

Articles
What Is A VFD In HVAC
Modified: December 7, 2023
Learn about VFDs in HVAC systems in our informative articles. Discover how Variable Frequency Drives enhance energy efficiency and optimize performance.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
When you think of your HVAC system, you may picture the thermostat, the ductwork, or even the air conditioning unit itself. However, there is a crucial component that often goes unnoticed but plays a significant role in the operation and efficiency of the entire system: the Variable Frequency Drive (VFD).
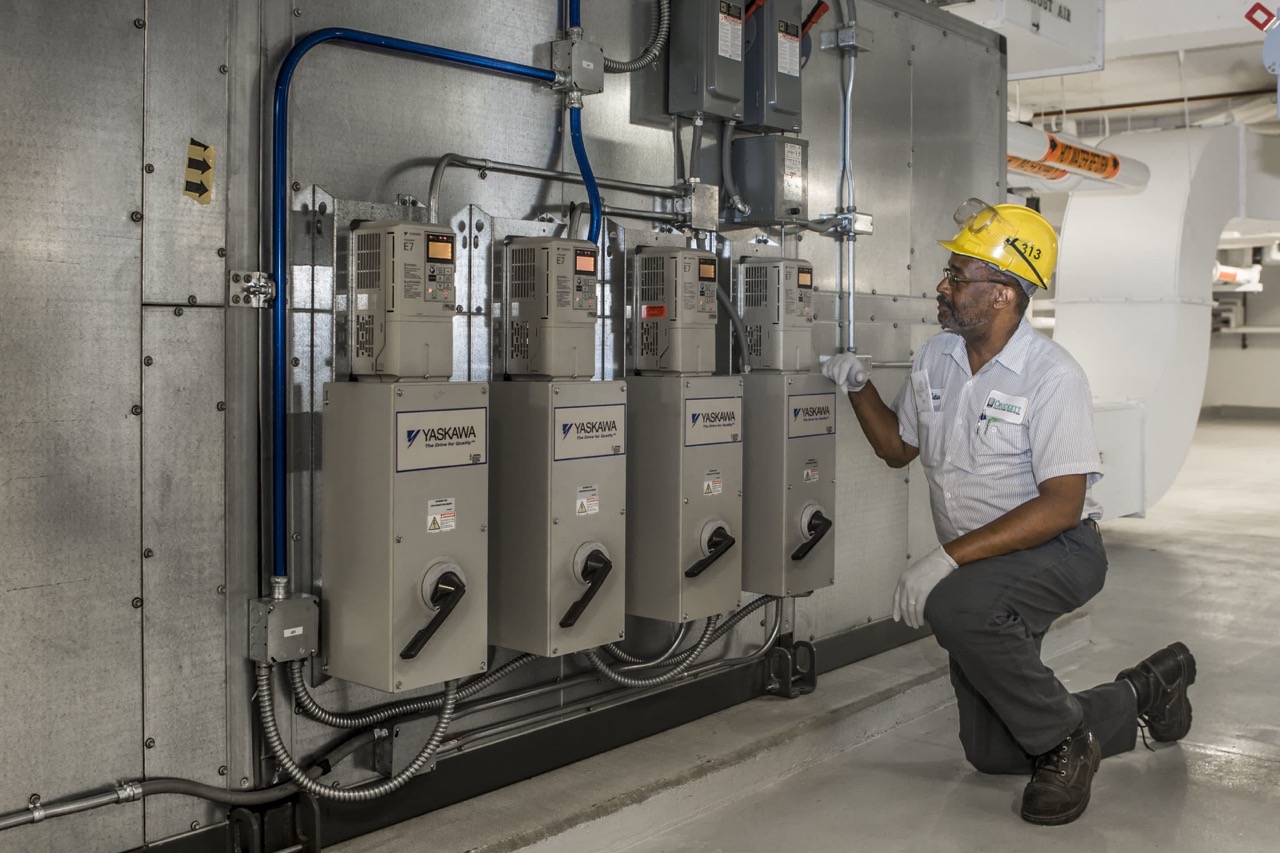
A VFD, also known as a variable speed drive or adjustable speed drive, is an electronic device used to control the speed and power output of an electric motor. In the context of HVAC systems, VFDs are commonly used to regulate the speed of the motor that drives the fan or pump, allowing for precise control and optimization of air circulation or fluid flow.
The purpose of this article is to provide a comprehensive understanding of VFDs in HVAC systems, their functionality, and the benefits they offer. Whether you are a homeowner looking to upgrade your HVAC system or an industry professional seeking to optimize energy efficiency, read on to discover the power of VFDs.
