
Articles
What Is The Maximum Conduit Fill
Modified: February 22, 2024
Learn about the maximum conduit fill requirements and guidelines in this informative article. Find out how to calculate and ensure compliance with industry standards.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
In the world of electrical installations, one crucial aspect that electricians and engineers must consider is the maximum conduit fill. Conduit fill refers to the amount of space occupied by electrical conductors inside a conduit system. It plays a vital role in ensuring the safety and performance of the electrical infrastructure.
Having a clear understanding of conduit fill is essential to prevent potential issues such as overheating, voltage drops, and interference. In this article, we will delve into the definition of conduit fill, its importance, relevant regulations, factors affecting conduit fill, calculating conduit fill, maximum conduit fill guidelines, consequences of exceeding maximum fill, and provide some examples to illustrate these concepts.
Before we proceed, it is important to note that the content of this article is intended for informational purposes only. It is always essential to consult the National Electrical Code (NEC) and seek professional advice when conducting electrical installations.
Now, let’s explore this critical aspect of electrical systems in more detail.
Key Takeaways:
- Proper conduit fill is crucial for safety, performance, and compliance with regulations in electrical installations. Accurate calculations and adherence to guidelines prevent issues like overheating and voltage drops, ensuring efficient operation.
- Exceeding maximum conduit fill can lead to overheating, voltage drops, and challenges with maintenance. Adhering to guidelines and consulting professionals ensures safety, compliance, and efficient electrical installations.
Read more: What Is The Maximum Slope For A Driveway
Definition of Conduit Fill
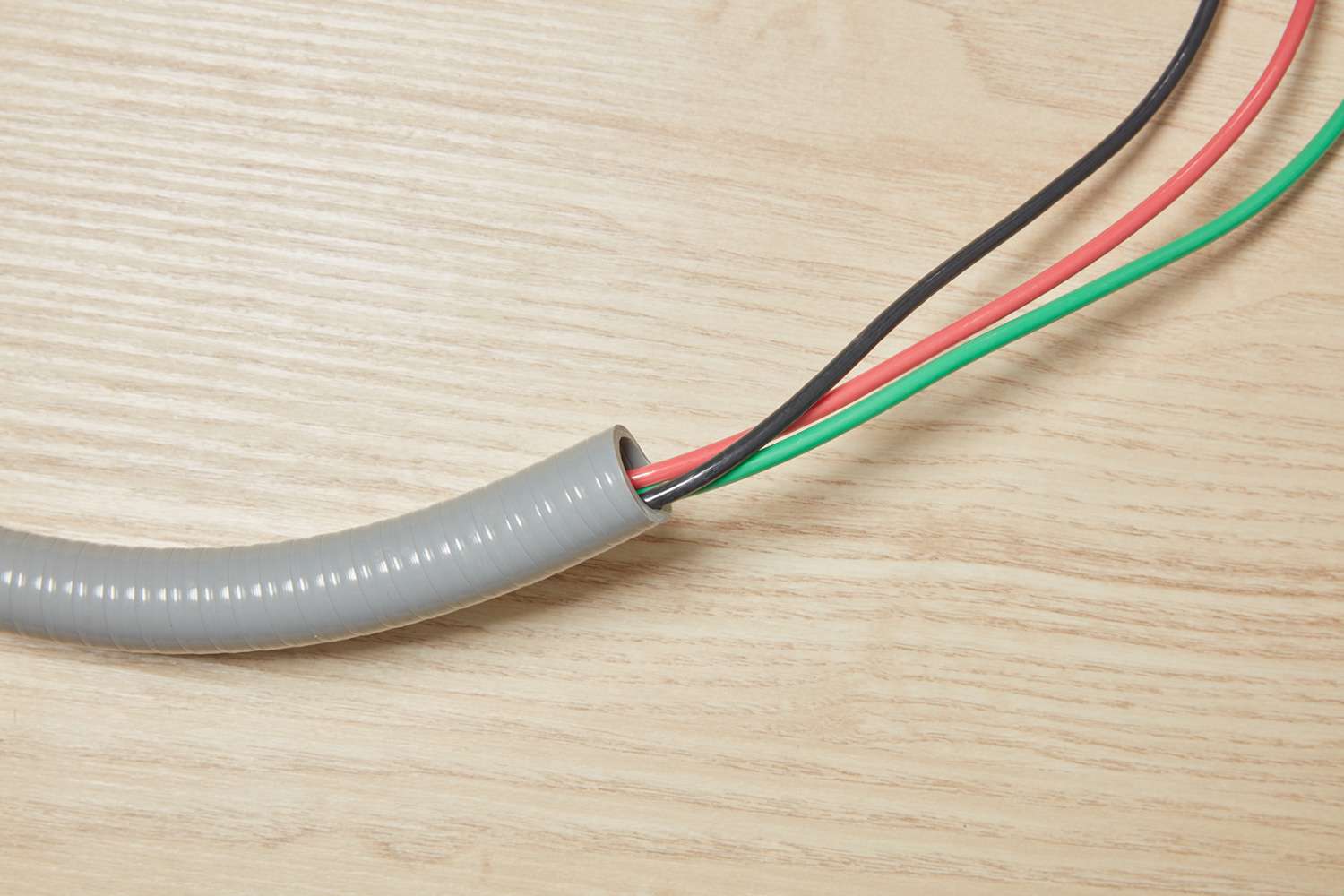
Conduit fill refers to the process of determining the maximum number and size of electrical conductors that can be safely installed inside a conduit system. A conduit system is a series of pipes or tubes that protect and contain electrical wiring, ensuring its proper organization and insulation.
The purpose of determining conduit fill is to prevent the overcrowding of wires, which can lead to various issues such as overheating, voltage drops, and difficulty in future maintenance and repairs. Conduit fill calculations help electricians and engineers ensure that the size of the conduit chosen is sufficient to accommodate all the necessary wires without compromising their performance.
