

Articles
What Is A Scroll Compressor For HVAC
Modified: August 17, 2024
Learn all about scroll compressors for HVAC systems in this informative article. Discover how they work and why they are beneficial for cooling and heating applications.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
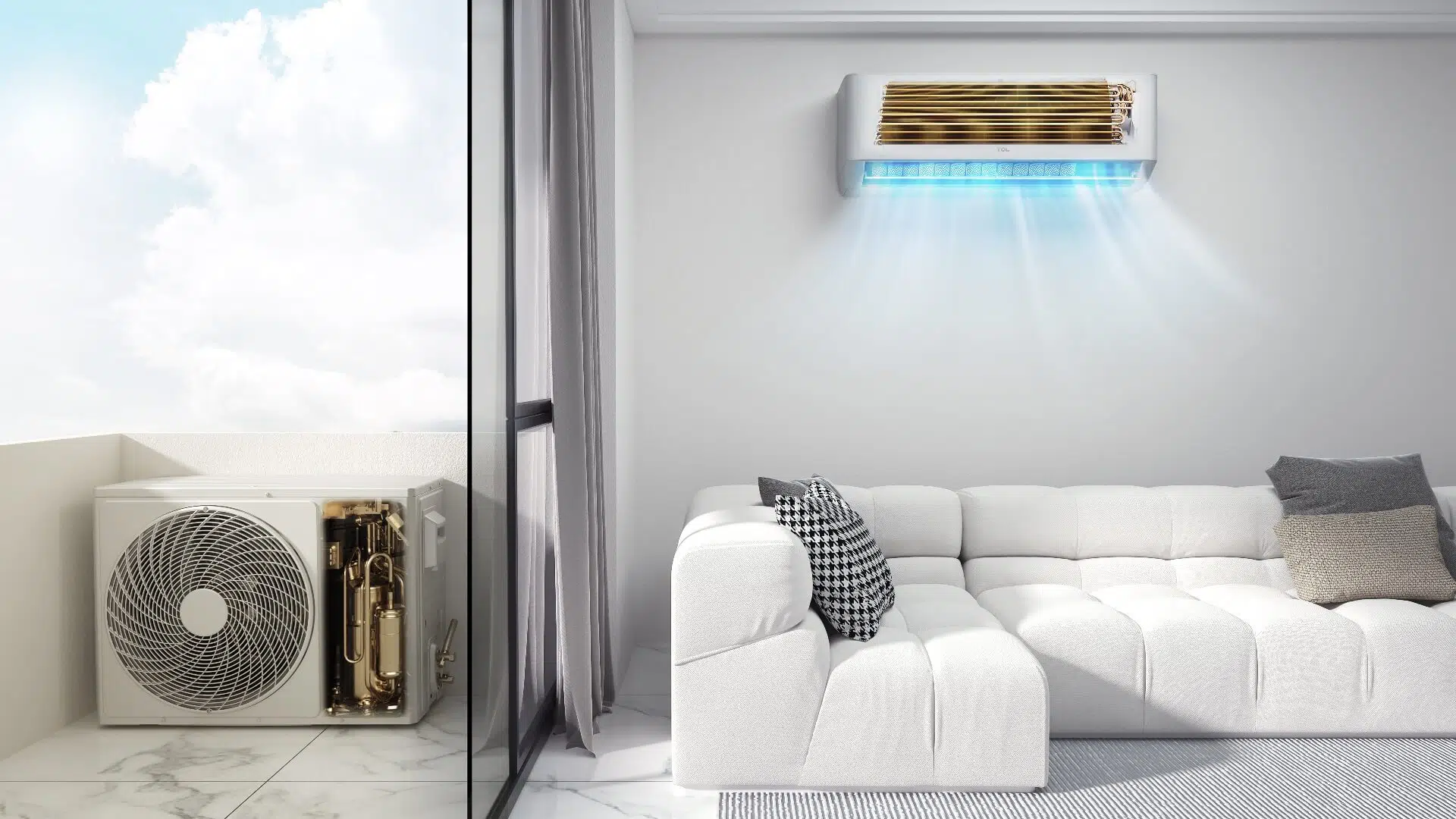
The scroll compressor is a crucial component in HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems. It plays a vital role in the cooling and heating process, ensuring that the desired temperature is maintained in residential, commercial, and industrial buildings.
