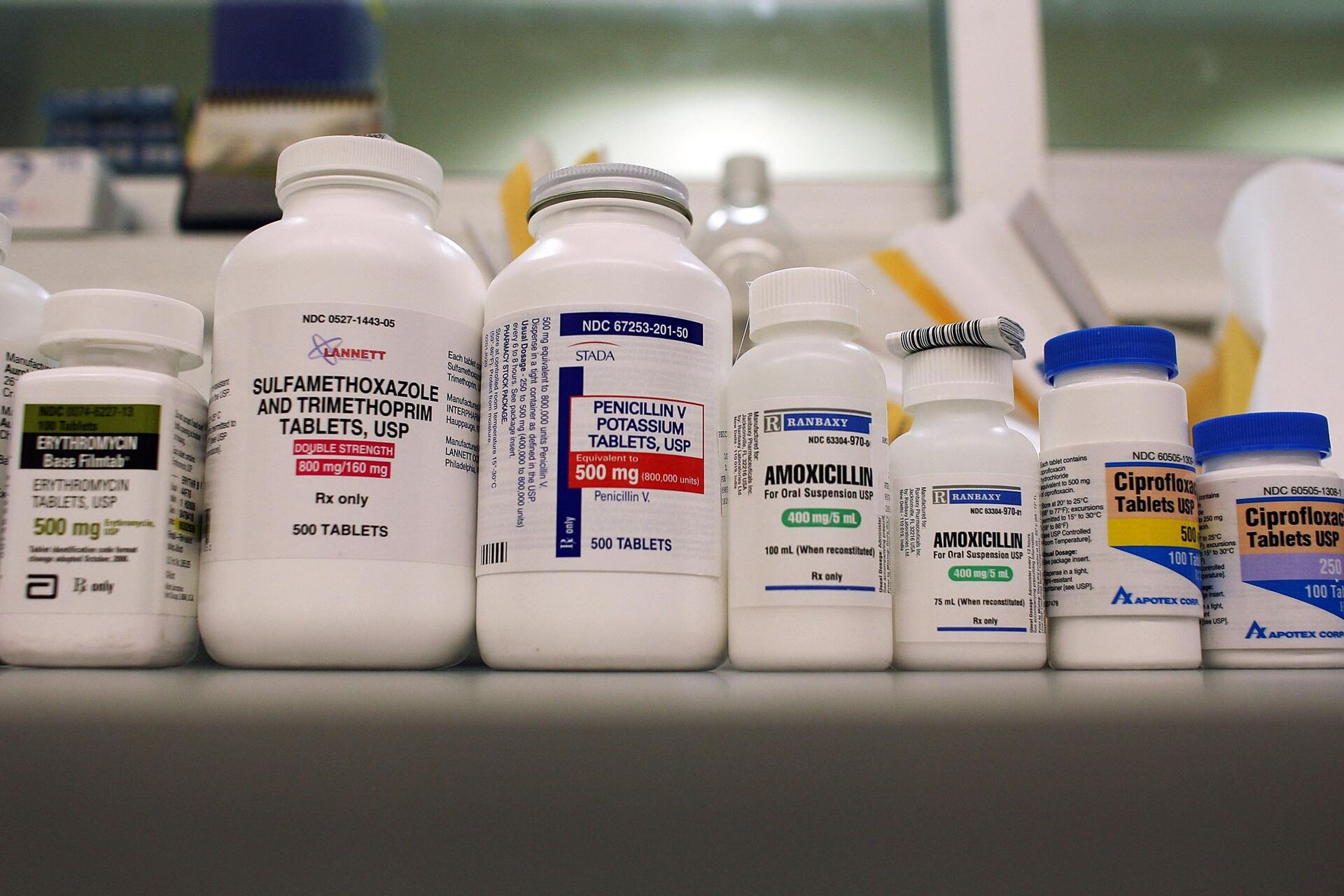

Articles
How To Store Antibiotics
Modified: January 20, 2024
Learn how to properly store antibiotics to ensure their effectiveness and safety. Read our informative articles on antibiotic storage and preservation.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Welcome to the world of antibiotics! These powerful pharmaceuticals have revolutionized the field of medicine, saving countless lives from bacterial infections. However, it’s important to remember that the effectiveness of antibiotics heavily depends on how well they are stored.
