Home>Home Appliances>Heating & Cooling>What Is Forced Air Heating: Gas Or Electric?


Heating & Cooling
What Is Forced Air Heating: Gas Or Electric?
Published: February 16, 2024
Learn about the differences between gas and electric forced air heating systems and choose the best option for your heating and cooling needs.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Forced air heating is a popular and efficient method of keeping homes warm and comfortable. Whether it's the chill of winter or a brisk autumn evening, having a reliable heating system is essential for creating a cozy indoor environment. When it comes to forced air heating, there are two primary options to consider: gas and electric systems. Each has its own set of advantages and considerations, making it crucial for homeowners to understand the differences between the two.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of forced air heating, exploring the nuances of both gas and electric systems. By the end of this article, you will have a clear understanding of the mechanics, benefits, and potential drawbacks of each type of forced air heating. Whether you're considering a new installation or seeking to optimize your existing system, this information will empower you to make informed decisions regarding your home's heating needs.
Let's embark on a journey through the world of forced air heating, unraveling the mysteries of gas and electric systems to uncover the best fit for your home.
Key Takeaways:
- Gas forced air heating offers rapid warmth and cost-effectiveness, but requires maintenance and safety precautions. It’s great for cold climates, but homeowners need to stay vigilant.
- Electric forced air heating is simple, quiet, and eco-friendly, but may have higher operational costs. It’s low maintenance and versatile, making it a peaceful choice for many homes.
Read more: What Is Oil Forced Air Heating?
Understanding Forced Air Heating
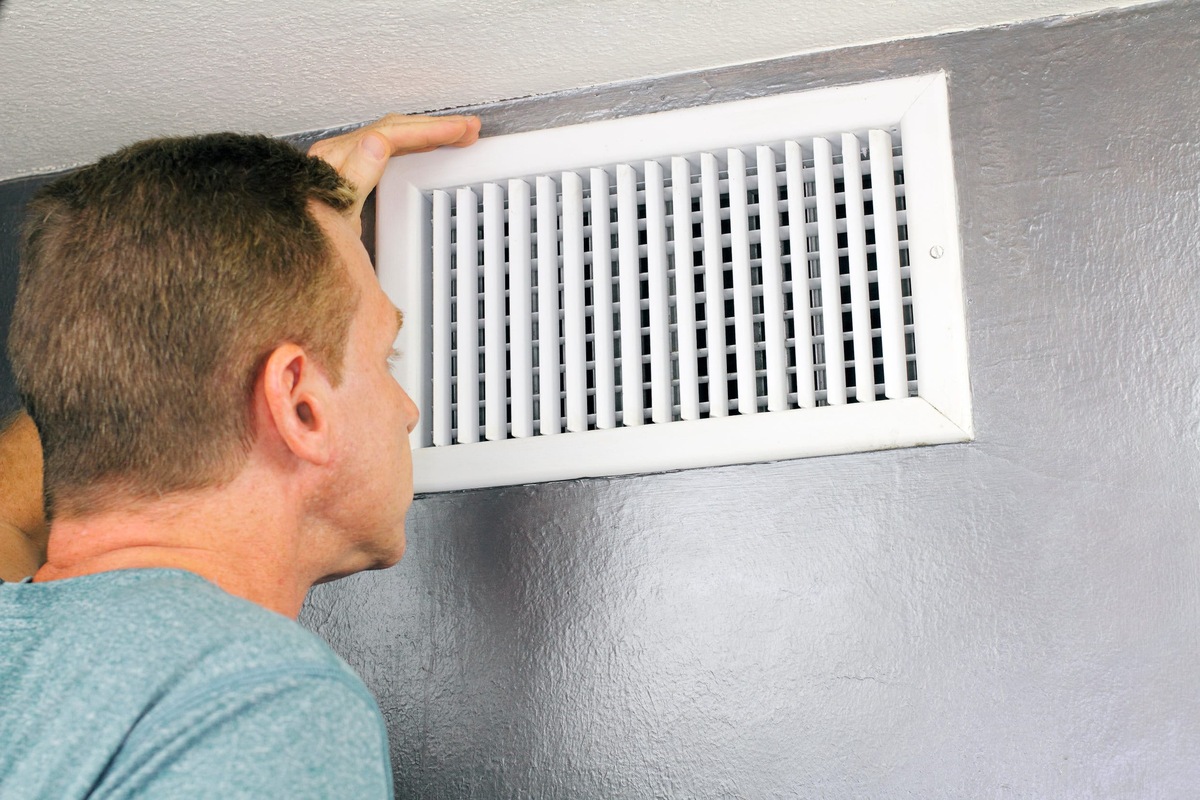
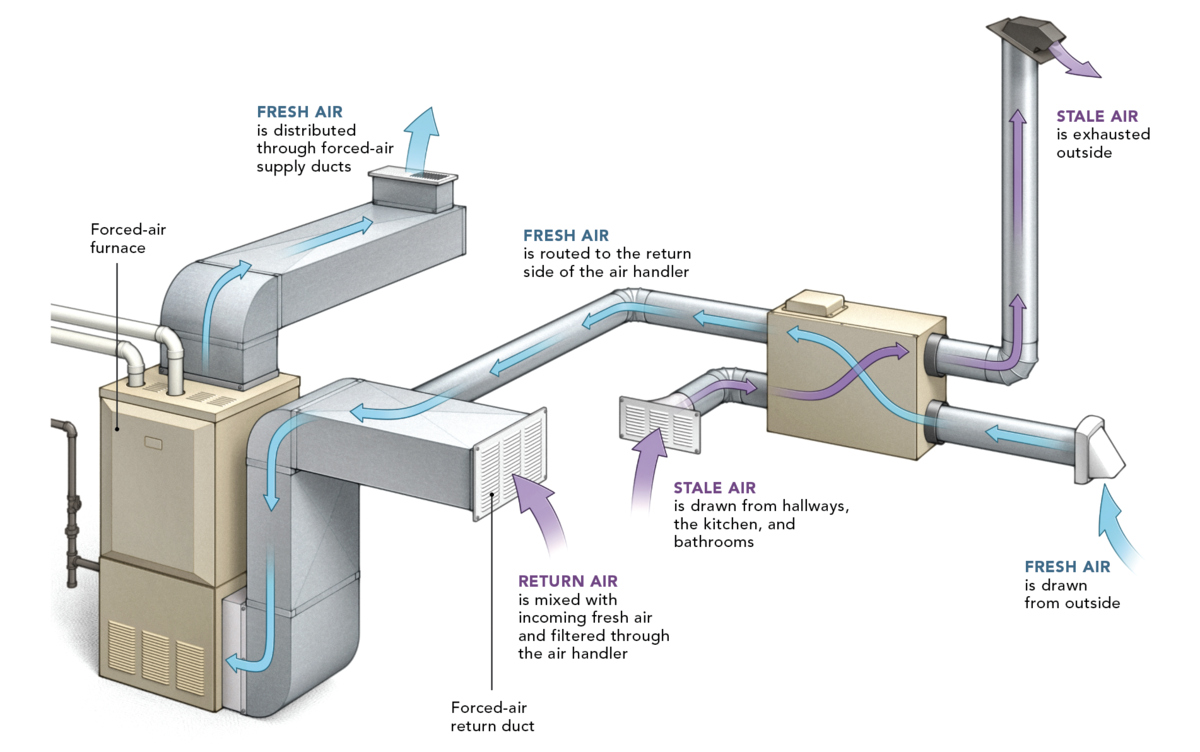
Forced air heating is a widely used method for maintaining a comfortable indoor temperature in residential and commercial spaces. This heating system operates by distributing warm air throughout the building via a network of ducts and vents. The process begins with the heating unit, which can be a furnace or heat pump, generating heat. The warm air is then propelled through the ductwork by a blower, effectively circulating it to every room in the building.
One of the key components of forced air heating is the thermostat, which allows users to regulate the temperature according to their preferences. When the indoor temperature falls below the set level, the thermostat triggers the heating system to kick in, initiating the heating cycle. As the warm air is distributed, it displaces the cooler air, gradually raising the overall temperature of the space.
