

Articles
How Much Do Curtains Help With Heat
Modified: December 7, 2023
Discover the impact of curtains on heat regulation in this insightful articles. Uncover how much curtains can help in keeping your space cool during hot days.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Curtains are not only decorative additions to a room; they also serve a functional purpose by providing privacy, blocking out light, and even helping with heat control. In this article, we will explore how curtains can assist in regulating the temperature of a space and contribute to energy savings.
Understanding how heat transfer works is crucial in comprehending the role curtains play in heat control. Heat transfer occurs through conduction, convection, and radiation. Conduction is the transfer of heat through direct contact between objects, while convection is the movement of heat through fluids like air or water. Radiation, on the other hand, is the emission of heat in the form of infrared radiation.
When it comes to curtailing heat transfer, curtains act as a barrier. They can help reduce the amount of heat that enters or escapes a room through windows. The thermal performance of curtains largely depends on their design, thickness, and specific features such as insulation and light-blocking properties.
To fully comprehend how curtains help insulate against heat, it’s essential to understand the role of insulation. Insulation works by inhibiting the transfer of heat between spaces of different temperatures. In the case of curtains, they act as an additional layer of insulation between the room and the window, effectively slowing down the heat transfer process.
Several factors affect the thermal performance of curtains. These include the material, color, and thickness of the fabric, as well as the presence of additional insulating layers or linings. The positioning and fit of the curtains also play a role, as any gaps or protrusions can compromise their effectiveness in controlling heat.
Key Takeaways:
- Curtains act as a versatile tool for heat control, providing insulation, blocking sunlight, and contributing to energy savings. By choosing the right materials and utilizing them strategically, you can create a comfortable and eco-friendly living environment.
- Factors such as fabric material, color, thickness, fit, and coverage influence the thermal performance of curtains. Understanding these factors and implementing energy-saving tips can maximize the insulation properties of curtains, reducing energy consumption and utility costs.
Read more: How Much Do Curtains Weigh
Understanding Heat Transfer
Heat transfer is the process by which thermal energy is exchanged between different objects or regions. It occurs in three main ways: conduction, convection, and radiation.
Conduction is the transfer of heat through direct contact between two objects or surfaces. For example, when you touch a hot pan, heat is transferred from the pan to your hand through conduction. In terms of curtains and heat transfer, conduction can occur when warm air comes into direct contact with the surface of the curtain and transfers heat to the cooler side.
Convection is the transfer of heat through the movement of fluids, such as air or water. When warm air rises and colder air sinks, this creates a circulation of air known as convection currents. In the context of curtains, convection can occur when warm air from the outside comes into contact with the back of the curtain and creates a layer of warm air that acts as an insulating barrier.
Radiation is the transfer of heat through electromagnetic waves. When an object absorbs heat energy, it emits infrared radiation. This is how the sun heats the Earth. In the case of curtains, radiation can occur when heat radiated from a warm surface, such as a radiator or a sunlit window, is absorbed by the curtain and either reflected back or dissipated.
Understanding these mechanisms of heat transfer is crucial in designing curtains that can effectively control heat. By manipulating or interrupting these processes, curtains can play a significant role in regulating the temperature of a room.
It’s worth noting that curtains alone may not be able to completely eliminate heat transfer. Factors such as the type of windows, insulation of the room, and external temperature conditions will also impact the overall heat control. However, curtains can significantly reduce heat transfer and help create a more comfortable and energy-efficient environment.