Conduit fill is typically expressed as a percentage, indicating the amount of cross-sectional area filled by the wires inside the conduit. This percentage is based on the diameter or size of the wires, which is measured using the American Wire Gauge (AWG) system.
It is important to note that conduit fill calculations not only consider the size of the wires but also take into account other components such as fillers, spacers, and fittings present in the conduit system. These components occupy additional space and should be accounted for in the calculations to ensure compliance with safety standards.
Overall, conduit fill is a crucial aspect of electrical installations as it helps maintain the integrity and efficiency of the electrical system. By properly determining the conduit fill, electricians can ensure the smooth and safe operation of the electrical infrastructure.
Importance of Conduit Fill
Conduit fill plays a critical role in electrical installations, and its importance should not be underestimated. Here are some key reasons why conduit fill is essential:
1. Safety: Proper conduit fill ensures that electrical conductors are not overcrowded, which helps prevent overheating. Overheating can lead to insulation deterioration, increased resistance, and potential fire hazards. By adhering to conduit fill guidelines, the risk of electrical accidents and injuries can be significantly reduced.
2. Performance: Adequate conduit fill ensures optimal performance of the electrical system. When wires are spread out properly within the conduit, it minimizes the chances of voltage drops and interference. This helps maintain a stable power supply and prevents disruptions in various electrical circuits.
3. Future Maintenance: With proper conduit fill, future maintenance and repairs become easier and more efficient. Sufficient space in the conduit allows for the addition or replacement of wires without the need for extensive modifications. This reduces the time, effort, and cost associated with maintenance activities.
4. Compliance with Regulations: Electrical installations must comply with the regulations set forth by the National Electrical Code (NEC) or other applicable codes and standards. Conduit fill guidelines are part of these regulations, and adherence ensures that installations meet safety standards and pass inspections.
5. Organization and Neatness: Conduit fill helps maintain a clean and organized electrical infrastructure. With the proper arrangement of wires within the conduit, it becomes easier to trace and identify specific circuits when needed. This simplifies troubleshooting and ensures efficient cable management.
