Home>Home Appliances>Heating & Cooling>How To Design A Forced Air Heating System

Heating & Cooling
How To Design A Forced Air Heating System
Published: February 16, 2024
Learn how to design an efficient forced air heating system for your home with our comprehensive guide. Find expert tips and advice for heating and cooling systems.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
When it comes to creating a comfortable and cozy indoor environment, a well-designed heating system plays a crucial role. Among the various heating options available, forced air heating systems have gained popularity for their efficiency and effectiveness in distributing warmth throughout a space. Whether you are considering installing a new heating system or upgrading an existing one, understanding the fundamentals of forced air heating system design is essential to ensure optimal performance and energy efficiency.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of designing a forced air heating system, covering everything from the underlying principles to the practical steps involved in the process. By the end of this article, you will have a clear understanding of the key factors to consider and the systematic approach to designing a forced air heating system that meets your specific needs.
So, let's embark on this journey to unravel the art and science of creating a heating system that not only keeps you warm during chilly days but also aligns with your energy-saving goals. Whether you are a homeowner, a contractor, or an HVAC enthusiast, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and insights to make informed decisions and achieve optimal comfort and efficiency in your indoor spaces.
Key Takeaways:
- Designing a forced air heating system involves considering factors like heating load, energy source, ductwork design, zoning, and air quality. It’s like creating a customized warmth puzzle for your home!
- By following a step-by-step approach, you can design a heating system that not only keeps you warm but also saves energy and ensures clean indoor air. It’s like crafting a personalized comfort experience for your space!
Read more: When Did Forced Air Heating Start?
Understanding Forced Air Heating Systems
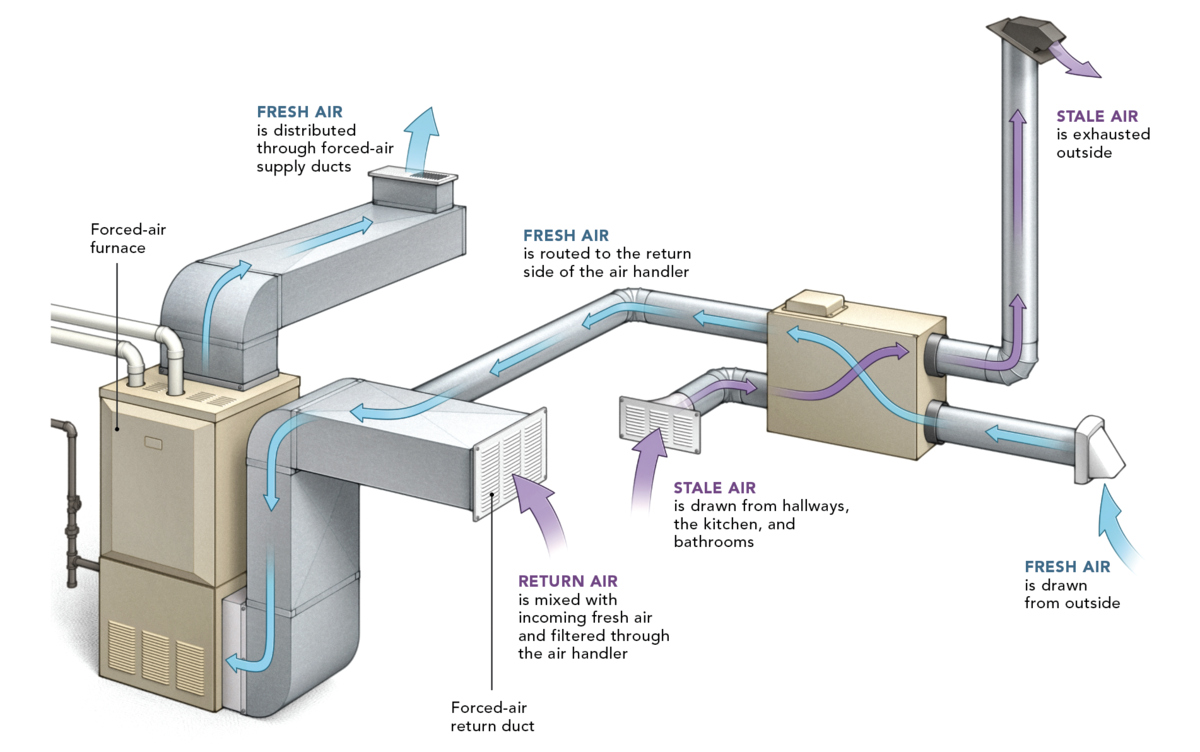
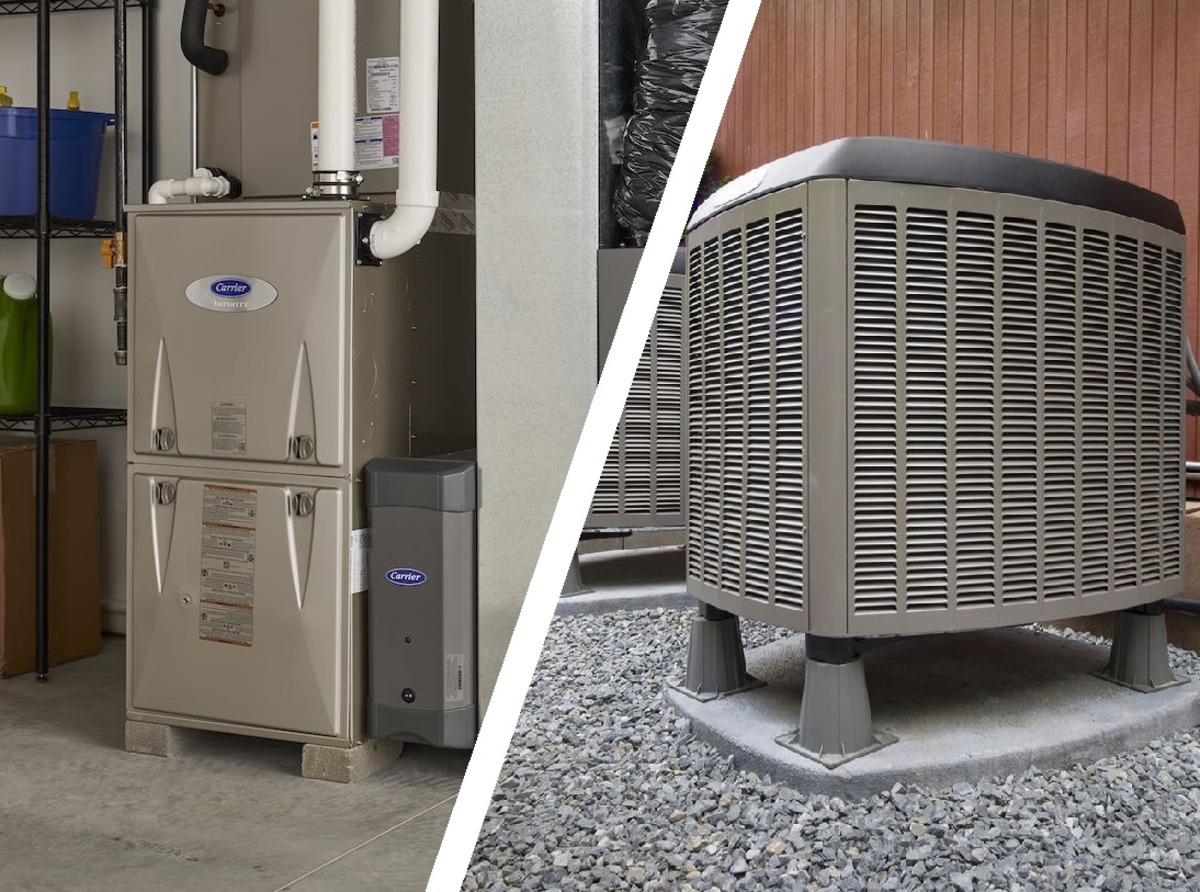
Forced air heating systems are a popular choice for heating residential and commercial spaces due to their efficiency and ability to quickly distribute warmth. These systems operate by heating air within a furnace and then circulating it throughout the building via a network of ducts and vents. The key components of a forced air heating system include the furnace, ductwork, vents, and a thermostat for temperature control.
The heart of a forced air heating system is the furnace, which can be powered by natural gas, propane, electricity, or oil. When the thermostat detects a drop in temperature, it signals the furnace to ignite and begin heating the air. Once the air reaches the desired temperature, a blower fan pushes it through the ductwork and into the various rooms of the building.
