

Articles
What Is A HVAC Sequencer
Modified: January 6, 2024
Learn about different types of sequencers used in HVAC systems in this informative article. Discover how sequencers work and their importance in controlling heating and cooling equipment.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Welcome to the world of HVAC! If you’re not familiar with this acronym, it stands for Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning. HVAC systems are essential components of any building, ensuring a comfortable and controlled environment for occupants. One crucial element of an HVAC system is the sequencer, which plays a pivotal role in maintaining the efficiency and functionality of the system.
In this article, we will delve into the world of sequencers in HVAC systems. We will explore what exactly a sequencer is, its functions, different types available, and how it operates within the broader HVAC system. Moreover, we will discuss the benefits of using sequencers in HVAC systems and common troubleshooting issues that may arise.
Whether you are an HVAC professional, a building owner, or simply a curious individual wanting to learn more, this article will provide you with all the necessary insights into the world of HVAC sequencers. So, let’s get started!
Key Takeaways:
- HVAC sequencers optimize energy efficiency by controlling the activation of heating elements, ensuring gradual heat output, and protecting against circuit overload. They contribute to cost savings and a comfortable indoor environment.
- Troubleshooting sequencer issues involves checking power supply, inspecting wiring, and replacing faulty components. Seeking professional assistance for complex problems ensures optimal HVAC system performance and safety.
Read more: What Is A HVAC System?
What is HVAC?
HVAC, an acronym for Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning, refers to the technology used to control and maintain temperature, humidity, and air quality in indoor spaces. HVAC systems are commonly found in homes, office buildings, schools, hospitals, and other commercial spaces.
