

Articles
What Is MUA In HVAC
Modified: December 7, 2023
Discover what MUA in HVAC refers to and learn about its importance in this collection of articles. Gain valuable insights and stay informed.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Welcome to the world of HVAC, where temperature control and indoor air quality are of paramount importance. HVAC, which stands for Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning, is a system that ensures comfortable living and working environments by regulating the temperature, humidity, and airflow in a building. It plays a crucial role in providing thermal comfort and maintaining good air quality.
Within the realm of HVAC, one term you may come across is MUA, which stands for Make-Up Air. MUA is an essential component of HVAC systems, and understanding its purpose and functionality is crucial for efficient and effective operation of these systems.
In this article, we will delve into the world of MUA in HVAC, exploring its definition, importance, components, types, installation factors, benefits, and challenges associated with its implementation. So, let’s dive in and demystify the concept of MUA in HVAC systems.
Key Takeaways:
- MUA, or Make-Up Air, is a vital component of HVAC systems, ensuring proper ventilation, pressure balance, and indoor air quality. It plays a crucial role in creating a comfortable and healthy indoor environment for occupants.
- Incorporating MUA systems in HVAC designs offers benefits such as improved indoor air quality, regulated temperature and humidity, energy efficiency, and enhanced occupant comfort. However, challenges like air quality, energy consumption, and maintenance need to be addressed for effective operation.
Read more: What Is A HVAC System?
Definition of HVAC
HVAC, an acronym for Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning, refers to the technology and system that is designed to control and maintain the indoor environment of a building or space. It involves the regulation of temperature, humidity, air quality, and airflow to create a comfortable and healthy living or working environment.
The primary function of HVAC systems is to provide thermal comfort by controlling the temperature, ensuring that it remains within a desirable range. They achieve this by heating the air in colder climates or cooling it in warmer climates. Additionally, HVAC systems also help regulate humidity levels, eliminating excess moisture that can lead to mold growth or discomfort.
Another crucial aspect of HVAC systems is ventilation. Ventilation is the process of exchanging indoor air with outdoor air, providing fresh air for breathable and clean indoor environments. Proper ventilation helps remove pollutants, odors, and airborne contaminants, ensuring good air quality and reducing the risk of respiratory issues.
Overall, an HVAC system combines heating, cooling, and ventilation technologies to create a comfortable, healthy, and energy-efficient indoor environment, not just in residential buildings but also in commercial, industrial, and institutional spaces.
Now that we have a basic understanding of HVAC, let’s explore the concept of MUA in more detail.
Understanding MUA in HVAC
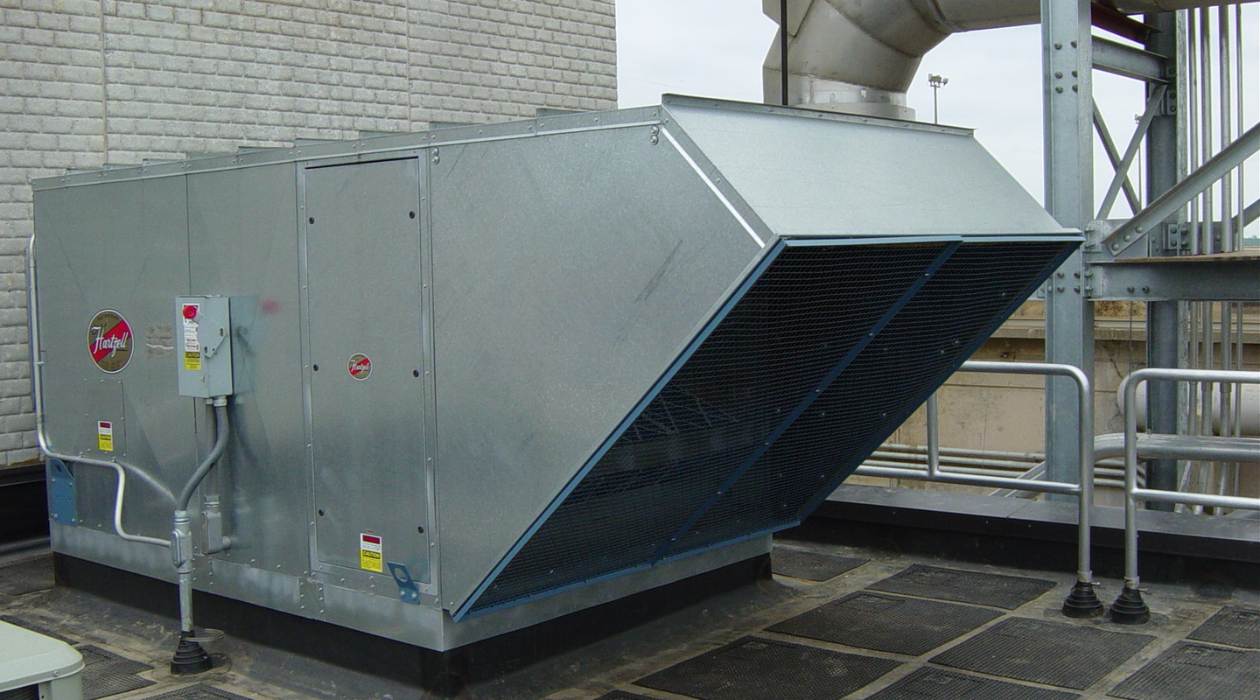