Key Takeaways:
- VFDs in HVAC systems offer energy efficiency, cost savings, and enhanced control. By adjusting motor speed based on demand, VFDs optimize performance, reduce wear and tear, and contribute to a greener approach to HVAC operation.
- The integration of VFDs in HVAC systems provides precise control, extended equipment lifespan, and reduced maintenance expenses. VFDs offer dynamic load management, soft start and stop capabilities, and proactive maintenance, resulting in long-term cost savings and uninterrupted operations.
Read more: What Is A HVAC System?
Definition of VFD
A Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) is an electronic device that controls the speed and power output of an electric motor by varying the frequency and voltage supplied to it. This allows for precise control and manipulation of the motor’s rotational speed, allowing it to be operated at different speeds and power levels as needed.
VFDs utilize advanced power electronics and control algorithms to achieve this variable speed control. They typically consist of three main components: an input rectifier, a DC bus capacitor, and an inverter. The input rectifier converts the incoming AC power into DC power, which is then stored in the DC bus capacitor. The inverter then converts the DC power back into AC power with variable frequency and voltage, which is supplied to the motor.
One of the key features of VFDs is their ability to provide a smooth and continuous control of motor speed over a wide range, from very low speeds to full load operating conditions. This flexibility allows for precise control and optimization of motor-driven systems, such as fans, pumps, and compressors, in various applications.
VFDs are designed to work with three-phase AC motors, which are commonly used in HVAC systems. By adjusting the speed of the motor based on the current demand, VFDs ensure that the motor operates at its most efficient point, resulting in significant energy savings, reduced wear and tear on the motor, and improved system performance.
Overall, VFDs provide a means of achieving energy efficiency, cost savings, and enhanced control in HVAC systems. In the next section, we will delve deeper into how VFDs work and their impact on energy consumption in HVAC applications.
How VFDs Work
Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) operate by adjusting the frequency of the electrical power supplied to an AC motor, thereby controlling the motor’s rotational speed. This control is achieved through a process known as pulse width modulation (PWM).
When an input signal is received by the VFD, it processes the signal and generates pulses of variable width and frequency. These pulses are then sent to the inverter, which converts the DC power from the DC bus capacitor back into AC power. The width and frequency of the pulses determine the speed and power output of the motor.
The VFD continuously monitors the demand from the motor or system it is driving and adjusts the frequency of the output power accordingly. This allows the motor to operate at different speeds and power levels, matching the requirements of the system at any given moment.
By adjusting the frequency of the output power, VFDs can provide precise control over motor speed. This is crucial in HVAC systems, where different operating conditions may require varying levels of airflow or fluid flow.
In addition to speed control, VFDs also offer various other control features, such as torque control, acceleration and deceleration ramps, and dynamic braking. These features allow for smooth and controlled operation of the motor, reducing stress on the system and extending the lifespan of the motor.
Furthermore, VFDs incorporate advanced control algorithms and sensors to continuously monitor motor performance and system conditions. This enables the VFD to make real-time adjustments to maintain optimal performance and efficiency.
Overall, the ability of VFDs to adjust the speed and power output of motors in HVAC systems provides significant advantages in terms of energy efficiency, system control, and equipment longevity. In the next section, we will explore the benefits of using VFDs in HVAC systems.
Benefits of VFDs in HVAC Systems
Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) offer numerous benefits when incorporated into HVAC systems. Let’s explore some of the key advantages they provide:
1. Energy Efficiency: One of the primary benefits of using VFDs in HVAC systems is improved energy efficiency. By adjusting the speed of the motor based on the demand, VFDs ensure that the motor operates at its most efficient point. This eliminates energy wastage that occurs when motors run at full speed even when less power is required. The result is lower energy consumption, reduced utility costs, and a greener approach to HVAC operation.
2. Cost Savings: Due to their energy-saving capabilities, VFDs can significantly reduce operational costs for HVAC systems. By consuming less energy, the system requires less power, resulting in decreased utility bills. Additionally, the ability to control the motor speed also reduces wear and tear on the motor, extending its lifespan and reducing maintenance and replacement costs.
3. Enhanced Control and Precision: VFDs offer precise control over motor speed, allowing for fine-tuning of HVAC system performance. This is particularly beneficial in situations where airflow or fluid flow needs to be adjusted based on specific requirements. By providing variability and flexibility in the system, VFDs enable HVAC systems to adapt to changing conditions, resulting in optimal comfort and performance.
