Home>Home Appliances>Home Automation Appliances>Where Does The Thermostat Get Power From


Home Automation Appliances
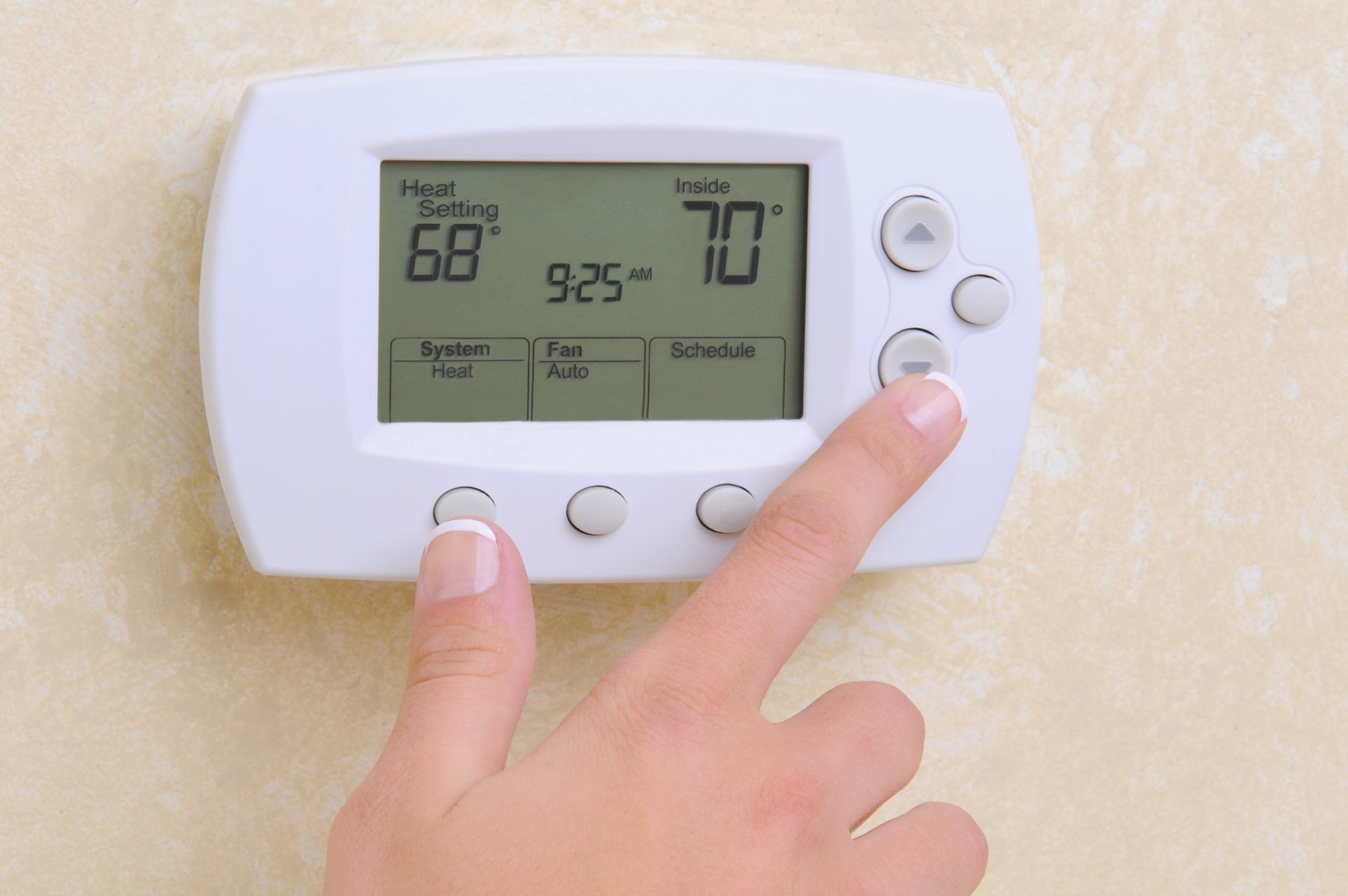
Where Does The Thermostat Get Power From
Published: January 4, 2024
Learn how home automation appliances power their thermostats and optimize your energy usage with our comprehensive guide. Discover the source of power for your thermostat.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Welcome to the heart of home automation – the thermostat. This unassuming device plays a pivotal role in maintaining the comfort and energy efficiency of your living space. It acts as the gatekeeper of your HVAC system, regulating the temperature to ensure a cozy ambiance while optimizing energy consumption. However, have you ever wondered where this essential gadget draws its power from?