MUA, short for Make-Up Air, is a crucial component of HVAC systems that ensures proper ventilation and maintains the balance of air pressure within a building. In simple terms, MUA refers to the process of introducing fresh outdoor air into the building to replace the stale indoor air that has been exhausted.
During the operation of HVAC systems, air is constantly being circulated and conditioned to maintain the desired temperature. However, this process can create a negative pressure imbalance within the building. If not addressed, this negative pressure can lead to several problems, such as difficulty in opening doors, backdrafts, and even potential health hazards.
MUA serves as a solution to these problems by bringing in fresh outside air to compensate for the exhaust air that is being removed. This helps maintain a neutral or positive pressure balance within the building, ensuring proper ventilation and a healthy indoor environment.
Moreover, MUA also plays a vital role in regulating humidity levels. By introducing outside air, especially in humid climates, MUA helps prevent excessive moisture buildup and reduces the risk of mold growth and associated health issues.
Additionally, MUA systems can be equipped with air filtration mechanisms to remove pollutants, allergens, and contaminants from the incoming outdoor air, further improving the indoor air quality.
Now that we understand the purpose and significance of MUA in HVAC systems, let’s explore why it is important to incorporate MUA in HVAC system designs.
Importance of MUA in HVAC Systems
MUA (Make-Up Air) is an integral part of HVAC systems, and its significance cannot be overstated. Here are a few key reasons why MUA is important in HVAC system designs:
- Ventilation and Indoor Air Quality: MUA ensures proper ventilation by introducing fresh outdoor air into the building. This helps remove indoor pollutants, odors, and contaminants, thereby improving the overall indoor air quality. Adequate ventilation is essential for maintaining a healthy and comfortable living or working environment.
- Pressure Balance: MUA plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance of air pressure within a building. By introducing outside air to compensate for the exhaust air, it helps prevent negative pressure imbalances, which can lead to various issues such as difficulty in opening doors, backdrafts, and unwanted airflow patterns. A neutral or positive pressure balance ensures smoother operation of the HVAC system and a more comfortable environment for occupants.
- Temperature and Humidity Regulation: MUA can help regulate temperature and humidity levels within a building. In colder climates, MUA systems can preheat the incoming outdoor air before it is introduced, minimizing heat loss and reducing the need for additional heating. In humid climates, MUA systems can remove moisture from the incoming air, preventing excess humidity and the growth of mold and mildew.
- Energy Efficiency: Incorporating MUA systems in HVAC designs can contribute to energy efficiency. By utilizing energy recovery mechanisms, such as heat exchangers, MUA systems can recover energy from the exhaust air to condition the incoming outdoor air. This reduces the overall energy demand of the HVAC system and can result in significant energy savings.
