Home>Technology>Home Entertainment Systems>How Is Television Broadcast


Home Entertainment Systems
How Is Television Broadcast
Modified: January 9, 2024
Discover how television broadcast has evolved with the latest home entertainment systems. Explore the advancements in technology and enhance your viewing experience.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Television broadcast has revolutionized the way we consume media and transformed the entertainment industry. From the early days of black and white television sets to the high-definition screens we have today, television broadcast has become an integral part of our daily lives.
Television broadcast refers to the transmission of audiovisual content over the airwaves to be received by televisions in households across the country. It allows us to access a wide range of programming, including news, sports, movies, documentaries, and more, right from the comfort of our own homes.
In this article, we will explore the role of television broadcast in the media industry, delve into the technology and infrastructure behind it, discuss the different types of television broadcast, examine the process of how it works, uncover the challenges faced by broadcasters, analyze its impact on society, and speculate on its future.
Television broadcast has come a long way since its inception. It has evolved from being a limited number of channels to a vast array of options catering to a diverse range of interests. The availability of cable and satellite TV has expanded our choices, offering hundreds of channels to choose from.
Unlike streaming services that require an internet connection, television broadcast allows us to enjoy uninterrupted viewing without the need for a stable internet connection. This has made it a popular choice for people in areas with limited internet access or unreliable connectivity.
One of the key advantages of television broadcast is its ability to reach a large audience simultaneously. Live events such as sports games, award shows, and news broadcasts can be viewed by millions of people in real-time, creating a shared experience that brings people together.
Television broadcast has also played a crucial role in shaping popular culture. Iconic shows and characters have become engrained in our society, influencing fashion, language, and even social norms. The ability to see and hear stories unfold on the screen has captivated audiences for decades, creating a deep emotional connection.
In the following sections, we will dive deeper into the fascinating world of television broadcast, exploring the technology, processes, challenges, and impact it has had on our lives. So, buckle up and get ready to embark on an exciting journey through the world of television broadcast.
Key Takeaways:
- Television broadcast has evolved from black and white screens to high-definition, shaping societal values, influencing culture, and providing a platform for information, entertainment, and shared experiences.
- The future of television broadcast holds exciting possibilities, including streaming services, personalized content, enhanced accessibility, and advancements in picture quality and interactivity. Broadcasters must adapt to technological advancements and evolving consumer preferences to thrive in the dynamic media landscape.
Read more: Which Is An Effect Of The Rise Of Television Broadcasting On The American Political Process?
Role of Television Broadcast in the Media Industry
Television broadcast plays a critical role in the media industry, serving as a powerful medium for the dissemination of information, entertainment, and cultural content. It has the ability to reach a wide audience, making it an essential tool for news organizations, content creators, advertisers, and more.
One of the key roles of television broadcast is its function as a primary source of news and information. News channels provide up-to-date coverage of local, national, and international events, keeping viewers informed about current affairs. The visual nature of television allows for a more immersive and engaging experience, as viewers can witness events unfolding in real-time.
Television broadcast also plays a significant role in entertainment. It serves as a platform for the distribution of movies, TV shows, and other forms of audiovisual content. This has paved the way for the rise of popular channels and networks dedicated to specific genres, such as sports, reality TV, and drama. The availability of diverse programming caters to the varied interests and preferences of viewers.
In addition to news and entertainment, television broadcast contributes to the preservation and promotion of cultural content. Documentaries, travel shows, and educational programs allow viewers to explore different cultures, traditions, and historical events. This helps foster a sense of understanding, tolerance, and appreciation for the diversity of the world.
Television broadcast also serves as a powerful advertising platform. Advertisers can leverage the wide viewership of popular TV channels to reach their target audience. Commercial breaks during popular shows and live events provide opportunities for brands to showcase their products and services to a captive audience. This form of advertising continues to be a significant revenue source for broadcasters.
Furthermore, television broadcast plays a crucial role in shaping public opinion and influencing societal discourse. Talk shows, debates, and opinion-based programs provide a platform for discussions on various social, political, and cultural issues. They allow people from different perspectives to share their views and engage in constructive dialogue, promoting healthy civic participation.
Overall, television broadcast holds immense influence and power within the media industry. Its ability to reach a wide audience, provide news and entertainment, preserve and promote culture, facilitate advertising, and foster public opinion makes it a fundamental component of the media landscape.
