Home>Gardening & Outdoor>Plant Care & Gardening Tips>How Deep Are Wildflower Roots


Plant Care & Gardening Tips
How Deep Are Wildflower Roots
Modified: January 5, 2024
Discover the depth of wildflower roots and get expert plant care and gardening tips to help them thrive. Learn how to nurture your wildflowers for a vibrant and healthy garden.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Welcome to the enchanting world of wildflowers, where nature’s vibrant hues and delicate blooms paint the landscape with breathtaking beauty. While the captivating petals of wildflowers often steal the spotlight, their roots play a crucial role in sustaining these picturesque plants. Understanding the depth and significance of wildflower roots is essential for nurturing these natural wonders and preserving their ecological importance.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the captivating realm of wildflower roots, uncovering their depth, importance, and the factors that influence their growth. Whether you’re an avid gardener, a nature enthusiast, or simply curious about the wonders of the natural world, join us on this enlightening journey to discover the hidden treasures beneath the wildflower-covered meadows and woodlands.
Key Takeaways:
- Wildflower roots stabilize soil, prevent erosion, and enrich ecosystems by cycling nutrients and promoting biodiversity, showcasing their vital role in sustaining the natural world.
- Wildflower roots vary in depth based on species and environmental factors, with shallow-rooted wildflowers thriving in moderate water availability and deep-rooted ones adapting to diverse environments, highlighting their resilience and adaptability.
Read more: How Deep Is Turf Grass Root
The Importance of Wildflower Roots
Wildflower roots are the unsung heroes that anchor these exquisite plants in the earth, providing them with essential nutrients, water, and structural support. These intricate root systems not only sustain the wildflowers themselves but also contribute to the overall health of the ecosystems in which they thrive.
One of the primary roles of wildflower roots is their ability to prevent soil erosion. By weaving through the soil, wildflower roots create a network that helps bind the earth together, reducing the risk of erosion caused by wind and water. This vital function not only maintains the integrity of the landscape but also safeguards the habitats of countless organisms that rely on stable soil conditions.
Furthermore, wildflower roots play a pivotal role in nutrient cycling. As these roots delve into the soil, they extract essential minerals and organic matter, contributing to the breakdown of nutrients and the enrichment of the surrounding soil. This process not only nourishes the wildflowers themselves but also fosters a fertile environment for a diverse array of plant and animal species.