- Occupant Comfort and Productivity: Proper ventilation provided by MUA systems ensures a fresh and comfortable indoor environment, promoting occupant well-being and productivity. Good air quality and temperature control contribute to a healthier and more pleasant environment, allowing occupants to focus and perform at their best.
As you can see, MUA is vital for maintaining indoor air quality, pressure balance, temperature regulation, energy efficiency, and occupant comfort. It is a critical component of HVAC systems and should be carefully considered and integrated into the design and implementation processes.
Now that we understand the importance of MUA, let’s explore the components that make up an MUA system in HVAC.
Components of MUA System
A comprehensive MUA (Make-Up Air) system consists of several key components that work together to ensure the efficient and effective introduction of fresh outdoor air into a building. Understanding these components is crucial for designing and implementing an MUA system in HVAC. Let’s explore the main components of an MUA system:
- Outdoor Air Intake: This is the entry point where fresh outdoor air is brought into the building. It is typically located in a well-ventilated area away from potential sources of contamination.
- Air Filters: Air filters clean the incoming outdoor air by removing particles, dust, allergens, and pollutants. Different types of filters, such as mechanical filters or electrostatic filters, can be used depending on the specific air quality requirements.
- Air Handler: The air handler is responsible for conditioning the incoming outdoor air before it is introduced into the building. It may include components such as heating coils, cooling coils, and humidifiers/dehumidifiers to adjust the temperature and humidity levels as needed.
- Blowers or Fans: Blowers or fans are used to facilitate the flow of air throughout the MUA system. They help ensure proper air circulation and distribution within the building.
- Ductwork: Ductwork serves as the pathway for the air to travel from the MUA system to various areas of the building. It distributes the fresh air to different zones, rooms, or spaces, ensuring proper ventilation throughout the building.
- Controls and Sensors: Controls and sensors are essential for monitoring and regulating the MUA system. They can include temperature sensors, humidity sensors, pressure sensors, and control panels that allow for adjustments and optimization of airflow and air quality.
- Exhaust Systems: Exhaust systems work in conjunction with the MUA system to remove stale or contaminated indoor air from the building. They help create the necessary air exchange and maintain a balanced airflow within the HVAC system.
- Energy Recovery Systems: Energy recovery systems, such as heat exchangers or desiccant wheels, are optional components that can be included in MUA systems to improve energy efficiency. These systems capture and reuse energy from the exhaust air to condition the incoming outdoor air, reducing energy consumption and costs.
By integrating these components, an MUA system ensures the proper intake, filtration, conditioning, and distribution of fresh outdoor air throughout the building. This results in improved indoor air quality, pressure balance, and occupant comfort.
Now that we understand the components of an MUA system, let’s explore the different types of MUA systems used in HVAC.
MUA in HVAC stands for Makeup Air Unit, which is responsible for bringing in fresh air from outside to replace the air that is exhausted from a building. It is important for maintaining indoor air quality and proper ventilation.
Read more: What Is A HVAC Contractor
Types of MUA Systems
Make-Up Air (MUA) systems come in various types, each designed to meet specific ventilation requirements and building characteristics. The choice of MUA system depends on factors such as building size, occupancy, climate conditions, and energy efficiency goals. Let’s explore some common types of MUA systems:
- Direct-Fired MUA: This type of MUA system directly introduces fresh outdoor air into the building after being heated by a burner or electric heater. The advantage of direct-fired MUA is that it can provide a significant amount of heating quickly. However, it is important to ensure proper ventilation and combustion safety measures are in place to avoid any potential hazards.
- Indirect-Fired MUA: In an indirect-fired MUA system, the outdoor air is heated using a separate heat exchanger. This ensures that the combustion products generated during the heating process are kept separate from the supply air. This type of system is preferred when avoiding direct contact between the supply air and the combustion by-products is necessary, such as in food processing facilities or areas with strict air quality requirements.