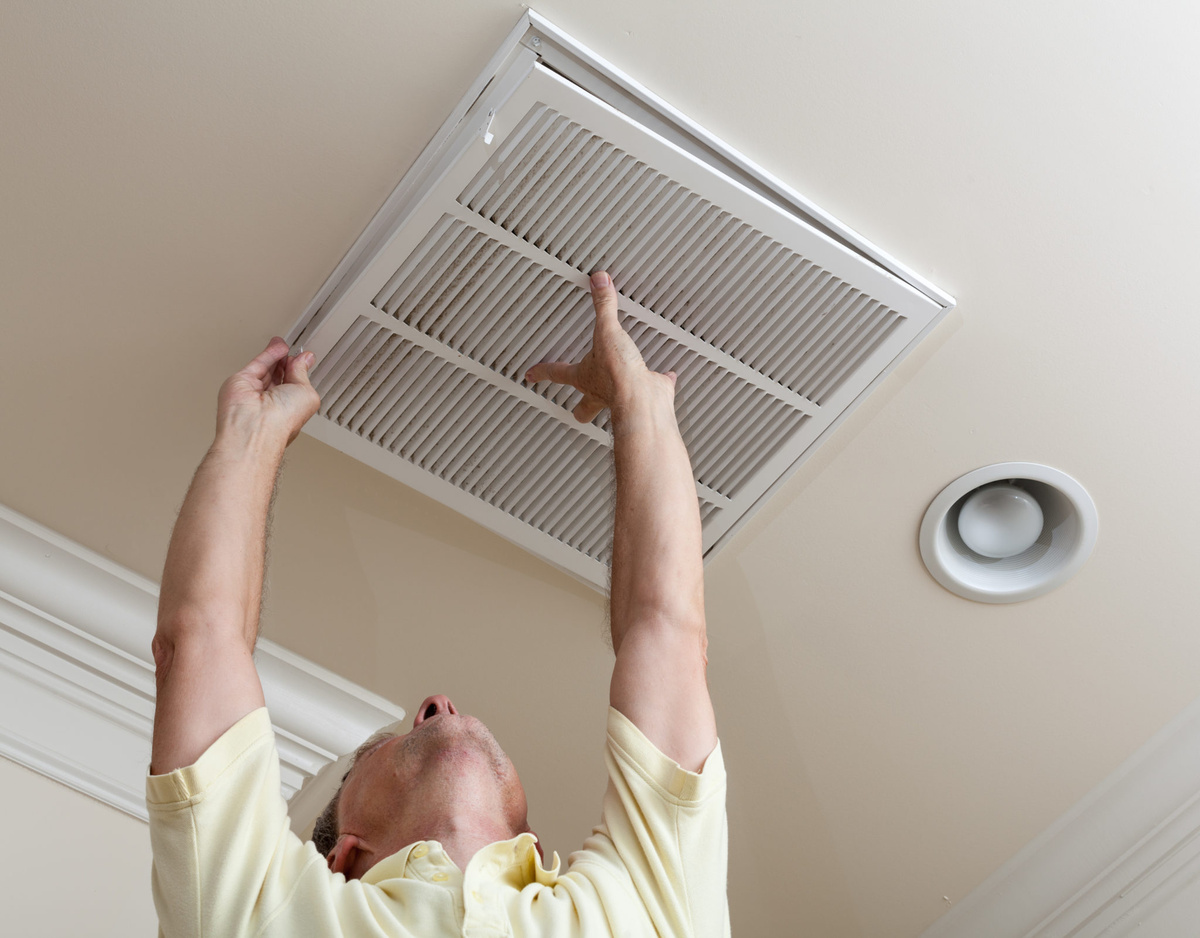
The ductwork plays a pivotal role in forced air heating, serving as the conduit through which the heated air travels. Properly designed and maintained ducts ensure efficient airflow and consistent heating throughout the building. Additionally, air filters within the ductwork help to improve indoor air quality by capturing dust, allergens, and other airborne particles.
Forced air heating systems can also be equipped with humidifiers and air purifiers to further enhance indoor comfort and air quality. These additional features contribute to creating a healthier and more pleasant living environment, especially during the dry winter months when humidity levels tend to drop.