4. Reduced Wear and Tear: Traditional HVAC systems often experience excessive wear and tear on motors due to continuous operation at full speed. By using VFDs, the motor can operate at reduced speeds when there is lower demand, leading to less stress on the motor and prolonging its lifespan. This not only saves on maintenance and repair costs but also improves system reliability and reduces downtime.
5. Improved System Performance: The precise speed control offered by VFDs allows HVAC systems to respond quickly and efficiently to varying conditions. This enables better temperature and humidity control, resulting in improved indoor air quality and comfort. Additionally, VFDs can optimize the performance of fans and pumps, ensuring airflow and fluid flow are precisely matched to the required levels, enhancing overall system performance.
6. Environmental Impact: By reducing energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions, the use of VFDs in HVAC systems contributes to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly approach. This aligns with the global efforts to reduce carbon footprints and mitigate climate change.
Overall, the incorporation of Variable Frequency Drives in HVAC systems brings significant benefits in terms of energy efficiency, cost savings, enhanced control, reduced wear and tear, improved performance, and environmental impact. As a result, VFDs have become an essential technology in modern HVAC applications.
Energy Efficiency
One of the most significant advantages of using Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) in HVAC systems is the improvement in energy efficiency. By controlling the speed of the motor based on the demand, VFDs ensure that the motor operates at its most efficient point, resulting in significant energy savings.
Traditional HVAC systems often run motors at a fixed speed, regardless of the current demand. This means that the motor operates at full power even when it is not necessary, resulting in energy wastage. In contrast, VFDs allow the motor to adjust its speed based on the required airflow or fluid flow, matching the output to the actual demand. This dynamic operation prevents excessive energy consumption and reduces unnecessary power usage.
By modulating the speed of the motor, VFDs can reduce the energy consumption of HVAC systems by up to 50%. This reduction not only leads to immediate cost savings but also contributes to a more sustainable approach to energy usage.
VFDs achieve energy savings by employing several mechanisms:
1. Motor Speed Optimization: HVAC systems typically require different levels of airflow or fluid flow at various times. With VFDs, the motor speed can be adjusted to match the actual demand. For example, during low-demand periods, the motor can operate at a slower speed, consuming less energy. Conversely, during peak demand, the motor can ramp up to deliver the necessary output. This optimization of motor speed ensures that energy is only used when it is needed, minimizing wastage.
2. Soft Start and Stop: VFDs allow for smooth acceleration and deceleration of the motor, eliminating the sudden power surges associated with traditional motor starters. This soft start and stop reduce stress on the motor and minimize energy spikes. By gradually ramping up or down the motor speed, VFDs ensure energy-efficient operation from the moment the system is turned on to when it is shut down.
3. Power Factor Correction: VFDs can also improve the power factor of HVAC systems. Power factor is a measure of how effectively the system uses electrical power. A low power factor indicates a less efficient use of power, resulting in increased energy consumption. VFDs can adjust the power factor by optimizing the voltage and current supplied to the motor, improving the overall energy efficiency of the system.
4. Energy Monitoring and Optimization: Many VFDs come with built-in energy monitoring and optimization features. These capabilities allow for real-time tracking of energy usage and system performance. By analyzing the data, potential energy-saving opportunities can be identified, and adjustments can be made to optimize system operation.
By utilizing the energy-saving capabilities of VFDs, HVAC systems can significantly reduce their energy consumption, resulting in cost savings and a reduced environmental impact. Whether in residential or commercial settings, the integration of VFDs in HVAC systems is an effective strategy for enhancing energy efficiency and achieving sustainability goals.
When selecting a VFD for HVAC systems, make sure to consider the motor’s horsepower, voltage, and current ratings to ensure compatibility and optimal performance.
Read more: What Is A HVAC Contractor
Cost Savings
One of the major advantages of incorporating Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) in HVAC systems is the potential for significant cost savings. VFDs offer various cost-saving benefits that can positively impact both residential and commercial applications.
1. Energy Cost Reduction: By adjusting the speed of the motor to match the required demand, VFDs minimize energy consumption. Traditional HVAC systems often run motors at a fixed speed, leading to energy inefficiency and unnecessary power usage. In contrast, VFDs allow the motor to operate at lower speeds during periods of lower demand, resulting in substantial energy savings. These energy cost reductions can translate into significant savings on utility bills, especially in settings with high HVAC usage.
2. Demand-Based Operation: HVAC systems with VFDs can adapt to varying demand conditions, ensuring that the motor operates at the appropriate speed at all times. In situations where the demand for cooling or heating is low, such as during off-peak hours or in unoccupied zones, VFDs can adjust the motor speed to a lower setting. This demand-based operation eliminates unnecessary energy consumption and lowers energy costs by avoiding the constant operation of motors at full speed when it is not needed.
