

Articles
What Is A Furnace In HVAC
Modified: October 20, 2024
Get valuable insights on furnace HVAC systems with our informative articles. Learn about different types, maintenance tips, and troubleshooting techniques. Stay informed!
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Welcome to the world of furnace HVAC systems! If you’re a homeowner or someone interested in heating and cooling, you’ve probably come across the term “furnace HVAC” before. But what exactly is a furnace HVAC and how does it work? In this article, we’ll delve into the definition, components, types, benefits, and common problems associated with furnace HVAC systems. We’ll also provide some helpful tips for maintaining these systems to keep them running efficiently.
First things first, let’s start with the basics. A furnace HVAC, or Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning system, is a crucial component of a comfortable and well-functioning home. It plays a vital role in providing warmth during the colder months and maintaining optimal indoor air quality throughout the year.
Now that we have a general idea of what a furnace HVAC is, let’s explore the key components that make up these systems.
Key Takeaways:
- Understanding the components, operation, and maintenance of a furnace HVAC system is crucial for homeowners and HVAC professionals to ensure efficient and reliable heating, ventilation, and air conditioning.
- Regular maintenance, including filter replacement, cleaning vents, and scheduling professional inspections, is essential for optimizing the performance, energy efficiency, and lifespan of a furnace HVAC system.
