Home>Garden Essentials>How Does Green Space Lower Energy Usage


Garden Essentials
How Does Green Space Lower Energy Usage
Modified: November 1, 2024
Discover how having a garden can lower energy usage and create a greener environment. Learn the benefits of green space in reducing energy consumption.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
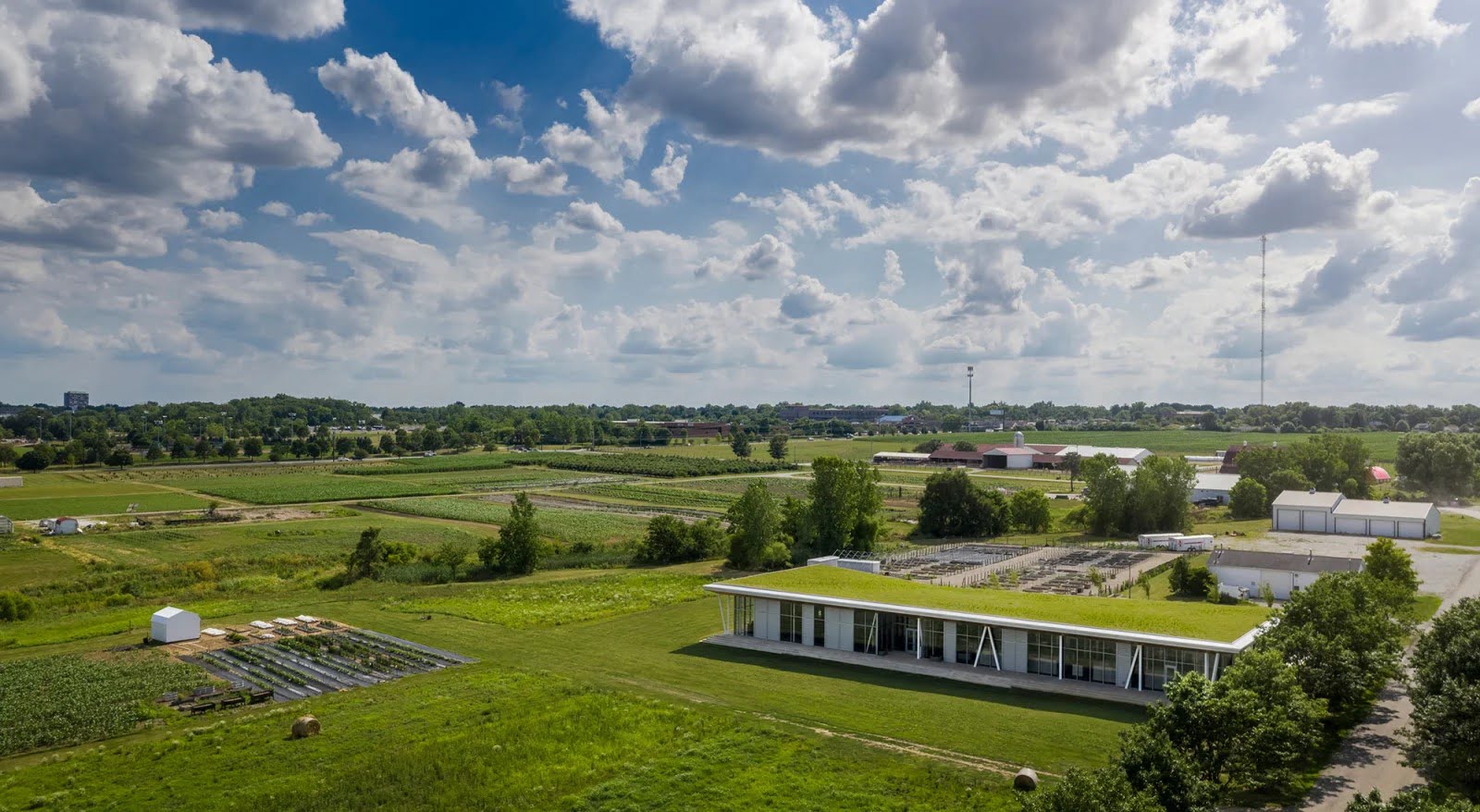
Welcome to the world of green spaces! From lush gardens to tree-lined streets, green spaces offer more than just visual beauty. They play a crucial role in promoting sustainability, improving air quality, and enhancing our overall well-being. But did you know that green spaces also have a significant impact on energy usage? In this article, we will explore the fascinating ways in which green spaces can help lower energy consumption.