Proper storage of antibiotics ensures that they retain their potency and efficacy, allowing them to effectively combat infections when needed. Whether you’re a healthcare professional or an individual with antibiotics at home, understanding how to store these medications correctly is crucial.
In this article, we’ll explore the importance of proper antibiotic storage and provide you with useful guidelines to ensure that your antibiotics remain safe and effective for their intended use. So, let’s dive in and uncover the secrets to storing antibiotics the right way!
Key Takeaways:
- Proper storage of antibiotics is crucial for maintaining their potency and effectiveness, preventing bacterial resistance, avoiding wastage, and ensuring patient safety. Following specific guidelines and best practices is essential for maximizing the therapeutic benefits of antibiotics.
- Choosing the right storage location, considering temperature considerations, avoiding sunlight and moisture, organizing and labeling, and prioritizing safety precautions are key elements in maintaining the integrity and effectiveness of antibiotics. Adhering to these practices contributes to combating bacterial infections effectively and reducing the risk of antibiotic resistance.
Read more: How To Store Antibiotics Long Term
Importance of Proper Antibiotic Storage
Proper storage of antibiotics is vital for maintaining their potency and effectiveness. When antibiotics are not stored correctly, their chemical composition can become altered, rendering them less effective or even completely ineffective against bacterial infections.
Here are a few key reasons why proper antibiotic storage is so important:
- Maintaining Potency: Antibiotics are chemical substances that can degrade over time or under certain storage conditions. By storing antibiotics properly, you can help them retain their potency for a longer period, ensuring their effectiveness when you need them.
- Preventing Bacterial Resistance: Inadequate storage may lead to the growth of bacteria within the antibiotic, making it less effective or promoting the development of antibiotic resistance. Proper storage can help prevent bacterial contamination and preserve the antibiotic’s ability to fight specific bacteria.
- Avoiding Wastage and Cost: By storing antibiotics properly, you can extend their shelf life and avoid unnecessary wastage. This can help you save money in the long run, as you won’t need to replace expired or improperly stored antibiotics.
- Patient Safety: Storing antibiotics correctly is crucial to ensure patient safety. Using expired or ineffective antibiotics can result in inadequate treatment and potential harm to patients with bacterial infections. Proper storage practices help safeguard patients’ health and well-being.
It’s important to note that these principles of proper storage are applicable not just to antibiotics, but also to other medications. However, antibiotics are particularly sensitive to storage conditions due to their nature as antimicrobial agents.
Now that we understand the significance of proper antibiotic storage, let’s explore some general guidelines to help you store your antibiotics appropriately.
General Guidelines for Storing Antibiotics
When it comes to storing antibiotics, following some general guidelines can help ensure their longevity and effectiveness. Here are a few essential tips:
- Read the Label: Always read the label and package insert that comes with your antibiotics. The manufacturer’s instructions will provide specific guidance on how to store the medication properly. Follow these instructions carefully.
- Keep in the Original Packaging: It’s best to store antibiotics in their original packaging. The packaging is designed to protect the medication from light, moisture, and temperature fluctuations. The original container also contains important information such as the expiration date and batch number.
- Avoid Repackaging: Do not transfer antibiotics into different containers unless instructed to do so by a healthcare professional or pharmacist. The original packaging is designed to provide optimal protection and preserve the integrity of the medication.
- Store at Room Temperature: Most antibiotics should be stored at room temperature, around 20-25 degrees Celsius (68-77 degrees Fahrenheit). Avoid storing antibiotics in extremely hot or cold areas, such as near radiators or in the freezer.
- Avoid Humidity: Moisture can degrade the quality of antibiotics. Store them in a dry place, away from areas with high humidity, such as the bathroom or kitchen. Avoid storing antibiotics near sinks, showers, or areas prone to splashing water.
- Keep Away from Direct Sunlight: Exposure to sunlight can accelerate the deterioration of antibiotics. Store them in a dark place, away from direct sunlight or bright indoor lighting. A cabinet or drawer can be an ideal storage location.
- Out of Reach of Children: Ensure that antibiotics are stored safely out of the reach of children. Consider using childproof containers or storing them in a locked cabinet to prevent accidental ingestion.
- Do Not Freeze: Freezing can alter the chemical composition of antibiotics, rendering them ineffective. Avoid storing antibiotics in the freezer or any extremely cold environment.
- Monitor Expiration Dates: Check the expiration dates on the packaging and discard any antibiotics that have expired. Expired antibiotics may lose their effectiveness or pose potential health risks. Properly dispose of expired medications according to local regulations.
