

Articles
What Is A Mezzanine Floor
Modified: October 29, 2024
Discover the benefits of mezzanine floors with our informative articles. Learn how they can maximize your space and increase efficiency.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
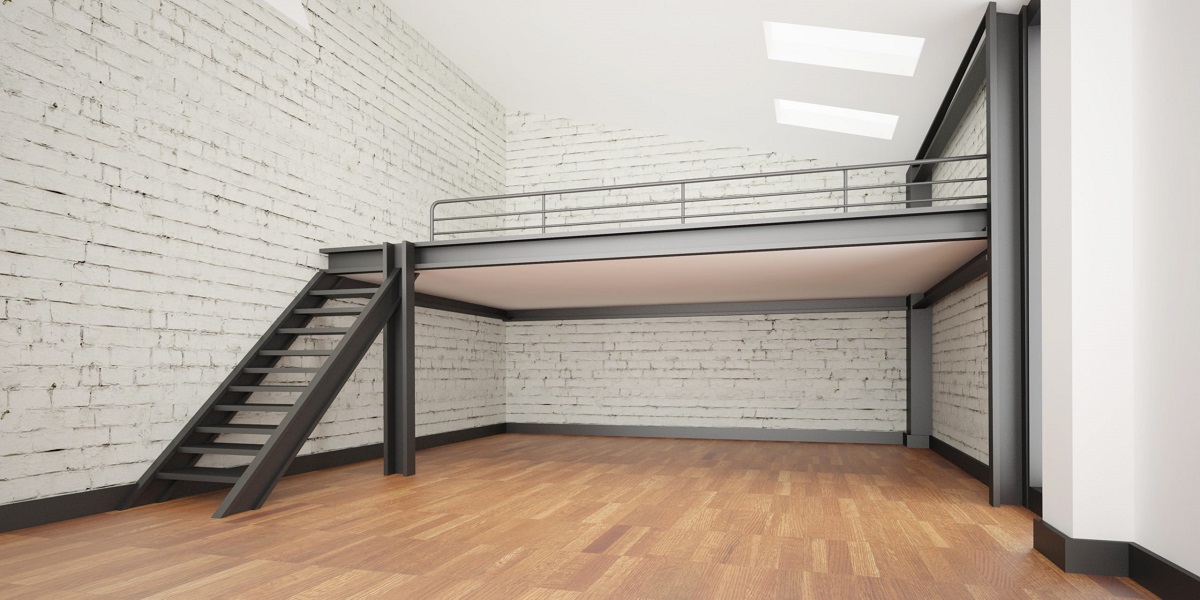
A mezzanine floor is a raised platform, typically constructed within an existing building, that provides additional floor space. It is a versatile and practical solution for maximizing the available space in commercial and industrial settings. Mezzanine floors are becoming increasingly popular thanks to their flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and ability to adapt to changing business needs.
In this article, we will delve into the various aspects of mezzanine floors, including their definition, purpose, benefits, construction process, safety considerations, applications, cost factors, and maintenance requirements. By the end, you’ll have a comprehensive understanding of mezzanine floors and their potential benefits for your business.
Key Takeaways:
- Mezzanine floors offer businesses a versatile and cost-effective solution to maximize space, increase productivity, and adapt to changing needs without the expense of construction or relocation.
- Regular maintenance and upkeep are essential to ensure the longevity, safety, and functionality of mezzanine floors, allowing businesses to create a safe and efficient working environment while maximizing their available space.
Read more: What Is A Floor Plan
Definition of a Mezzanine Floor
A mezzanine floor, also known as an intermediate floor or entresol, is a raised platform that is inserted between the main floors of a building. It is typically a semi-permanent structure made of steel or other robust materials, and it can be installed within an existing building or incorporated into the design of a new one.
The primary purpose of a mezzanine floor is to make efficient use of vertical space by creating an additional level within a building. It provides valuable extra square footage for various purposes, such as storage, office space, retail displays, production areas, or any other activity that requires additional space.
Mezzanine floors are typically open structures, meaning they do not have full-height walls like regular floors. They are usually supported by columns or pillars and can be designed to cover the entire floor area or just a portion of it, depending on the specific requirements of the space.
One of the key advantages of mezzanine floors is their versatility. They can be easily adapted and reconfigured to meet changing business needs. They are also customizable in terms of size, shape, and layout, allowing businesses to maximize the use of their available space. Additionally, mezzanine floors can be designed to integrate seamlessly with existing infrastructure, ensuring a cohesive and functional workspace.