The primary purpose of HVAC systems is to provide a comfortable environment for occupants by regulating the temperature and humidity levels. In addition to temperature control, HVAC systems also incorporate ventilation and air filtration to ensure proper airflow and maintain indoor air quality.
Heating systems within HVAC are responsible for raising the temperature of the indoor space during colder months. This can be achieved through various methods such as furnaces, boilers, or heat pumps. These systems generate heat and distribute it throughout the building via ductwork or radiant heat sources.
Ventilation is a crucial aspect of HVAC as it involves the exchange of stale indoor air with fresh outdoor air. Ventilation helps remove pollutants, odors, and excess moisture from the indoor space, improving the overall air quality.
Air conditioning, often the most familiar aspect of HVAC, involves the cooling and dehumidification of indoor air. Air conditioning systems use refrigeration cycles to remove heat from the indoor air and maintain a comfortable temperature, especially during hot summer months.
Modern HVAC systems also incorporate advanced technologies, such as programmable thermostats and zoning systems, which provide greater control and energy efficiency. These technologies allow for customized temperature settings in different areas of a building and can be programmed to adjust settings based on occupancy patterns, saving energy and reducing costs.
In summary, HVAC systems are responsible for regulating temperature, humidity, and air quality in indoor spaces. By providing heating, ventilation, and air conditioning, these systems create a comfortable and healthy environment for occupants throughout the year.
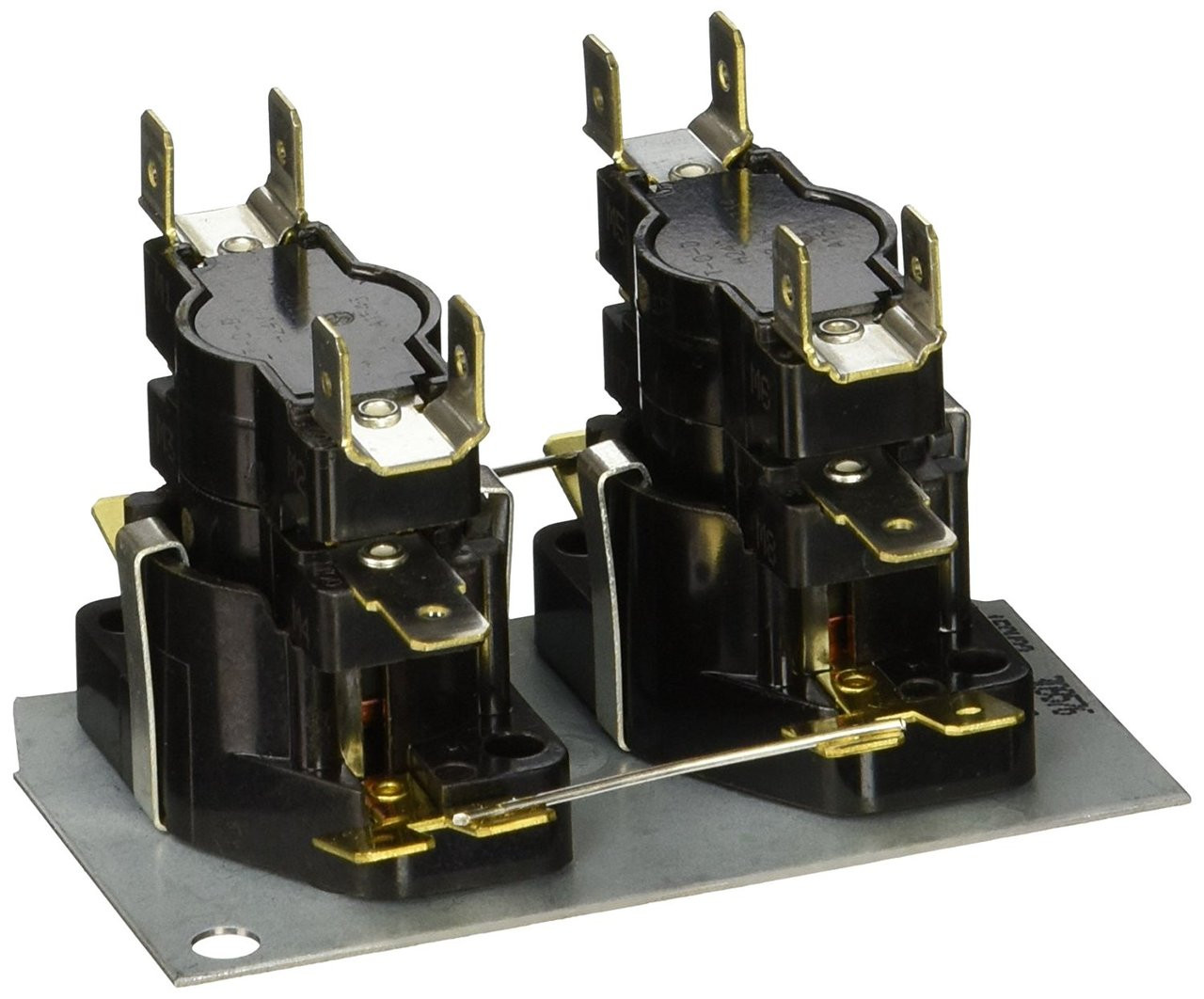
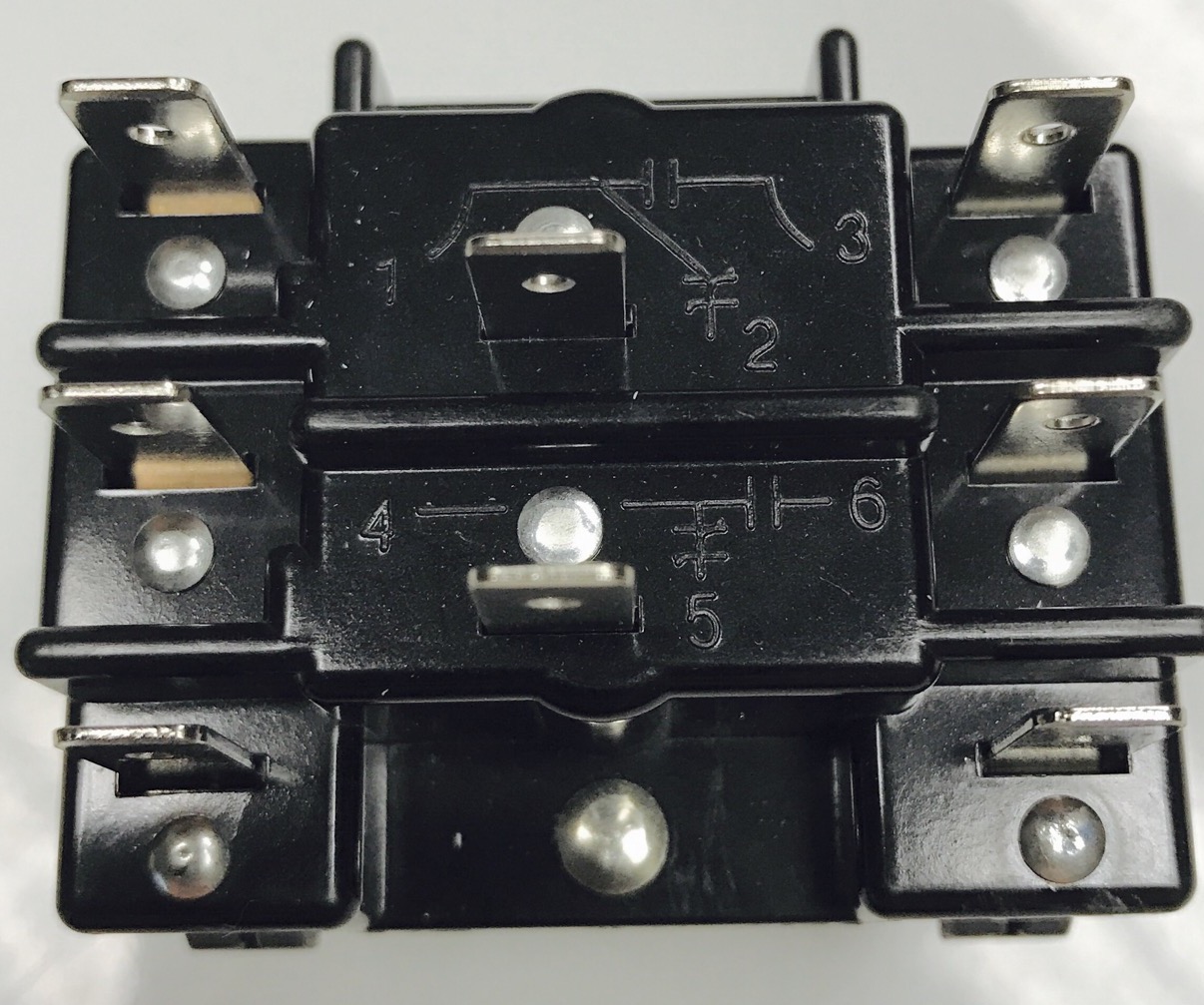
What is a Sequencer?
A sequencer, in the context of HVAC systems, is a device or control component that regulates the operation and sequencing of heating elements in electric furnaces or heat pump systems. It ensures that the heating elements or stages are activated in the correct order, providing efficient and controlled heating.