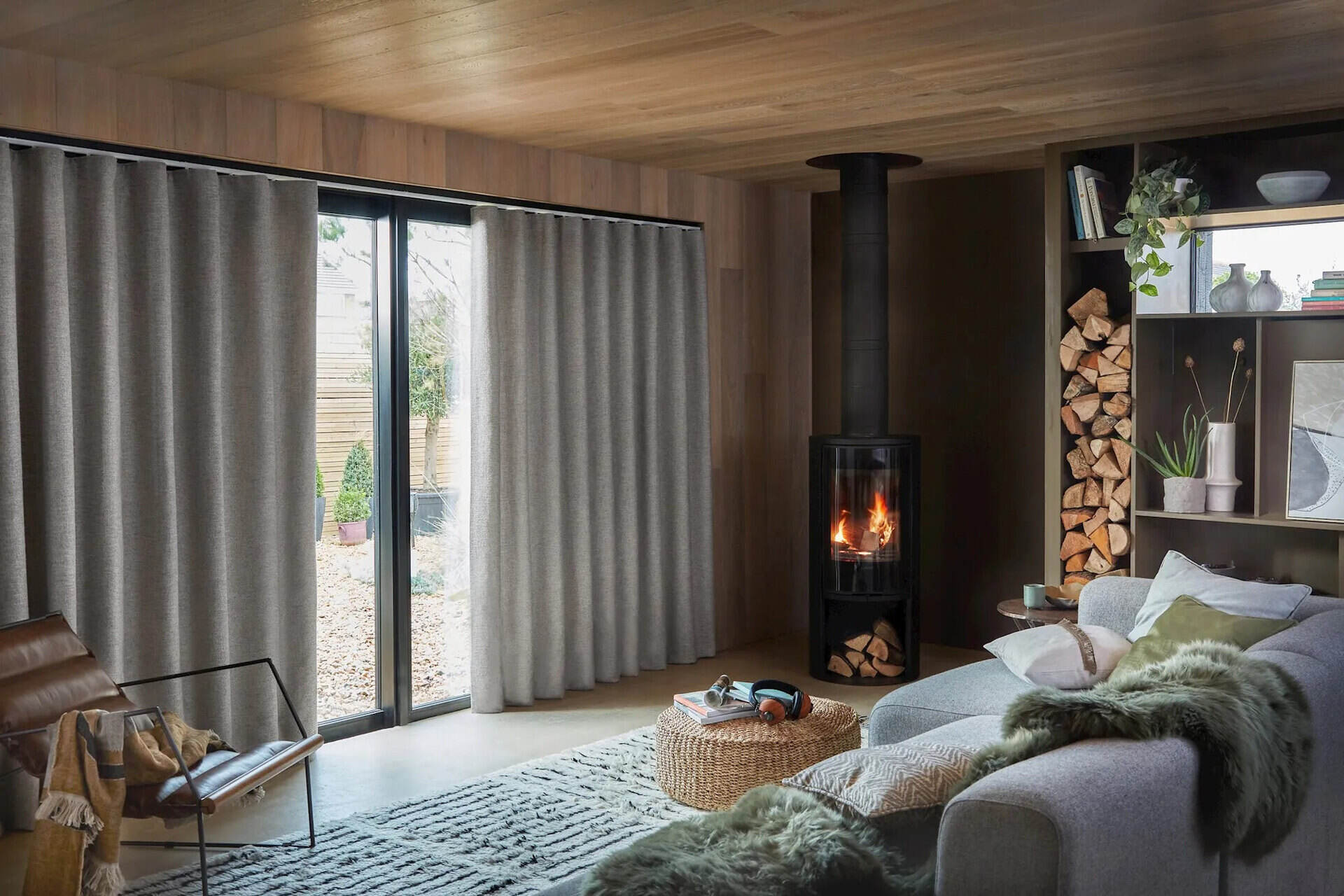
The Role of Curtains in Heat Control
When it comes to heat control, curtains serve as a versatile tool that can help regulate the temperature of a room. They provide insulation, block sunlight, and contribute to energy savings. Let’s explore the different roles that curtains play in heat control.
Insulation is one of the key functions of curtains when it comes to heat control. By creating an additional layer between the room and the window, curtains act as a barrier to reduce the transfer of heat. They help to keep the warm air inside during colder months and prevent heat from entering during hotter periods. A well-insulated curtain can significantly minimize heat loss or gain, thereby reducing the need for excessive heating or cooling.