Purpose and Benefits of Mezzanine Floors
Mezzanine floors serve a multitude of purposes and offer several benefits for businesses across various industries. Here, we will explore the primary reasons why businesses choose to incorporate mezzanine floors into their facilities.
1. Maximizing Space: One of the primary purposes of mezzanine floors is to maximize the use of available space within a building. By utilizing the vertical space, businesses can effectively double their floor area without the need for costly expansions or relocations.
2. Flexible and Customizable: Mezzanine floors provide businesses with the flexibility to adapt their space to changing needs. They can be easily constructed, modified, or relocated based on the evolving requirements of the business.
3. Increased Productivity: Mezzanine floors create additional space for various operations, such as storage, production, or office functions. This allows businesses to improve workflow efficiency and productivity by separating different tasks and processes.
4. Cost-Effective Solution: Compared to traditional building expansions or relocations, mezzanine floors offer a more cost-effective solution for expanding workspace. They are typically less expensive to construct and can be completed in a shorter timeframe, resulting in minimal disruption to daily operations.
5. Improved Organization and Accessibility: Mezzanine floors enable businesses to organize their operations more effectively. They provide a dedicated space for specific functions, allowing for easier access, better inventory management, and streamlined workflows.
6. Enhanced Storage Capacity: Mezzanine floors are commonly utilized for storage purposes. Businesses can optimize their storage capacity by utilizing the vertical space, freeing up valuable floor space for other functions.
7. Retail Displays and Showrooms: Mezzanine floors are often utilized in retail environments to create additional space for product displays, showrooms, or customer interaction areas. They enable retailers to showcase their products effectively while maximizing floor space for increased sales potential.
8. Expansion without Disruption: Mezzanine floors offer a way to expand a business without the need for a complete relocation or significant interruption to ongoing operations. This allows businesses to grow and adapt while maintaining continuity and minimizing downtime.
Overall, mezzanine floors provide businesses with a versatile and cost-effective solution to address their space needs. They offer numerous benefits, including increased productivity, improved organization, enhanced storage capacity, and the ability to adapt to changing business requirements. Whether it is for storage, office space, or retail displays, mezzanine floors offer businesses the opportunity to optimize their available space and enhance their operational capabilities.
Types of Mezzanine Floors
Mezzanine floors come in various types, each designed to suit different purposes and accommodate specific requirements. Here are some common types of mezzanine floors:
1. Free-standing Mezzanines: Free-standing mezzanines are independent structures that do not rely on existing building walls or columns for support. They are self-supporting and can be installed in open warehouse or industrial spaces. This type of mezzanine provides maximum flexibility as it can be easily relocated or modified.
2. Rack-supported Mezzanines: Rack-supported mezzanines are built on top of pallet racking systems. These mezzanines utilize the existing rack framework as support structures, maximizing both floor and vertical space. They are commonly used for storage purposes in warehouses and distribution centers.
3. Shelving-supported Mezzanines: Shelving-supported mezzanines are similar to rack-supported mezzanines but utilize shelving systems instead of pallet racking. These mezzanines are ideal for smaller storage spaces or areas where frequent picking and inventory access is required.
4. Structural Steel Mezzanines: Structural steel mezzanines are robust and durable, typically made from steel beams and columns. They are capable of supporting heavy loads and are commonly used in industrial and manufacturing settings. Structural steel mezzanines offer a high load capacity and can accommodate various operations, including offices, production areas, and storage.
5. Retail Mezzanines: Retail mezzanines are designed specifically for the retail sector, providing additional display space or customer interaction areas. They are often used in department stores, shopping centers, or showrooms to maximize the presentation of products and enhance the shopping experience.
6. Office Mezzanines: Office mezzanines are constructed to create additional office space within a building. They are a popular choice for businesses looking to expand their administrative areas without the need for costly modifications or renovations. Office mezzanines can be customized to include partitions, meeting rooms, and other amenities required for a functional workspace.
7. Multi-tier Mezzanines: Multi-tier mezzanines consist of two or more levels, providing multiple tiers of additional floor space. They are an excellent solution for large warehouses or industrial facilities with high ceilings. Multi-tier mezzanines can be designed to accommodate various operations, such as storage, production, or office spaces.
It’s important to consider the specific requirements of your business when choosing a type of mezzanine floor. Factors such as available space, load capacity, intended use, and cost considerations will influence your decision. Consulting with a professional mezzanine floor provider can help you determine the most suitable type of mezzanine for your needs and ensure a successful installation.