Sequencers are commonly used in electric furnaces and heat pumps to control the timing and duration of the heating elements or stages. In electric furnaces, these heating elements may be arranged in multiple stages to provide gradual and efficient heating. Heat pumps, on the other hand, may have multiple stages of electric heat backup to supplement the heat pump’s heating capacity in colder weather.
A sequencer typically consists of multiple switches or relays, each associated with a specific heating element or stage. These switches are interconnected and are controlled by a timing mechanism, ensuring that the heating elements are activated in the correct order and for the appropriate duration.
The sequencing of heating elements allows for a more efficient use of energy and prevents excessive electrical loads that could trip circuit breakers. By activating the heating elements incrementally, the sequencer ensures that the electric furnace or heat pump operates within its optimal capacity and avoids power surges.
Sequencers may also incorporate safety features such as temperature limits to prevent overheating. These safety features help protect the heating elements from damage caused by prolonged or excessive use.
It is important to note that the specific design and functionality of sequencers may vary depending on the HVAC system and manufacturer. Some sequencers may be integrated into the circuit board of the furnace or heat pump, while others may be standalone components.
In summary, a sequencer in HVAC systems is a control device that regulates the sequencing and operation of heating elements or stages in electric furnaces or heat pumps. By ensuring the proper order and timing of activation, sequencers optimize energy efficiency and prevent electrical overload, providing efficient and controlled heating for indoor spaces.
Functions of a Sequencer in HVAC Systems
A sequencer plays several important functions in HVAC systems, primarily in electric furnaces and heat pumps. Let’s explore the key functions of a sequencer in more detail:
- Control of Heating Elements: One of the main functions of a sequencer is to control the activation and deactivation of the heating elements in the system. By sequencing the heating elements in the correct order, the sequencer ensures that the electric furnace or heat pump operates efficiently and provides consistent heating.