Read more: What Is A UV Lamp On A Furnace
Definition of a Furnace HVAC
A furnace HVAC, also known as a heating, ventilation, and air conditioning system, is a mechanical system designed to control the temperature, humidity, and air quality in residential and commercial buildings. It consists of various components that work together to provide comfortable and healthy indoor environments.
The primary function of a furnace HVAC is to generate and distribute warm air throughout a building during the colder months. It achieves this by using energy sources such as natural gas, propane, oil, or electricity to heat the air. The heated air is then circulated through ductwork and delivered to different rooms via vents or registers.
In addition to heating, furnace HVAC systems also incorporate ventilation and air conditioning capabilities. Ventilation involves the exchange of indoor and outdoor air, removing contaminants and odors and ensuring a fresh supply of oxygen. Air conditioning refers to the cooling and dehumidifying of indoor air during hot weather.
The main components of a furnace HVAC system include the furnace unit, ductwork, vents or registers, thermostats, and filters. Let’s take a closer look at each of these components:
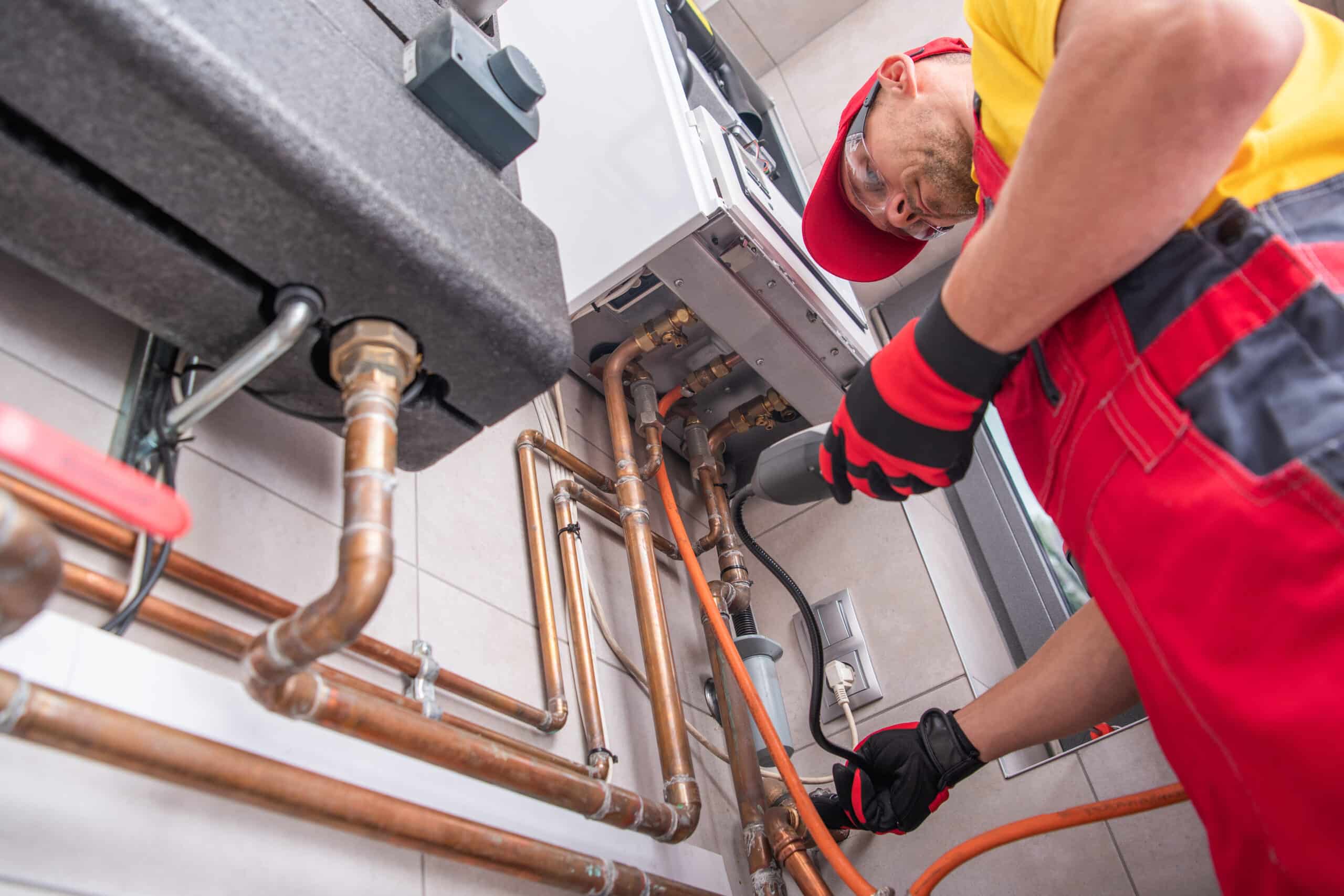
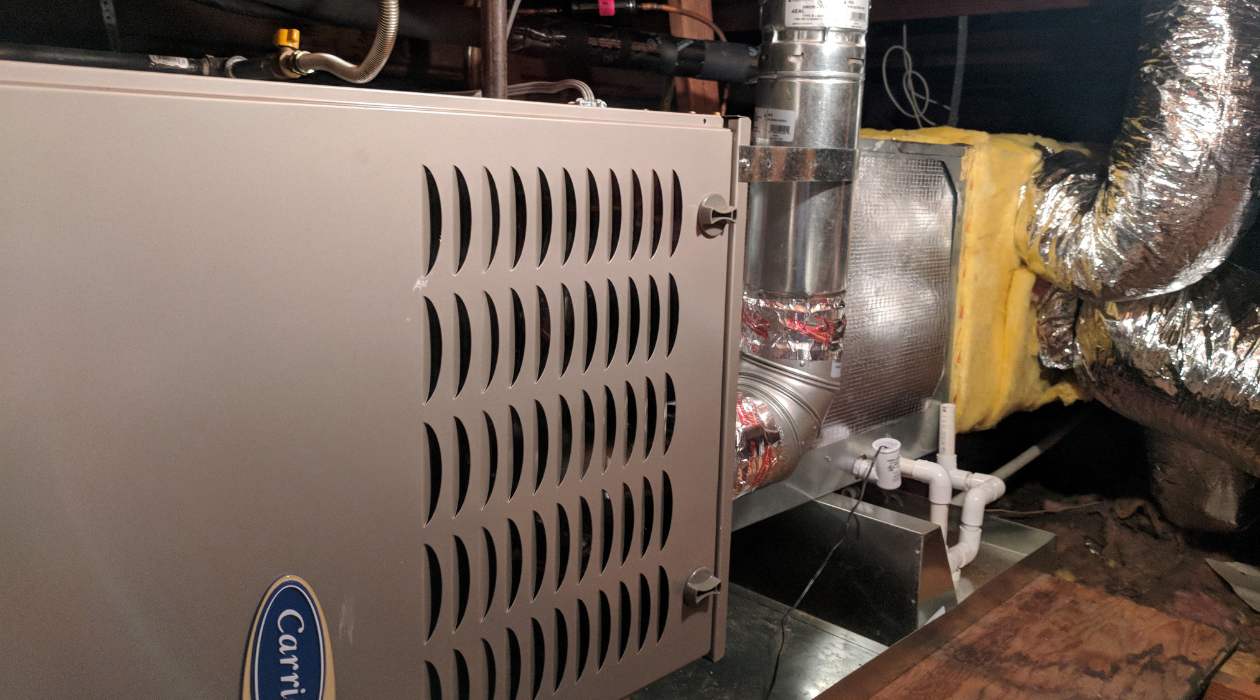
- Furnace Unit: This is the heart of the HVAC system, responsible for heating the air. It consists of a burner, heat exchanger, blower, and control panel. The type of fuel used determines the type of furnace, such as gas, oil, electric, or dual-fuel.