By following these general guidelines, you can ensure that your antibiotics remain safe and effective for their intended use. However, it’s also important to consider specific storage recommendations based on the type of antibiotics you have and any additional instructions provided by your healthcare provider.
In the next sections, we’ll dive deeper into choosing the right storage location for your antibiotics, temperature considerations, organizing and labeling, and other essential safety precautions to keep in mind. So, let’s continue our journey into the world of proper antibiotic storage!
Choosing the Right Storage Location
When it comes to storing antibiotics, choosing the right storage location is of utmost importance. Here are some factors to consider:
- Cool and Dry Place: Select a cool and dry place in your home to store antibiotics. Avoid areas that are directly exposed to sunlight, extreme temperatures, or high humidity.
- Away from Heat Sources: Keep antibiotics away from heat sources such as radiators, stovetops, or heating vents. Heat can degrade the medication and affect its effectiveness.
- Out of the Bathroom: The bathroom may seem convenient, but it often has high humidity levels due to showers and baths. It’s best to keep antibiotics away from the bathroom to prevent moisture-related damage.
- Childproof Storage: If you have children in the house, make sure to store antibiotics in a location that is out of their reach. Consider using childproof caps or locking cabinets to prevent accidental ingestion.
- Away from Pet Access: Similarly, keep antibiotics away from areas where pets can reach. Pets may mistake medications for treats, so it’s important to ensure their safety as well.
- Accessible but Secure: While it’s important to store antibiotics securely, ensure that the storage location is still easily accessible to you when needed. This will allow you to retrieve the medication quickly, especially during emergencies.
- Consider Storage Containers: If you live in a particularly humid or unstable environment, consider using airtight storage containers to add an extra layer of protection against moisture and temperature fluctuations.
- Away from Food and Drinks: It’s important to avoid storing antibiotics near food or drinks to prevent the possibility of accidental contamination.
- Separation from Cleaning Supplies: Keep antibiotics separate from cleaning supplies or chemicals that may emit strong odors. Antibiotics can absorb odors, potentially altering their composition.
By selecting the right storage location for your antibiotics, you can minimize the risk of environmental factors affecting their potency and efficacy. Remember to always follow the specific instructions provided by the manufacturer or your healthcare professional for any additional storage recommendations.
Now that you’ve chosen the perfect storage location, let’s explore the temperature considerations for storing antibiotics properly.
Temperature Considerations
Proper temperature control is crucial for maintaining the effectiveness of antibiotics. Temperature fluctuations can impact the stability and potency of these medications. Here are some temperature considerations to keep in mind when storing antibiotics:
- Room Temperature: Most antibiotics should be stored at room temperature, between 20-25 degrees Celsius (68-77 degrees Fahrenheit). This temperature range provides optimal conditions for preserving the potency of the medication.
- Avoid Extreme Temperatures: Avoid storing antibiotics in areas exposed to extreme heat or cold. High temperatures can lead to the breakdown of antibiotic molecules, while freezing temperatures can cause structural changes that render the medication ineffective.
- Monitor Storage Areas: Keep an eye on the storage areas to ensure they maintain a consistent temperature. Avoid areas that experience frequent temperature fluctuations, such as near windows or doors.
- Be Mindful of Travel: If you need to travel with antibiotics, ensure they are stored in a temperature-controlled environment. Use an insulated cooler or a thermal bag with ice packs to maintain the appropriate temperature during transit.
- Avoid Car Storage: Avoid storing antibiotics in a car, especially during hot summer months or in freezing winter weather. Cars can experience extreme temperature variations, which can compromise the integrity of antibiotics.
- Consider Refrigeration Requirements: Some antibiotics may require refrigeration, as indicated on the packaging or by your healthcare provider. If refrigeration is necessary, ensure the temperature remains between 2-8 degrees Celsius (36-46 degrees Fahrenheit) and store them away from items with strong odors to prevent absorption.
- Keep an Eye on Temperature Sensitive Labels: Some antibiotic packages come with temperature-sensitive labels that change color or indicate if the medication has been exposed to improper temperatures. If you notice any changes in these labels, consult your pharmacist or healthcare provider.
Remember, maintaining the correct temperature range is crucial for the stability and effectiveness of antibiotics. By adhering to proper temperature considerations, you can ensure that your antibiotics remain potent and safe to use when needed.
