

Articles
How Does An AC Unit Work
Modified: January 18, 2024
Discover how an AC unit works with this informative article. Learn about the different components and processes involved in cooling your home.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
An AC unit, also known as an air conditioner or air conditioning system, is a vital appliance that brings comfort and relief during hot summer months. It is designed to cool indoor spaces by removing heat and humidity from the air. AC units have become a common feature in homes, offices, and various commercial establishments.
Understanding how an AC unit works can help us appreciate the science behind its cooling capabilities. In this article, we will delve into the components, functioning, and key features of AC units, as well as tips for maintenance and troubleshooting.
Before the invention of air conditioning, people relied on natural ventilation methods, such as opening windows or using fans, to beat the heat. However, these methods were not always effective, especially in areas with high temperatures or humid climates. The advent of AC units revolutionized the way we control indoor temperatures, providing us with a more comfortable and livable environment.
AC units work by manipulating the thermal properties of air to create a cooling effect. They utilize a combination of mechanical, electrical, and chemical processes to achieve this. The basic principle behind an AC unit is the removal of heat from the indoor air, resulting in a decrease in temperature.
In the following sections, we will explore the different components of an AC unit, understand its functioning, learn about the role of refrigerants, discover key features, consider energy efficiency, and provide maintenance and troubleshooting tips to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Key Takeaways:
- Understanding the intricate process of how an AC unit works, from the refrigeration cycle to air circulation, empowers users to make informed decisions about maintenance and energy efficiency, ensuring optimal cooling comfort.