In the next section, we will delve into the technology and infrastructure behind television broadcast, unraveling the mechanisms that enable the transmission of content from broadcasters to households around the world.
Television Broadcast Technology and Infrastructure
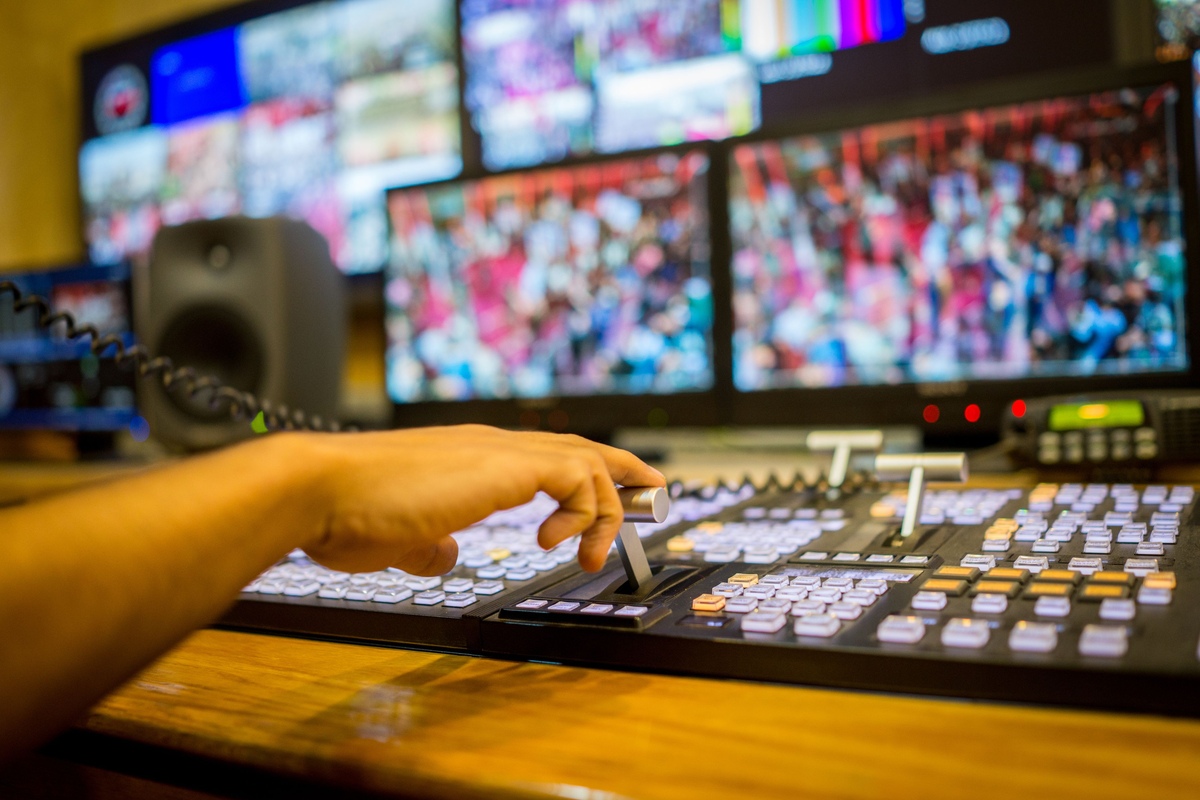
Behind the seamless transmission of television broadcast lies a complex network of technology and infrastructure. From the production of content to its distribution, a series of components work together to ensure that viewers can enjoy their favorite shows and programs. Let’s take a closer look at the technology and infrastructure that powers television broadcast.
1. Production: The production of television content involves capturing audiovisual elements, such as video footage and sound recordings. This is typically done using professional cameras, microphones, and other recording equipment. The content is then edited, processed, and formatted for broadcast, ensuring that it meets the technical specifications required for transmission.
2. Transmission: Once the content is ready for broadcast, it needs to be transmitted to viewers’ television sets. This is achieved through a combination of digital and analog transmission methods. Digital transmission involves encoding the audiovisual content into a digital format, which is then transmitted as data packets over the airwaves. Analog transmission, which was used in the past, involves modulating the audio and video signals onto radio waves. The transmission is usually done through broadcasting towers, satellite systems, or cable networks.