Construction and Installation Process
The construction and installation process of a mezzanine floor involves several steps to ensure a safe, sturdy, and functional structure. Here are the key stages involved:
1. Initial Assessment and Planning: The process begins with a thorough assessment of the available space and the specific requirements of the business. This includes determining the purpose of the mezzanine floor, load requirements, access points, and any additional design considerations.
2. Design and Engineering: Once the assessment is complete, the design and engineering phase begins. This includes creating detailed drawings and specifications that meet local building codes and regulations. Structural engineers may be involved to ensure the mezzanine’s stability and structural integrity.
3. Obtaining Permits: Depending on the location and regulations of the building, permits may need to be obtained before construction can begin. These permits ensure that the construction adheres to safety and building standards set by the local authorities.
4. Material Selection: The appropriate materials for the mezzanine floor are selected, taking into account factors such as load capacity, durability, aesthetics, and budget. Common materials used include steel beams, columns, decking, and handrails.
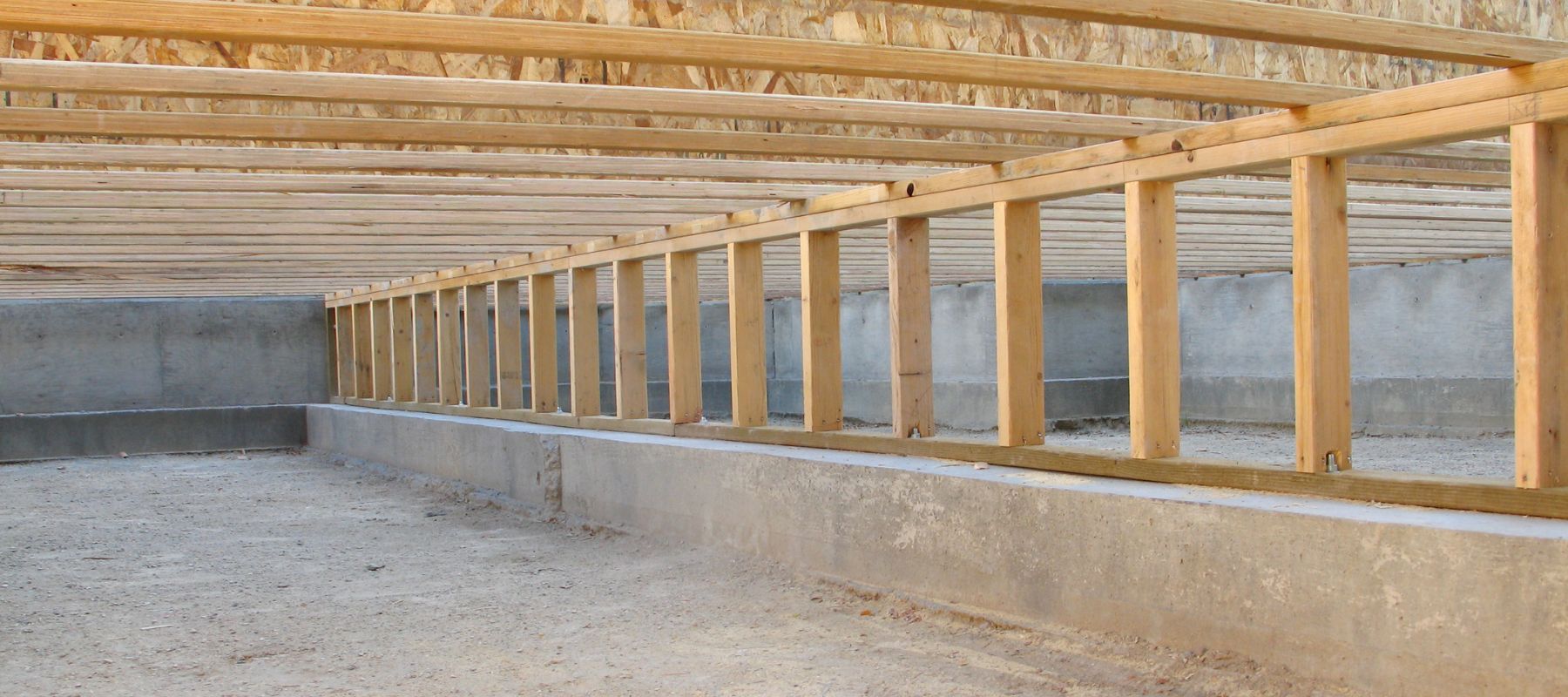
5. Site Preparation: Before installation, the site must be prepared by clearing the area and ensuring that the floor surface is clean and level. Any necessary modifications to the existing building, such as reinforcing columns or walls, may also be carried out at this stage.
