

Articles
What Is A Water Pump
Modified: January 8, 2024
Discover the importance of water pumps and how they play a crucial role in various industries. Read informative articles on water pump technologies and maintenance tips.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Overview
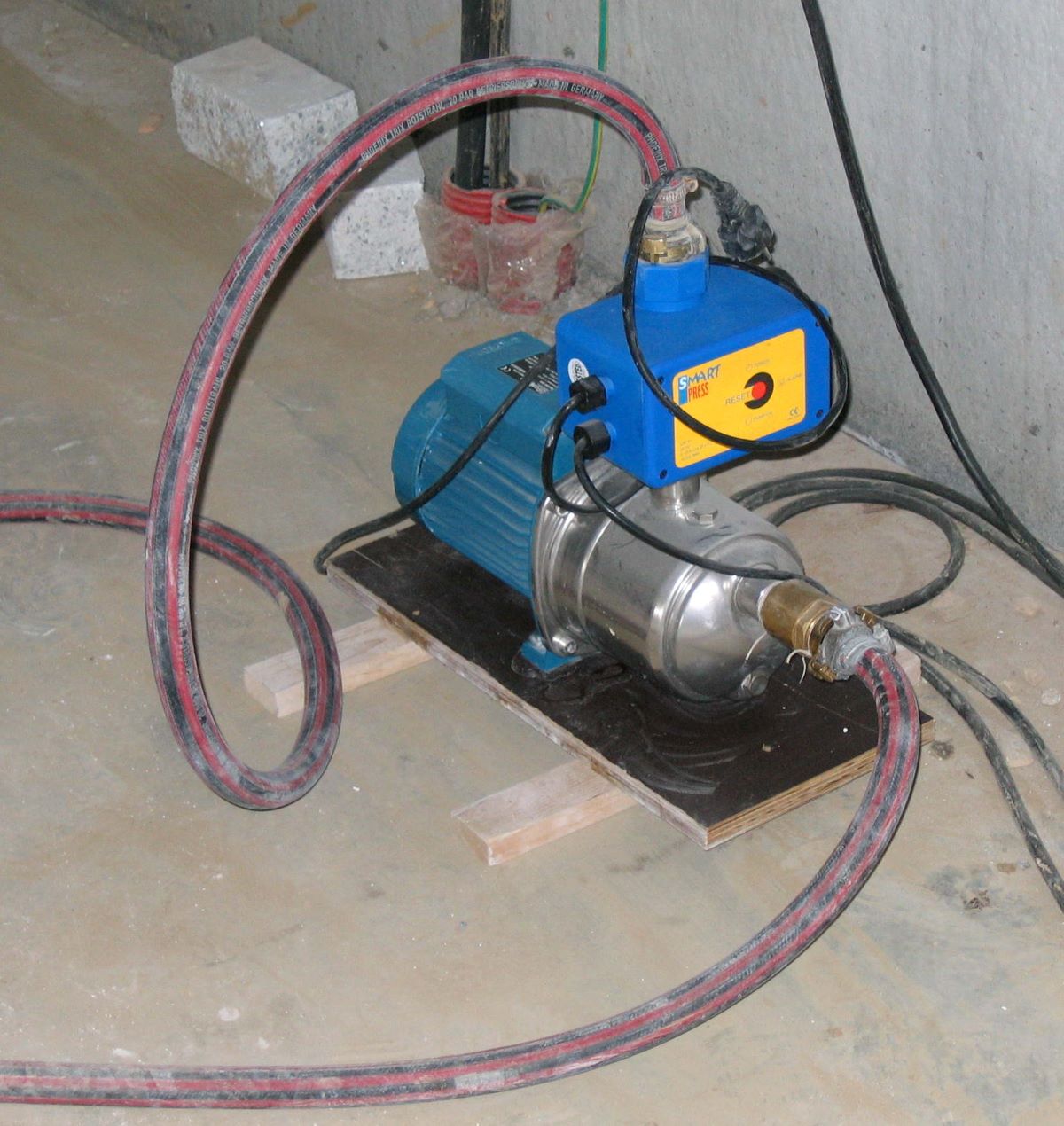
Water pumps play a crucial role in various industries and everyday life, ensuring the efficient movement of water from one location to another. These devices are used to supply water for irrigation, firefighting, drainage, and even in residential households. In simple terms, a water pump is a mechanical device used to enhance the flow of water by increasing its pressure and moving it through a system of pipes or hoses.
Water pumps are essential for maintaining a constant water supply in a wide range of applications. From agricultural irrigation systems to commercial buildings, they are vital for ensuring water is distributed efficiently and effectively. They can also be found in domestic settings, where they provide water for household needs, such as showers, washing machines, and toilets.
Understanding the different types of water pumps, how they work, and how to properly maintain them is essential for ensuring their longevity and performance. Regular maintenance and proper troubleshooting techniques can help prevent costly repairs and ensure a continuous water supply.
In this article, we will explore the different types of water pumps, their working principles, the components that make them up, common issues that may arise, and maintenance tips to keep them running smoothly.