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the fascinating realm of thermostat power sources, unraveling the mechanisms that keep these devices up and running. Whether you're a tech enthusiast, a homeowner seeking insights, or a curious mind eager to explore the inner workings of everyday technology, this journey promises to shed light on an often overlooked aspect of home automation. So, let's embark on this illuminating expedition to uncover the power behind the thermostat!
Key Takeaways:
- Thermostats can be powered by batteries or hardwired to the home’s electrical system, offering flexibility and reliability for temperature control in homes. Understanding the power source is crucial for seamless integration and uninterrupted functionality.
- Battery-powered thermostats provide flexibility and resilience, while hardwired thermostats offer a robust and integrated approach to HVAC management. Both options cater to different home infrastructures and maintenance needs, ensuring optimal temperature control.
Read more: How Does Ring Doorbell Get Power
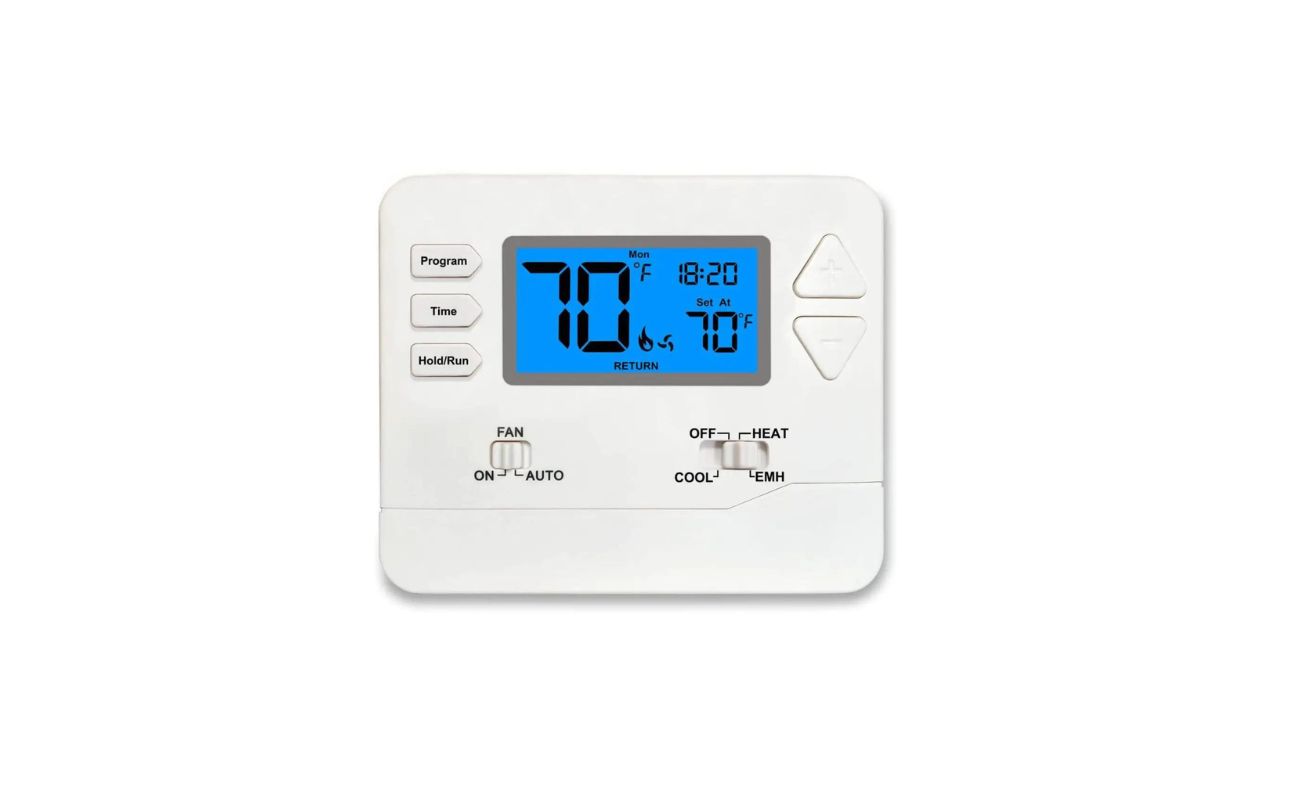
Understanding the Thermostat
Before delving into the intricacies of its power source, it’s essential to grasp the fundamental role of a thermostat. Essentially, a thermostat serves as the commander-in-chief of your heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) system. Its primary function is to maintain the desired temperature within your home by signaling the HVAC system to heat or cool the air as needed.