6. Frame Assembly: The frame of the mezzanine is assembled according to the design and engineering plans. This involves erecting the steel beams and columns and securely fastening them together. The frame is usually bolted or welded to ensure stability and strength.
7. Flooring Installation: The flooring for the mezzanine is installed, typically using steel decking, plywood, or other suitable materials. The flooring is securely attached to the frame, creating a stable and safe surface for walking and supporting loads.
8. Guardrails and Handrails: Guardrails and handrails are installed along the edges of the mezzanine to provide safety and prevent falls. These are designed to meet safety standards and regulations, ensuring a secure environment for workers and visitors.
9. Finishing Touches: The finishing touches may include painting the mezzanine, installing lighting fixtures, and adding any necessary electrical outlets or HVAC systems. These details are essential for creating a functional and aesthetically pleasing space.
10. Final Inspection and Certification: Once the construction is complete, a final inspection is carried out to ensure that the mezzanine meets all safety and building code requirements. If everything is in order, the mezzanine is certified for use.
It’s crucial to work with experienced professionals during the construction and installation process of a mezzanine floor. They will provide guidance and expertise to ensure that the project is executed successfully, from initial planning to final certification.
When designing a mezzanine floor, consider the weight capacity, access points, and building codes to ensure safety and functionality.
Read more: What Is An Epoxy Floor
Safety Considerations for Mezzanine Floors
Safety is of utmost importance when it comes to mezzanine floors, as they involve working at heights and must adhere to stringent regulations. Here are some essential safety considerations to keep in mind:
1. Structural Integrity: The structural integrity of the mezzanine floor is crucial for its safety. It should be designed, engineered, and constructed to withstand the intended loads, ensuring it does not sag or collapse under weight. Regular inspections and maintenance are necessary to identify and address any structural issues promptly.
2. Guardrails and Handrails: Guardrails and handrails are essential safety features that prevent falls from the edges of the mezzanine. They should be installed along all open sides of the floor and meet regulatory height and strength requirements, typically ranging between 42-48 inches (107-122 cm) in height. These railings should be regularly inspected to ensure they are secure and in good condition.
3. Proper Signage: Clear and visible signage should be installed to alert individuals to potential hazards, indicate safe entry and exit points, and provide instructions for emergency procedures. Signage should comply with local safety regulations and be easily understood by all personnel in the area.
4. Adequate Lighting: Proper lighting is essential for a safe working environment. The mezzanine floor should be well-lit to ensure good visibility, especially in areas with stairs, walkways, or potential obstructions. Adequate lighting helps prevent accidents and allows workers to navigate the space safely.
5. Slip Resistance: The flooring of the mezzanine must have slip-resistant properties, especially in areas where spills or moisture can occur. Proper flooring materials, such as non-slip coatings or grating, should be used to reduce the risk of slips, trips, and falls.
6. Fire Safety: Fire safety precautions should be in place to protect employees and the facility. This includes the installation of suitable fire detection and suppression systems, clear pathways for evacuation, and regular fire drills. Adequate fire extinguishers should be readily accessible on the mezzanine floor.
7. Load Capacity: Mezzanine floors are designed to support specific loads. It is important not to exceed the recommended weight limits, as overloading can compromise the structural integrity of the floor, leading to accidents or collapse. Proper training and signage should be in place to inform personnel about load capacities and safe weight distribution.
8. Regular Inspections and Maintenance: Mezzanine floors should undergo regular inspections to identify any safety hazards or damage. Maintenance tasks, such as repairing damaged flooring, tightening loose bolts, or replacing worn-out guardrails, should be conducted promptly to ensure the ongoing safety of the structure.
9. Employee Training and Awareness: Proper training and awareness programs should be implemented to educate employees about the potential hazards associated with working on or around mezzanine floors. Employees should be trained on safe practices, emergency procedures, and the proper use of fall protection equipment if required.
By taking these safety considerations into account and implementing appropriate measures, businesses can create a safe working environment that reduces the risk of accidents and maintains the well-being of employees and visitors on mezzanine floors.
Common Applications of Mezzanine Floors
Mezzanine floors are versatile and widely used in various industries due to their ability to create additional space within existing buildings. Here are some common applications of mezzanine floors:
1. Storage: Mezzanine floors are frequently utilized for storage purposes, especially in warehouses, distribution centers, and retail establishments. The additional level created by the mezzanine provides valuable space for inventory, spare parts, raw materials, or finished goods. This allows businesses to optimize their storage capacity and streamline their operations.