- Cooling-Coil MUA: Cooling-coil MUA systems are used in warm climates or situations where cooling is required. The outdoor air is cooled by passing it through a cooling coil before being delivered into the building. This helps lower the temperature and reduce humidity levels, ensuring occupant comfort and preventing moisture-related issues.
- Heat Recovery Ventilation (HRV) / Energy Recovery Ventilation (ERV) Systems: HRV and ERV systems are designed to recover energy from the exhausted air and transfer it to the incoming outdoor air. HRV systems exchange heat only, while ERV systems exchange both heat and moisture. These systems are highly energy-efficient and are suitable for environments where minimizing energy consumption is a priority.
- Dual-Duct MUA: Dual-duct MUA systems have separate ducts for delivering heated and cooled air to the building. This allows for more precise temperature control and is commonly used in buildings with varying occupancy levels or zones with different temperature requirements.
- Recirculating MUA: Recirculating MUA systems reuse a portion of the indoor air by recirculating it with the fresh outdoor air. This can help maintain building pressure control while still introducing fresh air to improve indoor air quality. However, it must be managed carefully to avoid inadequate air exchange or the build-up of contaminants.
These are just a few examples of the types of MUA systems available. The choice of MUA system depends on the specific needs of the building and the desired outcomes. Working with HVAC professionals can help determine the most suitable MUA system for a particular application.
Now that we have explored the types of MUA systems, let’s move on to the factors that need to be considered when installing MUA systems.
Factors to Consider when Installing MUA Systems
When installing a Make-Up Air (MUA) system in an HVAC setup, several important factors need to be taken into consideration. These factors can influence the effectiveness, efficiency, and overall performance of the MUA system. Let’s explore the key considerations when installing MUA systems:
- Ventilation Requirements: The first factor to consider is the specific ventilation requirements of the building or space. This includes factors such as the occupancy type, number of occupants, building codes, and industry regulations. Understanding the required airflow rates and air changes per hour is crucial for determining the capacity and design of the MUA system.
- Air Quality: The quality of the outdoor air being introduced into the building is of utmost importance. Factors such as pollution levels, allergens, and contaminants in the area should be assessed. Installing effective air filtration systems as part of the MUA system can help improve the indoor air quality by removing pollutants and allergens.
- Climate Conditions: The climate conditions in the area play a significant role in determining the heating and cooling requirements of the MUA system. For colder climates, the MUA system may need to incorporate a heating element to ensure the incoming outdoor air is at a comfortable temperature. In warmer climates, cooling or dehumidification may be required.
- Energy Efficiency: Energy efficiency is an essential consideration when installing MUA systems. Opting for energy recovery systems, such as heat exchangers or desiccant wheels, can help recover energy from the exhaust air and pre-condition the incoming outdoor air. This reduces the overall energy consumption and operating costs of the HVAC system.
- Ductwork Design: Proper ductwork design is crucial for the efficient distribution and delivery of fresh outdoor air throughout the building. The size, layout, and insulation of the ducts should be designed to minimize pressure losses and ensure optimal airflow. Additionally, proper sealing and insulation help prevent air leakage and maintain the desired temperature and humidity levels.
- Controls and Sensors: Incorporating intelligent control systems and sensors is essential for effective MUA system operation. These controls and sensors help monitor and adjust the airflow rates, temperature, humidity, and air quality within the building. They enable precise control and allow for adjustments based on occupancy levels and outdoor climate conditions.
- Maintenance and Serviceability: Consider the ease of maintenance and serviceability when selecting an MUA system. Components such as filters, fans, and heat exchangers should be easily accessible for routine maintenance and cleaning. Regular maintenance of the MUA system ensures optimal performance, extends the lifespan of equipment, and reduces the risk of breakdowns.
- Compliance and Safety: Ensure that the installation of the MUA system complies with local building codes, industry regulations, and safety standards. Proper installation, ventilation, and combustion safety measures are essential, especially in systems that include combustion elements. Compliance helps ensure occupant safety and prevents potential hazards.