Key Takeaways:
- Water pumps are essential for maintaining a continuous water supply in various industries and everyday life, from irrigation to residential use. Understanding their types, working principles, and maintenance is crucial for optimal performance and longevity.
- Regular maintenance, troubleshooting, and timely repairs are crucial for ensuring the efficient operation of water pumps. By understanding their importance, types, and components, you can maximize their lifespan and avoid costly replacements.
Read more: What Is The Function Of A Water Pump
Definition of Water Pump
A water pump is a mechanical device designed to move water from one place to another. It uses mechanical action to increase the pressure of the water, allowing it to be transported through a network of pipes or hoses. Water pumps are commonly used in various industries, including agriculture, construction, mining, and residential applications.
The primary function of a water pump is to generate enough pressure to overcome the frictional resistance of the pipes or hoses and gravity, enabling water to flow smoothly and efficiently. They can be powered by different energy sources, including electricity, gasoline, diesel, or even manual operation.
Water pumps are available in various sizes and capacities, depending on the specific application. They can range from small portable pumps for domestic use, to large-scale industrial pumps used for heavy-duty tasks. Some pumps are designed to handle clean water, while others are capable of handling liquids with solids or debris.
Water pumps can be classified into two main categories: centrifugal pumps and positive displacement pumps. Centrifugal pumps use centrifugal force to create pressure, while positive displacement pumps rely on the displacement of water to generate pressure.
Overall, water pumps are essential devices used to transport water efficiently, ensuring a continuous supply in various settings. They have become indispensable in various industries and play a vital role in managing water resources effectively.
Importance of Water Pump
Water pumps play a crucial role in numerous applications, making them an indispensable component in various industries and everyday life. Here are some key reasons why water pumps are important:
- Water Supply: One of the primary functions of a water pump is to provide a continuous and reliable water supply. Whether it’s for irrigation, commercial buildings, or residential use, water pumps ensure that water is transported from its source to the desired location.
- Irrigation: In agriculture, water pumps are vital for providing water to crops, ensuring proper irrigation and optimal growth. They help distribute water evenly across fields, maximizing crop yield and supporting sustainable agriculture practices.
- Dewatering: Water pumps are essential for removing excessive water from construction sites, mines, and areas prone to flooding. They help prevent water damage, maintain safe working conditions, and facilitate construction and mining activities.
- Firefighting: Fire pumps, a specialized type of water pump, are crucial for supplying water to fire sprinkler systems or firefighting equipment. They ensure a reliable flow of water to extinguish fires swiftly and efficiently, minimizing property damage and saving lives.