3. Motor Longevity: VFDs provide precise control over motor speed, which reduces wear and tear on the motor. Running an electric motor at full speed continuously can cause excessive strain on its components, leading to premature failure and the need for costly repairs or replacement. By allowing the motor to operate at lower speeds when the demand is lower, VFDs extend the motor’s lifespan, resulting in maintenance cost savings over time.
4. Reduced Maintenance Expenses: The controlled and optimized operation of HVAC systems with VFDs can reduce the frequency and severity of maintenance and repair needs. By adjusting the motor speed based on demand, VFDs minimize stress on the system, which helps prevent breakdowns and decreases the likelihood of unexpected repairs. With fewer maintenance requirements, the associated costs and potential disruptions to operations are reduced.
5. Enhanced System Performance: VFDs allow for precise control over the motor speed, optimizing the performance of HVAC systems. By adjusting the airflow or fluid flow according to the exact requirements, VFDs ensure that the system operates at its highest efficiency. This leads to improved temperature and humidity control, increased occupant comfort, and overall system performance. Efficient HVAC operation reduces the likelihood of system malfunctions, which can result in costly emergency repairs and downtime.
6. Retrofitting Opportunities: Retrofitting HVAC systems with VFDs is an excellent way to achieve cost savings without the need for a complete system replacement. VFDs can be installed in existing systems to enhance efficiency, decrease energy consumption, and realize cost savings. This allows for a cost-effective upgrade of HVAC systems, resulting in reduced energy expenses over time.
Overall, the implementation of VFDs in HVAC systems provides significant cost-saving opportunities. The reduction in energy costs, extended motor life, decreased maintenance expenses, improved system performance, and retrofitting possibilities contribute to long-term financial savings. Whether in residential, commercial, or industrial settings, VFDs offer a valuable solution for achieving cost-effectiveness in HVAC operations.
Enhanced Control and Precision
Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) offer enhanced control and precision in HVAC systems, allowing for optimized performance and flexibility. By adjusting the motor speed to match the required demand, VFDs provide precise control over airflow or fluid flow, resulting in improved system operation.
1. Variable Speed Control: The primary function of VFDs is to regulate the speed of the motor. This offers a significant advantage in HVAC systems as it allows for precise control over the airflow or fluid flow. For example, in air conditioning systems, VFDs can adjust the fan speed to match the cooling demand in different areas of a building. This enables better temperature control and improved indoor comfort.
2. Fine-Tuning Capabilities: VFDs provide the ability to fine-tune the system’s performance. With precise control over motor speed, HVAC systems can be adjusted to match specific requirements. For instance, in commercial applications, such as server rooms or laboratories, where precise temperature and humidity control are critical, VFDs allow for precise adjustments to meet these specific needs. This level of control ensures optimal performance and increased occupant comfort.
3. Demand-Based Operation: HVAC systems equipped with VFDs can respond dynamically to changing conditions. The speed of the motor can be adjusted based on the demand, ensuring that the system operates at the necessary level at any given time. This adaptability allows for efficient operation and prevents wasted energy by avoiding the constant operation of motors at full speed when it is not needed.
4. Zone Control: VFDs can be utilized in systems with multiple zones, such as in larger commercial buildings. Each zone can be controlled independently by adjusting the motor speed using VFDs. This enables customized temperature control in different areas, optimizing comfort and energy efficiency. By tailoring the system’s operation to each specific zone’s requirements, unnecessary energy consumption is avoided, leading to cost savings.
5. Controllable Acceleration and Deceleration: VFDs allow for controlled acceleration and deceleration of the motor. This gradual ramp-up and ramp-down of the motor speed reduces stress on the system and minimizes wear and tear. The smooth operation of the motor ensures reliable and efficient performance, extending the lifespan of the system components.
6. Integration with Building Automation Systems: VFDs can be seamlessly integrated into building automation systems (BAS), allowing for centralized control and monitoring of HVAC operations. BAS can adjust the motor speed in response to data collected from various sensors, such as temperature and occupancy sensors, ensuring optimal operation at all times. This integration permits intelligent control and automation of the system, optimizing energy efficiency and overall performance.
The enhanced control and precision offered by VFDs in HVAC systems result in improved system performance, better temperature and humidity control, and increased occupant comfort. The ability to match the motor speed to the specific demand leads to energy savings and cost reduction. Whether in residential, commercial, or industrial settings, VFDs provide a valuable solution for achieving precise control and optimizing overall HVAC system operations.