Additionally, wildflower roots contribute to the overall health of the ecosystem by enhancing soil structure and promoting microbial activity. The intricate network of roots improves soil aeration and drainage, creating a hospitable environment for beneficial microorganisms. These microorganisms, in turn, aid in nutrient uptake by the wildflowers and other plants, fostering a harmonious cycle of growth and sustenance.
Beyond their ecological contributions, wildflower roots also hold cultural and historical significance. Many wildflower species have been revered for their medicinal properties, and their roots have been utilized in traditional herbal remedies for centuries. Moreover, wildflowers have long been celebrated for their aesthetic allure, inspiring artists, poets, and nature enthusiasts with their captivating beauty and diverse array of colors.
As we continue to unravel the mysteries of wildflower roots, we gain a deeper appreciation for these remarkable plants and their profound impact on the natural world. Join us as we explore the depths of wildflower roots and uncover the secrets that lie beneath the surface of these enchanting blooms.
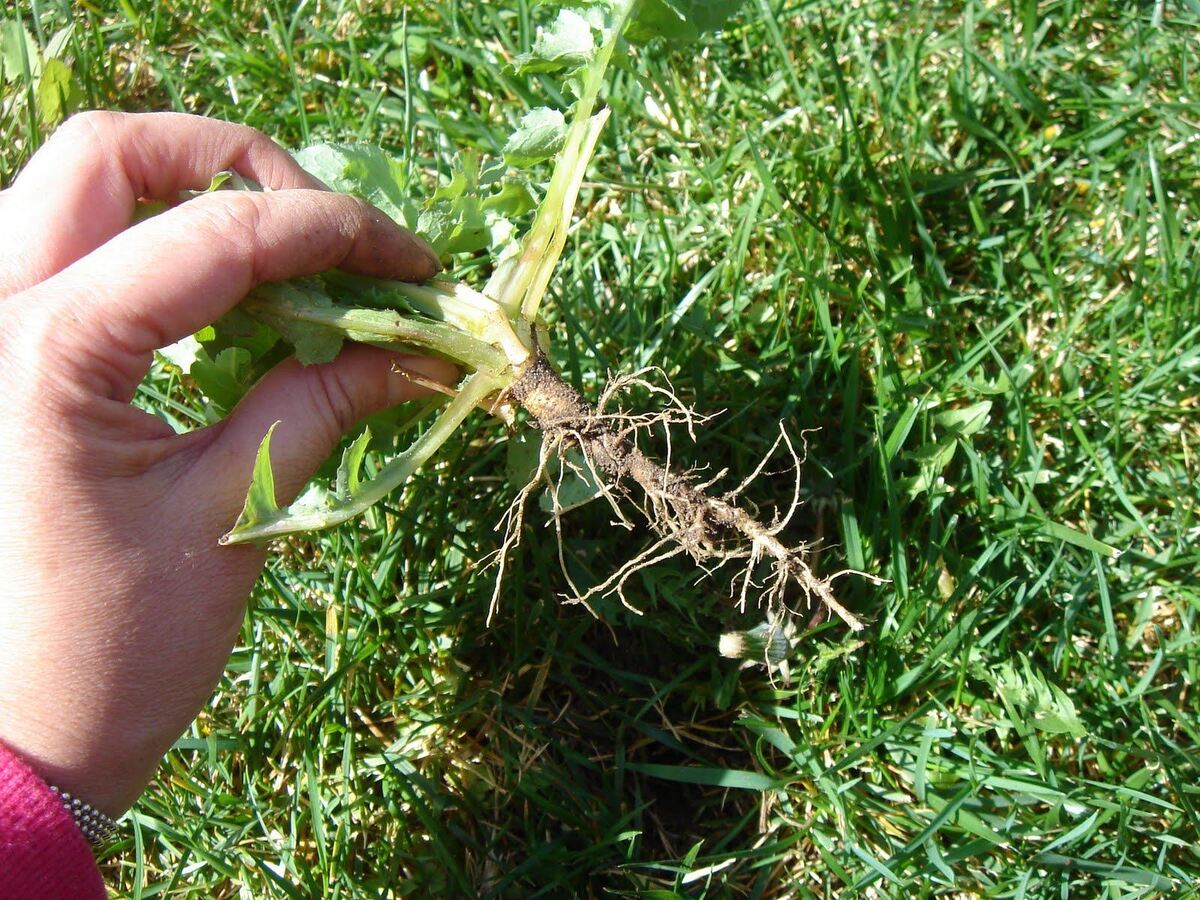
How Deep Do Wildflower Roots Grow?
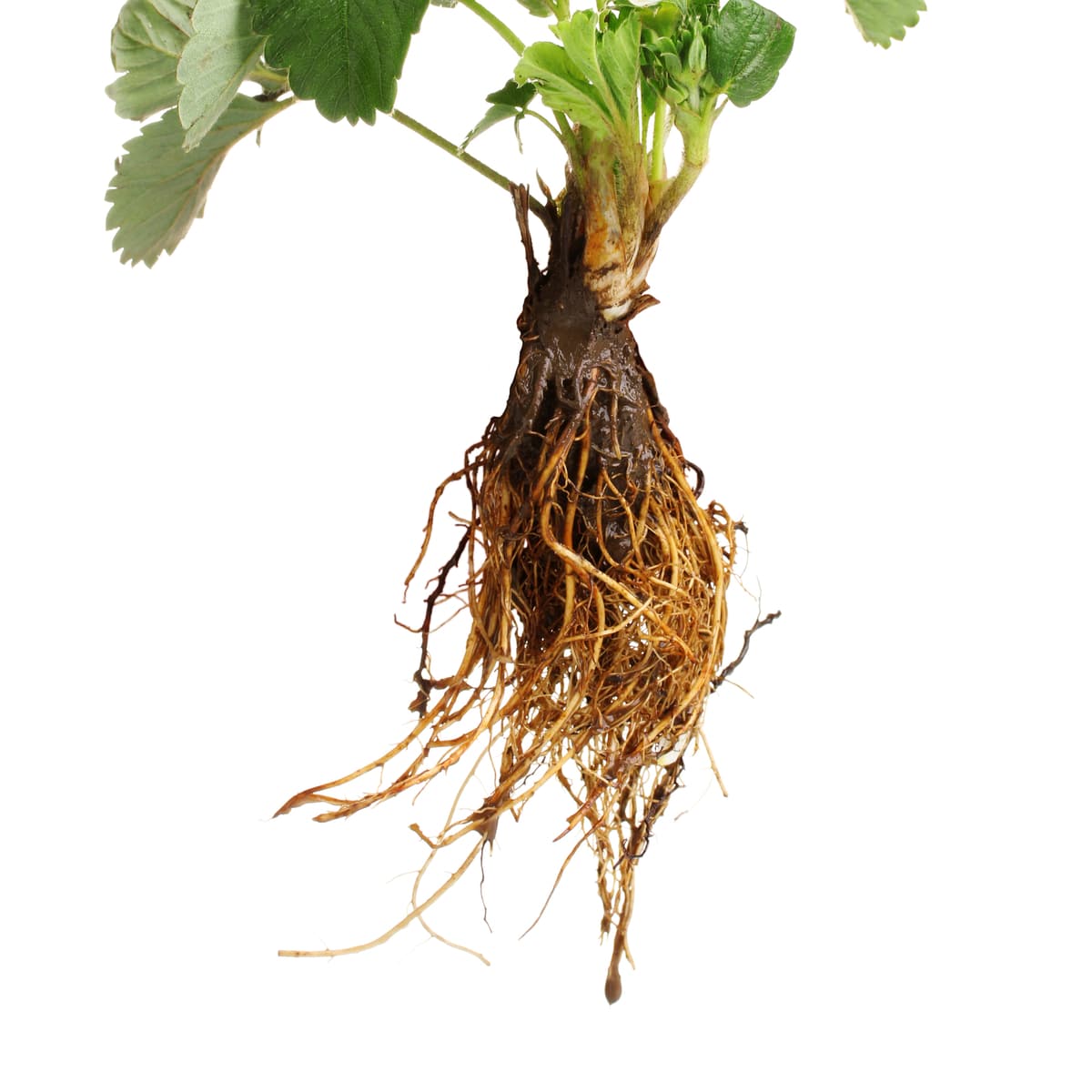
The depth to which wildflower roots extend into the earth varies significantly among different species, influenced by a myriad of factors including soil type, water availability, and environmental conditions. While some wildflowers develop shallow root systems that spread horizontally near the soil surface, others send their roots deep into the earth in search of water and nutrients.
Shallow-rooted wildflowers, such as the delicate Baby Blue Eyes (Nemophila menziesii) and the vibrant California Poppy (Eschscholzia californica), typically extend their roots close to the surface, often reaching depths of 6 to 12 inches. These shallow roots enable these wildflowers to efficiently absorb moisture from the upper layers of the soil, making them well-suited to thrive in areas with moderate water availability.
On the other hand, deep-rooted wildflowers, such as the iconic Purple Coneflower (Echinacea purpurea) and the resilient Black-Eyed Susan (Rudbeckia hirta), exhibit a remarkable ability to send their roots deep into the ground, often reaching depths of 2 to 4 feet or more. These extensive root systems enable these wildflowers to access water and nutrients from deeper soil layers, allowing them to withstand periods of drought and thrive in a diverse range of environments.