- Industrial Applications: Various industries rely on water pumps for their operations. They are used in manufacturing processes, cooling systems, wastewater treatment, and power generation, among other applications.
- Residential Use: Water pumps are found in residential settings, where they deliver water to homes for drinking, cooking, bathing, and sanitation. They are essential for supplying water to appliances such as washing machines, dishwashers, and showers.
- Efficiency and Productivity: By ensuring a steady flow of water, water pumps enhance efficiency and productivity in various tasks. They help reduce manual labor, increase output, and optimize processes in many industries.
Overall, water pumps are vital for maintaining water supplies, facilitating irrigation, managing floods, firefighting, and supporting numerous industries. Without water pumps, many essential functions and activities would be significantly compromised.
Types of Water Pumps
Water pumps come in various types, each designed to meet specific needs and applications. Here are the most common types of water pumps:
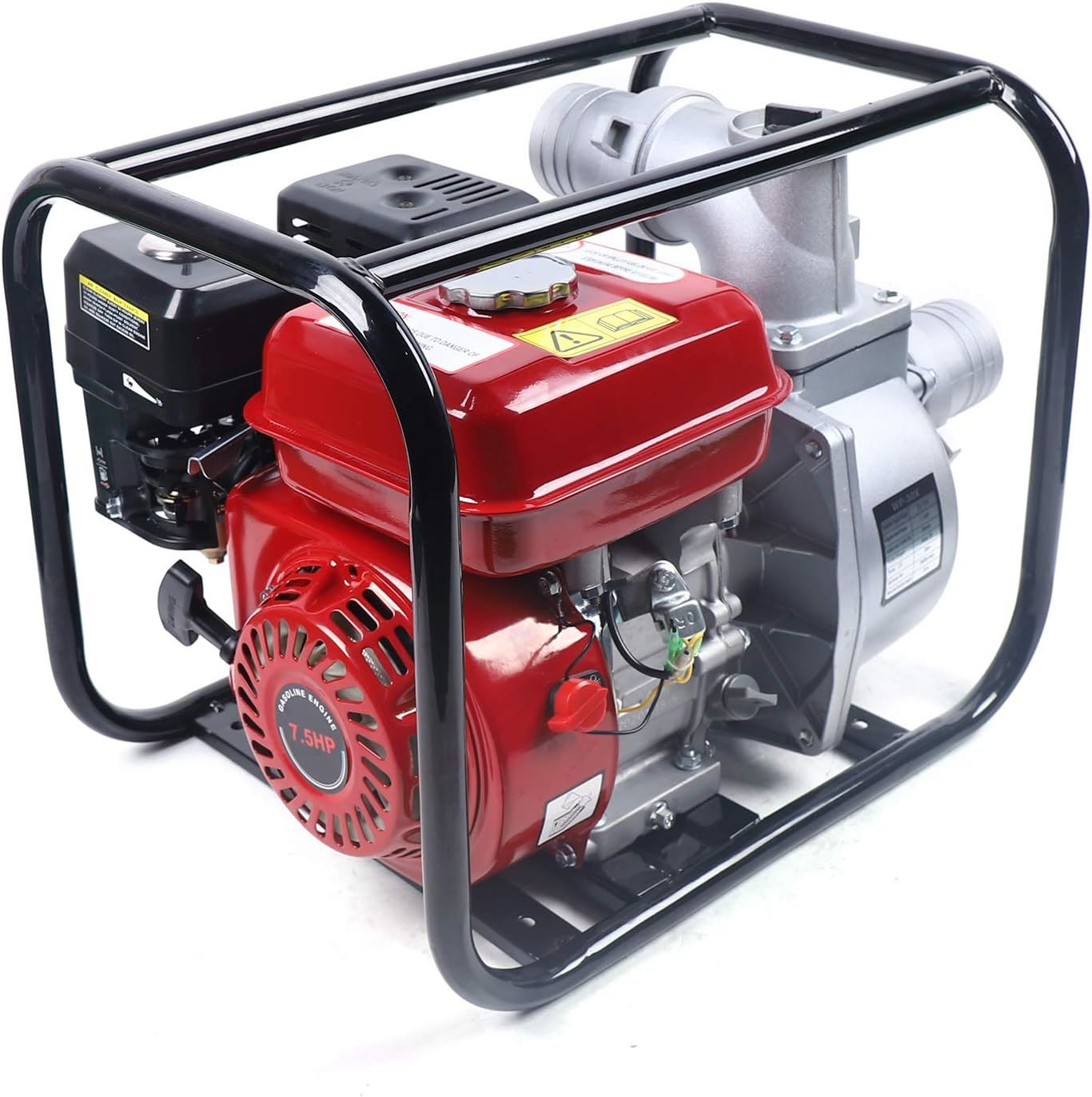
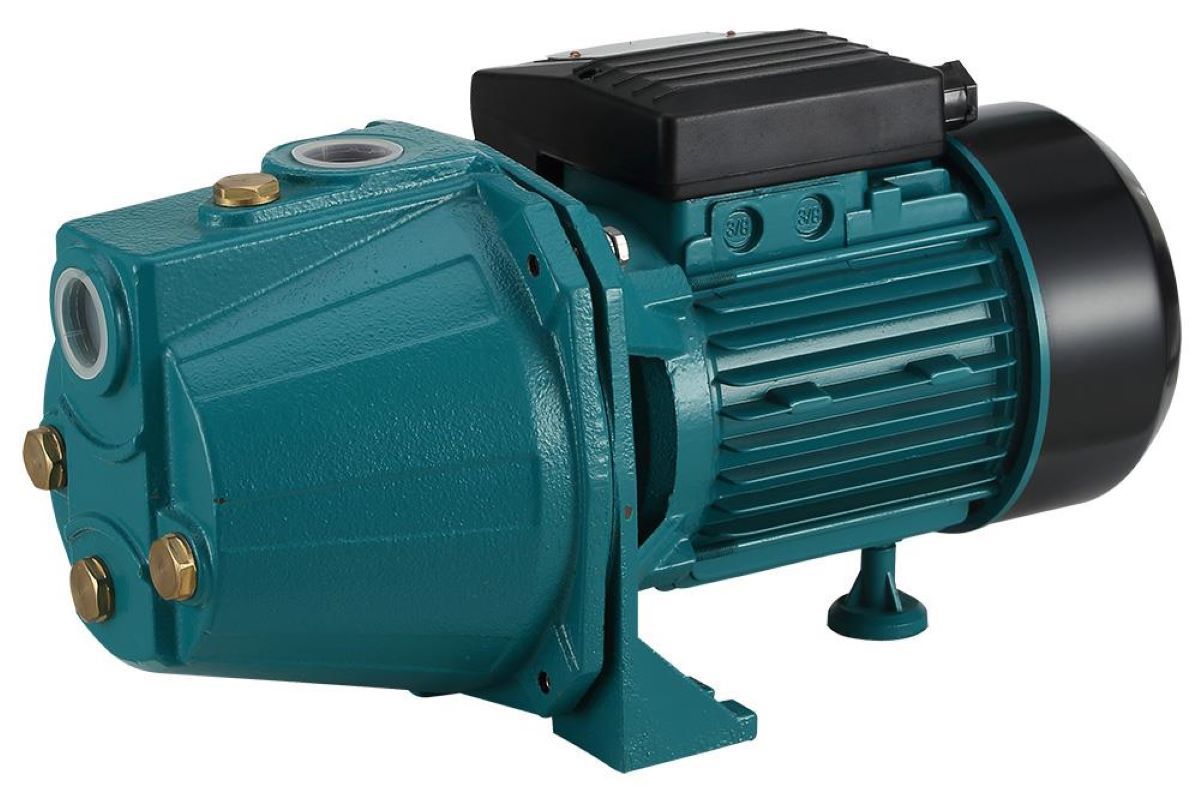
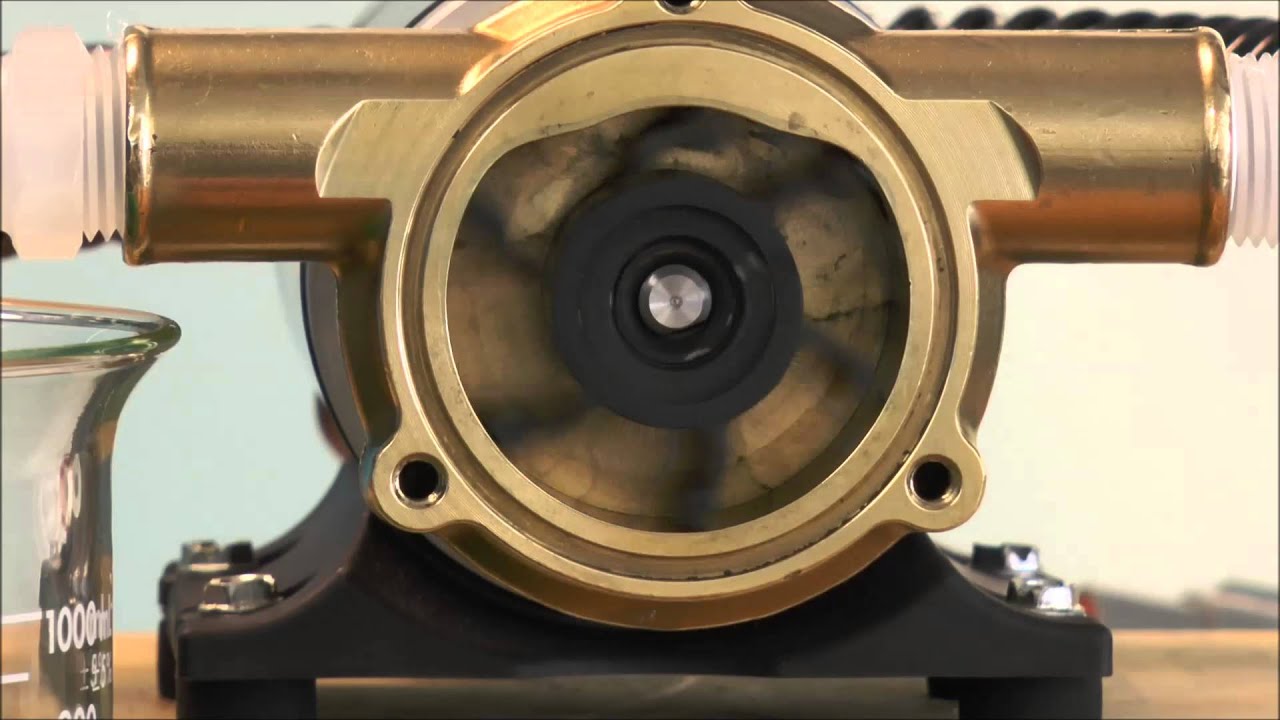
- Centrifugal Pumps: These are the most widely used pumps due to their efficiency and versatility. Centrifugal pumps work by converting rotational energy from an impeller to increase the water’s velocity and pressure. They can handle large volumes of water and are commonly used in irrigation, drainage systems, and industrial applications.