Ductwork plays a critical role in forced air heating systems, as it serves as the conduit for distributing heated air. Properly designed and installed ductwork ensures efficient airflow and consistent heating throughout the building. Vents, located in each room, allow the heated air to enter and circulate, while also providing an outlet for the return air to be recirculated back to the furnace for reheating.
One of the advantages of forced air heating systems is their ability to accommodate additional components for enhanced comfort and air quality. For example, air filters can be integrated into the system to remove dust, pollen, and other airborne particles, improving indoor air quality. Additionally, humidifiers and air purifiers can be installed to regulate moisture levels and further enhance the overall indoor environment.
Understanding the mechanics of forced air heating systems is essential for designing an effective and efficient heating solution for any space. By grasping the interplay between the furnace, ductwork, vents, and auxiliary components, one can make informed decisions when selecting, installing, and maintaining a forced air heating system.
In the next section, we will explore the crucial factors to consider before embarking on the design of a forced air heating system, laying the groundwork for a successful and tailored heating solution.
Factors to Consider Before Designing
Before diving into the design process of a forced air heating system, it's essential to carefully consider several key factors that will influence the system's performance, efficiency, and suitability for the specific space. By addressing these factors upfront, you can lay a solid foundation for a well-designed heating solution that meets your heating needs and aligns with your energy efficiency goals.
-
Heating Load Calculation: Understanding the heating load, or the amount of heat required to maintain a comfortable indoor temperature, is fundamental to designing an effective forced air heating system. Factors such as the building's size, insulation, windows, and local climate all contribute to the heating load. Conducting a thorough heating load calculation ensures that the heating system is appropriately sized to deliver the necessary warmth without unnecessary energy consumption.
-
Energy Source: The choice of energy source for the furnace, whether it's natural gas, propane, electricity, or oil, has significant implications for the system's operating costs, environmental impact, and availability. Evaluating the pros and cons of each energy source in relation to your location and heating requirements is crucial in selecting the most suitable option for your forced air heating system.
-
Ductwork Design and Layout: The design and layout of the ductwork profoundly impact the efficiency and effectiveness of a forced air heating system. Factors such as duct size, insulation, and the arrangement of supply and return ducts play a critical role in ensuring balanced airflow and consistent heating throughout the building. Additionally, considerations for accommodating air filters, dampers, and zoning systems should be integrated into the ductwork design.
-
Zoning and Control: Zoning the heating system allows for customized temperature control in different areas or zones within the building. By strategically dividing the space into zones and implementing individual thermostats, occupants can optimize comfort and energy usage based on their specific needs. Incorporating zoning capabilities into the system design enhances overall efficiency and flexibility.
-
Air Quality and Filtration: Addressing indoor air quality is an essential aspect of forced air heating system design. Integrating high-quality air filters, air purifiers, and humidity control systems can significantly enhance the indoor environment, providing clean, healthy air while protecting the heating system components from dust and debris.
-
Future Expansion and Upgrades: Anticipating future needs and potential system upgrades is prudent when designing a forced air heating system. Considering the flexibility to accommodate additional components or technologies, such as smart thermostats or advanced air filtration systems, ensures that the system remains adaptable to evolving requirements.
By carefully evaluating these factors before delving into the design phase, you can set the stage for a well-informed and tailored approach to creating a forced air heating system that delivers optimal comfort, efficiency, and reliability.
In the subsequent section, we will explore the systematic steps involved in designing a forced air heating system, providing a roadmap for translating these considerations into a well-executed heating solution.
When designing a forced air heating system, make sure to properly size the ductwork and choose the right size and type of furnace for the space to ensure efficient and effective heating.
Steps to Design a Forced Air Heating System
Designing a forced air heating system involves a systematic approach that encompasses various critical considerations to ensure optimal performance, energy efficiency, and tailored comfort. By following a structured series of steps, one can navigate through the design process with clarity and precision, ultimately culminating in the implementation of a well-crafted heating solution.
-
Heating Load Calculation: The initial step in designing a forced air heating system is to conduct a comprehensive heating load calculation. This involves assessing the specific heating requirements of the space, taking into account factors such as the building's size, insulation, window characteristics, and local climate. By accurately determining the heating load, one can ascertain the appropriate heating capacity needed to maintain a comfortable indoor temperature without unnecessary energy consumption.