2. Office Space: Mezzanine floors can be used to create additional office space within a building. By installing an office mezzanine, businesses can expand their administrative areas without the need for extensive construction or relocation. Office mezzanines provide a separate workspace for employees, enabling better organization and improving productivity.
3. Retail Displays and Showrooms: Mezzanine floors are popular in the retail sector, particularly for creating additional display areas and showrooms. Retailers can enhance their product presentations by utilizing the vertical space provided by the mezzanine. This allows for creative and engaging displays, improving the shopping experience for customers.
4. Production and Manufacturing: Mezzanine floors play a crucial role in production and manufacturing environments by providing additional space for production areas, assembly lines, or equipment installation. This enables businesses to optimize their workflow, separate different processes, and increase overall productivity.
5. Exhibition and Events: Mezzanine floors are commonly used for exhibition booths and event spaces. They provide a raised platform for showcasing products, conducting demonstrations, or hosting presentations. Mezzanines can be customized to create visually engaging and functional spaces for various events.
6. Gymnasiums and Fitness Centers: Mezzanine floors are often utilized in gymnasiums and fitness centers to create dedicated areas for exercise equipment, group classes, or additional workout space. This allows fitness facilities to maximize their floor area for accommodating more members and offering a wider range of activities.
7. Hospitality Industry: Mezzanine floors are commonly found in hotels, restaurants, and bars. They provide additional space for dining areas, private function rooms, or lounges. Mezzanine floors add an element of sophistication and create a unique ambiance within the hospitality establishment.
8. Mezzanine Offices: Mezzanine floors can be utilized as standalone offices within a larger workspace. They provide private and enclosed areas for meetings, conferences, or executive offices. Mezzanine offices offer a sense of privacy while still maintaining connectivity to the rest of the workspace.
These are just a few examples of the wide range of applications for mezzanine floors. With their adaptability and flexibility, mezzanine floors can be customized to meet the specific needs of businesses in various industries, providing a cost-effective solution for maximizing space and enhancing operational efficiency.
Cost Factors to Consider
When considering the installation of a mezzanine floor, there are several cost factors that need to be taken into account. It’s essential to have a clear understanding of these factors to accurately estimate the overall cost and make informed financial decisions. Here are some key cost factors to consider:
1. Size and Complexity: The size and complexity of the mezzanine floor directly impact the cost. Larger mezzanines require more materials and labor, resulting in higher costs. Similarly, mezzanines with complex designs, additional features, or customized elements may require specialized engineering and fabrication, increasing the overall expense.
2. Structural Requirements: The load-bearing capacity and structural requirements of the mezzanine floor influence the cost. Higher load capacities may require stronger materials, larger structural components, or additional reinforcements, which can increase the overall cost of the mezzanine.
3. Construction Material: The choice of construction materials impacts the cost of a mezzanine floor. Steel is commonly used due to its strength and durability, but it tends to be more expensive than other materials. Different flooring options, such as grating, plywood, or concrete, also vary in cost and should be considered based on the specific needs of the space.
4. Design and Customization: Customized designs, layouts, and additional features can significantly impact the cost of a mezzanine floor. Complex designs or specialized installations require more time, expertise, and materials, resulting in higher overall costs. Customization can also include added elements like access points, handrails, or specific finishes.
5. Installation and Labor Costs: The cost of installation and labor is an important consideration. Factors such as the complexity of the installation, site conditions, and the duration of the project will affect labor costs. It’s advisable to work with experienced professionals who can provide an accurate estimate of labor costs based on the project requirements.
6. Permits and Regulations: Depending on the location and building regulations, permits and inspections may be required, adding to the overall cost. It’s important to research and budget for any necessary permits, fees, or inspections to ensure compliance with local regulations.
7. Additional Expenses: In addition to the core costs, there may be additional expenses to consider, such as electrical work, lighting fixtures, HVAC systems, or fire safety measures. These costs will depend on the specific requirements of the mezzanine floor and should be factored into the overall budget.
8. Maintenance and Upkeep: While not directly related to the initial installation cost, it’s important to consider the long-term maintenance and upkeep costs of the mezzanine floor. Regular inspections, repairs, and upkeep will be required to ensure the safety and longevity of the structure.
By considering these various cost factors, businesses can develop a comprehensive understanding of the financial implications of installing a mezzanine floor. It’s advisable to consult with mezzanine floor experts who can provide accurate cost estimates and guide businesses in making informed decisions.