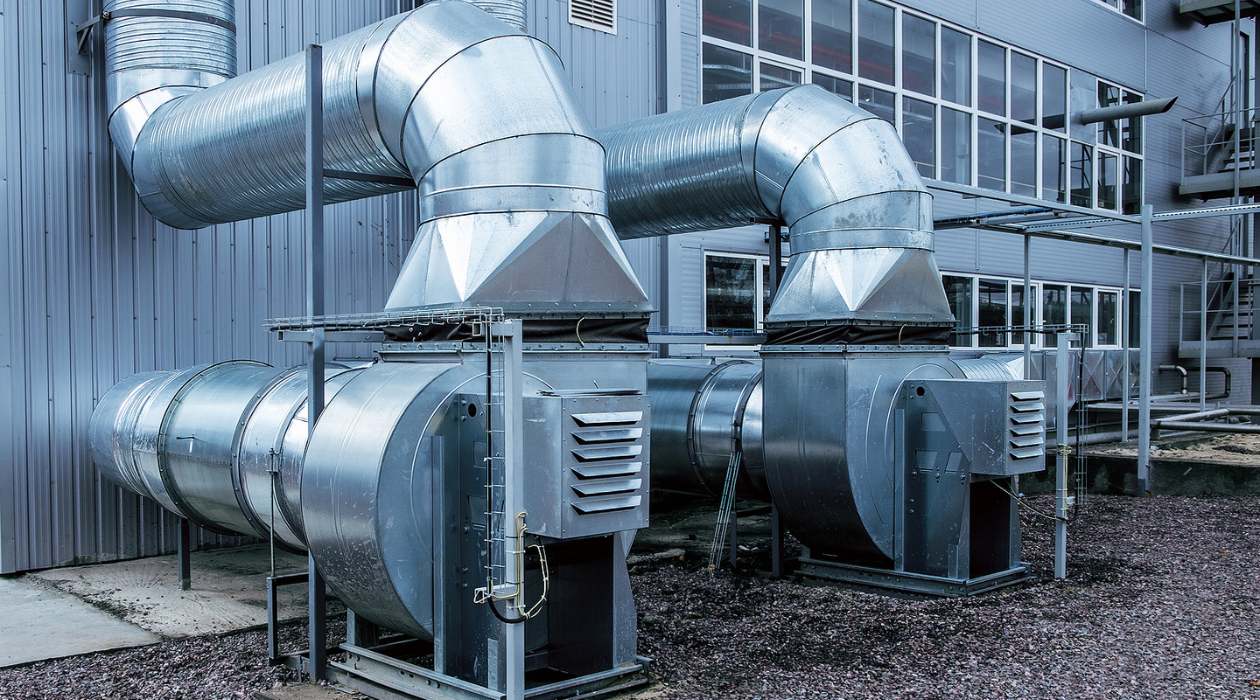
- Ductwork: This network of channels distributes the heated or cooled air throughout the building. It is typically made of metal or flexible material and is strategically installed to ensure proper airflow.
- Vents or Registers: These are the outlets through which the conditioned air is released into individual rooms. They can be adjusted to control the airflow and direct it where needed.