Overall, forced air heating offers a convenient and effective way to maintain a warm and comfortable indoor environment. Its ability to quickly distribute heat throughout a building, coupled with the flexibility of temperature control, makes it a popular choice for many homeowners and businesses. Understanding the fundamentals of forced air heating is essential for making informed decisions about heating system installation, maintenance, and optimization.
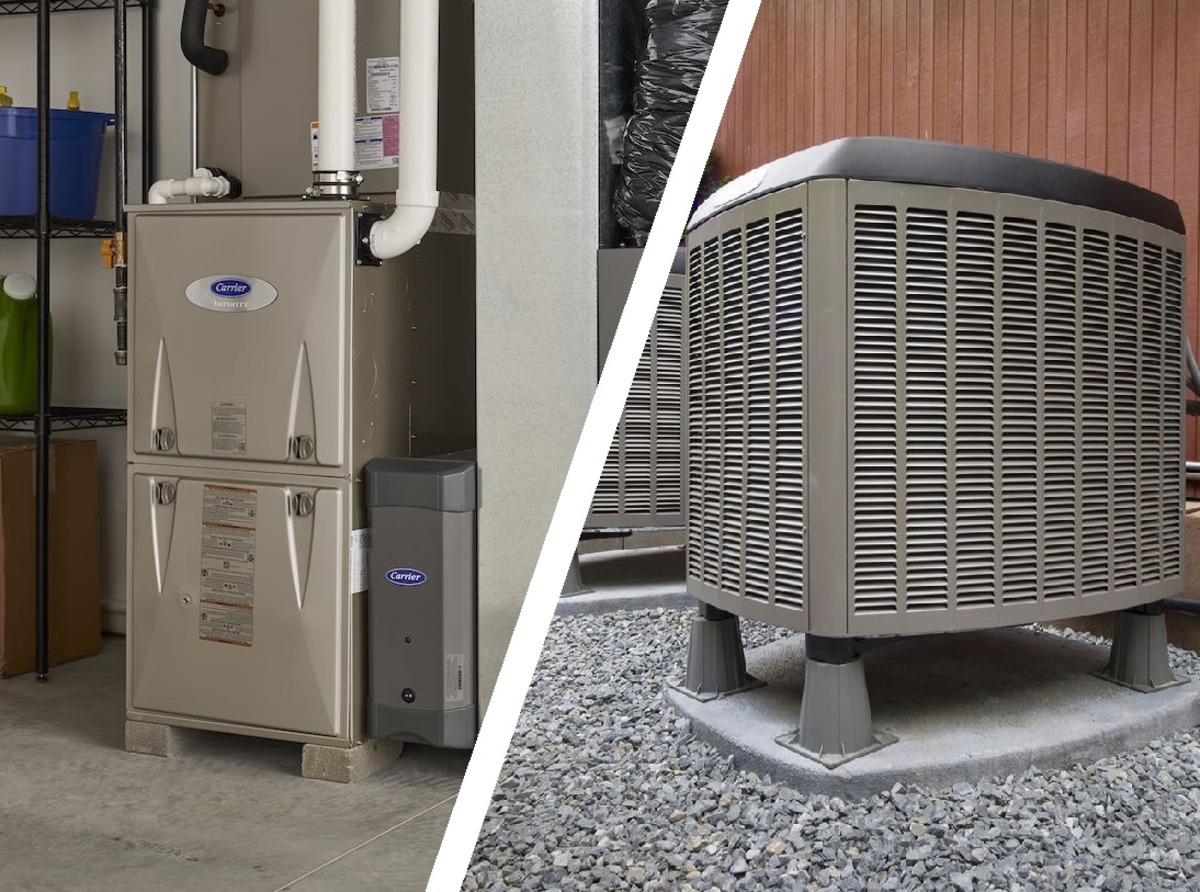
Gas Forced Air Heating
Gas forced air heating systems utilize natural gas or propane as the primary fuel source to generate heat. These systems feature a furnace that ignites the gas to produce warmth, which is then distributed throughout the building via the ductwork. The combustion process within the furnace creates heat, which is then transferred to the air that is circulated through the ducts.