A scroll compressor operates using a unique mechanism that sets it apart from other types of compressors. It offers several advantages over traditional reciprocating compressors, making it a popular choice for HVAC systems.
In this article, we will delve into the functionality of scroll compressors, explore their benefits, discuss their applications in HVAC systems, and provide essential considerations for selecting the right scroll compressor for your needs.
So, let’s dive into the world of scroll compressors and uncover how they contribute to the efficiency and effectiveness of HVAC systems.
Key Takeaways:
- Scroll compressors are a game-changer in HVAC systems, offering higher energy efficiency, quieter operation, and enhanced reliability. Their unique design and various types cater to diverse cooling and heating needs, making them a top choice for residential, commercial, and industrial applications.
- When selecting a scroll compressor for HVAC systems, factors such as cooling/heating capacity, efficiency rating, noise levels, and reliability must be carefully considered. Regular maintenance, including proper lubrication and filtration, is crucial for ensuring the longevity and optimal performance of scroll compressors.
Read more: How To Check HVAC Compressor
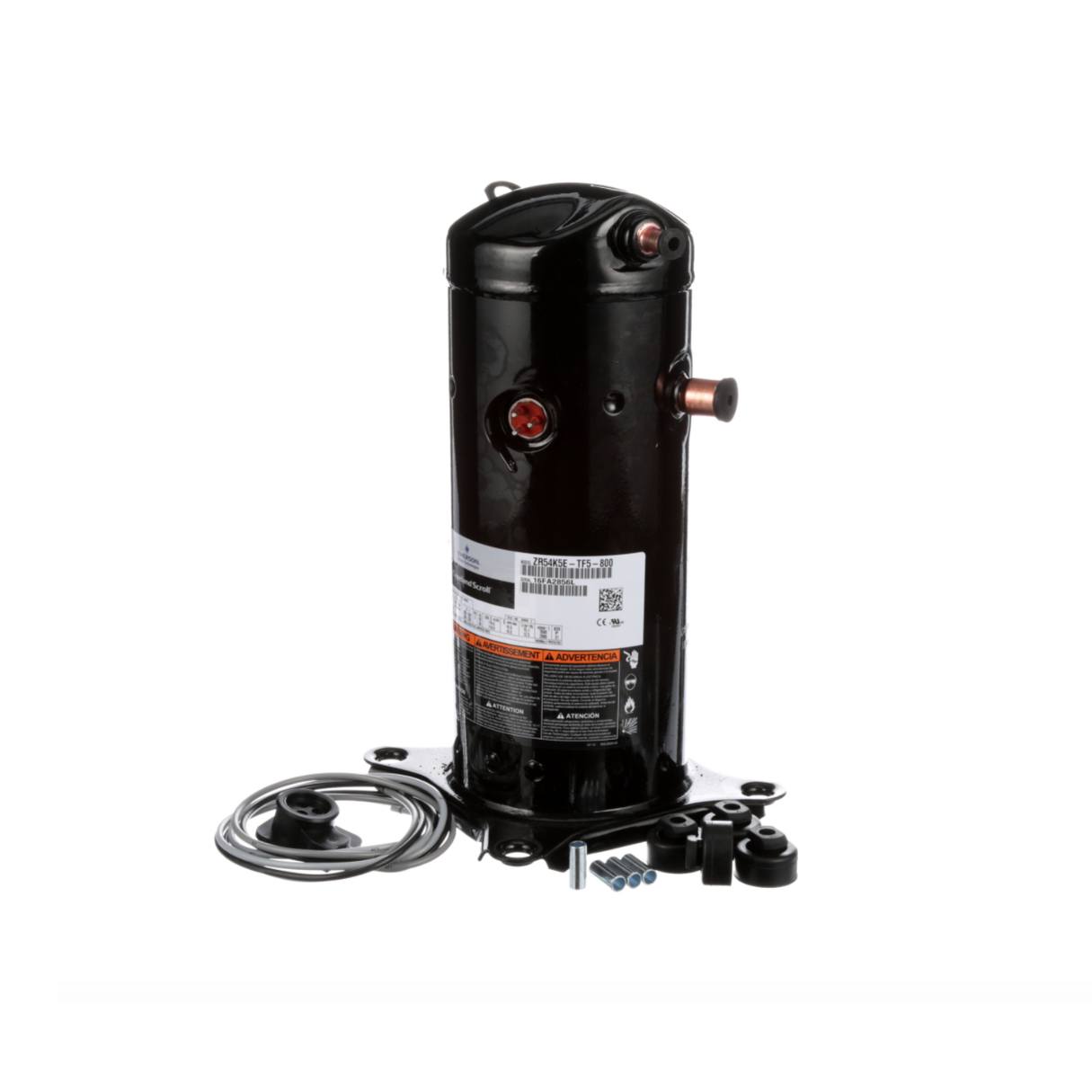
How Does a Scroll Compressor Work?