- Thermostats: These devices monitor and regulate the temperature in different zones or rooms. They allow users to set desired temperatures and can be programmed for energy-efficient operation.
- Filters: Furnace HVAC systems incorporate filters to trap airborne particles, such as dust, pollen, and pet dander, improving indoor air quality. Regular filter replacement or cleaning is essential for optimal system performance.
Now that we have a clear understanding of a furnace HVAC and its components, let’s explore how these systems work to provide heating, ventilation, and air conditioning functionality.
Components of a Furnace HVAC
A furnace HVAC system consists of various components that work together to provide heating, ventilation, and air conditioning functionality. Understanding these components is essential to grasp the overall functioning of the system. Let’s take a closer look at each component:
- Furnace Unit: The furnace unit is the core component of a furnace HVAC system. It is responsible for generating heat to warm the air. Furnaces can be fueled by natural gas, propane, oil, or electricity. The burner heats the air, while the heat exchanger transfers the heat to the circulating air. The blower then pushes the warmed air through the ductwork and into the living spaces.
- Ductwork: Ductwork is a network of channels that distribute heated or cooled air throughout the building. The ducts are typically made of metal or flexible material and are strategically installed to ensure proper airflow. Well-designed and properly sealed ductwork is crucial for efficient operation and even distribution of conditioned air.
- Vents or Registers: Vents or registers are the outlets through which the conditioned air is released into individual rooms. These can be found on walls, floors, or ceilings. Vents can be adjusted to control the airflow and direct it where it is needed most. It is important to ensure that all vents are unobstructed to allow for proper air circulation.
- Thermostats: A thermostat is a control device that allows users to set and regulate the desired temperature in different zones or rooms. It senses the current temperature and sends signals to the furnace to turn on or off accordingly. Modern thermostats often include programmable features, allowing users to set schedules for temperature adjustments and energy-efficient operation.
- Filters: Furnace HVAC systems incorporate filters to clean and purify the air before it is distributed throughout the building. Filters trap airborne particles, such as dust, pollen, pet dander, and allergens, improving indoor air quality. Regular filter maintenance, including replacement or cleaning, is crucial to ensure efficient system performance and prevent the build-up of pollutants.
These components work together seamlessly to provide optimal heating, ventilation, and air conditioning in a home or commercial building. Understanding the role of each component will help homeowners and HVAC professionals troubleshoot issues and ensure the system operates efficiently.
Now that we know the main components of a furnace HVAC system, let’s explore how the system works to heat and cool our indoor spaces effectively.
How Does a Furnace HVAC Work?
Understanding how a furnace HVAC system works is essential to grasp its overall functionality and its ability to provide heating, ventilation, and air conditioning. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how a furnace HVAC system operates:
- Step 1 – Thermostat: The first step in the process is when the thermostat senses that the indoor temperature has dropped below the desired set point. It sends a signal to the furnace to start the heating process.
- Step 2 – Ignition: Once the signal is received, the furnace’s ignition system ignites the fuel source. This can be a pilot light or an electronic ignition, depending on the type of furnace. The burner in the furnace then produces flames to generate heat.
- Step 3 – Heat Exchanger: The heat produced by the burner is transferred to the heat exchanger. The heat exchanger is a metal chamber that allows the heat to pass through while preventing combustion gases from mixing with the circulating air. As the hot combustion gases flow through the heat exchanger, the walls of the exchanger absorb the heat.
- Step 4 – Air Circulation: The blower motor in the furnace then kicks in, pulling air from the surrounding environment into the furnace. The air passes over the hot heat exchanger and absorbs the heat. The blower motor then pushes the now warmed air through the ductwork and into the living spaces of the building.
- Step 5 – Ventilation and Air Conditioning: In addition to heating, furnace HVAC systems also provide ventilation and air conditioning capabilities. Ventilation is achieved through the exchange of indoor and outdoor air. Fresh air is drawn in from outside, while stale air is expelled. Air conditioning involves cooling and dehumidifying the indoor air during hot weather. This is usually achieved by incorporating a separate cooling unit, such as an air conditioner or heat pump, in the system.