One of the key advantages of gas forced air heating is its efficiency in quickly and effectively raising the indoor temperature. Gas furnaces are known for their rapid heat production, allowing spaces to warm up swiftly, even in extremely cold conditions. This makes them particularly well-suited for regions with harsh winters, where a reliable and efficient heating system is essential for maintaining comfort and safety.
Additionally, gas forced air heating systems are often favored for their cost-effectiveness. Natural gas and propane are generally more affordable than electricity, making gas furnaces an economical choice for heating homes and commercial buildings. The lower operational costs associated with gas heating can result in significant savings on energy bills over time, providing a compelling incentive for many homeowners to opt for this type of heating system.
Furthermore, gas forced air heating is known for its consistent and reliable performance. Once the thermostat triggers the heating cycle, the furnace quickly generates heat, ensuring a steady supply of warm air is distributed throughout the building. This reliability is a key factor in the popularity of gas heating systems, as it provides peace of mind and comfort, especially during the coldest months of the year.
However, it's important to consider the maintenance requirements and safety considerations associated with gas forced air heating. Regular maintenance, including professional inspections and filter replacements, is crucial to ensure the safe and efficient operation of gas furnaces. Additionally, homeowners must be mindful of potential carbon monoxide risks and ensure that their heating systems are properly ventilated and equipped with carbon monoxide detectors for added safety.
In summary, gas forced air heating systems offer rapid, cost-effective, and reliable warmth, making them a popular choice for many households and businesses. Understanding the unique benefits and considerations of gas heating is essential for making informed decisions when it comes to selecting the most suitable heating system for a specific property.
Electric Forced Air Heating
Electric forced air heating systems rely on electricity as the primary energy source to generate warmth and maintain comfortable indoor temperatures. These systems feature an electric furnace or heat pump, which converts electrical energy into heat, subsequently distributing it throughout the building via the ductwork.
One of the notable advantages of electric forced air heating is its simplicity and ease of installation. Unlike gas heating systems, electric furnaces do not require a flue or venting system for exhaust gases, making them more versatile in terms of placement within a property. This streamlined installation process can result in cost savings and greater flexibility for homeowners seeking an efficient heating solution.
Moreover, electric forced air heating systems are known for their quiet operation. Without the combustion process present in gas furnaces, electric heating eliminates the noise associated with igniting and burning fuel. This quiet performance contributes to a peaceful and undisturbed indoor environment, enhancing the overall comfort of the occupants.
Another benefit of electric forced air heating is its relatively low maintenance requirements. Electric furnaces typically have fewer moving parts compared to gas furnaces, reducing the need for frequent maintenance and repairs. This can translate to long-term cost savings and convenience for homeowners, as they can enjoy reliable heating with minimal upkeep.
Furthermore, electric forced air heating systems are considered environmentally friendly, as they produce zero emissions at the point of use. Unlike gas heating, which involves the combustion of fossil fuels, electric heating does not release any pollutants or greenhouse gases into the atmosphere within the property. This clean and sustainable aspect of electric heating aligns with the growing emphasis on eco-friendly home heating solutions.
However, it's important to note that electric forced air heating systems may lead to higher operational costs compared to gas heating, especially in regions where electricity prices are relatively high. Additionally, electric heating may not be as efficient as gas heating in extremely cold climates, where the rapid heat production of gas furnaces is particularly advantageous.
In summary, electric forced air heating systems offer straightforward installation, quiet operation, low maintenance requirements, and environmental friendliness. Understanding the unique benefits and considerations of electric heating is essential for homeowners and property managers seeking an effective and sustainable heating solution tailored to their specific needs.
Pros and Cons of Gas and Electric Forced Air Heating
Gas and electric forced air heating systems each offer distinct advantages and considerations, making it essential for homeowners to carefully evaluate their specific needs and preferences when selecting the most suitable heating solution for their property.
Read more: What Is An Advantage Of Forced Air Heating?
Pros of Gas Forced Air Heating
-
Rapid Heat Production: Gas furnaces are renowned for their ability to quickly generate warmth, making them particularly effective in swiftly raising indoor temperatures, especially in cold climates.
-
Cost-Effectiveness: Natural gas and propane, the primary fuels for gas heating, are often more affordable than electricity, resulting in lower operational costs and potential long-term savings on energy bills.
