Home>Home Appliances>Heating & Cooling>Is Forced Air Heating The Same As A Heat Pump?


Heating & Cooling
Is Forced Air Heating The Same As A Heat Pump?
Modified: February 18, 2024
Learn the differences between forced air heating and heat pumps for efficient heating and cooling. Find out which option is best for your home.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Heating and cooling systems are essential for maintaining a comfortable indoor environment, especially during extreme weather conditions. When it comes to heating, forced air heating and heat pumps are two popular options that homeowners often consider. Understanding the differences and similarities between these systems is crucial for making informed decisions about home comfort.
In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of forced air heating and heat pumps, exploring their unique features, functionalities, and benefits. By the end of this comprehensive guide, you will have a clear understanding of how these systems operate and how they differ from each other. Whether you are a homeowner looking to upgrade your heating system or simply curious about the mechanics of indoor climate control, this article will provide valuable insights into the world of heating and cooling technology.
Key Takeaways:
- Forced air heating uses fuel combustion to generate warmth, while heat pumps transfer heat from outdoors. Both offer year-round comfort and energy efficiency, but heat pumps are more eco-friendly.
- Both systems distribute air and are controlled by thermostats. Forced air heating can be noisier, while heat pumps are quieter. Regular maintenance is crucial for optimal performance and longevity of both systems.
Read more: When Did Forced Air Heating Start?
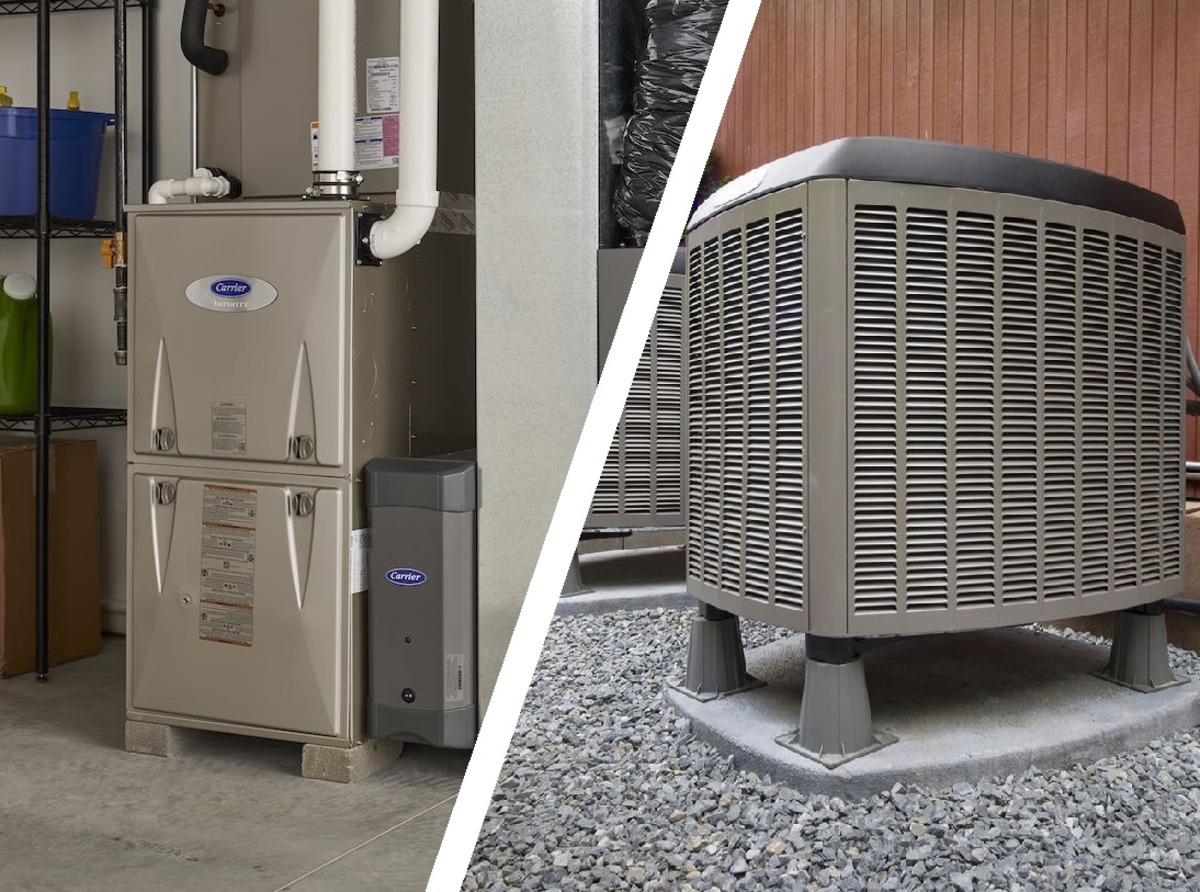
Understanding Forced Air Heating
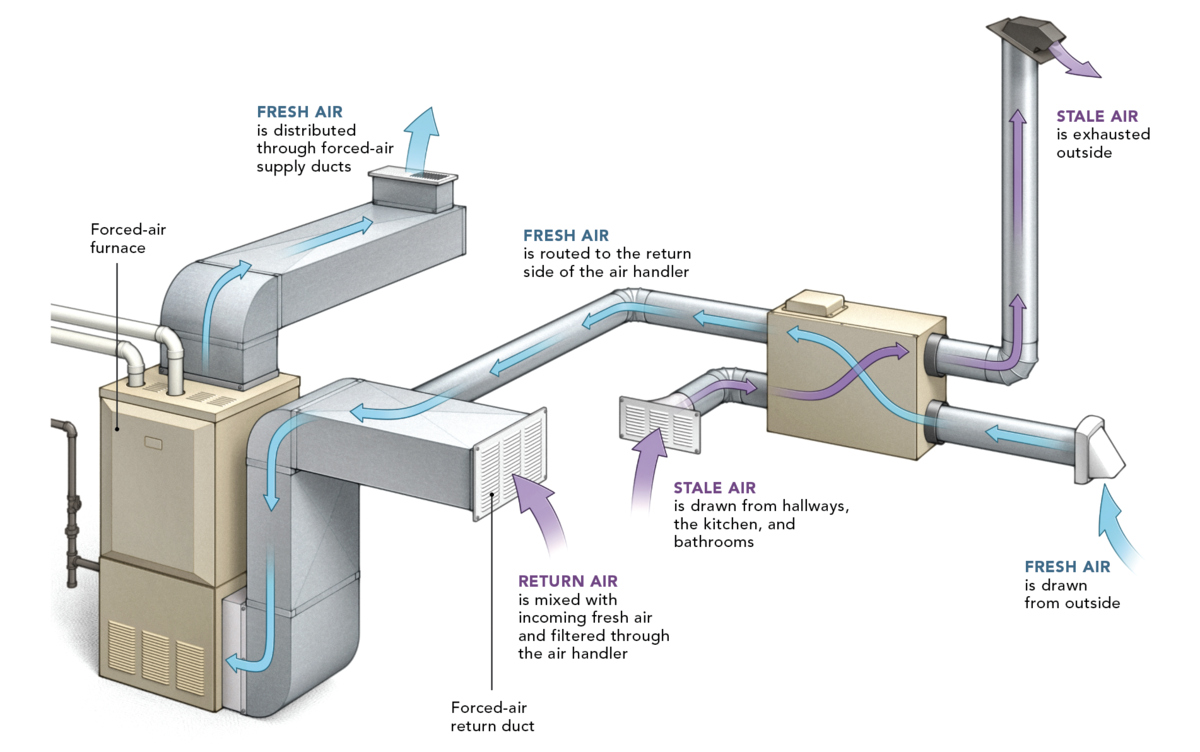