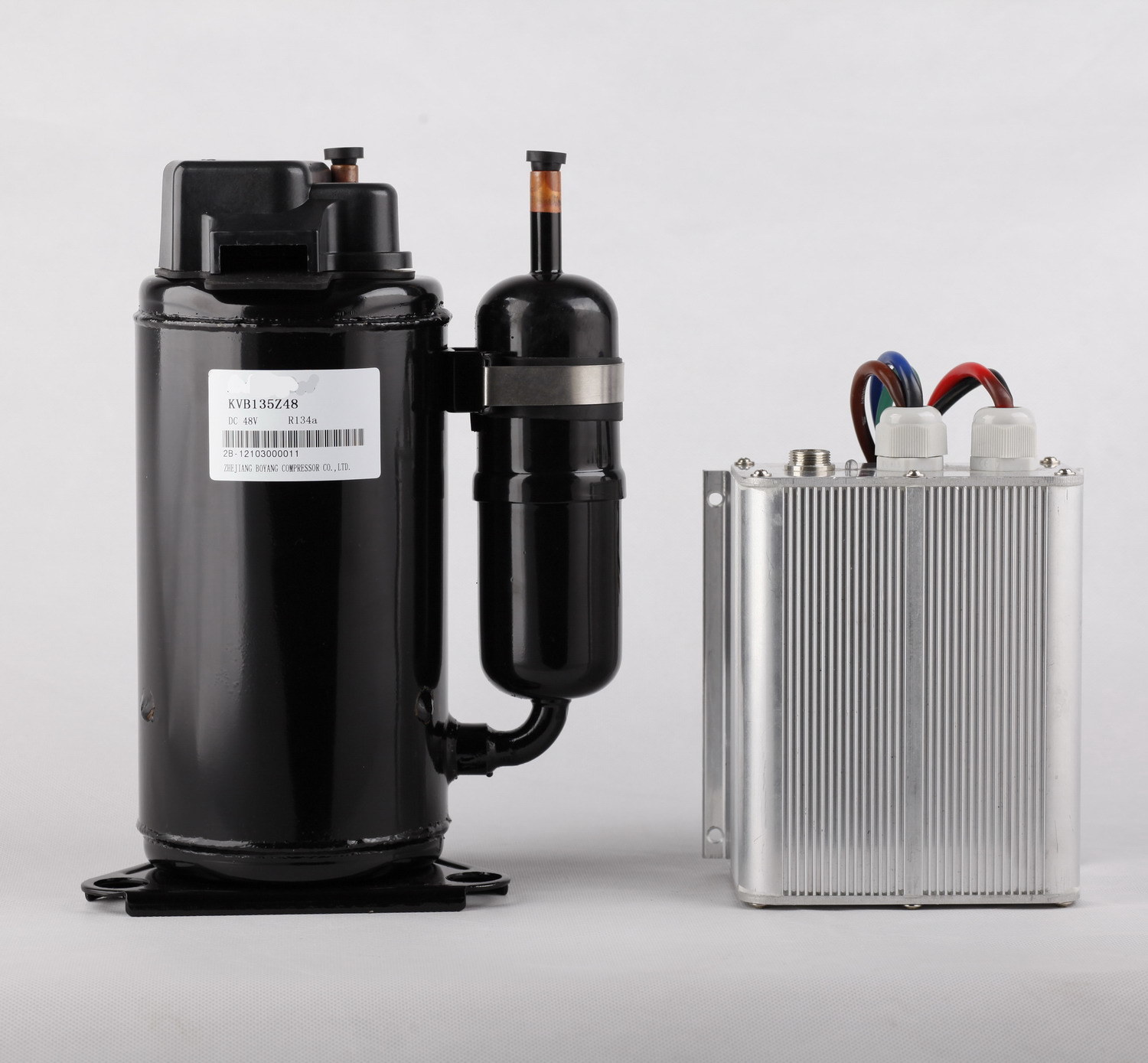
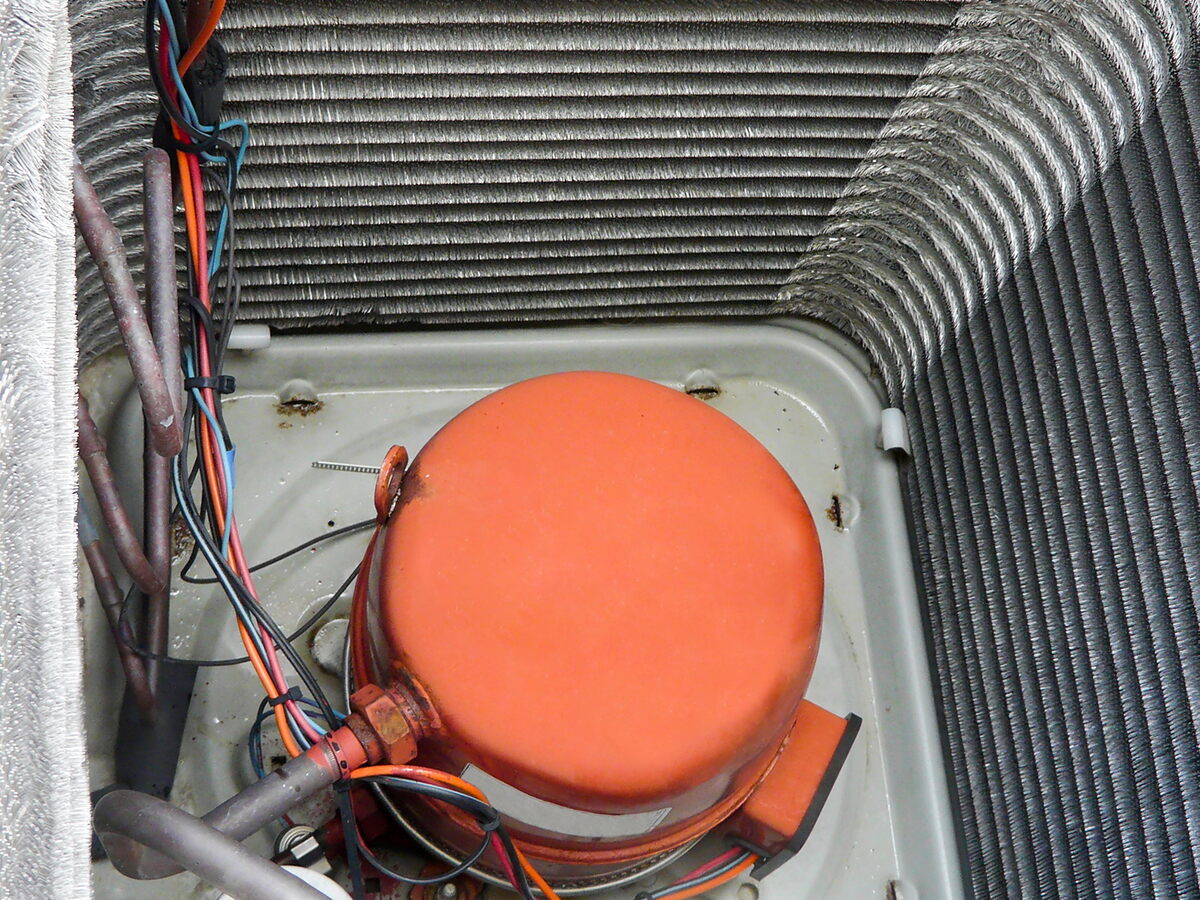
A scroll compressor operates on the principle of two interleaving spiral or scroll-shaped scrolls. One of the scrolls remains stationary, while the other orbits around it, creating a series of gas pockets or compartments of varying sizes.
