heights, and street layouts to create a cohesive and pedestrian-friendly environment.
5. Transit-Oriented Development Overlay: This overlay encourages development that prioritizes public transportation, walking, and cycling. It typically includes regulations that promote mixed-use development, higher density, and improved pedestrian and transit infrastructure near transit hubs or corridors.
6. Mixed-Use Overlay: A mixed-use overlay allows for a combination of residential, commercial, and sometimes industrial uses within a specific area. It aims to create vibrant and walkable neighborhoods where people can live, work, and play in close proximity, reducing the need for long commutes and increasing overall community convenience.
7. Inclusionary Zoning Overlay: This overlay mandates the inclusion of affordable housing units in new residential developments. It aims to create a diverse and inclusive community by ensuring that a percentage of housing units are affordable to individuals or families with lower incomes.
8. Floodplain Overlay: A floodplain overlay regulates development within areas prone to flooding. It includes regulations to minimize the risk of flood damage, such as requiring elevated building designs, limiting impermeable surfaces, and preserving natural flood storage areas.
These are just a few examples of the various types of zoning overlays that exist. Each type caters to specific needs, goals, and challenges within a particular area or community, ensuring that development aligns with desired outcomes and contributes to the overall well-being of the residents.
A zoning overlay is a regulation that is added to an existing zoning district to address specific issues or goals, such as historic preservation, environmental protection, or affordable housing. It can add additional restrictions or incentives to the base zoning regulations.
Examples of Zoning Overlays
Let’s take a look at some real-world examples of zoning overlays to better understand how they are implemented and their impact on land use:
1. Historic Preservation Overlay: In the historic district of Charleston, South Carolina, a historic preservation overlay is in place to protect the city’s rich architectural heritage. The overlay includes regulations for preserving the historic character of buildings, such as guidelines for façade restoration, paint colors, and architectural elements.
2. Architectural Design Overlay: The city of Santa Barbara, California, is known for its Spanish Colonial Revival architecture. To maintain that distinctive aesthetic, an architectural design overlay is implemented in certain neighborhoods. It includes guidelines for building materials, roof design, window styles, and landscaping to ensure new construction aligns with the city’s architectural heritage.
3. Environmental Protection Overlay: The state of Oregon utilizes an environmental overlay to protect sensitive natural areas and wildlife habitats. Areas near rivers, wetlands, or critical habitats are subject to regulations that restrict development, preserve open spaces, and minimize impacts on the environment.
4. Form-Based Code Overlay: The town of Celebration, Florida, is known for its New Urbanism principles and form-based code overlay. It emphasizes walkability, mixed-use development, and pedestrian-friendly streetscapes. The overlay guides building placement, design, and street connectivity to create a cohesive and vibrant community.
5. Transit-Oriented Development Overlay: The city of Portland, Oregon, has implemented a transit-oriented development overlay along its light rail corridors. This overlay encourages higher density residential and commercial development within walking distance of transit stations, reducing car dependency and promoting sustainable transportation options.
6. Mixed-Use Overlay: The city of Austin, Texas, has a mixed-use overlay in its downtown district. This overlay allows for a combination of residential, commercial, and entertainment uses within the same buildings or developments. It creates a vibrant urban environment where residents can live, work, and access amenities within a compact area.
7. Inclusionary Zoning Overlay: Many cities across the United States, such as San Francisco, New York City, and Boston, have implemented inclusionary zoning overlays. These overlays require developers to include a percentage of affordable housing units in new residential projects, ensuring economic diversity and opportunities for individuals and families with lower incomes.
These examples demonstrate how zoning overlays are utilized in various contexts to address specific needs, preserve heritage, protect the environment, promote sustainable development, and create diverse and inclusive communities.
Read more: What Is Zoning For A School
Benefits and Challenges of Zoning Overlays
Zoning overlays offer several benefits in shaping land use and development, but they also come with certain challenges. Let’s examine both sides of the coin:
Benefits:
1. Tailored Regulations: Zoning overlays allow for more targeted regulations that address specific concerns and goals within a community. This customization ensures that development aligns with the unique characteristics and needs of particular areas, preserving the identity and enhancing the quality of neighborhoods.