In addition to insulation, curtains also play a crucial role in blocking sunlight. Sunlight carries heat, and when it enters a room through windows, it can rapidly increase the temperature. By using curtains with light-blocking properties or thicker fabrics, you can effectively reduce the amount of sunlight entering the room, thus minimizing heat gain. This is particularly useful in rooms that receive direct sunlight for extended periods, such as south-facing rooms.
Furthermore, curtains can contribute to energy savings by reducing the reliance on heating or cooling systems. By effectively controlling heat transfer, curtains help maintain a more stable and comfortable temperature in the room. This means that you can decrease the usage of heating or cooling devices, resulting in lower energy consumption and cost savings on utility bills.
Another benefit of using curtains for heat control is that they provide privacy. By keeping the curtains closed, you not only prevent heat from entering or escaping a room but also create a barrier that blocks the view from outside. This is particularly useful in bedrooms, living rooms, or any space where privacy is desired.
Overall, curtains play a multi-faceted role in heat control. They provide insulation, block sunlight, contribute to energy savings, and offer privacy. By choosing the right curtains and utilizing them effectively, you can create a more comfortable and energy-efficient environment in your home or office.
How Curtains Help Insulate Against Heat
Curtains are not just decorative additions to a room; they can also act as a powerful tool for insulation against heat. By understanding how curtains help insulate against heat, you can make informed choices when selecting curtains for your space.
One way curtains provide insulation is by creating an extra layer of protection between the room and the window. When curtains are closed, they create a pocket of still air between the fabric and the window, which acts as a buffer against heat transfer. This stagnant air layer adds an extra level of insulation by reducing the conduction of heat between the outside environment and the room.
The thickness and density of the curtain fabric also play a crucial role in its insulation capabilities. Thicker fabrics, such as velvet or heavy cotton, have a higher thermal resistance and are more effective at blocking heat transfer compared to lightweight materials. Additionally, certain curtain fabrics have insulating properties built into their structure, further enhancing their insulation abilities.
In addition to insulation, the color of the curtains also affects their heat-absorbing properties. Dark-colored curtains, such as deep burgundy or navy blue, tend to absorb more heat from sunlight compared to light-colored curtains. This absorption can help in reducing the amount of heat that enters the room, especially in areas where direct sunlight is a concern.
Another way curtains help insulate against heat is by reducing drafts and air movement around windows. Even well-insulated windows can still allow a small amount of air leakage, creating drafts that can contribute to heat loss or heat gain. By properly fitting the curtains and ensuring they reach the floor or windowsill, you can minimize these drafts and prevent unwanted air exchange.
Lining the curtains with insulating materials, such as thermal linings or blackout linings, can also enhance their heat insulation capabilities. These linings are designed to trap air and provide an additional layer of thermal protection. Thermal linings typically have an acrylic foam layer that helps to regulate temperature, while blackout linings have multiple layers that block both light and heat.
It’s important to note that while curtains can provide insulation against heat, their effectiveness will depend on various factors, including the material, thickness, color, and fitting of the curtains, as well as the specific environmental conditions. It’s recommended to choose curtains carefully based on the specific needs of your space and to ensure they are properly installed for maximum insulation benefits.
By harnessing the insulation properties of curtains, you can create a more comfortable and energy-efficient environment by reducing heat transfer and minimizing the reliance on heating or cooling systems.
Thick, insulating curtains can help reduce heat loss through windows by up to 25%, so consider using them to improve the energy efficiency of your home and save on heating costs.
Factors Affecting the Thermal Performance of Curtains
The thermal performance of curtains is influenced by various factors that can impact their ability to insulate against heat. Understanding these factors will help you make informed decisions when selecting curtains for optimal thermal efficiency.
Material: The type of fabric used for curtains plays a significant role in their thermal performance. Dense and heavy fabrics like velvet, wool, or thick cotton tend to have better insulation properties compared to lightweight materials such as sheer or silk. These thicker materials provide a higher level of thermal resistance, reducing heat transfer through the curtain.
Color: The color of the curtains can also affect their thermal performance. Dark-colored curtains, such as deep blues or blacks, have a higher ability to absorb heat compared to lighter colors. This can be advantageous in colder climates as they absorb sunlight and help to warm the room. However, in warmer climates or sun-exposed areas, light-colored curtains can reflect sunlight and lower the heat absorption, keeping the room cooler.
