Home> Solar Energy
Solar Energy: Unleashing the Power of the Sun for Sustainable Living
Explore the infinite potential of Solar Energy. Learn how to harness, use it judiciously, and transition towards a sustainable future.
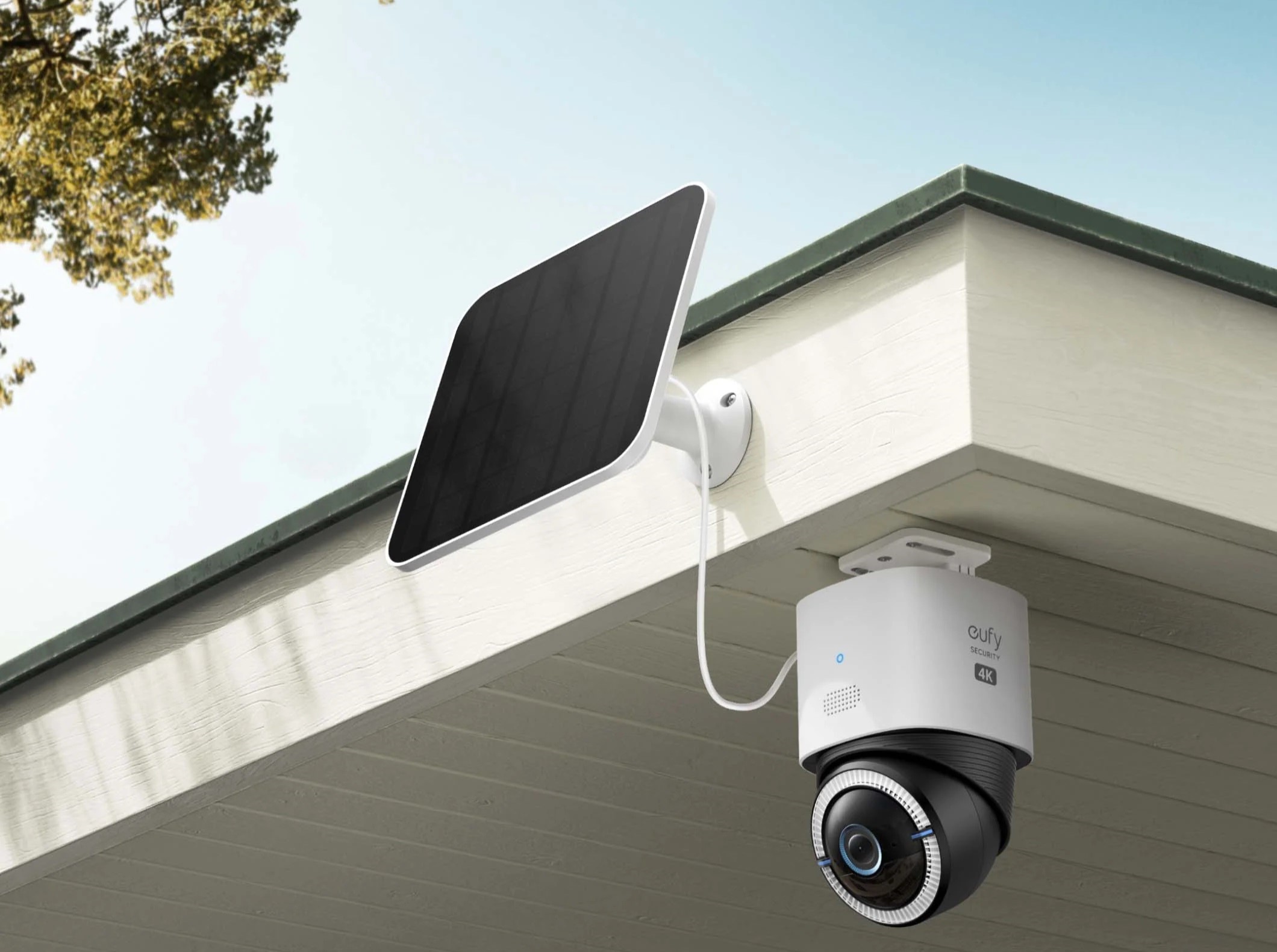
Smart Outdoor Camera with Solar Panel for a Wireless Power Solution