It’s important to note that the depth of wildflower roots also varies based on the structure and composition of the soil. In loose, well-draining soils, wildflower roots may penetrate deeper to access moisture and nutrients, while in compacted or clay-rich soils, their growth may be more constrained, leading to shallower root systems.
Understanding the depth to which wildflower roots grow is essential for cultivating these plants successfully and creating sustainable, vibrant ecosystems. Whether you’re tending to a wildflower garden or seeking to restore natural habitats, recognizing the diverse root structures of wildflowers is crucial for promoting their health and longevity.
Factors Affecting Wildflower Root Depth
The depth at which wildflower roots grow is influenced by a multitude of factors, each playing a crucial role in shaping the development of these intricate root systems. From environmental conditions to soil composition, these factors collectively determine the depth and resilience of wildflower roots, ultimately impacting the plants’ ability to thrive in their respective habitats.
1. Soil Type
The composition and structure of the soil significantly influence the depth of wildflower roots. Well-draining, loose soils allow roots to penetrate deeper, accessing moisture and nutrients from lower soil layers. In contrast, compacted or clay-rich soils may restrict root growth, leading to shallower root systems.
Read more: How Deep Do Grass Roots Grow
2. Water Availability
The availability of water in the soil directly impacts the depth to which wildflower roots extend. In regions with ample moisture, wildflowers may develop shallow roots to efficiently absorb water from the upper soil layers. Conversely, in arid or drought-prone environments, wildflowers may develop deep root systems to access water reserves deep within the earth.
3. Environmental Conditions
Environmental factors, such as temperature, sunlight exposure, and wind patterns, can influence wildflower root depth. In colder climates, wildflowers may develop shallower roots to minimize exposure to freezing temperatures, while in sun-drenched habitats, deep-rooted species may thrive by accessing moisture from deeper soil layers.
4. Plant Species
The genetic makeup of wildflower species plays a significant role in determining root depth. Different species have evolved unique root structures to adapt to specific environmental conditions, leading to variations in root depth and architecture among wildflower populations.
5. Competition and Adaptation
Wildflowers often compete with neighboring plants for resources, shaping the development of their root systems. In crowded ecosystems, wildflowers may adapt by developing either shallow or deep roots to access essential nutrients and water while minimizing competition with other plants.