-
Energy Source Selection: Once the heating load is determined, the next step is to select the most suitable energy source for the furnace. Whether it's natural gas, propane, electricity, or oil, evaluating the availability, cost, and environmental impact of each energy source is crucial. The chosen energy source should align with the heating load and the specific requirements of the space, ensuring efficient and cost-effective operation of the forced air heating system.
-
Ductwork Design and Layout: Designing the ductwork is a pivotal aspect of the process, as it directly influences the distribution of heated air throughout the building. Factors such as duct size, insulation, and the arrangement of supply and return ducts must be carefully considered to achieve balanced airflow and consistent heating. Additionally, integrating provisions for air filters, dampers, and zoning systems into the ductwork design enhances the overall functionality and efficiency of the heating system.
-
Zoning and Control Implementation: Implementing zoning capabilities allows for customized temperature control in different areas or zones within the building. This step involves strategically dividing the space into zones and integrating individual thermostats to optimize comfort and energy usage based on specific needs. By incorporating zoning and control features, the forced air heating system can adapt to varying heating demands, enhancing overall efficiency and flexibility.
-
Air Quality Integration: Addressing indoor air quality is an integral part of the design process. Integrating high-quality air filters, air purifiers, and humidity control systems enhances the indoor environment, providing clean, healthy air while safeguarding the heating system components from dust and debris. This step ensures that the forced air heating system not only delivers warmth but also promotes a comfortable and healthy indoor atmosphere.
-
Future-Proofing and Adaptability: Anticipating future needs and potential system upgrades is a prudent consideration during the design phase. Ensuring that the system is designed to accommodate future expansions or technological advancements, such as smart thermostats or advanced air filtration systems, enhances its adaptability and longevity, aligning with evolving requirements and preferences.
By following these systematic steps, one can navigate the intricacies of designing a forced air heating system with a comprehensive and tailored approach. Each step contributes to the overall functionality, efficiency, and comfort provided by the heating system, culminating in the creation of a well-designed solution that meets the specific needs of the space and its occupants.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the design of a forced air heating system is a multifaceted endeavor that requires a deep understanding of the underlying principles, meticulous planning, and a systematic approach. By comprehensively assessing the heating load, selecting the appropriate energy source, designing efficient ductwork, implementing zoning and control features, integrating air quality solutions, and future-proofing the system, one can create a heating solution that not only delivers warmth but also prioritizes energy efficiency, comfort, and indoor air quality.
The significance of conducting a thorough heating load calculation cannot be overstated, as it forms the basis for determining the heating capacity required to maintain a comfortable indoor environment. This foundational step sets the stage for the subsequent decisions regarding energy source selection, ductwork design, and zoning implementation, ensuring that the heating system is precisely tailored to the specific needs of the space.
The choice of energy source for the furnace is a pivotal decision, with implications for operating costs, environmental impact, and overall system efficiency. Evaluating the available options in relation to the heating load and local considerations enables informed decision-making, leading to the selection of an energy source that aligns with both performance and sustainability goals.
The design and layout of the ductwork play a critical role in ensuring balanced airflow and consistent heating throughout the building. By meticulously planning the ductwork, integrating zoning capabilities, and addressing air quality considerations, one can optimize the distribution of heated air while enhancing comfort and indoor air quality.
Furthermore, the integration of zoning and control features empowers occupants to customize temperature settings based on specific preferences, optimizing energy usage and comfort. This tailored approach to heating control enhances overall system efficiency and flexibility, adapting to varying heating demands within the building.
Addressing indoor air quality through the integration of air filters, purifiers, and humidity control systems contributes to creating a healthy and comfortable indoor environment. By safeguarding the system components from dust and debris, these measures not only improve air quality but also contribute to the longevity and reliability of the forced air heating system.
Finally, future-proofing the system by considering potential expansions and upgrades ensures that the heating solution remains adaptable to evolving needs and technological advancements, maximizing its longevity and relevance.
In essence, the design of a forced air heating system is a holistic process that encompasses technical expertise, thoughtful planning, and a commitment to delivering optimal comfort, efficiency, and indoor air quality. By following the systematic steps outlined in this guide, one can navigate the complexities of designing a forced air heating system with confidence, ultimately creating a tailored solution that meets the unique requirements of the space and its occupants.
Frequently Asked Questions about How To Design A Forced Air Heating System
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.
















0 thoughts on “How To Design A Forced Air Heating System”