As our modern society becomes increasingly conscious of the need to reduce energy consumption and combat climate change, finding innovative ways to lower energy usage has become imperative. Green spaces provide a natural solution to this challenge, offering a range of benefits that extend far beyond aesthetics.
In the following sections, we will delve into the various advantages that green spaces bring, including their cooling effects, shading and insulation capabilities, and their role in reducing the urban heat island effect. We will also examine how green spaces can contribute to more efficient air conditioning systems. By exploring these aspects, we hope to highlight the significant role that green spaces can play in creating a more sustainable and energy-efficient future.
So, join us as we uncover the amazing relationship between green spaces and energy usage. Get ready to discover how the natural beauty of gardens, parks, and urban green spaces can have a positive impact on the environment and our energy consumption. Let’s dive in!
Key Takeaways:
- Green spaces, like parks and gardens, cool the air through evapotranspiration and shading, reducing the need for energy-intensive air conditioning and helping combat climate change.
- By strategically planting trees and vegetation, green spaces provide natural insulation, lower energy usage, and create cooler, more comfortable environments for people and wildlife.
Benefits of Green Space
Green spaces offer a multitude of benefits that contribute to our physical, mental, and environmental well-being. Let’s take a closer look at some of the key advantages:
- Improved air quality: Green spaces act as natural filters, absorbing pollutants and releasing oxygen. The plants and trees remove harmful substances from the air, resulting in cleaner and healthier oxygen for us to breathe.
- Reduced stress and increased well-being: Spending time in green spaces has been proven to reduce stress levels and improve overall mental well-being. The peaceful and serene ambience, combined with the presence of nature, has a calming effect on our minds.
- Biodiversity support: Green spaces provide habitat for a variety of plant and animal species, fostering biodiversity. By preserving and creating more green spaces, we help sustain and protect these diverse ecosystems.
- Enhanced physical health: Green spaces encourage physical activity and promote a healthier lifestyle. Whether it’s walking, jogging, playing sports, or simply enjoying outdoor activities, these spaces provide us with opportunities to engage in regular exercise.
- Community cohesion: Green spaces bring people together, fostering a sense of community and social interaction. They serve as gathering places for events, picnics, and recreational activities, creating opportunities for people to connect and bond.
These benefits demonstrate the immense value that green spaces hold for individuals and communities. But their positive impact doesn’t stop there. Green spaces also play a significant role in lowering energy usage, making them even more indispensable in today’s world of sustainability and conservation.
Green Space and Energy Efficiency
When it comes to energy efficiency, green spaces offer remarkable potential. By strategically incorporating green spaces into urban areas and buildings, we can significantly reduce energy consumption. Here are a few ways in which green spaces contribute to energy efficiency:
Cooling Effects of Green Space: Green spaces have a natural cooling effect on their surroundings. The evapotranspiration process, in which plants release moisture into the air, helps lower temperatures. This means that areas with ample greenery tend to be cooler compared to concrete-dominated environments.
Shading and Insulation: Trees and vegetation provide shade, reducing direct sunlight and heat exposure. By strategically planting trees around buildings, we can prevent excessive solar radiation from entering and heating up the interiors. This, in turn, reduces the need for air conditioning and helps conserve energy.
Reduction of Urban Heat Island Effect: Urban areas are prone to the “heat island” effect, where concrete and asphalt absorb and retain heat, creating higher temperatures. Green spaces act as natural heat sinks, absorbing and dissipating this heat, thus helping to cool down urban environments.
Green Roofs and Walls: Green roofs and walls are innovative solutions for energy-efficient buildings. These installations use vegetation to provide insulation, reducing the need for heating and cooling systems. They also help capture rainwater, reduce stormwater runoff, and improve air quality.
Energy-saving Landscaping: Designing landscapes with energy efficiency in mind can further enhance energy savings. By choosing native and drought-tolerant plants, implementing efficient irrigation systems, and incorporating features like rain gardens, we can minimize water use and reduce the energy needed for landscape maintenance.