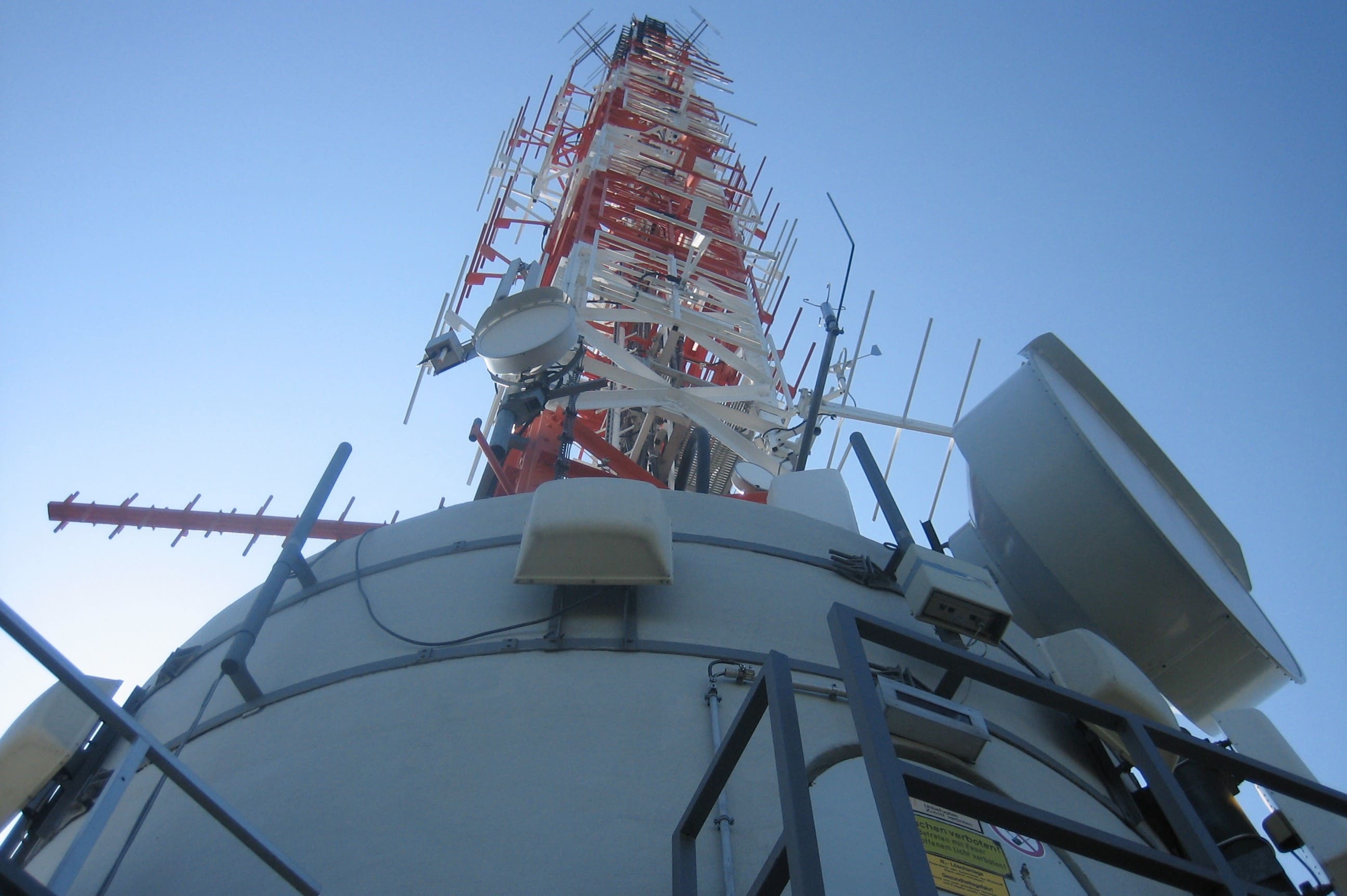
3. Broadcasting Towers: Broadcasting towers play a crucial role in transmitting television signals over long distances. These tall structures are equipped with transmitting antennas, which emit the encoded signals into the airwaves. Broadcasting towers are strategically located to ensure maximum coverage for viewers in a specific geographic area. The signals emitted by these towers can be picked up by television antennas on rooftops or indoor antennas to be decoded and displayed on television sets.