- Step 6 – Thermostat Regulation: As the warmed air is distributed throughout the building, the thermostat continuously monitors the temperature. Once the desired temperature is reached, the thermostat sends a signal to the furnace to stop heating. This ensures that the temperature remains consistent within the set parameters.
It’s important to note that modern furnace HVAC systems are equipped with advanced controls and sensors that allow for precise temperature regulation and energy-efficient operation. Some models come with zoning capabilities, which allow users to control the temperature in different areas or rooms independently. This further enhances comfort and energy savings.
Understanding how a furnace HVAC system works is essential for homeowners to troubleshoot any potential issues and provide proper maintenance. Now that we know how a furnace HVAC system operates, let’s explore the different types of furnace systems available.
Types of Furnace HVAC Systems
When it comes to furnace HVAC systems, there are several types available, each with its own set of characteristics and advantages. Let’s take a closer look at the most common types of furnace HVAC systems:
- Gas Furnace: Gas furnaces are the most popular choice for heating in residential and commercial settings. They use natural gas as the primary fuel source, which is efficient and affordable. Gas furnaces ignite the gas with a pilot light or electronic ignition and produce heat through a combustion process. They are known for their reliability and ability to quickly warm up a space.
- Oil Furnace: Oil furnaces use heating oil as their fuel source. These furnaces are commonly found in areas where access to natural gas is limited. Oil furnaces are known for their high heat output, making them suitable for colder climates. However, they require an on-site oil storage tank and regular fuel deliveries.
- Electric Furnace: Electric furnaces are powered by electricity, making them a convenient option for homes or buildings without access to gas or oil. Electric furnaces are relatively easy to install and operate silently. However, they tend to have higher operating costs compared to gas or oil furnaces.
- Dual-Fuel Furnace: Dual-fuel furnaces, also known as hybrid furnaces, combine the benefits of both gas and electric furnaces. They can switch between gas and electric heat sources, depending on the outdoor temperature and energy costs. Dual-fuel furnaces are an energy-efficient option and can help homeowners save on heating costs during milder weather.
- High-Efficiency Furnace: High-efficiency furnaces are designed to maximize energy efficiency and reduce energy consumption. They achieve this through features such as sealed combustion chambers, electronic ignition, and condensing technology. High-efficiency furnaces have a higher AFUE (Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency) rating, which indicates the percentage of energy that is converted into usable heat.
In addition to these common types of furnace HVAC systems, there are also specialty furnaces available for specific applications. For example, a modulating furnace adjusts its heat output based on the desired temperature, offering precise control and energy savings. There are also floor furnaces, which are installed directly in the floor, and wall-mounted furnaces for space-saving solutions.
Choosing the right type of furnace HVAC system depends on factors such as the fuel availability in your area, climate conditions, energy efficiency requirements, and budget. Consulting with a qualified HVAC professional can help determine the best option for your specific needs.
Now that we have explored the different types of furnace HVAC systems, let’s delve into the benefits of using a furnace HVAC system in your home.
Regular maintenance of your furnace HVAC system is essential to ensure it operates efficiently and safely. This includes changing air filters, cleaning the system, and scheduling professional inspections.
Read more: What Costs More: Space Heater Or Furnace?
Benefits of Using a Furnace HVAC
Investing in a furnace HVAC system offers a range of benefits that contribute to a comfortable and healthy indoor environment. Here are some of the advantages of using a furnace HVAC system:
- Efficient Heating: Furnace HVAC systems are designed to provide efficient and consistent heating throughout your home. They can quickly warm up the indoor space, ensuring a comfortable temperature even during the coldest months of the year.
- Ventilation: In addition to heating, furnace HVAC systems incorporate ventilation capabilities. These systems exchange indoor and outdoor air, removing stale air and introducing fresh air into the space. Proper ventilation helps maintain good indoor air quality and reduces the presence of pollutants, allergens, and odors.
- Improved Air Quality: Furnace HVAC systems often include air filters that trap dust, pollen, pet dander, and other airborne particles. By filtering the air, these systems help improve indoor air quality, reducing the risk of respiratory issues and allergies.
- Energy Efficiency: Modern furnace HVAC systems are designed to be energy-efficient, helping homeowners reduce their energy consumption and utility bills. High-efficiency furnaces, in particular, have a higher AFUE rating, which means they convert a larger percentage of fuel into usable heat, resulting in less wasted energy.