6. Longevity of Wires: Overcrowded conduits can put excessive pressure on the wires, leading to physical damage or insulation degradation over time. By following conduit fill guidelines, the lifespan of the wires is extended, reducing the need for frequent replacements and repairs.
In summary, conduit fill is crucial for ensuring the safety, performance, and longevity of electrical installations. By following proper conduit fill calculations and guidelines, electricians and engineers can create a reliable and efficient electrical system that meets regulatory requirements and provides a sustainable solution for long-term use.
National Electrical Code (NEC) Regulations
The National Electrical Code (NEC) is a set of regulations and standards developed by the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) for safe electrical installations in the United States. These regulations provide guidelines for various aspects of electrical systems, including conduit fill.
The NEC provides specific requirements for conduit fill to ensure the safety and performance of electrical installations. It outlines the maximum allowable fill percentages based on the size of the conduit and the size and type of the electrical conductors being used.
One of the key considerations in conduit fill calculations is the ampacity of the conductors. Ampacity refers to the maximum current that a conductor can carry safely without exceeding its temperature rating. The NEC provides tables and formulas to determine the allowable ampacity and the corresponding conduit size based on various factors such as wire size, insulation type, ambient temperature, and number of conductors.
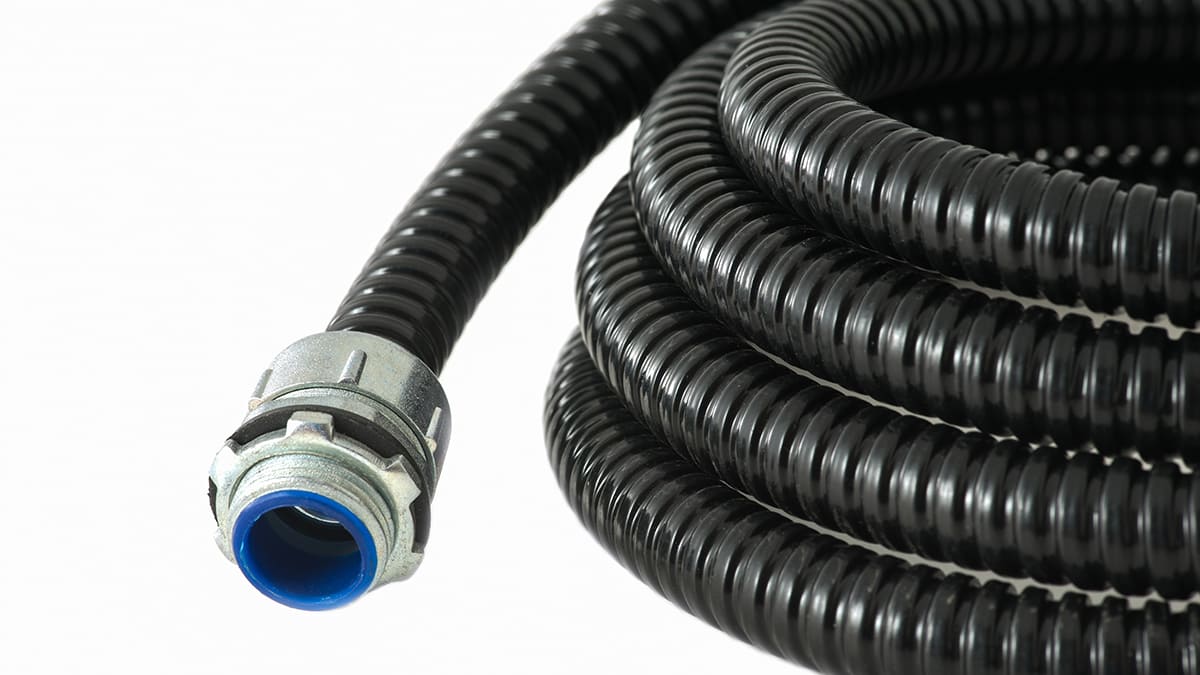
The NEC also includes guidelines for different types of conduits, such as PVC (polyvinyl chloride), EMT (electrical metallic tubing), and RMC (rigid metal conduit). Each type of conduit has specific maximum fill percentages to ensure proper wire spacing and heat dissipation.