Thickness: The thickness of the fabric used for curtains directly impacts their insulation capabilities. Thicker curtains generally offer better insulation against heat transfer compared to thinner ones. Multiple layers or curtains with thermal or blackout linings can further enhance their thermal performance by adding an extra barrier for heat absorption or prevention.
Fit and Coverage: The fit and coverage of curtains also influence their thermal performance. Curtains that extend from the ceiling to the floor and reach the sides of the window provide better coverage and help trap air between the fabric and the window. This creates a more effective insulation seal, minimizing heat transfer between the room and the outside environment. Ensuring a snug fit and minimizing any gaps or drafts also improves their thermal efficiency.
Window Type: The type of window you have can impact the thermal performance of curtains. Single-pane windows generally offer less insulation compared to double-pane or energy-efficient windows. If you have single-pane windows, opting for thicker and more insulating curtains can help compensate for their lower thermal efficiency.
External Conditions: The external environment and climate conditions also affect the thermal performance of curtains. In colder climates, curtains with better insulation properties can help trap heat inside, reducing heat loss. In hotter climates, light-colored and lightweight curtains can prevent excessive heat gain by reflecting sunlight and allowing for better airflow.
It is essential to consider these factors when selecting curtains for your space to ensure optimal thermal performance. By choosing the right materials, colors, thicknesses, and ensuring proper coverage and fit, you can maximize the insulation properties of curtains, creating a more energy-efficient and comfortable environment.
Read more: How Much Do Custom Curtains Cost
Choosing the Right Curtains for Heat Control
When it comes to selecting curtains for heat control, several factors should be considered to ensure optimal thermal performance. By choosing the right curtains, you can maximize their ability to insulate against heat transfer and create a more comfortable and energy-efficient space. Here are some key considerations:
Material: Opt for curtains made from dense and heavyweight fabrics that offer better insulation properties. Fabrics such as velvet, wool, or thick cotton are excellent choices for heat control. These materials provide a higher level of thermal resistance and can help reduce heat transfer through the curtain.
Color: The color of the curtains can impact their heat-absorbing or heat-reflecting properties. In colder climates or during the winter months, choose darker-colored curtains that absorb heat from sunlight, helping to warm the room. In contrast, light-colored curtains are ideal for warmer climates or sunny locations as they reflect sunlight, reducing heat absorption and keeping the room cooler.
Thickness: Consider the thickness of the curtain fabric. Thicker curtains generally provide better insulation against heat transfer compared to thinner ones. Multiple layers or curtains with thermal or blackout linings can enhance their thermal performance by adding an extra barrier for heat absorption or prevention.
Fitting and Coverage: Ensure that the curtains are properly fitted and provide adequate coverage for the window. Floor-to-ceiling curtains that reach the sides of the window create a more effective insulation seal, minimizing heat transfer between the room and the outdoors. Avoid any gaps or drafts by ensuring a snug fit and using curtain weights or magnetic strips to hold the fabric in place.
Additional Features: Consider curtains with additional features that enhance heat control. Thermal linings can provide an extra layer of insulation, while blackout linings not only block light but also reduce heat transfer. Some curtains may also incorporate thermal-insulating technology within the fabric itself for improved heat control.
Care and Maintenance: Keep in mind the care and maintenance requirements of the curtains. Some materials may require special cleaning or treatments, so ensure that they are suitable for your lifestyle and preferences. Regularly clean and maintain the curtains to prolong their lifespan and preserve their insulation properties.
Budget and Aesthetics: Finally, consider your budget and the desired aesthetics of the room. Curtains are not only functional but also contribute to the overall look and feel of the space. Balance your budget with the desired thermal performance and select curtains that match your style and preferences.
By considering these factors when choosing curtains for heat control, you can select the right materials, colors, thicknesses, and features that optimize their thermal performance. Remember to consider the specific climate, window type, and room requirements to ensure the curtains effectively minimize heat transfer and create a comfortable environment.