2. Preservation and Conservation: Overlays focused on historic preservation, environmental protection, or sensitive habitat conservation can help safeguard important resources. These overlays promote the preservation of significant historical buildings, protect natural features, and minimize the environmental impact of development.
3. Design Standards: Architectural design or form-based code overlays can contribute to aesthetically appealing and cohesive communities. By establishing design guidelines, overlays encourage high-quality architectural standards, creating visually attractive neighborhoods and enhancing the overall sense of place.
4. Sustainable Development: Zoning overlays can be effective tools in promoting sustainable development practices. They can include requirements for energy-efficient building designs, stormwater management, green spaces, and access to public transportation, contributing to a more environmentally friendly and resilient community.
5. Community Engagement: The implementation of zoning overlays often involves community input and participation. Residents, property owners, and stakeholders have the opportunity to voice their concerns, interests, and ideas, shaping the regulations that will govern their neighborhoods. This collaborative approach fosters a sense of ownership and involvement within the community.
Challenges:
1. Complexity: Zoning overlays can add an additional layer of complexity to the already intricate world of zoning regulations. The specifics and requirements of overlays need to be clearly articulated, understood, and effectively communicated to developers, property owners, and city officials to ensure compliance.
2. Potential for Conflict: Different groups within a community may have different perspectives and interests when it comes to zoning overlays. Balancing the desires of residents, developers, and other stakeholders can be challenging, and conflicts may arise during the approval and implementation process.
3. Administrative Burden: Zoning overlays require effective administration and enforcement to ensure compliance. This can place an additional burden on city planning departments, requiring dedicated staff, resources, and processes to review and oversee development within overlay areas.
4. Potential for Inconsistency: The creation and enforcement of zoning overlays must be done with careful attention to ensuring consistency and avoiding conflicts with existing zoning regulations. Inconsistencies or contradictions between different sets of regulations can lead to confusion and unintended consequences.
5. Limiting Flexibility: Zoning overlays, while offering targeted regulations, may also limit flexibility for property owners and developers. The additional requirements and design standards imposed by overlays can add costs and constraints to projects, potentially discouraging certain types of development or restricting creative design solutions.
While zoning overlays bring numerous benefits, addressing specific concerns and fostering community goals, they also present challenges and considerations that need to be carefully addressed to strike a balance between regulation and flexibility.
Conclusion
Zoning overlays serve as a valuable tool in the realm of urban planning and land use regulations. They provide an additional layer of tailored regulations that address specific concerns, enhance the character of neighborhoods, and promote sustainable development. By focusing on areas within a zoning district, overlays ensure that development aligns with the unique needs and goals of each community.
Through various types of overlays, such as historic preservation, architectural design, environmental protection, and more, cities can protect their heritage, promote high-quality design, and conserve natural resources. Zoning overlays also play a crucial role in shaping the built environment by encouraging mixed-use developments, fostering transit-oriented growth, and creating diverse and inclusive communities.
However, implementing zoning overlays comes with its own set of challenges. Complex regulations, potential conflicts between stakeholders, administrative burdens, and the need to strike a balance between flexibility and regulation require careful consideration. It is crucial to ensure clear communication, effective administration, and consistency with existing zoning regulations to maximize the benefits of overlays.
In conclusion, zoning overlays offer a way to customize and refine zoning regulations to address unique characteristics and goals within a community. They provide numerous benefits, including tailored regulations, preservation of heritage, promotion of sustainable development, and community engagement. Nevertheless, the challenges associated with overlays underscore the importance of careful planning, administration, and collaboration to ensure successful implementation.
With proper planning, thoughtful implementation, and continual evaluation, zoning overlays can play a vital role in creating vibrant, resilient, and livable communities that reflect the needs and aspirations of their residents.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is A Zoning Overlay
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.










0 thoughts on “What Is A Zoning Overlay”