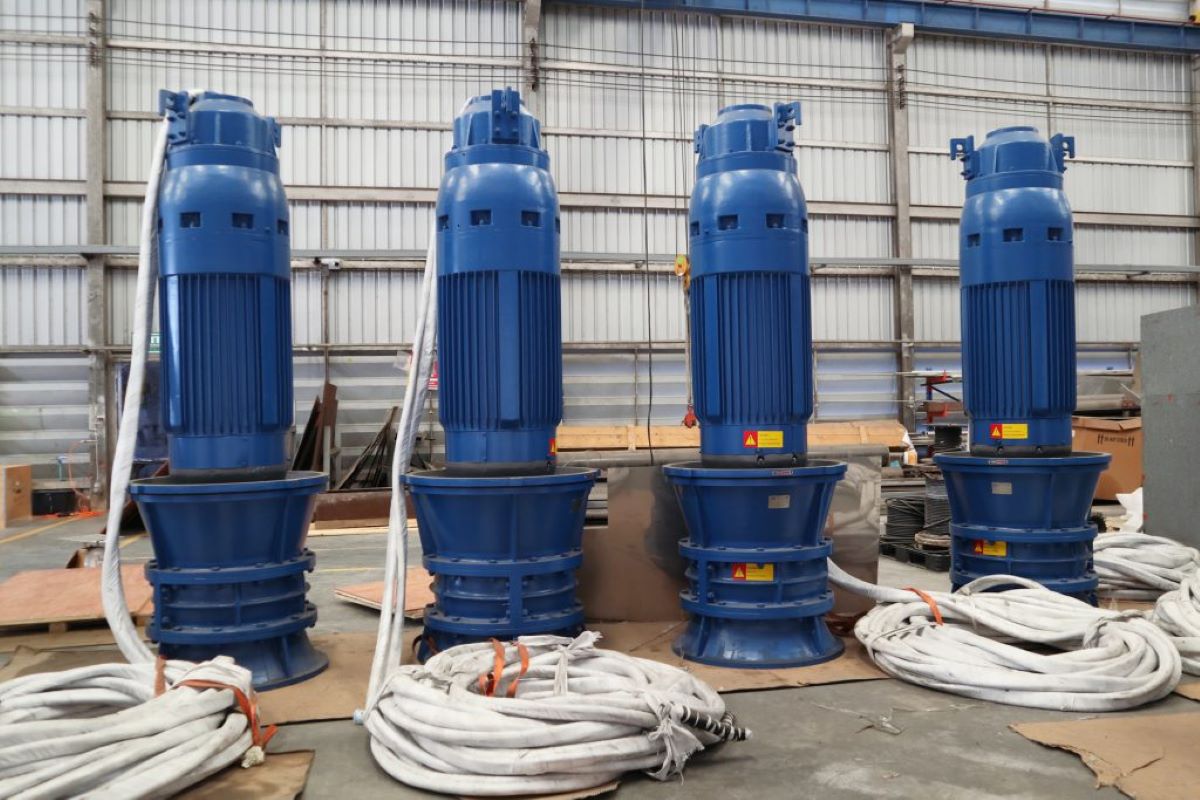
- Submersible Pumps: Submersible pumps are designed to be fully submerged in water. They are sealed to prevent water damage and often have built-in motors. These pumps are commonly used in wells, boreholes, and deep water applications, where they can pump water directly from the source.
- Jet Pumps: Jet pumps use high pressure to create suction that pulls water from a well or other water source. They are versatile and can be used for shallow well applications or in situations where a submersible pump is not feasible. Jet pumps are commonly used in residential water systems.
- Diaphragm Pumps: Diaphragm pumps use a flexible diaphragm to displace water and create pressure. They are self-priming and can handle liquids with solids or debris. Diaphragm pumps are commonly used in agriculture, construction, and wastewater applications.
- Gear Pumps: Gear pumps use interlocking gears to pump water. They are compact, efficient, and capable of generating high pressures. Gear pumps are commonly used in industrial settings where precise control and high pressures are needed.
- Well Pumps: Well pumps are specifically designed for extracting water from underground wells. They can be submersible or non-submersible, depending on the depth of the well.
- Booster Pumps: Booster pumps are used to increase water pressure in a system. They are often used in residential or commercial buildings where water pressure needs to be boosted for proper functioning of appliances and fixtures.
These are just a few examples of the many types of water pumps available. Each type is designed to meet specific requirements, whether it’s for residential, commercial, or industrial use. Choosing the right type of water pump depends on factors such as the application, water source, flow rate, and desired pressure.
Working Principle of Water Pumps
Water pumps operate based on the principles of fluid dynamics and energy conversion. While the specific working mechanisms can vary depending on the type of pump, most water pumps follow a similar basic principle. Here is an overview of the working principle of water pumps:
1. Energy Conversion: Water pumps convert mechanical, electrical, or manual energy into hydraulic energy, which is the energy carried by the movement of water.