By: Oliver Mitchell • Ideas and Tips
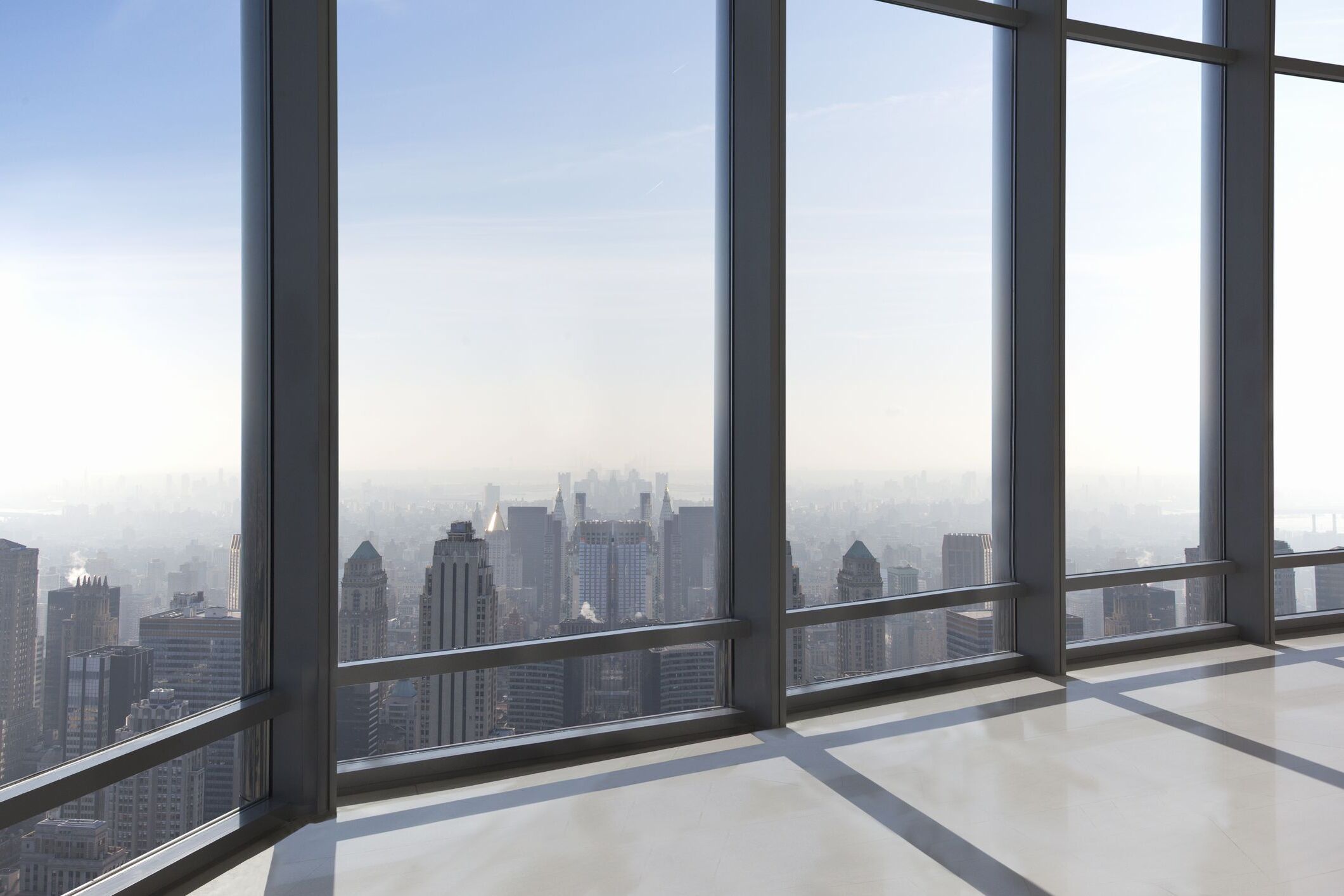
Solar Window Installation for Energy-Generating Glass Options
By: Grace Wilson • Ideas and Tips
What To Know Before Going Solar At Home To Save Money And The Planet
By: Grace Wilson • Articles