- Zoning Capability: Some furnace HVAC systems offer zoning capabilities, allowing homeowners to control the temperature in different areas or rooms independently. This allows for personalized comfort and energy savings, as you can heat only the occupied spaces and reduce energy consumption in unoccupied areas.
- Reliability: Furnace HVAC systems, when properly maintained, are known for their reliability. They are built to withstand continuous use and can provide heating and cooling for many years. Regular maintenance, including filter replacement and professional inspections, can help ensure the system operates smoothly and lasts for a long time.
- Flexibility: Furnace HVAC systems offer flexibility in terms of fuel options. Whether it’s natural gas, oil, or electricity, homeowners can choose the fuel source that best suits their needs and availability. This flexibility allows for customization and adaptability to different circumstances.
Overall, using a furnace HVAC system provides the convenience of efficient heating, improved air quality, and ventilation capabilities. It helps create a comfortable and healthy living environment while offering energy-saving benefits. By investing in a reliable furnace HVAC system, homeowners can enjoy the comfort and peace of mind they deserve.
Despite these benefits, it is important to be aware of common problems that can occur with furnace HVAC systems. Let’s explore some of these issues in the next section.
Common Problems with Furnace HVAC Systems
While furnace HVAC systems are generally reliable, it’s essential to be aware of common problems that can occur. Understanding these issues can help homeowners identify and address them promptly. Here are some of the most common problems with furnace HVAC systems:
- Lack of Maintenance: One of the primary causes of furnace HVAC problems is a lack of regular maintenance. Failure to clean or replace air filters, inspect and lubricate moving parts, and check for system malfunctions can lead to reduced efficiency, poor performance, and even system breakdowns.
- Ignition Issues: Ignition problems can prevent the furnace from starting or staying on. It could be due to a faulty ignition switch, pilot light, or electronic ignition system. These issues may require professional repair or replacement.
- Thermostat Malfunction: A malfunctioning thermostat can result in incorrect temperature readings or failure to communicate with the furnace. This can lead to inconsistent heating, discomfort, and increased energy consumption. Calibration, battery replacement, or thermostat replacement may be necessary to resolve the issue.
- Clogged Air Filters: Dirty or clogged air filters restrict airflow, reducing heating efficiency and putting strain on the furnace. This can result in poor air quality, increased energy consumption, and potential damage to the system. Regular filter cleaning or replacement is crucial to maintain optimal performance.
- Gas Supply Issues: If you have a gas furnace, issues with the gas supply can cause heating problems. This may stem from a faulty gas valve, a gas leak, or an issue with the gas line. Gas-related issues should always be addressed by a qualified professional to ensure safety.
- Noisy Operation: Unusual noises coming from the furnace, such as rattling, squeaking, or banging sounds, may indicate loose or worn-out components. Ignoring these noises can lead to further damage and system failure. Prompt inspection and repairs are necessary to resolve the issue.
- Carbon Monoxide Leaks: Carbon monoxide leaks are a serious safety concern with gas or oil furnaces. These leaks can occur due to a cracked heat exchanger or improper ventilation. Carbon monoxide is a poisonous gas, so any suspicion of a leak should be taken seriously. Carbon monoxide detectors are highly recommended to ensure early detection.
It’s important to remember that these are general problems that may occur with furnace HVAC systems. The specific issues can vary depending on the type, age, and maintenance of the system. Regular professional maintenance and inspections can help prevent many of these problems and ensure the smooth operation of your furnace HVAC system.
Now that we’ve explored common problems, let’s move on to some essential tips for maintaining your furnace HVAC system.
Tips for Maintaining a Furnace HVAC System
Maintaining your furnace HVAC system is crucial to ensure optimal performance, energy efficiency, and longevity. With regular maintenance, you can prevent potential issues, improve indoor air quality, and extend the lifespan of your system. Here are some essential tips for maintaining your furnace HVAC system:
- Regular Filter Replacement: One of the simplest yet most important maintenance tasks is to regularly clean or replace the air filters. Clogged filters restrict airflow, reducing system efficiency, and can lead to poor indoor air quality. Check your filters monthly and replace them as recommended by the manufacturer.