Forced air heating is a popular and efficient method of heating homes and commercial spaces. This system operates by distributing heated air through a network of ducts and vents, providing consistent warmth throughout the building. The process begins with a furnace, which serves as the heart of the forced air heating system. The furnace can be powered by various energy sources, including natural gas, electricity, propane, or oil, depending on the specific setup of the property.
When the thermostat detects a drop in temperature, it signals the furnace to ignite. As the furnace ignites, it heats the air within its combustion chamber. The heated air is then forced through the ductwork by a powerful blower, which propels the warm air into the living spaces. This continuous circulation of heated air ensures that the entire building is maintained at a comfortable temperature.
One of the key advantages of forced air heating is its ability to quickly and effectively distribute warmth. The system can also be equipped with air filters and humidifiers, contributing to improved indoor air quality and comfort. Additionally, forced air heating systems can accommodate air conditioning components, providing both heating and cooling capabilities within a single integrated system.
However, it's important to note that forced air heating systems may produce some operational noise due to the functioning of the blower and ductwork. Regular maintenance, including filter replacement and duct cleaning, is essential to ensure optimal performance and energy efficiency.
In summary, forced air heating offers efficient and reliable warmth distribution, making it a popular choice for many homeowners and businesses. Its ability to integrate with air conditioning and air quality enhancement components further enhances its appeal as a comprehensive indoor climate control solution.