- By embracing eco-friendly refrigerants, prioritizing energy-efficient features, and practicing regular maintenance, AC unit owners can enjoy cool indoor environments while minimizing their environmental impact and saving on electricity bills.
Read more: How Does AC Work In A Tesla
Components of an AC Unit
AC units consist of several essential components that work together to achieve the cooling process. These components include the compressor, evaporator coil, condenser coil, expansion valve, fan, and thermostat. Let’s take a closer look at each of these components and their roles in the AC unit.
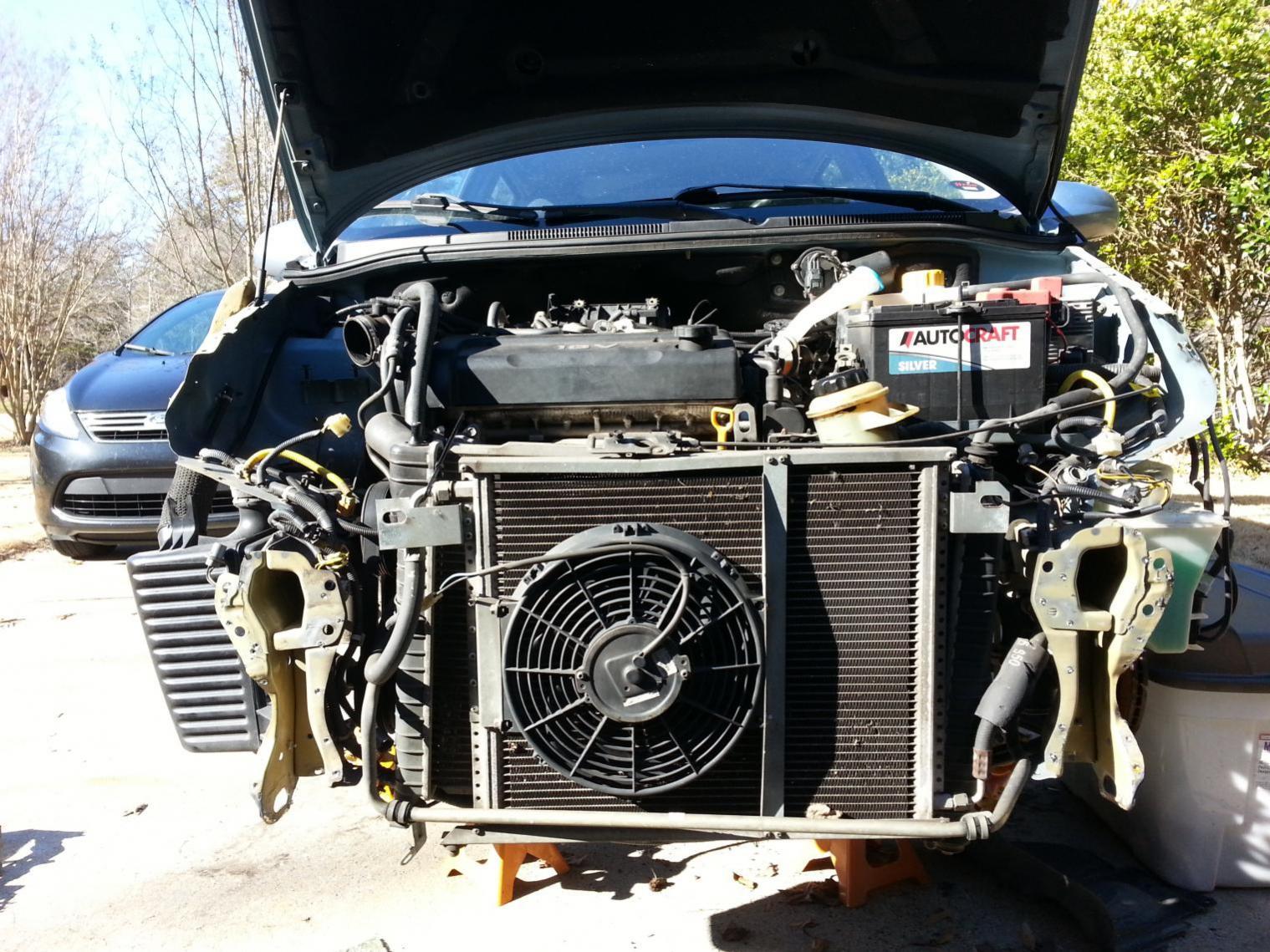
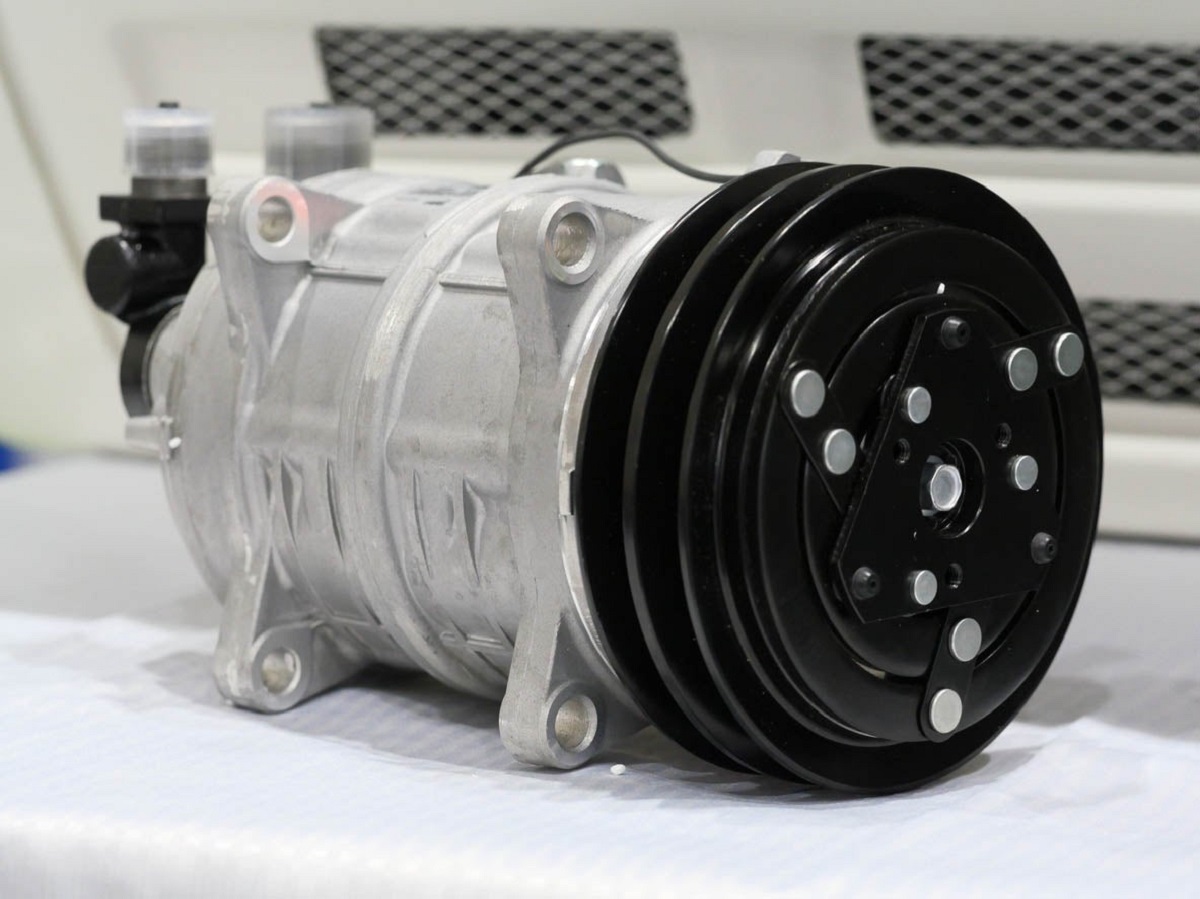
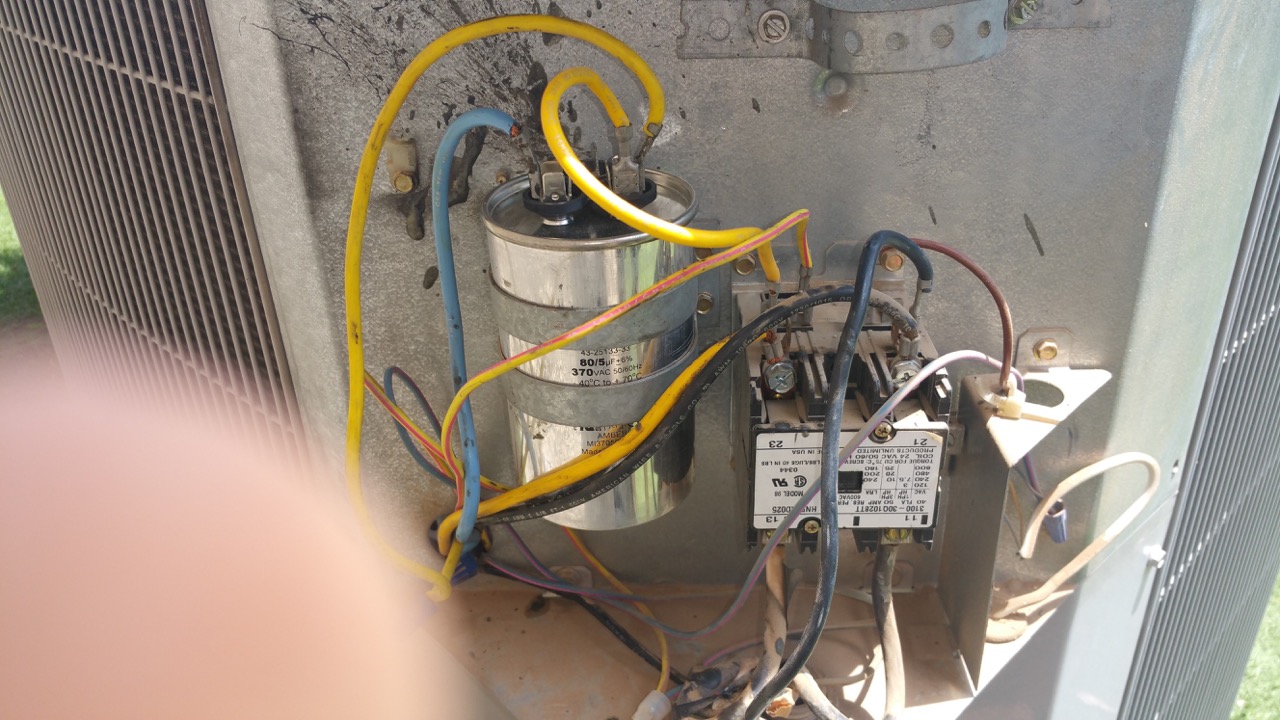
- Compressor: The compressor is considered the heart of the AC unit. It is responsible for compressing the refrigerant gas and raising its temperature and pressure. This high-pressure gas then moves to the condenser coil for the next stage of the cooling process.