- Optimized Energy Efficiency: Sequencers help optimize energy efficiency by controlling the activation of heating elements based on the heating demand. Instead of activating all heating elements simultaneously, which could overload the electrical system, the sequencer activates them incrementally, matching the required heating load. This prevents unnecessary energy consumption and leads to cost savings.
- Gradual Heat Output: Electric furnaces and heat pumps often have multiple stages of heating elements. The sequencer coordinates the activation of these stages, allowing for a gradual increase in heat output. This staged approach helps maintain a consistent and comfortable temperature within the indoor space.
- Circuit Protection: By sequencing the heating elements, the sequencer helps protect the electrical circuit from overload. It ensures that the power demand remains within the capacity of the circuit, preventing the circuit breaker from tripping. This safeguards the system and prevents potential damage or downtime.
- Safety Features: Many sequencers incorporate safety features to protect the system and heating elements. For instance, they may include temperature limit switches that monitor the temperature of the heating elements. If the temperature exceeds the specified limit, the sequencer will deactivate the corresponding heating element to prevent overheating and potential damage.
Overall, a sequencer plays a vital role in controlling and optimizing the operation of heating elements in HVAC systems. By sequencing the heating elements and managing the power demand, the sequencer ensures energy efficiency, consistent heat output, circuit protection, and safety. It is an essential component that contributes to the reliable and efficient functioning of electric furnaces and heat pumps in maintaining a comfortable indoor environment.
Types of Sequencers Used in HVAC Systems
In HVAC systems, various types of sequencers are employed to control the operation and sequencing of heating elements. These sequencers may differ in their design, functionality, and how they are integrated into the system. Let’s explore some of the common types of sequencers used:
- Electronic Sequencers: Electronic sequencers are commonly found in modern HVAC systems. They utilize electronic circuitry to control the timing and activation of the heating elements. These sequencers offer precise control and flexibility, allowing for efficient operation and energy management. They are often integrated into the control board of the furnace or heat pump.
- Timed Sequencers: Timed sequencers rely on a mechanical timer mechanism to coordinate the activation and deactivation of the heating stages. They use a series of mechanical switches or relays, each associated with a specific heating stage. The timer sets the duration for each stage, ensuring that the heating elements are activated in the correct sequence.
- Guardian Sequencers: Guardian sequencers are advanced types of sequencers that incorporate additional safety features. In addition to controlling the sequencing of heating elements, they include built-in temperature limit switches to protect against overheating. If the temperature exceeds a specified limit, the sequencer will deactivate the corresponding heating element to prevent damage or hazards. These sequencers prioritize safety and provide added protection for the system.
- Direct Replacement Sequencers: Direct replacement sequencers are designed to be compatible with specific HVAC systems as a direct replacement for an existing sequencer. They are manufactured to match the wiring and mounting configuration of the original sequencer, making installation and replacement relatively straightforward. Direct replacement sequencers are a convenient option when a sequencer needs to be replaced without modifying the existing system.
- Multi-Stage Sequencers: As the name suggests, multi-stage sequencers are designed to control heating elements or stages that operate in multiple stages. They allow for the activation of heating elements in a gradual and controlled manner, ensuring consistent heat output and optimal energy management. Multi-stage sequencers are commonly used in electric furnaces and heat pumps that have multiple stages of heating elements.
It’s important to note that the specific type of sequencer used in an HVAC system may vary depending on the manufacturer and model. HVAC professionals and technicians are typically familiar with the specific sequencer requirements for different systems and can recommend the appropriate type for replacement or installation.
By utilizing the appropriate type of sequencer for a given HVAC system, optimal performance, energy efficiency, and system reliability can be achieved. These sequencers ensure the proper sequencing and control of heating elements, contributing to a comfortable indoor environment and efficient operation of the heating system.
A sequencer in HVAC systems is a control device that regulates the operation of electric heating elements or stages in a heat pump. It ensures that the heating elements or stages are activated in the correct sequence to optimize energy efficiency and prevent overloading the system.
Read more: What Is A HVAC Contractor
How Does a Sequencer Work in an HVAC System?
A sequencer in an HVAC system, such as an electric furnace or a heat pump, is responsible for coordinating the activation and deactivation of the heating elements or stages. Let’s take a closer look at how a sequencer works within the broader HVAC system:
1. Control Logic: The sequencer operates based on a predetermined control logic. This logic determines the order and timing of the heating elements’ activation. It ensures that the heating elements are activated in the correct sequence, optimizing energy efficiency and heat distribution.