By considering these factors during the installation of MUA systems, you can ensure that the system is properly designed, efficiently operated, and meets the specific needs of the building. Consulting with HVAC professionals or engineers can provide valuable insights and guidance throughout the installation process.
Now that we have covered the installation factors, let’s move on to explore the benefits of incorporating MUA in HVAC systems.
Benefits of MUA in HVAC
Make-Up Air (MUA) systems play a vital role in HVAC systems, offering numerous benefits for both residential and commercial buildings. Let’s explore the key benefits of incorporating MUA in HVAC systems:
- Improved Indoor Air Quality: MUA systems ensure the proper ventilation and introduction of fresh outdoor air into the building. This helps remove indoor pollutants, allergens, and contaminants, resulting in improved indoor air quality. Clean air promotes a healthier living or working environment and reduces the risk of respiratory issues.
- Pressure Balance: MUA systems help maintain a balanced airflow and air pressure within the building. By introducing fresh outdoor air, they offset the exhaust air being removed, preventing negative pressure imbalances. Proper pressure balance improves the performance of HVAC systems, prevents door difficulties, and eliminates unwanted airflows and backdrafts.
- Regulated Temperature and Humidity: MUA systems can assist in regulating the temperature and humidity levels within the building. In colder climates, MUA systems can heat the incoming outdoor air before distribution, minimizing heat loss and reducing the need for additional heating. In humid climates, MUA systems can remove excess moisture, preventing high humidity levels and the growth of mold and mildew.
- Energy Efficiency: Integrating energy recovery mechanisms, such as heat exchangers or desiccant wheels, in MUA systems improves energy efficiency. These systems recover and reuse the energy from the exhaust air to condition the incoming outdoor air. This reduces energy consumption and lowers utility costs, making the HVAC system more sustainable and environmentally friendly.
- Occupant Comfort: MUA systems create a more comfortable indoor environment for occupants. The introduction of fresh outdoor air improves air quality, reduces stuffiness, and eliminates stagnant odors. MUA systems also help maintain proper temperature and humidity levels, ensuring occupant comfort and enhancing productivity in residential and commercial spaces.
- Moisture Control: MUA systems aid in moisture control, especially in humid climates or areas prone to moisture-related issues. By removing excess moisture from the incoming air, these systems help prevent the growth of mold, mildew, and bacteria, which can cause health concerns and damage to the building structure.
- Compliance with Building Codes and Regulations: Incorporating MUA systems ensures compliance with building codes and regulations related to ventilation and indoor air quality. Adequate ventilation and MUA are often required by local building authorities and health agencies to ensure the safety and well-being of building occupants.
These are just a few of the many benefits that MUA systems provide in HVAC systems. By implementing MUA systems, building owners and occupants can enjoy improved air quality, balanced airflow, regulated temperature and humidity, energy efficiency, and enhanced occupant comfort.
However, it is important to be aware of the challenges associated with MUA systems in HVAC. Let’s explore some of these challenges in the next section.
Challenges Associated with MUA in HVAC
While Make-Up Air (MUA) systems offer a range of benefits, there are also certain challenges that need to be considered when implementing MUA in HVAC systems. Understanding these challenges can help ensure effective system design and operation. Let’s explore some of the challenges associated with MUA in HVAC:
- Air Quality and Contamination: One challenge is the quality of the outdoor air being introduced into the building. Depending on the location, the outdoor air may contain pollutants, allergens, or contaminants that can impact indoor air quality. Implementing adequate air filtration mechanisms is essential to mitigate these concerns and maintain a healthy indoor environment.
- Energy Consumption: MUA systems can impact the energy consumption of HVAC systems. Introducing outdoor air requires additional energy for heating, cooling, or conditioning. Without energy recovery mechanisms, this can increase the overall energy demand and operational costs of the HVAC system. Employing energy-efficient equipment and optimizing system design can help offset these energy consumption challenges.