In the next section, we’ll discuss the importance of avoiding sunlight and moisture when storing antibiotics. So, let’s dive in!
Read more: How To Store Antibiotics Long-Term
Avoiding Sunlight and Moisture
Exposure to sunlight and moisture can have detrimental effects on the stability and efficacy of antibiotics. It’s important to protect antibiotics from these elements to ensure their effectiveness. Here are some important considerations:
- Avoid Direct Sunlight: Sunlight, especially ultraviolet (UV) rays, can degrade antibiotics. Store them in a dark place, away from direct sunlight or bright indoor lighting. A cabinet or drawer can provide the necessary protection.
- Choose an Optimal Storage Location: Select a storage location that is not prone to condensation or high humidity. Bathrooms, kitchens, and basements are often high-humidity areas and should be avoided.
- Protect from Moisture: Moisture can alter the chemical composition of antibiotics and diminish their effectiveness. Keep antibiotics in a dry place, away from sinks, showers, and other sources of water. Consider using desiccant packs or silica gel packets to absorb excess moisture.
- Avoid Storing in the Fridge Door: Although refrigeration may be necessary for some antibiotics, avoid storing them in the refrigerator door. The door is subjected to frequent temperature fluctuations when opened, which can compromise the stability of the medication.
- Keep Caps Tightly Closed: Ensure that the caps of antibiotic containers are tightly closed after each use to prevent the entry of moisture. Always use clean hands or tools to remove and replace the medication.
- Avoid Exposing to Steam: Steam from hot showers or boiling water can introduce moisture into the storage area and potentially affect the antibiotics. Store them away from areas prone to steam and condensation.
- Be Cautious in Humid Climates: If you live in a humid climate, take extra precautions to protect antibiotics from moisture. Consider using airtight containers or storing them with moisture-absorbing packets.
- Inspect Packaging for Water Damage: Prior to storing antibiotics, check the packaging for any signs of water damage or compromised seals. If you notice any issues, consult your pharmacist or healthcare provider for guidance.
By avoiding sunlight and moisture, you can maintain the integrity and effectiveness of your antibiotics. Remember, even small exposure to these elements over time can degrade the medication. Take the necessary precautions to protect your antibiotics and ensure their optimal performance.
In the next section, we’ll discuss organizing and labeling your antibiotics for easy identification and safety. Let’s continue our journey into proper antibiotic storage!
Store antibiotics in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and moisture. Keep them in their original packaging with the label intact. Check the expiration date and properly dispose of any expired medication.
Organizing and Labeling Antibiotics
Organizing and labeling your antibiotics is crucial for easy identification, proper dosage administration, and maintaining a safe storage environment. Here are some key considerations for organizing and labeling your antibiotics:
- Categorize by Type: Group antibiotics together based on their type, such as penicillins, cephalosporins, or macrolides. This helps you quickly locate the specific antibiotic you need.
- Separate Oral and Topical Antibiotics: Keep oral antibiotics separate from topical antibiotics to prevent confusion and ensure correct usage. Use separate storage containers or compartments for each type.
- Use Clear Containers or Labels: Transparent containers or labels allow for easy identification of the antibiotic inside. This not only helps you find the right medication but also allows you to monitor the quantity and expiration date.
- Maintain Proper Labelling: Ensure that each antibiotic container is labeled with the medication’s name, strength, dosage instructions, and expiration date. This information is essential for proper administration and tracking of antibiotics.
- Include Additional Instructions: If you have specific instructions from your healthcare provider, such as taking the medication with food or avoiding certain substances, note them on the label or in a separate information sheet.
- Store Small Containers Together: When storing multiple small containers, such as antibiotic eye drops or ointments, keep them together in a designated section or box. This prevents them from getting lost or becoming disorganized.
- Consider a Medication Log: Maintaining a log of your antibiotics can help you track when they were started, the recommended duration, and when they need to be replenished. This prevents accidental overuse or running out of medication.
- Keep Medication Information Handy: Store the package inserts or any relevant medication information together with your antibiotics. This allows you to refer to important details whenever needed.
- Regularly Check Expiry Dates: Periodically review your antibiotics for expiration dates. Use the “first in, first out” principle to ensure that you use the oldest medications first and discard any that have expired.
By organizing and labeling your antibiotics effectively, you can easily access the right medication when needed, avoid confusion, and stay on top of important information. These simple practices promote a safe and efficient storage system for your antibiotics.