Maintenance and Upkeep of Mezzanine Floors
Maintenance and upkeep are essential for ensuring the longevity, safety, and functionality of mezzanine floors. Regular maintenance practices not only extend the lifespan of the structure but also help identify and address any potential issues before they become significant problems. Here are some key considerations for the maintenance and upkeep of mezzanine floors:
1. Inspections: Regular inspections play a crucial role in identifying any signs of wear, damage, or structural issues. Inspections should be carried out by qualified professionals or experienced personnel who can thoroughly assess the condition of the mezzanine floor, including the structural components, flooring, handrails, and other safety features.
2. Repairs and Replacements: Prompt repair of any identified issues is vital to maintain the integrity and safety of the mezzanine floor. This may include repairing damaged flooring, replacing worn-out or corroded components, or reinforcing structural elements as necessary. Timely repairs prevent further deterioration and potential hazards.
3. Cleaning: Regular cleaning is essential to maintain the cleanliness and hygiene of the mezzanine floor. This includes routine sweeping, vacuuming, and mopping to remove any dust, debris, or spills. Proper cleaning practices help prevent slips, trips, and falls, and also prevent the accumulation of dirt or contaminants that can cause damage over time.
4. Surface Protection: Applying appropriate surface protection coatings, such as anti-slip coatings or sealants, can help prolong the lifespan of the mezzanine floor. These coatings provide additional protection against wear and tear, friction, and exposure to moisture or chemicals, ensuring the structural integrity and safety of the floor surface.
5. Safety Features: Regularly inspect and maintain safety features such as guardrails, handrails, and access gates to ensure they are secure and meet safety standards. Any damaged or loose safety features should be promptly repaired or replaced to prevent accidents and ensure compliance with safety regulations.
6. Load Capacity: Re-assess the load capacity of the mezzanine floor periodically to ensure that it is not being overloaded. As business requirements change, it’s important to ensure that the floor can support the intended loads safely. If modifications or reinforcements are required to accommodate increased loads, consult with professionals experienced in mezzanine floor design and engineering.
7. Regular Training and Awareness: Ensure that employees working on or around the mezzanine floor receive appropriate training on safety practices, emergency procedures, and the proper use and maintenance of the mezzanine. Regularly reinforce safety protocols and raise awareness about potential hazards to help prevent accidents and ensure a safety-conscious work environment.
8. Documentation and Record-Keeping: Maintain thorough documentation of inspections, repairs, maintenance activities, and any modifications made to the mezzanine floor. This helps track the history of the floor, ensures regulatory compliance, and facilitates future maintenance and decision-making processes.
By following a proactive approach to maintenance and regular upkeep, businesses can ensure that their mezzanine floors remain safe, functional, and aesthetically appealing for years to come. Regular inspections, timely repairs, and proper cleaning practices are crucial to maintaining the integrity and longevity of mezzanine floors.
Read more: What Is A Threshing Floor
Conclusion
Mezzanine floors offer a versatile and cost-effective solution for businesses seeking to optimize their space and meet their growing needs. These raised platforms provide valuable additional square footage within existing buildings, accommodating various functions such as storage, office space, retail displays, and manufacturing operations.
Throughout this article, we have explored the definition and purpose of mezzanine floors, their benefits, different types available, the construction and installation process, safety considerations, common applications, cost factors, and the importance of maintenance and upkeep.
Mezzanine floors are designed to maximize space while maintaining functionality and safety. They provide businesses with the opportunity to expand their operations without the need for costly construction or relocation. With proper planning, customization, and attention to safety regulations, mezzanine floors can be tailored to suit the specific requirements of different industries and businesses.
It’s crucial to work with experienced professionals when designing, constructing, and maintaining mezzanine floors. They have the expertise and knowledge to ensure the structural integrity, safety, and compliance of the floors with applicable regulations.
By investing in a mezzanine floor, businesses can make the most of their available space, increase productivity, enhance organization, and adapt to changing needs. Mezzanine floors offer a practical and scalable solution that enables businesses to grow without compromising efficiency or incurring extensive costs.
In conclusion, mezzanine floors provide an efficient and economical way to unlock the full potential of existing space. Whether it’s for storage, office space, retail displays, or manufacturing operations, mezzanine floors offer businesses the opportunity to maximize their floor area, improve workflow efficiency, and support the overall growth and success of their operations.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is A Mezzanine Floor
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.













0 thoughts on “What Is A Mezzanine Floor”