- Airflow Balance and Distribution: Achieving proper airflow balance and distribution can be challenging with MUA systems. Improper design or installation can lead to uneven airflow, stagnant areas, or areas with inadequate air supply. This can result in areas with compromised air quality or discomfort. Proper system design, including the selection and placement of vents and grilles, is critical to address these challenges and ensure adequate airflow throughout the building.
- Moisture Control and Condensation: MUA systems can introduce outdoor air with different humidity levels, which can impact moisture control within the building. In humid climates, the introduction of outdoor air can increase humidity levels, potentially leading to condensation on surfaces or moisture-related issues. Proper humidity control mechanisms, such as dehumidification, insulation, and airflow management, need to be considered to mitigate these challenges.
- Design and Installation Constraints: MUA systems need to be carefully integrated into the overall design of the HVAC system. Building layout, space availability, and architectural constraints can pose challenges in installing the required ductwork, air handling units, and other MUA components. Engaging experienced HVAC professionals can help navigate these design and installation constraints to ensure an effective and efficient MUA system.
- System Sizing and Capacity: Proper sizing and capacity determination is crucial for MUA systems. Oversizing or undersizing the system can result in inefficiencies, inadequate air supply, or excessive energy consumption. Accurate calculations, including factors such as peak occupancy, ventilation requirements, and climate conditions, should be considered to ensure optimal system sizing and capacity.
- Maintenance and Cleaning: Regular maintenance and cleaning of MUA systems are essential for optimal performance and indoor air quality. Filters, heat exchangers, and other components need to be inspected, cleaned, or replaced as required. Neglecting maintenance can lead to reduced system efficiency, compromised air quality, and potential equipment breakdowns.
While these challenges are important to consider, they can be effectively managed with proper planning, system design, and maintenance protocols. By addressing these challenges, the benefits of MUA systems can be maximized, providing a comfortable, healthy, and efficient indoor environment.
Now that we have explored the challenges associated with MUA systems, let’s conclude our discussion.
Read more: What Is A HVAC Sequencer
Conclusion
MUA, or Make-Up Air, is a crucial component of HVAC systems that ensures proper ventilation, pressure balance, and indoor air quality in residential, commercial, and industrial buildings. By introducing fresh outdoor air to replace the stale indoor air, MUA systems play a significant role in creating a comfortable and healthy indoor environment.
In this article, we have explored the definition of HVAC and the role MUA plays within it. We’ve delved into the importance of MUA in HVAC systems, highlighting its impact on ventilation, pressure balance, temperature and humidity regulation, energy efficiency, and occupant comfort.
Understanding the components of an MUA system is crucial for effective system design and operation. The outdoor air intake, air filters, air handler, blowers or fans, ductwork, controls and sensors, exhaust systems, and energy recovery systems all work together to ensure proper distribution of fresh outdoor air throughout the building.
We’ve also explored the different types of MUA systems, including direct-fired, indirect-fired, cooling-coil, HRV/ERV, dual-duct, and recirculating systems. Each type has its own advantages and is suitable for specific applications and environments.
During the installation of MUA systems, several factors need to be considered, including ventilation requirements, air quality, climate conditions, energy efficiency, ductwork design, controls and sensors, maintenance, and compliance with building codes and regulations. Addressing these factors ensures optimal system performance and occupant comfort.
By incorporating MUA systems in HVAC designs, building owners and occupants can enjoy improved indoor air quality, pressure balance, temperature and humidity control, energy efficiency, and occupant comfort. However, it is important to be aware of challenges such as air quality, energy consumption, airflow balance, moisture control, design constraints, system sizing, and maintenance.
Addressing these challenges through proper system design, regular maintenance, and adherence to industry best practices can help overcome any potential drawbacks and ensure the effective operation of MUA systems.
In conclusion, MUA is a critical aspect of HVAC systems that cannot be overlooked. It contributes to the overall functionality, comfort, and efficiency of buildings, while also ensuring the health and well-being of occupants. By understanding and implementing MUA systems effectively, we can create indoor environments that are not only comfortable but also promote a higher quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is MUA In HVAC
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.













0 thoughts on “What Is MUA In HVAC”