4. Satellite Systems: Satellite systems are another important component of television broadcast infrastructure. Satellites in geostationary orbit receive television signals from the broadcasters and retransmit them to a wide geographic area. Viewers with satellite dishes can receive these signals and decode them using set-top boxes connected to their TVs. Satellite systems enable viewers to access a wide range of international channels and ensure reliable reception, even in remote or rural areas.
5. Cable Networks: Cable networks are commonly used to deliver television signals to households. These networks consist of a series of cables, amplifiers, and distribution hubs that carry the audiovisual signals from the broadcasting source directly to viewers’ homes. Cable networks offer a wide variety of channels and services, including digital cable, video-on-demand, and interactive features. They provide a reliable and high-quality viewing experience, particularly in densely populated areas.
6. Set-Top Boxes: Set-top boxes are devices that are connected to television sets to receive and decode television signals. These devices can convert digital signals into analog signals or vice versa, depending on the requirements of the TV set. Set-top boxes may also provide additional features, such as digital video recording (DVR), on-demand services, and interactive program guides.
Together, these technological components and infrastructure form the backbone of television broadcast. They enable the production, transmission, and reception of audiovisual content, ensuring that viewers can enjoy their favorite shows, movies, news programs, and more from the comfort of their living rooms.
In the next section, we will explore the different types of television broadcast, shedding light on the various methods through which content is delivered to viewers.
Types of Television Broadcast
Television broadcast comes in different forms, each offering unique ways to deliver content to viewers. Let’s explore the various types of television broadcast and how they differ in terms of distribution and accessibility.
1. Terrestrial Broadcast: Terrestrial broadcast is the traditional form of television broadcast that utilizes the airwaves to transmit signals over a specific geographic area. This type of broadcast relies on broadcasting towers to emit signals that are picked up by television antennas. Terrestrial broadcast provides free over-the-air access to a range of channels, including local and national networks. It is the most widely accessible form of television broadcast, as it only requires a compatible television set and an antenna.
2. Satellite Broadcast: Satellite broadcast involves the transmission of television signals via communication satellites in geostationary orbit. These satellites receive signals from broadcasters and then retransmit them back to Earth across a wide coverage area. Satellite broadcast enables viewers to access a vast array of channels, including international networks and specialty channels. To receive satellite broadcast, viewers need a satellite dish and a compatible receiver or set-top box.
3. Cable Broadcast: Cable broadcast utilizes cable networks to deliver television signals directly to households. Cable networks consist of a network of cables, amplifiers, and distribution hubs that deliver a wide range of channels and services. Cable broadcast offers a high-quality viewing experience and provides additional features like digital cable, video-on-demand, and interactive features. To access cable broadcast, viewers need a cable subscription and a cable box or a television with a built-in cable tuner.
4. Internet Protocol Television (IPTV): IPTV is a digital television broadcasting method that uses internet protocol (IP) networks to transmit television signals. It allows viewers to access live TV, on-demand content, and interactive features through an internet connection. IPTV services are usually provided by internet service providers (ISPs) and require a set-top box or smart TV with IPTV capabilities. This type of broadcast offers flexibility and convenience, as viewers can watch their favorite shows on multiple devices, such as TVs, computers, tablets, and smartphones.
5. Streaming Services: Streaming services have gained immense popularity in recent years. These services deliver television content over the internet, allowing viewers to stream shows and movies on-demand. Streaming services, such as Netflix, Hulu, and Amazon Prime Video, provide a vast library of content that can be accessed on various devices with an internet connection. They often require a subscription fee and offer the convenience of watching content anytime, anywhere.
Each type of television broadcast has its own advantages and considerations. Terrestrial broadcast provides free access to basic channels, while satellite and cable broadcast offer a wider range of channels for a subscription fee. IPTV and streaming services provide greater flexibility and convenience, allowing viewers to access content on-demand. The choice of television broadcast type depends on factors such as budget, geographical location, available infrastructure, and personal viewing preferences.
In the next section, we will dive into the process of television broadcast, uncovering the steps involved in bringing content from broadcasters to the screens of viewers.