Next, let’s explore some essential safety precautions you should take when handling antibiotics. Stay tuned!
Safety Precautions
When handling antibiotics, it’s important to prioritize safety to protect yourself, others, and the efficacy of the medication. Here are some crucial safety precautions to keep in mind:
- Follow Dosage Instructions: Always follow the dosage instructions provided by your healthcare provider or as indicated on the packaging. Taking the correct dosage ensures optimal treatment outcomes and reduces the risk of side effects or antibiotic resistance.
- Wash Your Hands: Before handling antibiotics, wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water to reduce the risk of contamination. Clean hands prevent the transfer of bacteria or other harmful substances to the medication.
- Use Appropriate Tools: Use clean and appropriate tools such as a medicine dropper, spoon, or syringe when administering liquid antibiotics. This helps ensure accurate dosage measurements and reduces the risk of contamination.
- Avoid Touching Antibiotics: Minimize direct contact between your hands and the antibiotic pills or capsules to prevent contamination. If necessary, use clean tools or gloves to handle the medication.
- Do Not Share Antibiotics: Never share antibiotics with others, even if they have similar symptoms. Each person’s condition may require a specific type and dosage of medication, determined by a healthcare professional.
- Dispose of Unused Antibiotics Properly: If you have any unused or expired antibiotics, it’s important to dispose of them properly to prevent unintended use. Follow local regulations or consult your pharmacist for safe disposal methods.
- Report Adverse Reactions: If you experience any unusual side effects or allergic reactions after taking antibiotics, immediately contact your healthcare provider. Prompt reporting can help ensure your safety and guide future treatment decisions.
- Avoid Alcohol and Drug Interactions: Certain antibiotics may interact with alcohol or other medications, affecting their efficacy or causing adverse effects. Follow the instructions provided by your healthcare provider and avoid consuming alcohol or other medications that may interfere with the antibiotic.
- Keep Medications Separate: Store antibiotics separately from other medications to prevent mix-ups and accidental ingestion. This applies to both prescription and over-the-counter medications.
- Consult a Healthcare Provider: If you have any questions or concerns about your antibiotics or their storage, consult your healthcare provider or pharmacist. They can provide guidance and address specific queries related to your situation.
Following these safety precautions helps ensure that you handle antibiotics responsibly and minimize risks associated with their use. By prioritizing safety, you can maintain the effectiveness of antibiotics and protect the health and well-being of yourself and others.
Now that we’ve covered safety precautions, let’s move on to the importance of checking expiration dates. Stay tuned!
Checking Expiration Dates
Checking the expiration dates of antibiotics is essential to ensure their safety and effectiveness. Here’s why it’s important and how to go about it:
Preserving Effectiveness: Over time, antibiotics can degrade and lose their potency. By checking the expiration dates, you can ensure that the antibiotics you are using are still effective in fighting bacterial infections. Using expired antibiotics may result in inadequate treatment and potentially compromised health outcomes.
Following Proper Storage: When stored correctly, antibiotics can retain their potency for the duration indicated on the packaging. However, improper storage conditions such as exposure to heat, light, or moisture can accelerate the degradation process. Checking the expiration date allows you to assess whether the antibiotics have been stored properly and whether they are still safe to use.
Avoiding Potential Health Risks: Expired antibiotics may have reduced effectiveness or could have undergone chemical changes that make them harmful. Using expired antibiotics can increase the risk of treatment failure and potentially contribute to the development of antibiotic resistance. Checking expiration dates helps ensure that you are administering medications that are safe for consumption.
To check the expiration date of an antibiotic:
- Consult the Packaging: Look for the expiration date on the antibiotic packaging. It is typically printed on the label or container, along with other important information.
- Check for Legibility: Ensure that the expiration date is legible and clearly visible. If the date is smudged or difficult to read, it’s best to consult a pharmacist or healthcare provider for guidance.
- Verify the Date: Compare the current date with the expiration date printed on the packaging. If the antibiotic has expired, it should be discarded and replaced with a new supply.
- Dispose Properly: If you find any expired antibiotics, follow local regulations or consult a pharmacist for safe disposal methods. Improper disposal can contribute to environmental contamination and potential harm.
Regularly checking expiration dates is an important practice to ensure that you are using antibiotics that are within their efficacy period. It’s a simple yet effective way to promote safety and maintain optimal treatment outcomes.