Modern thermostats have evolved far beyond their conventional counterparts. With the advent of smart technology, these devices have become intuitive and adaptive, capable of learning your preferences and adjusting the temperature settings accordingly. From programmable thermostats that adhere to your schedule to smart thermostats that can be controlled remotely via a smartphone, the options are diverse and sophisticated.
Furthermore, thermostats often incorporate additional features such as humidity control, air quality monitoring, and energy usage tracking. This multifaceted functionality underscores the pivotal role of the thermostat in ensuring not only comfort but also efficiency and environmental sustainability within your living space.
Now that we’ve established the significance of the thermostat in the realm of home automation, let’s unravel the mystery surrounding its power source, a vital yet often overlooked aspect of this indispensable device.
Power Sources for Thermostats
Thermostats rely on various power sources to operate seamlessly and maintain control over your HVAC system. Understanding these power sources is essential for ensuring the uninterrupted functionality of the thermostat within your home. Whether you opt for a traditional or smart thermostat, the power source plays a critical role in its performance.
Commonly, thermostats are powered by either batteries or a hardwired connection to the home’s electrical system. Each power source has its unique advantages and considerations, catering to different preferences and home setups.
As we explore the power sources for thermostats, we’ll delve into the distinctive features and benefits of battery-powered and hardwired thermostats, providing insights to help you make informed decisions when selecting or maintaining a thermostat for your home.
Common Power Sources
Thermostats draw power from a variety of sources, with the most prevalent being low-voltage electrical systems. These systems typically supply 24 volts of electricity to the thermostat, ensuring safe and efficient operation. While low-voltage systems are the standard for most residential HVAC setups, it’s important to note that line-voltage systems, which directly utilize 120 volts from the electrical grid, are also present in certain homes.
Low-voltage systems are renowned for their safety and energy efficiency. They utilize a step-down transformer to reduce the standard 120-volt household electricity to a lower voltage suitable for the thermostat and HVAC equipment. This approach minimizes the risk of electrical hazards and provides a stable power supply for the thermostat to regulate the HVAC system effectively.
On the other hand, line-voltage systems deliver the full 120 volts directly to the thermostat, bypassing the need for a step-down transformer. While this simplifies the wiring process, it’s crucial to adhere to stringent safety protocols when working with line-voltage systems due to the higher electrical potential involved.
Understanding the type of power source prevalent in your home is pivotal when installing or replacing a thermostat. It ensures compatibility and safety, allowing for a seamless integration of the thermostat into your home’s HVAC system. Additionally, being aware of the power source empowers homeowners to make informed decisions when selecting a thermostat that aligns with their specific electrical setup and preferences.
The thermostat gets power from the HVAC system or from batteries. Make sure to check the power source if your thermostat is not working properly.
Battery-Powered Thermostats
Battery-powered thermostats offer a convenient and versatile solution for regulating the temperature within your home. These thermostats are powered by internal batteries, eliminating the need for a direct electrical connection. This feature makes them particularly suitable for homes where hardwiring a thermostat to the electrical system may be challenging or impractical.
The primary advantage of battery-powered thermostats lies in their flexibility and ease of installation. Without the constraints of wiring to an electrical supply, these thermostats can be placed in various locations within the home, providing optimal temperature control without being limited by existing wiring configurations. This versatility is especially beneficial when retrofitting older homes or when seeking to install a thermostat in a location where running new wiring is not feasible.