Process of Television Broadcast
The process of television broadcast involves a series of steps to ensure that content created by broadcasters reaches viewers’ screens seamlessly. Let’s delve into the key stages of television broadcast, from content production to transmission.
1. Content Creation: The process starts with the creation of television content, which includes filming, editing, and formatting. Producers, directors, cameramen, and editors work together to capture the necessary video footage, record audio, and assemble the content into a cohesive and engaging program.
2. Signal Encoding: Once the content is ready, it needs to be encoded into a format suitable for transmission. Encoding involves compressing the audio and video signals into a digital format, reducing the file size while maintaining quality. Common encoding formats include MPEG-2 and H.264. This encoded content is then stored in servers or transmitted in real-time for live events.
3. Transmission: The encoded content is ready for transmission to viewers’ television sets. The transmission process varies depending on the type of broadcast. For terrestrial broadcast, the encoded signals are sent to broadcasting towers, where they are propagated over the airwaves for reception by TV antennas. Satellite broadcast involves transmitting the signals to communication satellites, which then retransmit them back to Earth for reception with satellite dishes. Cable broadcast utilizes cable networks to directly deliver the signals to households.
4. Signal Reception: Viewers receive the transmitted signals using different equipment, depending on the type of broadcast. For terrestrial broadcast, viewers need a television antenna to capture the signals and a TV tuner to decode and display the content on their screens. Satellite broadcast requires a satellite dish and a set-top box or receiver to receive and decode the signals. Cable broadcast requires a cable subscription and a cable box or a TV with a built-in cable tuner.
5. Decoding and Display: The received signals are then decoded using set-top boxes or TV tuners, depending on the type of broadcast. These devices extract the audio and video information from the signals and convert them into a format that can be displayed on television screens. The decoded content is sent to the TV screen for viewers to watch and enjoy.
6. Quality Control: Throughout the entire process, quality control measures are implemented to ensure the broadcast meets technical standards and provides an optimal viewing experience. Broadcasters conduct rigorous tests to check for any issues in picture and sound quality, syncing issues, and adherence to content standards and regulations. Any discrepancies or technical glitches are rectified to maintain the highest quality broadcast.
These steps, from content creation to transmission and reception, demonstrate the complexity and precision involved in the television broadcast process. Television broadcasters work diligently to deliver high-quality content to viewers, ensuring an enjoyable and immersive television viewing experience.
In the next section, we will explore the challenges faced by broadcasters in the ever-evolving landscape of television broadcast.
When setting up a television broadcast, ensure that you have a strong and stable internet connection to prevent any interruptions or buffering during the live stream. Additionally, test your equipment and audiovisual settings beforehand to ensure everything is working properly.
Challenges in Television Broadcast
The world of television broadcast is not without its challenges. Broadcasters and industry professionals face various hurdles as they strive to deliver high-quality content to viewers. Let’s explore some of the significant challenges in the landscape of television broadcast.
1. Technological Advances: The rapid pace of technological advancements presents a continuous challenge for broadcasters. As new technologies emerge, broadcasters must adapt and upgrade their infrastructure to keep up with the changing landscape. This includes investing in equipment, software, and training to ensure compatibility and optimal performance.
2. Bandwidth Limitations: The demand for more channels, higher picture quality, and interactive features puts strain on the available bandwidth for television broadcast. Bandwidth limitations can lead to compression techniques that may sacrifice some picture quality. Broadcasters need to find a balance between delivering high-quality content and managing the limitations of available bandwidth.
3. Signal Interference: Interference from various sources, such as weather conditions, tall buildings, or other electronic devices, can disrupt television signals. This can result in signal degradation or complete loss of reception. Broadcasters continually work on mitigating signal interference through advanced signal processing techniques and infrastructure improvements.
4. Content Piracy: The rise of digital streaming platforms and the internet has given rise to content piracy. Unlicensed streaming and illegal distribution of copyrighted television content pose a significant challenge for broadcasters, content creators, and copyright holders. Broadcasters need to implement robust digital rights management systems and work with law enforcement agencies to combat piracy.
5. Audience Fragmentation: With the proliferation of streaming services and online content platforms, audiences are increasingly fragmented. Viewers have more options available to them, leading to a shift away from traditional broadcast channels. Broadcasters must adapt their programming and distribution strategies to cater to changing audience preferences and compete in a crowded media landscape.