Understanding Heat Pumps
Heat pumps are versatile heating and cooling systems that offer energy-efficient solutions for maintaining indoor comfort. Unlike traditional heating systems that generate heat, heat pumps utilize a heat transfer process to move warmth from one area to another. This innovative technology enables heat pumps to provide both heating and cooling functions, making them a popular choice for environmentally conscious homeowners.
At the core of a heat pump system is the refrigeration cycle, which facilitates the transfer of heat between the indoor and outdoor environments. During the heating mode, the outdoor unit of the heat pump extracts heat from the ambient air, even in cold temperatures, and transfers it indoors. This process is made possible by the refrigerant circulating within the system, absorbing heat from the outdoor air and releasing it inside the building. As a result, the indoor space is effectively heated, even when outdoor temperatures are chilly.
Conversely, during the cooling mode, the heat pump reverses the refrigeration cycle to remove heat from indoors and release it outside, thereby cooling the indoor environment. This dual functionality makes heat pumps a versatile and cost-effective solution for year-round temperature control.
Furthermore, heat pumps are renowned for their energy efficiency, as they can deliver up to three times more heating or cooling energy than the electrical energy they consume. This high level of efficiency can lead to significant cost savings on energy bills, making heat pumps an attractive option for budget-conscious homeowners.
Another notable benefit of heat pumps is their eco-friendly operation. By utilizing the heat transfer process instead of burning fossil fuels to generate heat, heat pumps significantly reduce carbon emissions, contributing to a greener and more sustainable living environment.
In summary, heat pumps offer a compelling combination of heating and cooling capabilities, energy efficiency, and environmental friendliness. Their ability to provide year-round comfort while minimizing energy consumption makes them a desirable choice for modern homes seeking reliable and sustainable indoor climate control.
Forced air heating and heat pumps are not the same. Forced air heating uses a furnace to heat air, while a heat pump moves heat from one place to another.
Differences Between Forced Air Heating and Heat Pumps
Forced air heating and heat pumps represent two distinct approaches to indoor climate control, each offering unique features and functionalities. Differentiating between these systems is essential for homeowners seeking the most suitable heating and cooling solutions for their properties.
-
Heating Mechanism: The fundamental variance between forced air heating and heat pumps lies in their heating mechanisms. Forced air heating relies on the combustion of fuel, such as natural gas, propane, or oil, within a furnace to generate warmth. In contrast, heat pumps utilize a heat transfer process, extracting heat from the outdoor air (even in cold temperatures) and transferring it indoors to provide heating.
-
Cooling Capabilities: While forced air heating systems can be integrated with air conditioning components to deliver cooling, heat pumps inherently offer both heating and cooling functions within a single system. This dual functionality allows heat pumps to efficiently regulate indoor temperatures throughout the year, providing a comprehensive climate control solution.
-
Energy Efficiency: Heat pumps are renowned for their exceptional energy efficiency, as they can deliver up to three times more heating or cooling energy than the electrical energy they consume. On the other hand, forced air heating systems may exhibit lower energy efficiency, especially when relying on fossil fuels for heat generation.
-
Environmental Impact: In terms of environmental impact, heat pumps hold a significant advantage over forced air heating systems. By utilizing the heat transfer process instead of burning fossil fuels, heat pumps contribute to reduced carbon emissions and a greener living environment, aligning with sustainable and eco-friendly practices.
-
Operational Noise: Forced air heating systems may produce operational noise due to the functioning of blowers and ductwork, which can impact the overall indoor ambiance. In contrast, heat pumps are generally quieter during operation, offering a more peaceful and undisturbed living environment.
-
Installation Considerations: The installation requirements for forced air heating systems and heat pumps differ significantly. Forced air heating systems involve the installation of ductwork throughout the property, which may be challenging in existing structures. Conversely, heat pumps require outdoor and indoor units, with the outdoor unit serving as the source of heat exchange, necessitating specific spatial considerations during installation.
Understanding these differences is crucial for homeowners evaluating their heating and cooling options. By considering the specific features and functionalities of forced air heating and heat pumps, individuals can make informed decisions that align with their comfort preferences, energy efficiency goals, and environmental consciousness.
Similarities Between Forced Air Heating and Heat Pumps
While forced air heating and heat pumps exhibit distinct characteristics and operational principles, they also share several noteworthy similarities. Understanding these commonalities can provide valuable insights into the fundamental aspects of indoor climate control, offering a holistic perspective on heating and cooling technologies.