Furthermore, battery-powered thermostats offer a reliable backup power source. In the event of a power outage, the internal batteries ensure that the thermostat continues to function, maintaining control over the HVAC system and preserving your desired temperature settings. This resilience is particularly valuable during extreme weather conditions when uninterrupted heating or cooling is essential for comfort and safety.
It’s important to note that while battery-powered thermostats offer flexibility and reliability, regular maintenance of the batteries is crucial to ensure uninterrupted operation. Periodically replacing the batteries, typically every 6 to 12 months depending on the specific thermostat model, is essential to prevent disruptions in the thermostat’s functionality.
With advancements in battery technology, modern battery-powered thermostats boast extended battery life and energy-efficient operation, reducing the frequency of battery replacements and minimizing environmental impact. These features contribute to the overall sustainability and user-friendliness of battery-powered thermostats, making them a compelling choice for homeowners seeking a hassle-free and adaptable temperature control solution.
Read more: Where Does Jenga Come From
Hardwired Thermostats
Hardwired thermostats are directly connected to the home’s electrical system, drawing power from the low-voltage or line-voltage supply to operate seamlessly. This hardwired configuration offers a reliable and continuous power source for the thermostat, eliminating the need for battery replacements and ensuring uninterrupted control over the HVAC system.
One of the primary advantages of hardwired thermostats is their consistent power supply. By being directly connected to the electrical system, these thermostats do not rely on batteries, mitigating the need for regular maintenance and battery replacements. This feature provides peace of mind, especially in homes where uninterrupted temperature control is paramount.
Moreover, hardwired thermostats are often perceived as a permanent and integrated solution for temperature regulation. Once installed and connected to the electrical system, they become an intrinsic part of the home’s HVAC infrastructure, offering a seamless and reliable mechanism for controlling the heating and cooling systems.
Additionally, hardwired thermostats are well-suited for homes with advanced HVAC systems or those incorporating smart technology. They provide a stable power supply for sophisticated features such as programmable schedules, remote access, and energy usage tracking, enhancing the overall efficiency and convenience of the HVAC system.
While hardwired thermostats offer a robust and continuous power source, their installation may require professional expertise, particularly when integrating them into the existing electrical system. Adhering to electrical codes and safety standards is crucial when working with hardwired thermostats, emphasizing the importance of engaging qualified professionals for installation and maintenance.
Ultimately, hardwired thermostats present a dependable and permanent solution for temperature control within the home. Their integration with the electrical system ensures consistent power supply, enabling seamless operation and advanced functionality, making them an ideal choice for homeowners seeking a long-term and integrated approach to HVAC management.
Conclusion
As we conclude our exploration of thermostat power sources, it’s evident that the choice between battery-powered and hardwired thermostats is influenced by various factors, including home infrastructure, convenience, and long-term maintenance considerations.
Battery-powered thermostats offer flexibility and resilience, making them an excellent choice for homes where hardwiring may be challenging or impractical. Their ability to function independently of the home’s electrical system, coupled with reliable backup power during outages, provides homeowners with a convenient and adaptable solution for temperature control.
On the other hand, hardwired thermostats present a robust and integrated approach to HVAC management. By drawing continuous power from the home’s electrical system, these thermostats offer seamless operation, advanced functionality, and long-term reliability, making them an ideal choice for homeowners seeking a permanent and dependable solution for temperature regulation.
Regardless of the power source, modern thermostats have evolved to incorporate smart features, energy-efficient operation, and intuitive interfaces, enhancing the overall comfort and sustainability of residential spaces. Whether you opt for a battery-powered or hardwired thermostat, the key lies in understanding your home’s infrastructure and selecting a solution that aligns with your preferences and lifestyle.
As technology continues to advance, the landscape of thermostat power sources is poised to evolve, offering homeowners even more options for efficient and user-friendly temperature control. By staying informed about these developments and understanding the unique advantages of each power source, homeowners can make informed decisions to optimize comfort, energy efficiency, and convenience within their living spaces.
In essence, the power behind the thermostat is not merely electrical; it’s the power to create a comfortable and sustainable home environment, tailored to your preferences and lifestyle.
Frequently Asked Questions about Where Does The Thermostat Get Power From
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.














0 thoughts on “Where Does The Thermostat Get Power From”