By harnessing the energy-saving potential of green spaces, we can create more sustainable and efficient urban environments. Incorporating green spaces into our cities and buildings not only beautifies our surroundings but also helps reduce energy consumption and combat climate change. It’s a win-win situation for both the environment and our wallets.
Cooling Effects of Green Space
One of the primary ways in which green spaces contribute to energy efficiency is through their cooling effects. Green spaces have the remarkable ability to naturally lower temperatures in their surroundings. Here’s how:
Green spaces, such as parks, gardens, and tree-lined streets, utilize a process called evapotranspiration to cool the surrounding air. Evapotranspiration is the combined effect of plant transpiration, where plants release moisture through their leaves, and evaporation from the soil. This process helps to remove heat from the environment and contributes to the overall cooling effect of green spaces.
When it comes to cooling, trees play a vital role. The expansive canopy of trees provides shade and reduces direct sunlight on the ground, lowering surface temperatures. Additionally, the process of transpiration by trees releases moisture into the air, which further cools the immediate environment.
Studies have shown that well-designed green spaces with a high density of trees can significantly reduce temperatures in urban areas. In fact, a study conducted in Los Angeles found that increasing tree canopy coverage by just 10% could lower surface temperatures by as much as 7°F (3.9°C).
By creating a cooler microclimate, green spaces reduce the need for air conditioning and other cooling systems. This directly translates to lower energy consumption and reduced greenhouse gas emissions. According to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, a well-designed landscape can reduce air conditioning costs by as much as 50%.
It’s not just the large parks and gardens that have cooling effects; even small green spaces such as rooftop gardens and pocket parks can make a difference. These compact green spaces absorb heat and provide relief from the heat island effect in urban areas.
Furthermore, the cooling effects of green spaces are not limited to the immediate vicinity. The breezes created by green spaces can extend their cooling influence to neighboring areas, enhancing the overall comfort and reducing the need for widespread air conditioning.
Incorporating green spaces with ample tree coverage into urban planning and building design is crucial for maximizing the cooling effects. By strategically planting trees and creating green areas, we can create a more comfortable and energy-efficient environment for all.
The cooling effects of green spaces not only contribute to energy efficiency but also have a positive impact on human health and well-being. By providing a respite from the scorching heat, green spaces offer a sanctuary for relaxation, recreation, and connection with nature.
So, next time you seek some relief from the sweltering heat, head to a nearby park or find shade under a tree-lined street. Not only will you feel cooler, but you’ll also be contributing to a more energy-efficient and sustainable future.
Planting trees and creating green spaces around buildings can lower energy usage by providing shade, reducing the need for air conditioning, and improving air quality.
Shading and Insulation
One of the key ways in which green spaces contribute to energy efficiency is through their shading and insulation capabilities. By strategically placing trees and vegetation around buildings, green spaces can provide natural shade and insulation, reducing the need for artificial cooling and heating systems. Let’s explore how shading and insulation work:
Shading: The lush canopy of trees offers valuable shade, blocking direct sunlight from reaching buildings and other structures. This shading effect can significantly reduce solar heat gain, especially during hot summer months. By preventing excessive solar radiation from entering buildings, less energy is required to cool indoor spaces. As a result, air conditioning systems can operate more efficiently with reduced energy consumption and costs. Additionally, shaded outdoor areas provide a comfortable and enjoyable environment for outdoor activities and gatherings.
Insulation: In addition to shading, green spaces provide natural insulation. Vegetation, including trees and vegetation-covered walls, acts as a buffer between the outdoor environment and buildings. This insulation helps to regulate indoor temperatures, reducing heat transfer through walls and roofs. In warmer climates, green roofs and walls can offer substantial thermal insulation, keeping buildings cooler and decreasing the need for cooling systems. Conversely, in colder climates, vegetation can provide added insulation, reducing heat loss and decreasing the demand for heating.
Together, shading and insulation provided by green spaces can significantly improve the energy efficiency of buildings. Studies have shown that buildings with well-planned shade trees can experience a substantial reduction in cooling energy consumption, up to 30%. Moreover, the insulation effect of green roofs and walls can lower energy usage by enhancing thermal performance and reducing the need for additional heating or cooling.