- Clean Vents and Registers: Regularly clean the vents and registers throughout your home. Dust and debris can accumulate, obstructing airflow and reducing the efficiency of the system. Use a vacuum attachment or a damp cloth to remove any dirt or debris from the vents.
- Keep the Area Around the Furnace Clear: Make sure the area around your furnace is kept clear of any obstructions. Keep flammable materials, furniture, and boxes away from the furnace to reduce the risk of fire hazards and ensure proper airflow.
- Schedule Professional Maintenance: It’s highly recommended to schedule annual maintenance with a qualified HVAC technician. A professional can inspect, clean, and tune-up your furnace HVAC system, identifying any potential issues and ensuring it operates at peak efficiency.
- Check Carbon Monoxide Detectors: If you have a gas or oil furnace, ensure that you have properly functioning carbon monoxide detectors installed in your home. Regularly check and test the detectors to ensure they are in good working condition, providing an early warning system for any potential carbon monoxide leaks.
- Monitor Energy Consumption: Keep an eye on your energy bills and monitor any significant changes in consumption. Drastic increases in energy usage may indicate an issue with your furnace HVAC system. Promptly address any unusual changes by contacting a professional HVAC technician for inspection and repairs.
- Use Programmable Thermostats: Consider installing programmable thermostats to help regulate the temperature and reduce energy consumption. Program your thermostat to lower the temperature when you’re away from home or asleep and raise it when you need the heat. This can lead to significant energy savings without compromising comfort.
- Address Issues Promptly: If you notice any unusual noises, odors, or performance issues with your furnace HVAC system, address them promptly. Ignoring these signs can result in more significant problems and potential system failures. Contact a professional HVAC technician to diagnose and resolve the issue.
Following these maintenance tips will help ensure the efficient and reliable operation of your furnace HVAC system. Regular maintenance not only improves energy efficiency but also enhances indoor air quality and extends the lifespan of your system.
By taking care of your furnace HVAC system, you can enjoy a comfortable and healthy home for years to come. Remember, when in doubt or if you require professional assistance, it’s always best to consult with a qualified HVAC technician.
Now that we’ve covered furnace HVAC maintenance, let’s conclude our article.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a furnace HVAC system plays a vital role in providing heating, ventilation, and air conditioning for residential and commercial buildings. Understanding the components, operation, and maintenance of these systems is essential for homeowners and HVAC professionals alike.
We began our journey by defining a furnace HVAC system and discussing its key components, including the furnace unit, ductwork, vents or registers, thermostats, and filters. We then explored the process of how a furnace HVAC system works, from the thermostat signaling the furnace to start heating, to the air circulation and ventilation capabilities.
Furthermore, we examined the different types of furnace HVAC systems, including gas, oil, electric, dual-fuel, and high-efficiency furnaces. Each type offers unique advantages and is suited for specific needs and circumstances.
Using a furnace HVAC system offers numerous benefits, such as efficient heating, improved air quality, energy efficiency, and heating customization through zoning capabilities. However, it’s important to be aware of common problems that can occur, such as maintenance neglect, ignition issues, thermostat malfunctions, and clogged filters.
To ensure the optimal performance of your furnace HVAC system, we provided essential maintenance tips, including regularly replacing filters, cleaning vents and registers, scheduling professional maintenance, monitoring energy consumption, and promptly addressing any issues that arise.
Maintaining a well-functioning furnace HVAC system not only ensures comfort and energy efficiency but also contributes to a healthy indoor environment. Regular maintenance and addressing problems promptly can extend the lifespan of your system and save you from costly repairs in the long run.
We hope this comprehensive guide has provided you with valuable insights into furnace HVAC systems. Remember, when it comes to installation, repairs, or maintenance, it’s always best to consult with a qualified HVAC professional to ensure safe and optimal operation.
By understanding and properly caring for your furnace HVAC system, you can enjoy a comfortable, energy-efficient, and healthy home for many years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is A Furnace In HVAC
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.














0 thoughts on “What Is A Furnace In HVAC”