As the rotating scroll moves, it pushes the gas from the outer pockets towards the center, gradually compressing it. This continuous compression process increases the pressure and temperature of the gas. The compressed gas is then discharged through an outlet port for further use in the HVAC system.
The scroll compressor’s unique design eliminates the need for pistons, valves, and complex mechanical parts that are often found in reciprocating compressors. Instead, it relies on a simple and efficient scroll mechanism, resulting in reduced vibrations, smooth operation, and enhanced energy efficiency.
Furthermore, the scroll compressor has a built-in suction and discharge mechanism that allows for uninterrupted gas flow. This results in a higher volumetric efficiency and reduced energy consumption compared to other compressor types.
Overall, the scroll compressor’s efficient design and operation make it an ideal choice for HVAC systems, where reliability, quiet operation, and energy efficiency are paramount.
Advantages of Scroll Compressors in HVAC Systems
Scroll compressors offer several advantages that make them highly desirable for use in HVAC systems. Let’s explore some of these advantages:
- Higher Energy Efficiency: Scroll compressors have a higher energy efficiency compared to other types of compressors. With their unique design and continuous compression process, they can deliver higher cooling or heating capacities while consuming less energy. This results in lower energy bills and reduced environmental impact.
- Quieter Operation: Scroll compressors are known for their relatively quiet operation. The absence of reciprocating parts and their smooth operation result in reduced vibrations and noise levels. This makes scroll compressors ideal for noise-sensitive environments such as bedrooms, offices, and libraries.
- Compact Size: Scroll compressors have a compact and lightweight design, making them space-saving and easy to install. Their smaller footprint allows for flexible installation options, especially in tight or confined spaces.
- Higher Reliability: The scroll compressor’s simple design with fewer moving parts contributes to its increased reliability. With fewer components that can fail or wear out, the chances of breakdowns and malfunctions are reduced. This results in longer equipment lifespan and reduced maintenance costs.
- Capability to Handle Varying Loads: Scroll compressors are capable of operating efficiently under varying load conditions. They can modulate their capacity based on the cooling or heating demand, providing optimal performance and energy savings. This makes scroll compressors ideal for buildings with fluctuating cooling or heating requirements, such as commercial spaces or multi-zone residential buildings.
- Enhanced Performance: Scroll compressors provide excellent temperature and humidity control, ensuring a comfortable indoor environment. Their ability to maintain stable and precise temperature levels, coupled with reduced cycling, results in improved overall HVAC system performance.
Overall, the advantages of scroll compressors make them a preferred choice for HVAC systems, offering improved energy efficiency, quiet operation, reliability, and enhanced performance.
Application of Scroll Compressors in HVAC
Scroll compressors find widespread application in various HVAC systems across residential, commercial, and industrial sectors. Let’s explore some of the key applications of scroll compressors:
- Residential Air Conditioning: Scroll compressors are commonly used in residential air conditioning units, providing efficient and reliable cooling for homes. Their compact size and quiet operation make them well-suited for residential use, ensuring comfort without compromising on space or noise levels.
- Commercial Air Conditioning: In commercial buildings such as offices, retail stores, and restaurants, scroll compressors are widely used in air conditioning systems. They offer reliable and energy-efficient cooling, maintaining comfortable temperatures for occupants while minimizing operating costs.
- Data Centers: Data centers require precise temperature and humidity control to ensure the optimal performance of servers and other equipment. Scroll compressors are often used in the cooling systems of data centers, providing efficient cooling and maintaining stable conditions for sensitive electronic equipment.
- Chillers: Scroll compressors are also utilized in chiller systems, which are responsible for cooling water or other fluids used to regulate temperatures in large buildings or industrial processes. Scroll compressors in chillers offer high efficiency and precise temperature control, making them suitable for applications where cooling loads can vary significantly.
- Heat Pumps: Heat pumps are an energy-efficient alternative to traditional heating systems. Scroll compressors play a critical role in heat pump systems by efficiently transferring heat between the indoor and outdoor environments. Their ability to provide both heating and cooling makes them versatile for residential and commercial applications.