Energy Saving Tips with Curtains
Curtains can be effective tools for energy savings when used strategically. By implementing the following tips, you can maximize the energy-saving potential of your curtains:
1. Open and close curtains strategically: Open curtains during the day to allow natural sunlight to warm the room. Sunlight is a free and renewable source of heat. However, remember to close the curtains at night to create an insulating barrier and prevent heat loss through windows.
2. Use curtains to block drafts: Ensure that your curtains are properly fitted and have a snug seal against the window frame. This will help prevent drafts and minimize heat loss during colder months. Use curtain weights or magnetic strips to hold the fabric in place and eliminate any gaps through which air can pass.
3. Layer curtains for added insulation: Consider layering curtains to enhance their insulation properties. You can use both sheer and heavyweight curtains together. During the day, draw the sheer curtains to allow natural light while blocking direct sunlight. At night, close the heavyweight curtains to provide an additional layer of insulation.
4. Utilize thermal or blackout linings: Invest in curtains with thermal or blackout linings. These linings are designed to provide extra insulation and keep the heat inside during winter or prevent excessive heat gain during summer. They can significantly improve the energy efficiency of your curtains and reduce heating and cooling costs.
5. Keep curtains clean and well-maintained: Regularly clean and maintain your curtains to ensure their optimal performance. Dust and dirt can settle on curtains over time, reducing their effectiveness as insulating barriers. Follow the manufacturer’s cleaning instructions and keep the curtains free from dust, pet hair, and debris.
6. Consider window film or blinds: In addition to curtains, consider using window film or blinds for added heat control. Window film can help to block harmful UV rays and reduce heat gain, while blinds can be adjusted to control the amount of light and heat entering the room. Pairing these options with curtains can enhance energy savings.
7. Manage curtains in rooms with air conditioning: If you have air conditioning, use curtains strategically to prevent heat from entering the room. Close curtains during the hottest parts of the day to block out sunlight and keep the room cooler. In combination with air conditioning, this can help reduce energy consumption and lower cooling costs.
Remember that effective energy savings with curtains require proper utilization and maintenance. By implementing these tips, you can harness the insulating power of curtains and significantly reduce your energy consumption, contributing to a more sustainable and eco-friendly living environment.
Conclusion
Curtains are not just decorative window coverings; they also play a crucial role in heat control and energy savings. By understanding how curtains function as insulation barriers and implementing proper techniques, you can harness their potential for optimal thermal efficiency.
From reducing heat transfer through conduction, convection, and radiation to blocking sunlight and preventing drafts, curtains provide a versatile and cost-effective solution to regulate the temperature of a room. By choosing the right curtain materials, colors, thicknesses, and fittings, you can effectively insulate against heat gain or loss, creating a more comfortable living environment while saving energy and reducing utility costs.
Factors such as the fabric material, color, thickness, fit, coverage, window type, and external conditions all influence the thermal performance of curtains. By carefully considering these factors, you can select curtains that suit your specific needs and the climate of your location.
Incorporating additional features such as thermal or blackout linings further enhances the insulation properties of the curtains. These linings trap air and create an extra layer of protection against heat transfer. Layering curtains and utilizing them strategically during different times of the day also helps maximize their energy-saving potential.
Proper maintenance, such as keeping curtains clean and ensuring a snug fit, is essential for maintaining their effectiveness as insulation barriers. Regularly cleaning curtains and removing any dust or debris will help them maintain their insulating properties and prolong their lifespan.
In conclusion, curtains are more than just decorative window dressings; they are valuable tools for heat control and energy savings. By selecting the right curtains, opening and closing them strategically, utilizing additional features, and properly maintaining them, you can create a more comfortable and energy-efficient living space. With these energy-saving practices, you not only reduce your carbon footprint but also enjoy the benefits of lower energy bills and a more sustainable lifestyle.
Frequently Asked Questions about How Much Do Curtains Help With Heat
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.














0 thoughts on “How Much Do Curtains Help With Heat”