-
Reliability: Gas forced air heating systems provide consistent and reliable performance, ensuring a steady supply of warm air throughout the building, contributing to comfort and peace of mind for occupants.
Cons of Gas Forced Air Heating
-
Maintenance Requirements: Gas furnaces necessitate regular maintenance, including professional inspections and filter replacements, to ensure safe and efficient operation, adding to the overall cost of ownership.
-
Safety Considerations: Homeowners must be vigilant about potential carbon monoxide risks and ensure proper ventilation and carbon monoxide detectors are in place to mitigate safety concerns associated with gas heating.
Pros of Electric Forced Air Heating
-
Simplicity and Versatility: Electric furnaces do not require a flue or venting system, simplifying the installation process and offering greater flexibility in placement within a property.
-
Quiet Operation: Electric heating systems operate quietly, devoid of the noise associated with the combustion process in gas furnaces, contributing to a peaceful indoor environment.
-
Low Maintenance: Electric furnaces typically have fewer moving parts, resulting in reduced maintenance requirements and potential long-term cost savings for homeowners.
-
Environmental Friendliness: Electric heating produces zero emissions at the point of use, aligning with the growing emphasis on sustainable and eco-friendly home heating solutions.
Cons of Electric Forced Air Heating
-
Operational Costs: Electric heating may lead to higher operational expenses, particularly in regions with relatively high electricity prices, potentially impacting long-term affordability.
-
Efficiency in Extreme Cold: In extremely cold climates, the rapid heat production of gas furnaces may outperform electric heating, posing a consideration for homeowners in such environments.
By weighing these pros and cons, homeowners can make informed decisions when selecting between gas and electric forced air heating systems, ensuring that their choice aligns with their heating needs, budget, and environmental considerations.
Forced air heating systems use a furnace to heat air, which is then distributed throughout the home via ducts. Gas furnaces are more common and generally more efficient than electric furnaces, but electric furnaces can be a good option in areas where natural gas is not readily available.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the choice between gas and electric forced air heating systems hinges on a multitude of factors, including efficiency, cost-effectiveness, maintenance requirements, and environmental considerations. Both gas and electric heating offer unique advantages and considerations, catering to diverse preferences and heating needs.
Gas forced air heating systems excel in their rapid heat production, making them particularly well-suited for swiftly raising indoor temperatures, especially in regions with harsh winters. The cost-effectiveness of natural gas and propane fuels further enhances the appeal of gas heating, potentially resulting in significant savings on energy bills over time. However, homeowners must remain vigilant about maintenance requirements and safety considerations associated with gas heating, ensuring the safe and efficient operation of their systems.
On the other hand, electric forced air heating systems offer simplicity, versatility, and quiet operation, making them an attractive option for homeowners seeking a streamlined and peaceful heating solution. The low maintenance requirements and environmental friendliness of electric heating contribute to its appeal, aligning with the growing emphasis on sustainable home heating solutions. Nonetheless, the potential for higher operational costs, particularly in regions with elevated electricity prices, poses a consideration for those considering electric heating.
Ultimately, the decision between gas and electric forced air heating should be guided by a thorough assessment of individual heating needs, budget constraints, and environmental priorities. By carefully weighing the pros and cons of each system, homeowners can make informed choices that align with their specific requirements and preferences.
Whether it's the rapid warmth of gas heating or the quiet efficiency of electric heating, both options offer reliable and effective ways to maintain a comfortable indoor environment. Understanding the nuances of gas and electric forced air heating empowers homeowners to make informed decisions, ensuring that their chosen heating system meets their expectations for performance, affordability, and environmental impact.
As technology continues to advance and environmental considerations gain prominence, the landscape of forced air heating is likely to evolve, offering homeowners an increasingly diverse array of options to meet their heating needs. By staying informed and attuned to the latest developments in heating technology, homeowners can navigate the choices available to them, securing a heating solution that aligns with their vision for a warm, comfortable, and sustainable living space.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is Forced Air Heating: Gas Or Electric?
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.













0 thoughts on “What Is Forced Air Heating: Gas Or Electric?”