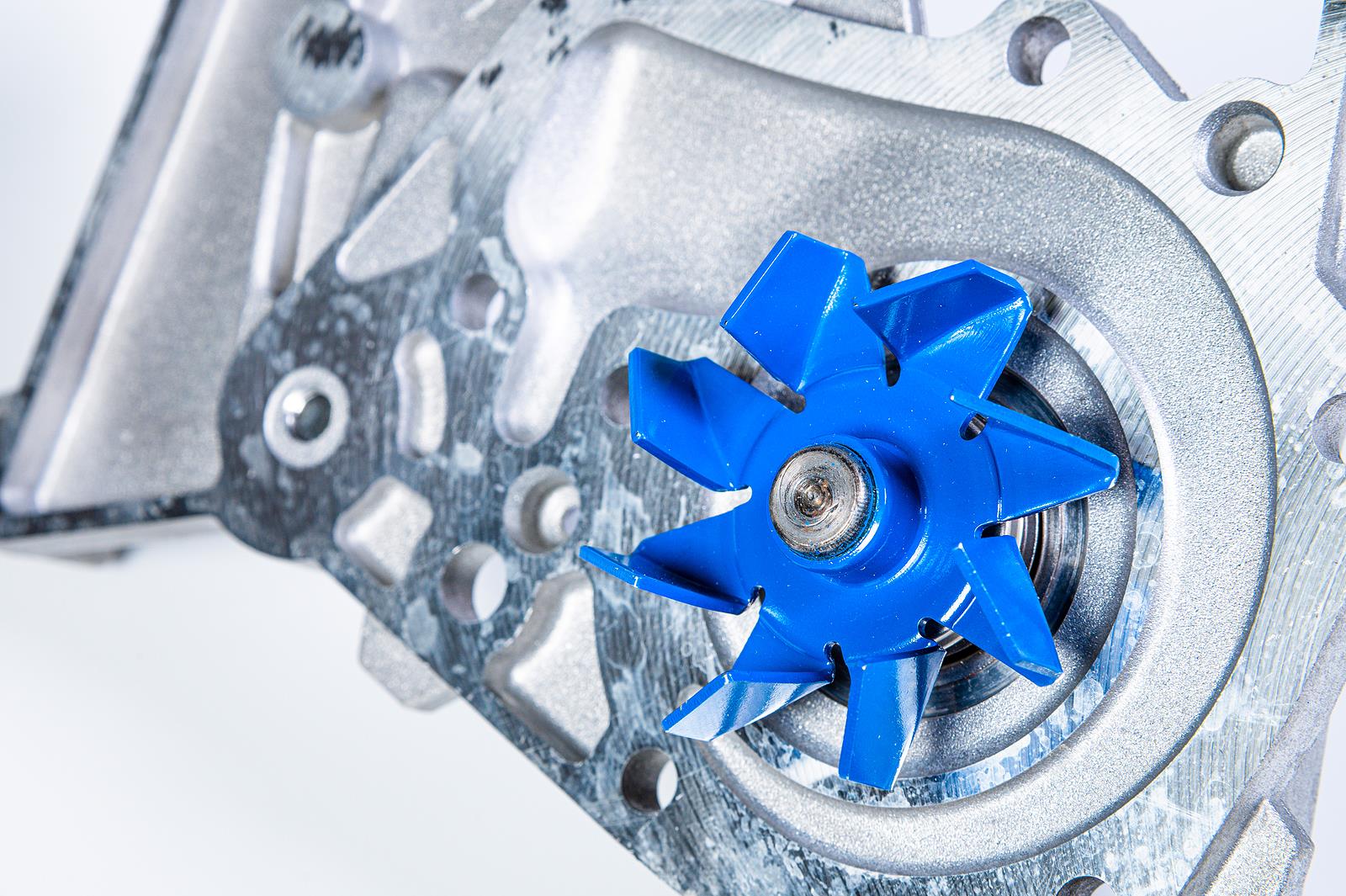
2. Impeller Action: In centrifugal pumps, the key component is the impeller, a rotating disc with curved blades. When the pump is activated, the impeller spins rapidly, creating a centrifugal force. The rotation of the impeller imparts kinetic energy to the water.
3. Increased Pressure: As water enters the pump through the inlet, it is accelerated by the rotating impeller. This acceleration increases the water’s velocity, simultaneously decreasing the pressure. However, the curved shape of the impeller’s blades redirects the water flow, converting its kinetic energy into potential energy and increasing the pressure.
4. Fluid Movement: The high-pressure water is then pushed out of the pump through the outlet, flowing through pipes or hoses to its intended destination.
5. Continuity: The flow of water is maintained by the continuous rotation of the impeller, ensuring a consistent water supply.
The working principle of other types of pumps, such as submersible pumps or jet pumps, may differ in certain aspects, but they ultimately rely on energy conversion and fluid movement to deliver water effectively.
It’s important to note that various factors, such as the motor power, impeller design, and speed, can impact the efficiency and performance of a water pump. Proper selection, installation, and maintenance of the pump are critical to ensuring optimum functionality and longevity.
When choosing a water pump, consider the flow rate and pressure requirements for your specific application. It’s important to select a pump that can meet the demands of your system without overworking or underperforming.