Green spaces also contribute to energy savings by reducing the urban heat island effect. Urban areas often experience higher temperatures due to the high concentration of concrete and asphalt, which absorb and radiate heat. By introducing green spaces, especially in densely populated areas, the urban heat island effect can be mitigated. The shading and cooling effects of trees and vegetation help to lower overall temperatures, creating a more comfortable and energy-efficient environment for residents and reducing the urban heat island effect.
Whether it’s parks with ample tree coverage, urban gardens, or green roofs on buildings, incorporating green spaces with shading and insulation properties offers multiple benefits. Not only do they contribute to lower energy usage, but they also enhance the visual appeal of our surroundings, improve air quality, and support biodiversity. Green spaces truly are nature’s solution to creating energy-efficient and sustainable built environments.
Reduction of Urban Heat Island Effect
Urban areas are notorious for their higher temperatures, a phenomenon known as the urban heat island effect. The abundance of concrete, asphalt, and buildings in cities absorbs and retains heat, creating pockets of intense warmth. However, incorporating green spaces into urban planning can significantly mitigate the urban heat island effect. Let’s explore how green spaces help reduce urban heat:
Natural Cooling: Green spaces, such as parks, gardens, and tree-lined streets, offer natural ways to cool down urban environments. The presence of vegetation, particularly trees, provides shade and lowers surface temperatures. The process of transpiration, where plants release water vapor, helps to cool the surrounding air, much like a natural air conditioner. These cooling effects can create a more pleasant and comfortable outdoor environment that isn’t as impacted by the urban heat island effect.
Evapotranspiration: The process of evapotranspiration plays a significant role in reducing urban heat. Trees and other plants release moisture into the air through transpiration. As the water evaporates, it absorbs heat from the surrounding environment, leading to a cooling effect. This natural cooling process is particularly effective in green spaces with a variety of plant species, promoting a more balanced and comfortable microclimate.
Shading and Canopy Cover: The shading provided by trees and green spaces helps to reduce surface temperatures in urban areas. By blocking direct sunlight and preventing the absorption of heat by buildings and pavement, shading helps lower the overall heat island effect. Larger canopy cover, achieved through strategic planting and maintenance of trees, plays a crucial role in providing shade and reducing the ambient temperatures. These green canopies work as natural shields against the sun’s rays, creating cooler spots and relieving the urban heat load.
Air Circulation: Green spaces also contribute to improved air circulation in urban areas. The presence of trees and vegetation helps create a gentle breeze and promote natural airflow, dispersing heat and reducing the stagnant hot air that often engulfs built-up areas. By increasing ventilation and air movement, green spaces assist in dissipating the heat and maintaining a healthier and cooler urban environment.
By effectively reducing the urban heat island effect, green spaces provide several benefits to urban dwellers. Lower temperatures contribute to increased comfort, especially during hot summer months. People are more likely to spend time outdoors, leading to enhanced physical and mental well-being. Additionally, green spaces reduce the reliance on air conditioning systems, resulting in lower energy consumption and decreased greenhouse gas emissions.
Efforts to combat the urban heat island effect involve incorporating green spaces into urban planning, promoting the use of indigenous trees and plants, and prioritizing greening initiatives in heavily built-up areas. These measures help create a more sustainable and resilient urban landscape, fostering a healthier and more comfortable living environment for all residents.
Embracing the power of green spaces can significantly contribute to reducing the urban heat island effect and creating more sustainable cities. By prioritizing the inclusion of green spaces in urban planning, we can create cooler, greener, and more livable environments for present and future generations.
Green Space and Air Conditioning
Air conditioning plays a crucial role in keeping indoor environments comfortable during hot summer months. However, the energy consumption associated with air conditioning systems contributes to increased greenhouse gas emissions and a higher demand for electricity. Incorporating green spaces into urban areas can help reduce the reliance on air conditioning and its associated environmental impact. Let’s delve into how green spaces can enhance air conditioning efficiency:
Cooling Microclimates: Green spaces, with their natural shading and cooling effects, can create microclimates that are significantly cooler than their surroundings. By strategically placing green spaces near buildings, we can reduce the heat load on structures, resulting in lower indoor temperatures. Cooler surroundings reduce the workload on air conditioning systems, allowing them to operate more efficiently and consume less energy.