- Evaporator Coil: The evaporator coil is located indoors and plays a vital role in cool air production. As the refrigerant flows through the coil, it absorbs heat from the indoor air, causing the air to cool down.
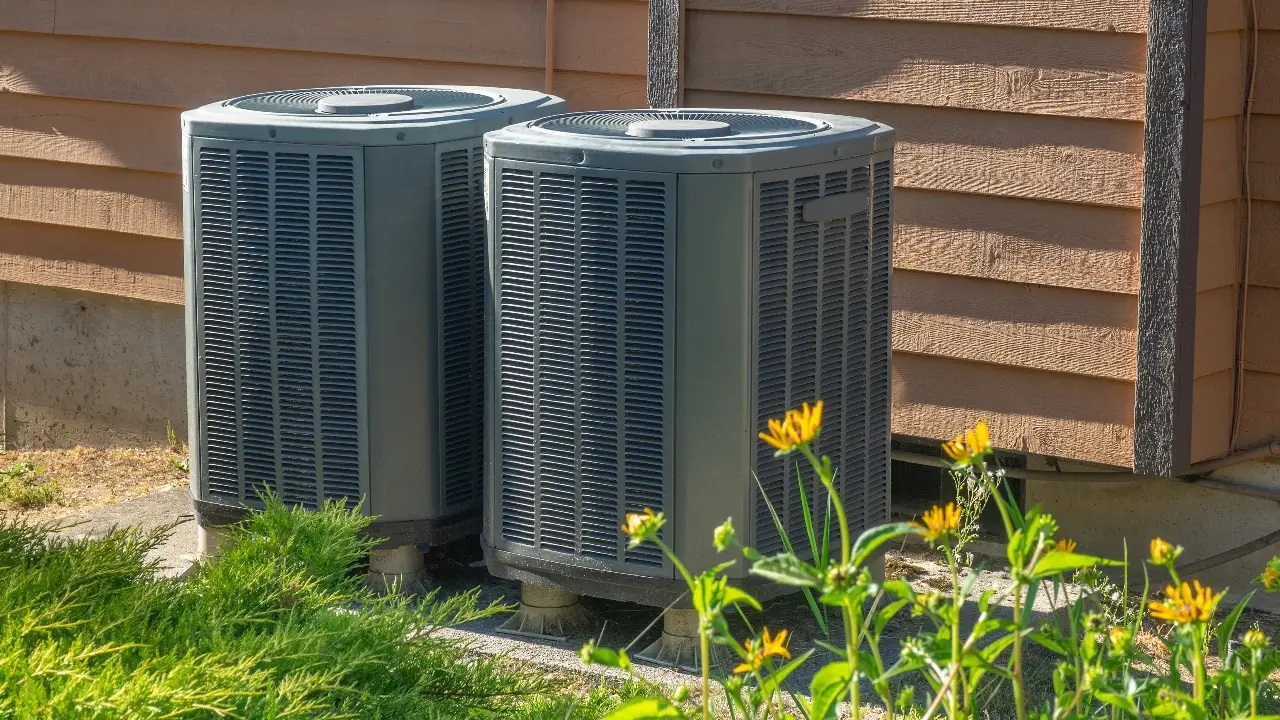
- Condenser Coil: The condenser coil is the counterpart to the evaporator coil and is located in the outdoor unit of the AC system. Its primary function is to release the heat absorbed by the refrigerant to the outside environment.
- Expansion Valve: The expansion valve regulates the flow of the refrigerant into the evaporator coil. By controlling the amount of refrigerant entering the coil, it helps maintain the desired cooling effect.
- Fan: AC units have two fans: the condenser fan and the evaporator fan. The condenser fan assists in dissipating heat from the system by blowing air through the condenser coil. The evaporator fan facilitates the circulation of cool air in the indoor space.
- Thermostat: The thermostat serves as the control panel of the AC unit. It allows users to set and regulate the desired temperature. Once the temperature reaches the set point, the thermostat signals the AC unit to turn on or off accordingly.
These components work in tandem to extract heat from the indoor air and release it outside, thereby creating a cool and comfortable environment. Understanding these components is crucial for troubleshooting and maintaining the AC unit’s optimal performance.