6. Content Regulation: Broadcasting content that adheres to content regulations and guidelines is a challenge for broadcasters. Different countries have specific regulations related to content standards, censorship, advertising, and other aspects of television broadcast. Compliance with these regulations requires careful monitoring and adherence to ensure that content meets the required standards.
7. Monetization and Ad Revenue: Television broadcast heavily relies on advertising revenue as a source of monetization. However, with the rise of ad-blocking technology, shifting consumer behavior, and competition from other digital platforms, broadcasters face challenges in generating sufficient ad revenue. Finding innovative ways to monetize content, such as branded content partnerships and subscription models, is crucial in sustaining the financial viability of television broadcast.
Despite these challenges, broadcasters continue to innovate and adapt to the evolving landscape of television broadcast. Through technological advancements, strategic partnerships, audience engagement, and creativity, they strive to overcome these hurdles and deliver compelling content to viewers worldwide.
In the next section, we will explore the impact of television broadcast on society and individuals.
Impact of Television Broadcast on Society
Television broadcast has had a profound impact on society, shaping our beliefs, influencing our culture, and providing a platform for information and entertainment. Let’s explore the various ways in which television broadcast has influenced society and individuals.
1. News and Information: Television broadcast plays a crucial role in providing news and information to the masses. News channels keep viewers informed about local, national, and global events, helping to shape public opinion and create a sense of awareness. Television news has the power to influence societal perspectives, driving conversations and discussions on important topics.
2. Education and Learning: Television broadcast has been instrumental in the field of education. Educational programs and documentaries provide a platform for learning, allowing viewers of all ages to explore various subjects and acquire knowledge. Through informative shows, documentaries, and educational channels, television broadcast has made education accessible to a wide audience, regardless of their geographical location or economic background.
3. Cultural Impact: Television broadcast has had a significant impact on cultural norms and traditions. Television shows and characters have become part of popular culture, influencing fashion, language, and social behavior. Television has the power to bring people together, creating shared experiences and fostering a sense of community. It has contributed to the evolution of societal values and the acceptance of diversity.
4. Entertainment: One of the primary purposes of television broadcast is to provide entertainment. Television shows, movies, and sports broadcasts have become a staple of leisure time for individuals across the globe. They offer a form of escapism, relaxation, and enjoyment. Television broadcast’s ability to provide a wide variety of entertainment options has contributed to a rich and vibrant global entertainment industry.
5. Advertising and Consumerism: Television broadcast has played a pivotal role in shaping consumer behavior. The presence of advertisements during television programs has influenced viewers’ purchasing decisions and preferences. It has given rise to consumer culture and has been an essential revenue source for broadcasters. Television commercials have the power to create trends, promote products, and shape consumer attitudes.
6. Social Awareness and Activism: Television broadcast has been instrumental in raising social awareness and promoting activism. Documentaries and investigative reports shed light on important social and environmental issues, motivating viewers to take action and make a positive difference in the world. Television has provided a platform for marginalized voices and social movements, amplifying their message and fostering social change.
7. Family Bonding: Television broadcast has been a significant catalyst for family bonding and shared experiences. Families gather around the television to watch their favorite shows, sports events, and movies together. It creates opportunities for conversation, laughter, and connection. Television has become a common ground for families to come together and spend quality time.
Television broadcast has undoubtedly had a far-reaching impact on society and individuals. It has shaped our understanding of the world, influenced our cultural values, and provided a platform for expression and entertainment. As the media landscape continues to evolve, television broadcast remains a powerful medium that has the potential to make a lasting impact.
In the final section, we will explore the future of television broadcast and its potential developments.
Future of Television Broadcast
The future of television broadcast holds exciting possibilities as technology continues to advance and consumer expectations evolve. While traditional broadcast methods will likely remain relevant, several notable trends and developments are shaping the future of television broadcast.
1. Streaming Services: Streaming services have disrupted the television broadcast industry, and their popularity is expected to continue to grow. With the rise of internet-connected devices and the increasing demand for on-demand content, streaming services like Netflix, Amazon Prime Video, and Disney+ are becoming primary sources of entertainment for many viewers. As these services expand their original programming and exclusive content, they are reshaping the way audiences consume television content.