Shade and Reduced Heat Gain: The strategic planting of trees and vegetation near buildings provides shade and helps to reduce heat gain. By blocking direct sunlight and minimizing solar radiation, the need for cooling is reduced. Shaded areas have lower surface temperatures and experience decreased heat transfer, resulting in less demand for air conditioning. This not only saves energy but also increases the comfort of indoor spaces.
Latent Heat Reduction: Green spaces, through the process of evapotranspiration, help to reduce latent heat in the surrounding area. The release of moisture by plants creates a cooling effect in the air, similar to how perspiration cools our bodies. This natural cooling process reduces the need for mechanical cooling and improves the overall effectiveness of air conditioning systems. The combination of reduced sensible heat and latent heat can lead to significant energy savings.
Improving Outdoor Air Quality: Green spaces provide natural air purification by capturing and filtering pollutants, thus improving outdoor air quality. By reducing outdoor pollution levels, green spaces minimize the influx of contaminants into buildings. This can enhance the indoor air quality and, in turn, reduce the reliance on air conditioning systems to filter and circulate air. The cleaner air provided by green spaces creates a healthier and more comfortable indoor environment.
Psychological Benefits: Green spaces have a positive impact on human well-being and mental health. Being surrounded by nature in outdoor spaces can enhance mood, reduce stress, and improve focus and productivity. This psychological benefit can lead to a reduced need for artificial cooling, as people feel more comfortable and content in naturally cool and pleasant environments.
By leveraging the benefits of green spaces, we can optimize air conditioning efficiency and reduce energy consumption. Incorporating greenery into urban design and building projects, such as green roofs and walls, can significantly contribute to energy savings and create more sustainable indoor environments.
It’s important to note that green spaces alone may not eliminate the need for air conditioning entirely, particularly in regions with extreme heat. However, by leveraging the natural cooling effects and creating more energy-efficient indoor environments, we can reduce the reliance on air conditioning and move towards a greener and more sustainable future.
So, the next time you step outside into a shady park or enjoy the cool breeze under a tree, remember that green spaces not only offer respite from the heat but also play a vital role in reducing the energy demands of air conditioning systems.
Conclusion
Green spaces are more than just visually appealing landscapes—they are powerful contributors to energy efficiency and sustainability. By incorporating green spaces into our urban environments, we can reap multiple benefits, from improved air quality and reduced stress levels to enhanced physical health and community cohesion.
Throughout this article, we have explored the various ways in which green spaces lower energy consumption. The cooling effects of green spaces, through evapotranspiration and shading, create a more comfortable and energy-efficient environment. Green spaces also help to combat the urban heat island effect, mitigating the elevated temperatures in urban areas and reducing the need for energy-intensive cooling systems.
Furthermore, green spaces provide natural insulation and reduce heat gain in buildings. By strategically placing trees and vegetation, we can harness the shading and insulation properties of green spaces to lower indoor temperatures, reducing reliance on air conditioning systems and conserving energy.
Green spaces also contribute to the efficient operation of air conditioning. By creating cooler microclimates and reducing heat gain, they allow air conditioning systems to work more effectively and consume less energy. The psychological benefits of green spaces, such as improved well-being and reduced stress levels, can also lead to a decreased demand for artificial cooling.
In conclusion, green spaces have a significant role to play in our efforts to reduce energy usage, combat climate change, and create sustainable urban environments. Through their cooling effects, shading and insulation capabilities, and mitigation of the urban heat island effect, green spaces provide a natural and cost-effective solution to energy efficiency in both indoor and outdoor spaces. Embracing the power of green spaces in urban planning and building design can lead us towards a greener, healthier, and more energy-efficient future.
So, let us appreciate and cherish the beauty and benefits of green spaces. Whether it’s a small garden in your backyard, a neighborhood park, or a vibrant rooftop garden, every green space contributes to a more sustainable and energy-efficient world. Let’s continue to embrace and nurture green spaces for the well-being of both people and the planet.
Frequently Asked Questions about How Does Green Space Lower Energy Usage
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.














0 thoughts on “How Does Green Space Lower Energy Usage”