Functioning of an AC Unit
To understand the functioning of an AC unit, let’s walk through the step-by-step process of how it cools the indoor space. The functioning of an AC unit can be summarized in three main stages: the refrigeration cycle, air circulation, and temperature control.
Refrigeration Cycle: The refrigeration cycle is the core mechanism through which an AC unit cools the air. It starts with the compressor, which compresses the refrigerant gas, increasing its temperature and pressure. This hot, high-pressure gas then flows to the condenser coil, where it is cooled and condensed into a liquid state due to the surrounding air or a fan-assisted process.
Once in its liquid form, the refrigerant moves through the expansion valve, which regulates its flow rate into the evaporator coil. As the liquid refrigerant enters the evaporator coil, it expands, causing a drop in pressure. This drop in pressure allows the refrigerant to absorb heat from the surrounding air, cooling it down in the process. The cooled air is then blown into the indoor space by the evaporator fan, while the heat absorbed by the refrigerant is carried back to the condenser for release.
Air Circulation: Air circulation plays a crucial role in the functioning of an AC unit. The cooled air generated by the evaporator fan is distributed throughout the indoor space, creating a comfortable environment. The AC unit pulls in warm air from the room, passes it over the evaporator coil to cool it down, and then circulates the cooled air back into the room. This continuous cycle ensures the maintenance of a desired temperature and humidity level.
Temperature Control: The temperature control aspect of an AC unit is managed by the thermostat. The thermostat allows users to set the desired temperature, and it continuously monitors the current temperature in the room. When the temperature rises above the set point, the thermostat sends a signal to the AC unit to turn on and start the cooling process. Once the temperature reaches the desired level, the AC unit shuts off to conserve energy until the temperature rises again.
By understanding the functioning of an AC unit, users can appreciate the intricate process involved in cooling the indoor space. It is important to note that proper maintenance and regular servicing are essential to ensure the optimal performance and longevity of an AC unit.
The Role of Refrigerants
Refrigerants play a vital role in the functioning of AC units. They are substances with unique thermodynamic properties that enable them to transfer heat efficiently. These substances undergo various phase transitions, changing from a gas to a liquid and vice versa, as they move through the refrigeration cycle.
The primary function of refrigerants in an AC unit is to absorb heat from the indoor air and release it outside. During the first stage of the refrigeration cycle, the refrigerant gas is compressed and heated by the compressor, turning it into a hot, high-pressure gas. As it flows through the condenser coil, the refrigerant releases heat to the surrounding environment, causing it to condense into a liquid.
The liquid refrigerant then passes through the expansion valve, where its pressure is reduced, causing it to evaporate and turn back into a gas. This phase change from liquid to gas is crucial, as it absorbs heat from the surrounding air, cooling it down. The cooled air is then circulated into the indoor space by the evaporator fan.
Refrigerants are chosen based on their thermodynamic properties, environmental impact, and safety considerations. The most commonly used refrigerants in AC units were chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs), as they offered excellent cooling properties. However, due to their harmful impact on the ozone layer, these refrigerants have been phased out and replaced with more environmentally friendly alternatives.
The most widely used refrigerants in modern AC units are hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), such as R-410A and R-134a. These refrigerants have zero ozone depletion potential (ODP), meaning they do not harm the ozone layer. However, they still have a high global warming potential (GWP), contributing to climate change.
In recent years, there has been a growing focus on developing refrigerants with lower GWPs. Refrigerants, such as R-32 and R-1234yf, are emerging as more sustainable options. These refrigerants have significantly lower GWPs and are considered to be more eco-friendly alternatives to HFCs.
Efforts are also being made to develop natural refrigerants, such as ammonia (R-717), carbon dioxide (R-744), and hydrocarbons (R-290, R-600a). These natural refrigerants have minimal or no impact on the ozone layer and have low GWPs. However, they require specialized equipment and safety measures due to their flammability or toxicity.
The role of refrigerants in AC units is crucial for achieving efficient and effective cooling. As environmental awareness increases, there is a continuous drive toward using refrigerants with minimal environmental impact and improved efficiency. The selection of the appropriate refrigerant for an AC unit is essential for ensuring optimal performance while minimizing harm to the environment.
Regular maintenance of your AC unit, including cleaning or replacing filters, can improve its efficiency and extend its lifespan.