2. Over-the-Top (OTT) Services: Over-the-top services deliver television content over the internet, bypassing traditional broadcast platforms. OTT services offer the flexibility of streaming on various devices, including smart TVs, smartphones, and tablets. With the increasing popularity of OTT services, traditional broadcasters are also adopting hybrid models, combining their broadcast channels with internet streaming platforms to cater to changing viewer preferences.
3. High-Definition and 4K Broadcasting: High-definition (HD) and 4K broadcasting are becoming more prevalent, enhancing the viewing experience with crystal-clear visuals and immersive sound. As technology advances, we can expect an increase in 4K content availability and the eventual transition to 8K broadcasting. These advancements in picture quality will provide viewers with a more immersive and lifelike television experience.
4. Personalized and Interactive Content: The future of television broadcast will embrace personalization and interactivity. Viewers will have more control over the content they consume, with personalized recommendations, customized playlists, and interactive features that allow them to engage with the content in real-time. Interactive advertising and targeted messaging will also become more prevalent, tailoring advertisements to individual viewer preferences and demographics.
5. Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality: Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) technologies have the potential to transform the television broadcast experience. AR can overlay additional information or graphics onto the screen, providing enhanced context and interactivity. VR can transport viewers into immersive virtual environments, creating a fully interactive and immersive viewing experience. These technologies will provide new avenues for storytelling and audience engagement.
6. Enhanced Accessibility: The future of television broadcast will prioritize accessibility for all viewers. Subtitles, closed captions, and audio descriptions will be more readily available, ensuring that people with hearing or visual impairments can fully engage with the content. User-friendly interfaces and voice-controlled navigation will also enhance accessibility, making it easier for everyone to navigate through channels and content options.
7. Convergence of Broadcast and Internet Technologies: The lines between traditional broadcast and internet technologies will continue to blur. Broadcasters will embrace internet-based distribution methods to reach audiences beyond the limitations of terrestrial or satellite transmission. Hybrid models that combine broadcast and streaming technologies will allow viewers to seamlessly switch between live content and on-demand programming.
As the future of television broadcast unfolds, it will be shaped by technological advancements, evolving consumer preferences, and the need to adapt to an ever-changing media landscape. While the core principles of television broadcast will persist, embracing innovation and staying attuned to viewer demands will be key for broadcasters to thrive in the dynamic and exciting future ahead.
As we conclude our exploration of television broadcast, it is clear that this medium continues to play a significant role in our lives, providing us with information, entertainment, and shared experiences. The future promises even more immersive, personalized, and interactive viewing experiences that will captivate and engage audiences for years to come.
Conclusion
Television broadcast has revolutionized the way we access and consume media, making it an integral part of our daily lives. From the early days of black and white television sets to the high-definition screens we have today, television broadcast has continuously evolved to meet the demands of viewers and adapt to technological advancements.
Throughout this article, we have explored the role of television broadcast in the media industry and its impact on society. We have delved into the technology and infrastructure behind television broadcast, including terrestrial, satellite, cable, and internet-based methods of transmission. We have also discussed the process of television broadcast, from content creation to transmission and reception.
Television broadcast has had a profound impact on society. It has shaped our beliefs, influenced our culture, and provided a platform for information, entertainment, and education. The power of television to bring people together, raise awareness, and promote social change cannot be understated.
The future of television broadcast looks promising, with streaming services, personalized content, enhanced accessibility, and advancements in picture quality and interactivity. Television broadcast will continue to evolve and adapt, embracing technological advancements and consumer preferences to provide innovative and compelling viewing experiences.
As broadcasters and industry professionals navigate the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead, it is essential to remain committed to delivering high-quality content, fostering diversity, and promoting ethical practices. By staying connected with viewers, embracing new technologies, and adapting to the changing media landscape, television broadcast will continue to thrive and captivate audiences worldwide.
In conclusion, television broadcast has played a transformative role in shaping our world and will continue to be a powerful medium for information, entertainment, and cultural expression. Whether through the news that keeps us informed, the shows that entertain us, or the shared experiences that bring us together, television broadcast has become an inseparable part of our modern society.
Frequently Asked Questions about How Is Television Broadcast
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.














0 thoughts on “How Is Television Broadcast”