-
Air Distribution: Both forced air heating systems and heat pumps rely on the distribution of conditioned air to maintain comfortable indoor temperatures. In the case of forced air heating, the heated air is propelled through ductwork and distributed via vents, ensuring consistent warmth throughout the building. Similarly, heat pumps utilize air distribution to circulate the conditioned air, whether for heating during colder periods or cooling during warmer seasons. This shared emphasis on effective air distribution underscores the importance of balanced and uniform temperature regulation within indoor spaces.
-
Thermostat Control: Both forced air heating systems and heat pumps are controlled by thermostats, allowing users to set and maintain their desired indoor temperatures. The thermostat serves as the central command unit, communicating with the heating or cooling system to initiate operation based on the specified temperature settings. This common control mechanism empowers homeowners to customize their indoor climate preferences, promoting personalized comfort and energy efficiency.
-
Year-Round Comfort: While forced air heating primarily focuses on delivering warmth, it can be integrated with air conditioning components to provide comprehensive climate control throughout the year. Similarly, heat pumps offer dual functionality, capable of providing both heating and cooling, making them suitable for year-round comfort. This shared versatility enables both systems to adapt to seasonal temperature fluctuations, ensuring optimal indoor conditions regardless of external weather variations.
-
Energy Efficiency Considerations: Both forced air heating and heat pumps emphasize energy efficiency as a key attribute. While heat pumps are renowned for their high efficiency in converting electrical energy into heating or cooling power, forced air heating systems can also achieve notable energy efficiency through advancements in furnace technology and ductwork design. This mutual commitment to energy efficiency aligns with the growing emphasis on sustainable and cost-effective heating and cooling solutions.
-
Maintenance Requirements: Both forced air heating systems and heat pumps require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and longevity. This includes tasks such as filter replacement, duct cleaning, and periodic system inspections. By adhering to recommended maintenance schedules, homeowners can uphold the efficiency and reliability of their heating and cooling systems, promoting consistent comfort and operational effectiveness.
By recognizing these shared attributes, homeowners can gain a comprehensive understanding of the common principles that underpin forced air heating and heat pump technologies. This awareness can inform informed decisions regarding system selection, maintenance practices, and overall indoor comfort management.
Read more: What Is Oil Forced Air Heating?
Conclusion
In conclusion, the comparison between forced air heating and heat pumps reveals the diverse array of options available for homeowners seeking efficient and reliable indoor climate control. Forced air heating systems, powered by combustion-based furnaces, offer consistent warmth through the distribution of heated air via ductwork. On the other hand, heat pumps utilize innovative heat transfer technology to provide both heating and cooling functions, promoting energy efficiency and environmental sustainability.
The differences between these systems, including their heating mechanisms, cooling capabilities, energy efficiency, environmental impact, operational noise, and installation considerations, highlight the unique attributes that homeowners must consider when evaluating their heating and cooling options. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for making informed decisions that align with individual comfort preferences, energy efficiency goals, and environmental consciousness.
Despite their differences, forced air heating and heat pumps share commonalities in terms of air distribution, thermostat control, year-round comfort provision, energy efficiency considerations, and maintenance requirements. These shared attributes underscore the fundamental principles of effective indoor climate control, emphasizing the importance of balanced temperature regulation, personalized comfort, and sustainable energy practices.
Ultimately, the choice between forced air heating and heat pumps depends on various factors, including property-specific requirements, climate considerations, energy efficiency objectives, and environmental impact preferences. By weighing the distinct features and functionalities of each system, homeowners can make informed decisions that optimize indoor comfort while aligning with their sustainability and cost-effectiveness goals.
As the demand for energy-efficient and environmentally friendly heating and cooling solutions continues to grow, both forced air heating and heat pumps play pivotal roles in meeting these evolving needs. Whether it's the reliable warmth distribution of forced air heating or the versatile heating and cooling capabilities of heat pumps, both systems offer valuable options for enhancing indoor comfort while minimizing environmental impact.
In the dynamic landscape of indoor climate control, the comparison between forced air heating and heat pumps underscores the importance of technological innovation, energy efficiency, and sustainability in shaping the future of residential and commercial heating and cooling solutions. By staying informed about the latest advancements in heating and cooling technologies, homeowners can make informed choices that prioritize comfort, efficiency, and environmental responsibility, contributing to a more sustainable and comfortable living environment for all.
Frequently Asked Questions about Is Forced Air Heating The Same As A Heat Pump?
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.














0 thoughts on “Is Forced Air Heating The Same As A Heat Pump?”