Key Features of AC Units
AC units come with a variety of features that enhance their functionality and user experience. These features vary depending on the type and model of the AC unit. Let’s explore some of the key features commonly found in AC units.
- Adjustable Thermostat: AC units are equipped with adjustable thermostats that allow users to set and control the desired temperature. This feature ensures personalized comfort and energy efficiency by maintaining a consistent temperature in the room.
- Multiple Cooling Modes: Modern AC units offer different cooling modes to suit various preferences and climate conditions. These modes may include normal mode for regular cooling, fan-only mode for air circulation without cooling, and sleep mode for nighttime comfort while conserving energy.
- Programmable Timer: The programmable timer feature allows users to set specific start and stop times for the AC unit. This feature is beneficial for energy-saving purposes, as it enables automatic operation and the ability to cool a space before returning home.
- Remote Control: AC units often come with a remote control for convenient operation from a distance. This feature eliminates the need to physically adjust settings on the unit itself and provides easy access to temperature controls, fan speed, and other functions.
- Energy Efficiency Rating: AC units are rated for energy efficiency using the Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) for cooling performance. Higher SEER ratings indicate better energy efficiency, resulting in lower electricity bills and reduced environmental impact.
- Air Purification Filters: Many AC units are equipped with air purification filters that remove dust, pollen, and other airborne particles from the indoor air. These filters help improve indoor air quality by reducing allergens and pollutants.
- Smart Technology Integration: With the rise of smart home technology, some AC units are compatible with smart devices and can be controlled using smartphone apps or voice assistants. This feature provides convenience and remote access for controlling and monitoring the AC unit.
- Quiet Operation: AC units incorporate noise reduction technology to minimize operational noise. Quiet operation is especially important for bedrooms, living rooms, and office spaces to maintain a peaceful and comfortable environment.
These key features enhance the performance, convenience, and energy efficiency of AC units. When choosing an AC unit, consider the specific features that align with your needs and preferences to ensure optimal comfort and functionality.
Read more: How Does A AC Compressor Work
Energy Efficiency and AC Units
Energy efficiency is a crucial consideration when selecting an AC unit, as it not only impacts your electricity bills but also contributes to environmental sustainability. Energy-efficient AC units are designed to cool indoor spaces while consuming minimal power, reducing both energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. Understanding the energy efficiency rating and implementing a few simple practices can help maximize energy savings and minimize environmental impact.
One of the primary indicators of AC unit energy efficiency is the Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER). SEER ratings evaluate the cooling output of an AC unit over a cooling season relative to the energy it consumes. Higher SEER ratings indicate better efficiency, meaning the AC unit can cool a space using less energy, resulting in lower operating costs.
To ensure efficient operation, consider the size and capacity of the AC unit in relation to the room or space it will cool. An oversized AC unit may cool the space quickly, but it will turn on and off frequently, resulting in inefficient operation and increased energy consumption. Conversely, an undersized unit will struggle to cool the space effectively and may run continuously, wasting energy. Consult an HVAC professional to determine the appropriately sized AC unit for your needs.
To optimize energy efficiency, follow these best practices:
- Regular Maintenance: Clean or replace air filters regularly to ensure proper airflow and efficient operation. Dirty filters restrict airflow, making the AC unit work harder and consume more energy.
- Proper Insulation: Ensure that windows, doors, and other openings in the space are properly insulated to prevent heat infiltration and maximize cooling efficiency. Good insulation reduces the load on the AC unit, allowing it to operate more efficiently.
- Smart Thermostat Usage: Utilize programmable or smart thermostats to set temperature schedules and adjust settings based on occupancy. This allows for more energy-efficient cooling, especially when the space is unoccupied.
- Zoning Systems: Consider implementing a zoning system that allows you to cool specific areas or zones of your home independently. This helps minimize energy consumption by only cooling the areas that are actively being used.
- Natural Ventilation: During cooler periods, consider utilizing natural ventilation techniques by opening windows or using ceiling fans to circulate fresh air. This can help reduce reliance on the AC unit and save energy.
- Regular Maintenance: Schedule annual maintenance for your AC unit, including professional cleaning, lubrication, and inspection. Regular maintenance ensures that the AC unit performs optimally, maximizing energy efficiency and prolonging its lifespan.