Reduced Wear and Tear
Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) play a critical role in reducing wear and tear on HVAC system components, particularly on electric motors. By controlling the motor speed and allowing it to operate at lower speeds when demand is lower, VFDs minimize stress on the system, resulting in extended equipment lifespan and reduced maintenance requirements.
1. Soft Start and Stop: VFDs provide soft start and stop capabilities, which allow for gradual acceleration and deceleration of the motor. Traditional HVAC systems often use direct-on-line or across-the-line starting methods, which cause sudden high currents and mechanical stresses when the motor starts or stops. With VFDs, the motor speed is smoothly ramped up and down, resulting in reduced mechanical and electrical stress on the motor windings and other system components.
2. Optimal Speed Operation: VFDs enable the motor to operate at its most efficient speed, which reduces wear and tear on the system. When a motor runs continuously at full speed, it can lead to excessive friction, heat generation, and component fatigue. By adjusting the motor speed to match the required demand, VFDs ensure that the motor operates within its optimal speed range, minimizing wear on bearings, shafts, and other moving parts.
3. Dynamic Load Management: HVAC systems often experience varying load demands throughout the day. With the use of VFDs, the motor speed can be adjusted in response to these changing loads, preventing overloading and reducing the risk of mechanical failures. By dynamically managing the motor load, VFDs help distribute the stress evenly across the system, resulting in reduced component wear and increased system reliability.
4. Reduced Mechanical Shock: VFDs can mitigate the mechanical shock that occurs when a motor starts or stops abruptly. The gradual acceleration and deceleration provided by VFDs eliminate sudden jerks or shocks to the system, minimizing the stress on belts, gears, and other mechanical components. This reduces the likelihood of component failure and extends the lifespan of the equipment.
5. Preventive Maintenance: VFDs can contribute to a proactive maintenance approach by providing real-time condition monitoring and fault detection capabilities. Many VFDs are equipped with built-in diagnostic features that allow for continuous monitoring of motor performance and system conditions. By detecting and addressing issues at an early stage, maintenance interventions can be made before they turn into costly breakdowns. Regular maintenance and prompt repair of identified problems further reduce wear and tear on the system.
6. Extended Equipment Lifespan: The combined effects of soft start and stop, optimal speed operation, dynamic load management, and proactive maintenance contribute to extending the lifespan of HVAC system components. By reducing wear and tear on motors, bearings, belts, and other system parts, VFDs minimize the frequency of repairs and replacements, resulting in long-term cost savings.
The integration of VFDs in HVAC systems offers significant benefits in terms of reducing wear and tear on components. By optimizing motor speed, providing soft start and stop capabilities, managing dynamic loads, and facilitating preventive maintenance, VFDs contribute to the longevity and reliability of the system. The reduced maintenance requirements and extended equipment lifespan translate into cost savings and uninterrupted operations.
Conclusion
Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) are invaluable components in HVAC systems, offering a wide range of benefits that enhance efficiency, control, and longevity. By controlling the speed and power output of electric motors, VFDs enable precise control over airflow or fluid flow, resulting in optimized system performance.
VFDs provide energy efficiency by adjusting motor speed to match the required demand, reducing energy consumption and utility costs. The ability to operate at lower speeds during periods of low demand also reduces wear and tear on motors, extending their lifespan and minimizing maintenance and repair expenses.
Additionally, VFDs offer enhanced control and precision in HVAC systems. With variable speed control, fine-tuning capabilities, and demand-based operation, HVAC systems can adapt to changing conditions, ensuring optimal performance and occupant comfort. VFDs also provide improved motor control during startup and shutdown, reducing mechanical stress and component fatigue.
The use of VFDs in HVAC systems also contributes to cost savings. Energy cost reduction, extended equipment lifespan, reduced maintenance expenses, and improved system performance all add up to financial benefits. These advantages make VFDs a worthwhile investment in both residential and commercial applications.
Furthermore, VFDs align with sustainability goals by reducing energy consumption and minimizing environmental impact. Through energy efficiency and precise control, VFDs help to create greener HVAC systems that consume less power and produce fewer greenhouse gas emissions.
In conclusion, the integration of Variable Frequency Drives in HVAC systems provides significant advantages. These include energy efficiency, cost savings, enhanced control and precision, and reduced wear and tear. By incorporating VFDs, HVAC systems can operate at their utmost efficiency, delivering optimal comfort, performance, and environmental sustainability.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is A VFD In HVAC
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.














0 thoughts on “What Is A VFD In HVAC”