2. Sensor or Thermostat Input: The sequencer receives input from a temperature sensor or a thermostat in the system. This input provides the sequencer with information about the current temperature or the desired temperature set by the occupants. Based on this input, the sequencer determines the heating demand and initiates the appropriate sequencing.
3. Timing Mechanism: The sequencer incorporates a timing mechanism, which could be electronic or mechanical, that controls the duration of each heating element’s activation. This timing mechanism ensures that each stage of heating elements operates for the specified time before deactivating.
4. Sequencing Switches or Relays: The sequencer utilizes switches or relays to control the activation and deactivation of the heating elements. Each switch or relay is associated with a specific heating element or stage. These switches are interconnected, allowing the sequencer to control their activation in the desired sequence.
5. Sequencing Process: When the sequencer receives the input signal indicating the need for heating, it begins the sequencing process. It activates the first heating element or stage according to the predetermined control logic, allowing it to generate heat. The timing mechanism ensures that the heating element operates for the designated duration.
6. Sequencing Progression: Once the first heating element or stage completes its cycle, the sequencer moves on to activate the next heating element or stage in the sequence. This progression continues until all the heating elements have been activated and operated according to their specified time duration.
7. Temperature Monitoring: Many sequencers include temperature sensors or limit switches that monitor the temperature of the heating elements. If the temperature exceeds a predetermined limit, the sequencer may deactivate the corresponding heating element to prevent overheating. This built-in safety feature protects the system from damage and ensures safe operation.
By controlling the sequencing and duration of the heating elements, a sequencer optimizes energy efficiency, prevents overload, and ensures proper heat distribution within the HVAC system. It enables gradual heating, temperature control, and efficient operation, ultimately contributing to a comfortable indoor environment.
Benefits of Using Sequencers in HVAC Systems
Sequencers play a crucial role in HVAC systems, specifically in electric furnaces and heat pumps. Incorporating sequencers into these systems offers several benefits that contribute to the overall efficiency, performance, and comfort of the HVAC system. Let’s explore the key benefits of using sequencers:
- Energy Efficiency: Sequencers help optimize energy efficiency by controlling the activation of heating elements based on heating demand. Instead of using all heating elements simultaneously, sequencers activate them incrementally in stages. This approach matches the required heating load, avoiding unnecessary energy consumption and reducing utility costs.
- Gradual Heat Output: With a sequencer, the heating elements in an HVAC system can be activated in a staged manner. This allows for a gradual increase in heat output, maintaining a consistent and comfortable indoor temperature. By avoiding sudden temperature fluctuations, sequencers enhance occupant comfort and reduce the workload on the system.
- Improved System Performance: Sequencers ensure the correct sequencing and synchronization of heating elements, which improves the overall performance of the HVAC system. By activating the heating elements in the proper order, sequencers prevent system overload and optimize the heating process, resulting in efficient and effective heating performance.
- Preventing Circuit Overload: Sequencers help protect the electrical circuit from overloading. By coordinating the timing and duration of the heating elements, sequencers ensure that the power demand remains within the capacity of the circuit. This prevents circuit breakers from tripping and safeguards the system from potential damage or downtime.
- Enhanced Safety: Many sequencers incorporate safety features such as temperature limit switches. These switches monitor the temperature of the heating elements and deactivate them if the temperature exceeds a specified limit. By preventing overheating, sequencers contribute to the safety and longevity of the HVAC system, reducing the risk of equipment damage or fire hazards.
- Extended Equipment Lifespan: Proper sequencing and controlled operation of heating elements extend the lifespan of the HVAC system. By avoiding excessive strain and reducing wear and tear, sequencers help maintain the longevity and reliability of the heating equipment. This translates to fewer repairs, replacements, and overall cost savings for the building owner.