- Refrigeration Systems: Scroll compressors are widely used in commercial refrigeration systems, such as walk-in coolers, display cases, and freezer units. Their compact size, high efficiency, and reliable performance make them ideal for maintaining the desired temperatures and preserving the freshness of perishable goods.
These are just a few examples of how scroll compressors are applied in HVAC systems. Their versatility, energy efficiency, and reliable operation make them a preferred choice in a wide range of cooling and heating applications.
When choosing a scroll compressor for HVAC, consider the size and capacity of your system. A properly sized compressor will ensure efficient operation and optimal performance.
Types of Scroll Compressors
Scroll compressors are available in different configurations to meet the specific requirements of various HVAC applications. Let’s explore some of the common types of scroll compressors:
- Single-Stage Scroll Compressors: Single-stage scroll compressors are the most commonly used type and are suitable for applications where the cooling or heating demand remains constant. These compressors have a fixed capacity and operate at a single speed, providing reliable and efficient performance.
- Two-Stage Scroll Compressors: Two-stage scroll compressors offer the flexibility to operate at two different capacity levels. These compressors have two sets of scrolls: a smaller one and a larger one. During periods of lower cooling or heating demand, the compressor runs on the smaller set of scrolls, operating at a lower speed and consuming less energy. When the demand increases, the compressor switches to the larger scrolls, providing higher capacity. Two-stage scroll compressors are ideal for applications that experience varying cooling or heating requirements.
- Orbiting Scroll Compressors: Orbiting scroll compressors have a unique design where both the fixed and orbital scrolls are in an elliptical shape. This configuration allows for a longer contact between the scrolls, resulting in increased efficiency and improved sealing. Orbiting scroll compressors are known for their reliable and quiet operation, making them suitable for noise-sensitive environments.
- Tandem Scroll Compressors: Tandem scroll compressors consist of two identical scrolls that are connected and operate together. This configuration allows for increased cooling or heating capacity, making tandem scroll compressors ideal for large HVAC systems that require higher output. Tandem scroll compressors offer improved performance and better load distribution compared to single-stage compressors.
- Digital Scroll Compressors: Digital scroll compressors incorporate advanced technology that allows for step-less capacity modulation. These compressors can precisely adjust their capacity based on the cooling or heating demand, providing accurate temperature control and maximizing energy efficiency. Digital scroll compressors are commonly used in applications where precise climate control is essential, such as data centers and laboratories.
These are some of the common types of scroll compressors available in the market. Each type has its specific advantages and applications, offering a wide range of options for HVAC systems.
Read more: How Much Is An HVAC Compressor
Considerations for Choosing a Scroll Compressor for HVAC Systems
When selecting a scroll compressor for an HVAC system, several factors need to be considered to ensure optimal performance. Here are some key considerations to keep in mind:
- Cooling or Heating Capacity: Determine the required cooling or heating capacity of the HVAC system. This will help determine the appropriate scroll compressor size and output capacity to meet the desired cooling or heating demands.
- Efficiency Rating: Look for scroll compressors with high energy efficiency ratings. Consider the seasonal energy efficiency ratio (SEER) or heating seasonal performance factor (HSPF) for cooling and heating respectively. Higher efficiency ratings indicate better energy performance and reduced operating costs.
- Load Variation: Assess the typical load variation of the HVAC system. If the cooling or heating demand fluctuates significantly, consider a scroll compressor with modulation capabilities, such as a two-stage or digital scroll compressor, to match the changing requirements efficiently.
- Noise Levels: Evaluate the noise sensitivity of the application. If the HVAC system is installed in a noise-sensitive environment, choose a scroll compressor known for its quiet operation. Look for low noise level ratings and features like sound insulation or vibration dampening technology.
- Reliability and Durability: Consider the reliability and durability of the scroll compressor. Look for models with a proven track record of performance and longevity. Check for features like durable materials, advanced lubrication systems, and built-in protection mechanisms against overheating or high pressure conditions.
- Installation Requirements: Assess the available space and installation requirements. Choose a scroll compressor size that fits within the allotted space and can be easily integrated into the HVAC system. Consider factors like access for maintenance, airflow requirements, and electrical connections.
- Brand and Warranty: Research reputable brands known for manufacturing high-quality scroll compressors. Check the warranty offered by the manufacturer, as a longer warranty period typically indicates confidence in the product’s performance and durability.