Read more: How Deep Do Bermuda Grass Roots Grow
6. Human Intervention
Human activities, such as landscaping, soil compaction, and irrigation practices, can impact wildflower root depth. Alterations to natural landscapes and soil conditions may influence the growth and distribution of wildflower roots, highlighting the interconnectedness between human intervention and wildflower ecosystems.
By understanding the diverse factors that influence wildflower root depth, we can gain valuable insights into the intricate relationship between these captivating plants and their surrounding environment. This knowledge is essential for fostering healthy, resilient wildflower populations and promoting the conservation of these precious natural resources.
The Role of Wildflower Roots in Ecosystems
Wildflower roots serve as vital components of diverse ecosystems, contributing to the stability, fertility, and resilience of natural habitats. Through their intricate interactions with the soil, microorganisms, and neighboring flora, wildflower roots play a multifaceted role in shaping the ecological dynamics of their environments, fostering biodiversity, and sustaining the delicate balance of the natural world.
1. Soil Health and Stability
Wildflower roots are instrumental in promoting soil health and stability. By extending into the earth and forming a network of interconnected roots, wildflowers help bind the soil together, reducing erosion and preserving the integrity of the landscape. This function is essential for preventing soil loss and maintaining the structural stability of ecosystems, especially in regions prone to erosion.
2. Nutrient Cycling and Enrichment
Wildflower roots contribute to the cycling of nutrients within ecosystems, extracting essential minerals and organic matter from the soil. As wildflowers absorb nutrients, their roots release organic compounds and facilitate the breakdown of organic matter, enriching the soil and creating a fertile environment for other plant species. This process supports the growth of diverse flora and sustains the intricate web of life within the ecosystem.
Read more: How To Store Turmeric Root
3. Microbial Interaction and Soil Aeration
Wildflower roots foster a dynamic relationship with soil microorganisms, promoting microbial activity and enhancing soil aeration. The exudates released by wildflower roots provide nourishment for beneficial microorganisms, contributing to the development of healthy soil ecosystems. Additionally, the growth of wildflower roots improves soil structure, facilitating better aeration and drainage, which are essential for the survival of numerous soil-dwelling organisms.
4. Habitat Provision and Biodiversity
Wildflower roots create diverse microhabitats within ecosystems, offering shelter and sustenance for a wide array of organisms. Beneath the soil surface, the intricate network of wildflower roots provides a refuge for soil-dwelling invertebrates, microorganisms, and fungal communities. This underground habitat diversity supports the interconnected food web and fosters biodiversity within the ecosystem.
5. Ecological Resilience and Adaptation
Wildflower roots contribute to the resilience and adaptation of ecosystems, especially in the face of environmental challenges such as drought, flooding, or soil degradation. The ability of wildflower roots to access water and nutrients from varying soil depths enables these plants to thrive in diverse environmental conditions, contributing to the overall stability and adaptability of the ecosystem.
By recognizing the indispensable role of wildflower roots in ecosystems, we gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate web of interactions that sustains the natural world. These resilient roots not only support the growth and vitality of wildflowers but also contribute to the overall health and balance of the ecosystems in which they flourish.
Conclusion
As we conclude our exploration of wildflower roots, we are reminded of the profound impact these often overlooked components of nature have on the health and vitality of ecosystems. From their role in stabilizing soil to their contributions to nutrient cycling and biodiversity, wildflower roots are integral to the intricate web of life that sustains the natural world.
Understanding the depth and significance of wildflower roots provides us with valuable insights into the resilience and adaptability of these captivating plants. Whether they extend shallow roots to thrive in meadows and grasslands or delve deep into the earth to withstand arid environments, wildflowers have evolved diverse strategies that enable them to flourish in a myriad of habitats.
Moreover, the cultivation and conservation of wildflower populations are essential for preserving the delicate balance of ecosystems and supporting the myriad of organisms that depend on these plants for sustenance and shelter. By nurturing wildflowers and safeguarding their habitats, we contribute to the preservation of biodiversity and the protection of natural resources for future generations.
As we marvel at the vibrant blooms and delicate petals of wildflowers, let us also celebrate the intricate tapestry of roots that lies beneath the surface, anchoring these plants and sustaining the wondrous ecosystems they inhabit. Through our understanding and appreciation of wildflower roots, we embrace the interconnectedness of all living beings and the remarkable resilience of nature.
May the enchanting beauty and ecological importance of wildflowers and their roots continue to inspire us to cherish and protect the natural world, fostering a harmonious coexistence between humanity and the diverse ecosystems that enrich our lives.
Frequently Asked Questions about How Deep Are Wildflower Roots
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.












0 thoughts on “How Deep Are Wildflower Roots”