Read more: What Is The Weep Hole On A Water Pump For
Components of a Water Pump
A water pump consists of several key components that work together to facilitate the efficient movement of water. Understanding these components is essential for troubleshooting and maintenance. Here are the main components found in a typical water pump:
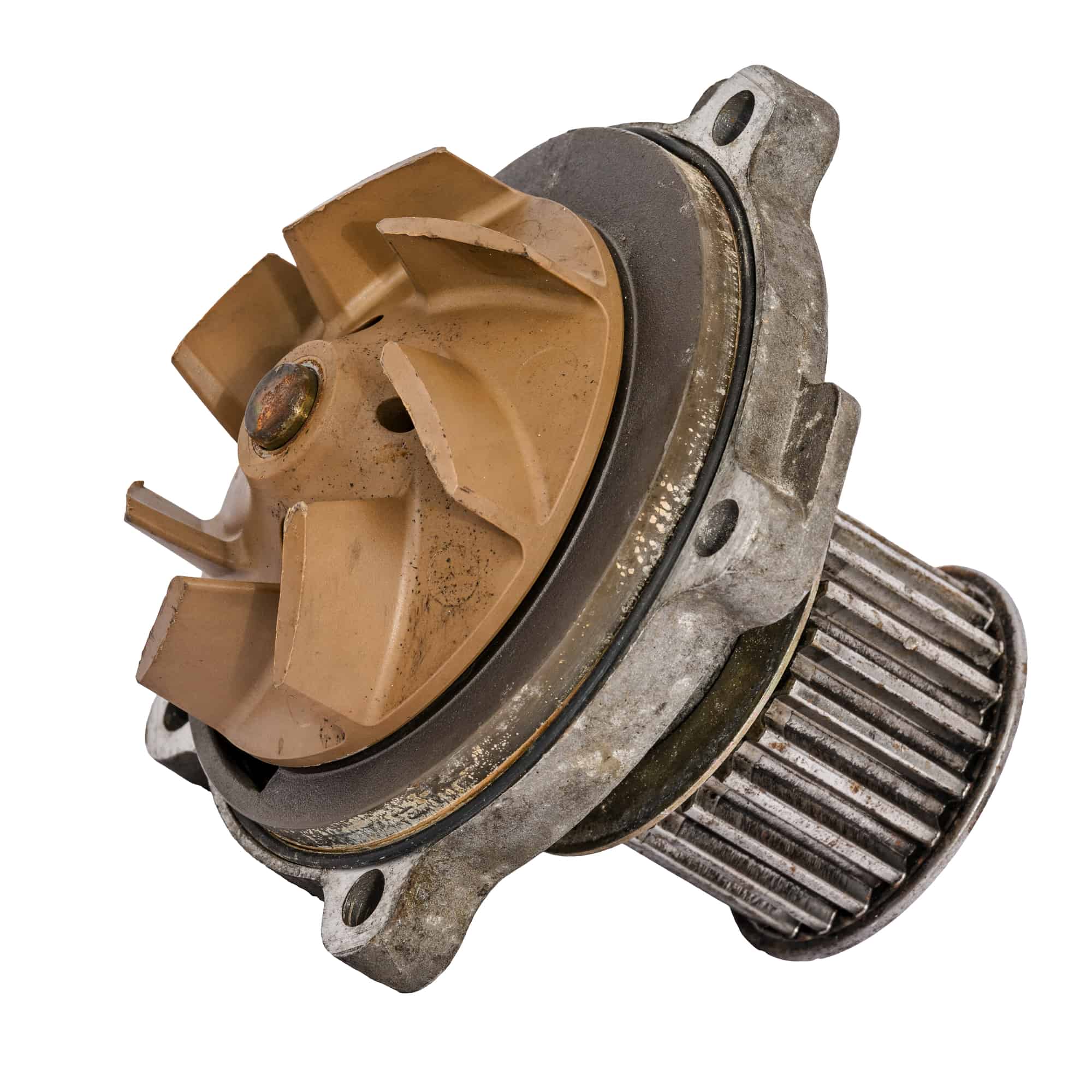
- Impeller: The impeller is a critical component responsible for creating centrifugal force and increasing water pressure. It is typically a rotating disc with curved blades that propel the water.
- Casing: The casing is the housing that encloses the impeller and other internal components. It is designed to direct and control the flow of water, optimizing efficiency.
- Seal: The seal prevents water from leaking out of the pump. It is typically located at the shaft where the rotating impeller is connected to the motor or drive mechanism.
- Inlet and Outlet: The inlet is the point where water enters the pump, while the outlet is where pressurized water is discharged. These openings are connected to pipes or hoses for fluid transfer.
- Motor or Drive Mechanism: The motor or drive mechanism powers the pump, providing the necessary energy to rotate the impeller and facilitate water movement. It can be an electric motor, internal combustion engine, or even a manual crank, depending on the type of pump.
- Bearings: Bearings support the rotating components, such as the impeller and motor shaft. They allow for smooth rotation and reduce friction, ensuring the longevity of the pump.
- Priming mechanism: Some water pumps, such as jet pumps, require priming to create suction and start the pumping process. Priming mechanisms vary depending on the pump type and may involve the use of a priming plug, valve, or pump.
- Control Panel: In larger or automated water pump systems, a control panel may be present to monitor and regulate pump operation. It can include features such as start/stop buttons, pressure sensors, and safety mechanisms.
These are the basic components found in most water pumps. However, the specific design and configuration of components may vary depending on the pump type, size, and manufacturer.
Understanding the functions and maintenance requirements of each component is crucial for ensuring proper pump operation, efficiency, and longevity. Regular inspection, lubrication, and replacement of worn-out parts are essential to prevent failures and prolong the lifespan of the water pump.
Common Issues with Water Pumps
While water pumps are designed to be reliable and durable, they can encounter issues over time. Understanding these common problems can help you identify and address them promptly, ensuring the smooth operation of your water pump. Here are some of the most common issues that can occur:
- Lack of Priming: Some pumps, such as jet pumps, require proper priming for suction. If the pump fails to prime or loses its prime, it may not be able to generate enough pressure to move water effectively.
- Low Water Flow: Insufficient water flow can be caused by various factors, such as a clogged inlet or outlet, worn-out impeller, or air leakage. This can result in reduced water pressure and inadequate water supply.