By considering these factors, you can make an informed decision when choosing a scroll compressor for your HVAC system. It is recommended to consult with HVAC professionals or engineers for expert advice and assistance in selecting the most suitable scroll compressor for your specific application.
Common Issues and Maintenance of Scroll Compressors
While scroll compressors are known for their reliability and durability, like any mechanical device, they can experience certain issues over time. Proper maintenance can help prevent these issues and ensure the longevity and optimal performance of the compressor. Here are some common issues and maintenance practices for scroll compressors:
- Lack of Lubrication: Insufficient or improper lubrication can cause excessive friction and wear on the compressor components. Regularly check the oil level and ensure the compressor is properly lubricated according to the manufacturer’s guidelines. Maintain a scheduled lubrication routine and use the recommended type and grade of lubricant.
- Contamination: Contaminants in the system, such as moisture, dirt, debris, or refrigerant impurities, can cause damage to the compressor. Proper filtration and regular maintenance of the system’s filters and driers are essential to prevent contamination. Regularly clean or replace filters as recommended by the manufacturer.
- Electrical Issues: Electrical problems can negatively impact the operation of the compressor. Inspect electrical connections, wiring, and components regularly to ensure they are in good condition. Check for loose connections, frayed wires, or signs of overheating. Also, monitor voltage levels to ensure they are within the recommended range.
- Overheating: Overheating can occur due to factors like high ambient temperatures, restricted airflow, or excessive refrigerant pressures. Ensure proper airflow around the compressor by keeping the surrounding area clear and clean. Monitor and maintain optimal refrigerant pressures within the recommended range.
- Vibration and Noise: Excessive vibration or unusual noise levels can indicate an issue with the compressor. Inspect mounting bolts and brackets to ensure they are secure. Check for damaged or worn-out isolation pads or rubber feet and replace them if necessary. Additionally, investigate any abnormal noise and address it promptly to prevent further damage.
- Regular Inspections and Cleaning: Perform regular inspections of the compressor to identify any signs of wear, leaks, or damage. Clean the compressor regularly to remove dirt and debris that can hinder its performance. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for cleaning methods and avoid using harsh chemicals that can damage the compressor.
- Professional Maintenance: Schedule regular maintenance by qualified HVAC professionals to thoroughly inspect and service the scroll compressor. This includes checking refrigerant levels, cleaning condenser coils, inspecting electrical connections, and performing any necessary adjustments or repairs.
Regular maintenance and prompt attention to any issues will help ensure the efficient and reliable operation of scroll compressors in HVAC systems. By following these maintenance practices, you can extend the lifespan of the compressor and avoid costly repairs or premature replacements.
Conclusion
The scroll compressor is a critical component in HVAC systems, providing efficient and reliable cooling or heating for residential, commercial, and industrial applications. With their unique design and operation, scroll compressors offer several advantages over other types of compressors, including higher energy efficiency, quieter operation, compact size, and enhanced reliability.
Scroll compressors find wide application in various HVAC systems, such as residential and commercial air conditioning, data centers, chillers, heat pumps, and refrigeration systems. They are available in different types, including single-stage, two-stage, orbiting, tandem, and digital scroll compressors, each catering to specific cooling or heating requirements.
When selecting a scroll compressor for an HVAC system, important considerations include cooling or heating capacity, efficiency rating, load variation, noise levels, reliability, and installation requirements. By carefully evaluating these factors, you can choose a scroll compressor that best suits your specific needs and ensures optimal performance.
To maintain the longevity and optimal performance of scroll compressors, regular maintenance is essential. This includes proper lubrication, filtration, inspection of electrical connections, monitoring of refrigerant levels and pressures, and addressing any issues promptly to prevent further damage or complications.
In conclusion, scroll compressors are a reliable and efficient choice for HVAC systems, contributing to the comfort and climate control of residential, commercial, and industrial spaces. By understanding their operation, benefits, applications, and maintenance requirements, HVAC professionals and users can optimize the performance and lifespan of scroll compressors, ensuring a comfortable and energy-efficient environment.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is A Scroll Compressor For HVAC
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.














0 thoughts on “What Is A Scroll Compressor For HVAC”