In summary, using sequencers in HVAC systems provides numerous benefits, including improved energy efficiency, consistent heat output, enhanced system performance, prevention of circuit overload, heightened safety, and extended equipment lifespan. By incorporating sequencers into electric furnaces and heat pumps, HVAC systems can operate more efficiently, reducing energy consumption and costs while ensuring a comfortable indoor environment.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting of Sequencers in HVAC Systems
While sequencers play a vital role in the operation of HVAC systems, like any component, they can encounter issues that may affect their performance. Understanding common issues and troubleshooting techniques for sequencers can help troubleshoot problems and restore optimal functionality. Here are some common issues and troubleshooting steps:
- Failure to Activate: One possible issue is when the sequencer fails to activate the heating elements. This could occur due to a faulty sequencer or a problem with the control circuit. Troubleshooting involves checking the power supply to the sequencer, ensuring adequate voltage, and inspecting the wiring and connections to identify any faults.
- Inconsistent Heating: If the heating output is inconsistent or uneven, it could indicate a sequencing problem. Check for any damaged or faulty switches or relays in the sequencer. Inspect the wiring connections and ensure they are secure. If necessary, replace the defective components to restore proper sequencing and consistent heat output.
- Overheating: Sequencers incorporate temperature limit switches to protect against overheating. If the heating elements continue to overheat, it may signal a malfunctioning temperature limit switch. Check the switch for proper operation and ensure it is set to the correct temperature threshold. Replace the temperature limit switch if necessary to prevent equipment damage and ensure safety.
- Short Cycling: Short cycling refers to frequent and rapid cycles of the sequencer, where the heating elements turn on and off rapidly. This may indicate a problem with the thermostat, such as improper calibration or incorrect placement. Verify the thermostat settings, recalibrate if needed, and ensure there are no obstructions affecting its operation. If the issue persists, consider replacing the thermostat.
- Inadequate Heating: If the HVAC system fails to provide adequate heating, it could be due to a sequencer issue. Inspect the sequencer for any defective switches, relays, or timing mechanisms that may be affecting the proper sequencing of the heating elements. Check for loose or damaged wiring connections and repair or replace as necessary. It’s also important to assess the overall capacity of the system to ensure it is adequate for the heating load.
- Professional Assistance: If troubleshooting the sequencer issues proves challenging or if there are complex electrical faults, it’s recommended to seek professional assistance from an HVAC technician. They have the expertise and tools to diagnose and address sequencer problems effectively, ensuring optimal performance and safety.
Remember, safety should always be a priority when troubleshooting sequencers. Ensure the power to the HVAC system is turned off before inspecting or working on any components. If you’re unsure about any troubleshooting steps or encounter complex issues, it’s best to consult a professional to avoid any risks or further damage to the system.
By understanding common issues and implementing appropriate troubleshooting techniques, HVAC professionals and technicians can rectify sequencer problems, ensuring the proper functioning and reliable performance of the HVAC system.
Conclusion
In conclusion, sequencers play a vital role in HVAC systems, specifically in electric furnaces and heat pumps, by controlling the activation and sequencing of heating elements. They optimize energy efficiency, provide consistent heat output, and ensure the safe and reliable operation of the system.
HVAC sequencers offer several benefits, including increased energy efficiency, gradual heat output, improved system performance, protection against circuit overload, enhanced safety features, and extended equipment lifespan. By incorporating sequencers into HVAC systems, property owners can enjoy reduced energy consumption, lower utility costs, and a comfortable indoor environment.
However, sequencers may encounter issues such as failure to activate, inconsistent heating, overheating, short cycling, or inadequate heating. Troubleshooting these issues involves checking power supply, inspecting wiring and connections, replacing faulty switches or relays, and ensuring proper temperature limit settings.
If troubleshooting becomes complex or involves electrical faults, it is advisable to seek professional assistance from an HVAC technician. They possess the necessary expertise to diagnose and address sequencer problems effectively, ensuring optimal system performance and safety.
Sequencers are a crucial component in HVAC systems, contributing to their overall efficiency, reliability, and functionality. Understanding the functions, types, and troubleshooting techniques associated with sequencers empowers HVAC professionals and technicians to maintain and optimize the performance of these systems.
Whether you are an HVAC professional, a building owner, or simply curious about HVAC systems, having knowledge about sequencers helps in better understanding the intricacies of heating systems and their role in maintaining a comfortable indoor environment.
So, next time you feel the warmth during chilly winters or enjoy the cool breeze in scorching summers, remember that sequencers are working behind the scenes, ensuring your HVAC system operates efficiently and provides the comfort you deserve.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is A HVAC Sequencer
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.














0 thoughts on “What Is A HVAC Sequencer”