- Noisy Operation: Unusual noises, such as grinding, rattling, or screeching, can indicate issues with the bearings, impeller, or motor. These can be a sign of wear and tear or misalignment, requiring immediate attention.
- Leakage: Water leaks can occur at various points in the pump, such as the seals, casing, or connections. These leaks not only waste water but can also contribute to reduced pump performance and potential damage to surrounding components.
- Loss of Pressure: A sudden drop in water pressure can indicate a problem with the pump, such as a clogged impeller or a malfunctioning pressure switch. This can result in inefficient water supply and poor performance.
- Motor Failure: The motor is a critical component of the water pump. Motor failures can occur due to various reasons, including overheating, electrical issues, or mechanical failure. This can lead to pump malfunctions or complete system shutdown.
- Impeller Damage: The impeller can become damaged or worn-out over time due to debris, corrosion, or improper usage. A damaged impeller can result in reduced water flow and lower pump efficiency.
- Poor Maintenance: Neglecting regular maintenance, such as lubrication, cleaning, and inspection, can contribute to various pump problems. It is essential to adhere to the manufacturer’s maintenance recommendations to ensure optimal pump performance and extended lifespan.
Regular inspection, maintenance, and timely repairs are crucial to prevent these issues and maintain the efficiency and performance of your water pump. If you encounter any problems, it is recommended to consult a professional for proper diagnosis and repair to avoid further damage.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting of Water Pumps
Maintaining and troubleshooting water pumps is essential for ensuring their longevity, optimal performance, and uninterrupted water supply. Regular maintenance can help prevent issues and identify potential problems before they escalate. Here are some maintenance and troubleshooting tips for water pumps:
- Regular Inspections: Perform visual inspections of the pump, checking for any leaks, loose connections, or signs of wear. Inspect the impeller for damage or debris buildup that could affect performance.
- Cleaning: Remove any debris, sediment, or foreign objects that may have accumulated in the pump or its intake. Clean the impeller and casing to maintain optimal water flow and prevent clogs.
- Lubrication: Follow the manufacturer’s instructions to properly lubricate any required parts, such as bearings or motor shafts. Regular lubrication helps reduce friction, extend the life of moving parts, and ensure smooth operation.
- Priming: If you have a pump that requires priming, ensure that it is properly primed before operating. Check for any air leaks in the suction line and address them promptly.
- Monitoring Pressure: Keep an eye on the water pressure. Sudden drops in pressure may indicate a clogged impeller, leak, or other issues. Adjust or replace the pressure switch if necessary.
- Electric Components: Inspect electrical connections, wires, and the motor for any signs of damage or overheating. Loose or damaged electrical connections can cause interruptions or motor failures. Consult a professional if you notice any electrical issues.
- Seal Inspection: Regularly check the seals for signs of wear or leakage. Replace any damaged or worn-out seals to prevent water leaks and maintain efficiency.
- Proper Usage: Ensure that the pump is used within its specified limits and for its intended purpose. Overloading the pump or using it with incompatible liquids can lead to premature wear and damage.
- Troubleshooting: If you encounter issues with your water pump, start by identifying the possible cause. Refer to the pump’s manual or contact a professional for troubleshooting guidance specific to your pump type.
- Professional Maintenance: Schedule periodic maintenance and service checks by a qualified technician to ensure proper functioning and address any complex issues. They can perform in-depth inspections, testing, and repairs as needed.
By following these maintenance and troubleshooting tips, you can maximize the lifespan of your water pump and avoid costly repairs or replacements. Remember that regular maintenance and timely attention to any issues are key to keeping your water pump operating efficiently and providing a continuous water supply.
Conclusion
Water pumps are indispensable devices that play a crucial role in various industries and everyday life. They ensure the efficient movement of water, providing a continuous water supply for irrigation, firefighting, drainage, and residential use. Understanding the different types of water pumps, their working principles, and the components that make them up is essential for proper maintenance and troubleshooting.
From centrifugal pumps to submersible pumps, each type of water pump has its unique features and applications. By selecting the right type of pump and maintaining it regularly, you can optimize its performance and extend its lifespan. Key components such as the impeller, casing, seals, motor, and control panel all contribute to the efficient functioning of a water pump.
Common issues with water pumps, such as low water flow, leaks, motor failures, and loss of pressure, can be resolved through regular inspection, cleaning, lubrication, and adherence to proper usage guidelines. Troubleshooting any problems that arise and seeking professional assistance when necessary can help prevent further damage and keep the water pump operating smoothly.
In conclusion, water pumps are essential for maintaining a steady water supply in various applications. By understanding their importance, types, working principles, components, and maintenance requirements, you can ensure the longevity and optimal performance of your water pump. Regular maintenance, proper troubleshooting, and timely repairs are essential for reliable water pump operation and the continued efficiency of water distribution systems.
So, whether it’s effectively irrigating crops, supplying water to households, or aiding in firefighting efforts, water pumps are invaluable devices that keep the flow of water moving smoothly.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is A Water Pump
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.













0 thoughts on “What Is A Water Pump”