By adopting these energy-efficient practices and investing in a high SEER-rated AC unit, you can reduce energy consumption, lower your carbon footprint, and save money in the long run. Additionally, supporting energy-efficient technology contributes to global efforts to combat climate change and promote sustainable living.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting Tips
Regular maintenance and troubleshooting are essential to keep your AC unit running smoothly and efficiently. By following these tips, you can prevent potential problems, extend the lifespan of your AC unit, and avoid costly repairs.
- Clean or Replace Air Filters: Dirty or clogged air filters can restrict airflow, reduce cooling efficiency, and strain the AC unit. Clean or replace filters every one to three months, depending on usage, to ensure proper airflow and maintain optimal performance.
- Inspect and Clean Condenser Coils: Over time, the condenser coils in the outdoor unit can accumulate dirt, dust, and debris, hindering airflow and heat transfer. Regularly inspect and clean the condenser coils to improve efficiency. Use a soft brush or vacuum cleaner to remove debris gently.
- Clear Debris around Outdoor Unit: Keep the area around the outdoor unit clear of debris, leaves, grass, and other obstructions. This will ensure proper airflow and prevent potential damage to the unit.
- Check Refrigerant Levels: Insufficient or excessive refrigerant levels can affect cooling performance. If you notice diminished cooling or icing on the evaporator coil, contact a professional to check and recharge the refrigerant if necessary.
- Inspect and Clean Evaporator Coil: Over time, the evaporator coil can collect dirt and dust, affecting the cooling process. Periodically inspect and clean the coil using a soft brush or a specialized cleaner to maintain efficient heat exchange.
- Inspect and Lubricate Fan Motors: Inspect the fan motors in the outdoor unit and the indoor unit to ensure they are clean and properly lubricated. Lack of lubrication can cause motor strain and increase energy consumption. Consult the manufacturer’s manual for proper lubrication guidelines.
- Check and Reset Circuit Breakers: If your AC unit is not powering on, check the circuit breaker box to see if a breaker has tripped. If so, reset the breaker. However, if the breaker trips repeatedly, contact an HVAC professional to identify and resolve any underlying electrical issues.
- Test and Calibrate Thermostat: Check the accuracy of your thermostat by comparing the displayed temperature with a reliable thermometer. If there is a significant difference, recalibrate or replace the thermostat to ensure accurate temperature control.
- Schedule Professional Maintenance: Even with regular DIY maintenance, it is essential to schedule annual professional maintenance. HVAC technicians can thoroughly inspect and service your AC unit, addressing any potential issues and ensuring its optimal performance.
Remember, if you encounter any complex issues or feel uncomfortable performing maintenance tasks, it is advisable to seek professional assistance. Regular maintenance and timely troubleshooting can prevent major breakdowns, ensure efficient operation, and keep your AC unit running reliably for years to come.
Conclusion
AC units have become an indispensable part of our lives, providing relief from the sweltering heat and humidity. Understanding the components, functioning, and key features of AC units is essential for making informed decisions about their purchase, maintenance, and efficient operation.
By comprehending the role of refrigerants, we can choose environmentally friendly options that promote sustainability and minimize climate impact. Additionally, recognizing the importance of energy efficiency helps us select AC units with high SEER ratings and implement energy-saving practices to reduce our carbon footprint and save on electricity bills.
Regular maintenance and troubleshooting are crucial for keeping AC units in optimal condition. Cleaning or replacing air filters, inspecting coils, clearing debris, and scheduling professional maintenance are essential steps to prevent problems, maximize performance, and extend the lifespan of the AC unit.
With proper care and attention, AC units can provide efficient and reliable cooling comfort for years to come. As technology advances, we can expect more innovative features and eco-friendly solutions to enhance the performance and energy efficiency of AC units.
In conclusion, AC units have revolutionized the way we experience and combat warm climates. By understanding their inner workings, implementing energy-efficient practices, and prioritizing maintenance, we can enjoy the benefits of a comfortable and cool indoor environment while minimizing the impact on our wallets and the environment.
Frequently Asked Questions about How Does An AC Unit Work
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.














0 thoughts on “How Does An AC Unit Work”