As we conclude this discussion on checking expiration dates, let’s move on to some general tips for handling antibiotics properly. Stay tuned!
Read more: How To Store Store-Bought Bread
Tips for Handling Antibiotics Properly
Proper handling of antibiotics is essential to maintain their effectiveness and ensure safe usage. Here are some important tips to keep in mind when handling antibiotics:
- Follow Instructions: Always follow the instructions provided by your healthcare provider or pharmacist regarding the dosage, frequency, and duration of antibiotic use. Strictly adhere to the prescribed regimen to maximize the effectiveness of the medication.
- Complete the Full Course: Even if you start feeling better before completing the full course of antibiotics, continue taking them as prescribed. Premature discontinuation can lead to incomplete eradication of bacteria, increasing the risk of recurrent infections or antibiotic resistance.
- Avoid Self-Medication: Antibiotics should only be taken when prescribed by a healthcare professional. Avoid self-medication or sharing antibiotics with others, as this can lead to inappropriate use and potential health risks.
- Read the Patient Information Leaflet: Familiarize yourself with the patient information leaflet that accompanies your antibiotic. This contains important details about the medication, such as potential side effects, drug interactions, and precautions.
- Use Proper Hygiene Practices: Wash your hands thoroughly before and after handling antibiotics to prevent the spread of bacteria and contamination. This is especially important when administering liquid antibiotics or handling antibiotic ointments.
- Avoid Crushing or Altering Medication: Unless specifically instructed by a healthcare professional, do not crush, break, or alter antibiotics in any way. This can affect the medication’s absorption and effectiveness.
- Store Medication in a Safe Location: Keep antibiotics out of reach of children and pets, ensuring they are stored securely in a designated storage area that complies with the proper storage guidelines discussed earlier.
- Take Precautions for Allergic Reactions: If you have a known allergy to a specific antibiotic or any other medication, inform your healthcare provider. They can prescribe an alternative antibiotic that is safe for you to use.
- Monitor for Side Effects: Keep a close eye on any potential side effects while taking antibiotics. If you experience severe or unusual side effects, contact your healthcare provider immediately.
- Don’t Save Antibiotics for Future Use: Avoid saving antibiotics from a previous prescription for future use. Always consult your healthcare provider for a new prescription if needed.
- Dispose of Unused Antibiotics: Safely dispose of any unused or expired antibiotics according to local regulations or by consulting your pharmacist. Do not keep antibiotics beyond their expiration date.
By following these tips for proper handling of antibiotics, you can ensure safe and effective usage, reducing the risk of treatment failure and promoting overall health and well-being.
Now that we’ve covered essential tips for handling antibiotics properly, let’s wrap up our discussion on proper antibiotic storage and usage.
Conclusion
Proper storage and handling of antibiotics are crucial for preserving their potency, ensuring their effectiveness, and promoting patient safety. By following a few guidelines and implementing best practices, you can maintain the quality of antibiotics and maximize their therapeutic benefits.
Throughout this article, we have discussed the importance of proper antibiotic storage, including temperature considerations, avoiding sunlight and moisture, organizing and labeling, safety precautions, checking expiration dates, and handling antibiotics properly. These key practices help ensure that antibiotics remain safe, effective, and ready for use when needed.
Remember to always read the instructions provided with your antibiotics and follow the guidance of your healthcare provider or pharmacist. Adhering to the prescribed dosage and completing the full course of treatment are essential to prevent antibiotic resistance and ensure optimal outcomes.
Additionally, proper storage conditions, such as storing antibiotics at room temperature, keeping them away from sunlight and moisture, and organizing them for easy identification, contribute to the long-term efficacy of these medications. Regularly checking expiration dates and appropriately disposing of unused or expired antibiotics also play a vital role in maintaining their safety and effectiveness.
By handling antibiotics responsibly and prioritizing patient safety, we can contribute to combating bacterial infections effectively and reducing the risk of antibiotic resistance in the long run.
It’s important to stay informed and consult healthcare professionals or pharmacists if you have any questions or concerns about antibiotic storage or usage. They can provide personalized guidance and address specific queries based on your unique situation.
With proper storage, handling, and usage, antibiotics can continue to save lives and play a significant role in maintaining public health. Let’s make every effort to ensure that these powerful medications are stored and used responsibly.
Frequently Asked Questions about How To Store Antibiotics
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.













0 thoughts on “How To Store Antibiotics”