It is important to note that the NEC is regularly updated to reflect changes in technology and safety requirements. Electricians and engineers need to stay up to date with the latest edition of the NEC and any local amendments or modifications that may apply in their jurisdiction.
Failure to comply with NEC regulations can lead to potential hazards, legal complications, and the rejection of electrical installations during inspections. It is crucial to consult the NEC and work with qualified professionals to ensure that conduit fill calculations and installations are done in accordance with the latest standards.
By adhering to the NEC regulations for conduit fill, electricians and engineers can ensure that their electrical installations meet the required safety standards, reduce the risk of electrical accidents, and create a reliable and efficient electrical system. Compliance with the NEC also demonstrates a commitment to professionalism and responsible electrical practices.
Factors Affecting Conduit Fill
Several factors come into play when determining the conduit fill for an electrical installation. Understanding these factors is crucial for accurate calculations and ensuring compliance with safety standards. Let’s explore the key factors that affect conduit fill:
1. Wire Size: The size or gauge of the electrical wires being used has a direct impact on conduit fill. Larger wires occupy more space within the conduit, reducing the available room for additional wires. The American Wire Gauge (AWG) system is used to measure wire sizes, with larger numbers indicating smaller wire sizes.
2. Conduit Size: The diameter or size of the conduit itself is a significant factor in conduit fill calculations. A smaller conduit will have less space to accommodate wires, whereas a larger conduit will have more room. It is essential to choose a conduit size that can adequately accommodate the required number and size of wires.
3. Type of Conductor: Different types of conductors have varying external diameters due to differences in insulation thickness. For example, conductors with thicker insulation, such as THHN, will occupy more space within the conduit compared to conductors with thinner insulation, such as THWN.
4. Conductor Insulation: The type and thickness of the insulation on the conductors can affect conduit fill. Insulation adds to the overall diameter of the wire, reducing the available space inside the conduit. It is important to consider the insulation diameter when calculating conduit fill.
5. Fillers, Spacers, and Fittings: Fillers, spacers, and fittings inside the conduit also occupy space and should be taken into account during conduit fill calculations. These components ensure proper wire spacing, provide support, and maintain the integrity of the electrical system. Ignoring the space occupied by these components can result in an inaccurate conduit fill calculation.
6. Bend Radius: The bend radius required for the wires inside the conduit can affect the conduit fill. Smaller bend radii may reduce the amount of available space for wires, whereas larger bend radii allow for more efficient wire arrangement. It is important to consider the required bend radius when determining conduit fill.
7. Voltage Drop Consideration: Voltage drop, the decrease in voltage along the length of a wire, is a critical aspect to consider in conduit fill calculations. Voltage drop can be affected by factors such as wire size, length, and the amperage of the circuit. Ensuring the proper wire size and calculating voltage drop allowances are important for maintaining the electrical system’s performance.
By considering these factors and accurately calculating conduit fill, electricians and engineers can ensure the optimal use of conduits, minimize safety risks, and comply with industry standards and regulations.
When calculating maximum conduit fill, remember to consider the size and number of conductors, as well as any equipment grounding conductors or support fittings. Use the NEC guidelines for accurate calculations.
Read more: What Is The Maximum Riser Height For Stairs
Calculating Conduit Fill
Calculating conduit fill involves determining the maximum number and size of electrical conductors that can be safely installed within a conduit system. Accurate calculations are essential to ensure compliance with safety standards and maintain the performance of the electrical installation. Let’s take a look at the steps involved in calculating conduit fill:
1. Gather Information: Start by collecting the necessary information for your calculation. This includes the size or gauge of the conductors, the type of conduit being used, the size of the conduit, and any fillers, spacers, or fittings that will be present in the conduit system.
2. Determine Conduit Size: Identify the size of the conduit that will be used for the installation. This is typically based on the number and size of conductors required for the specific application. You can refer to conduit sizing tables provided by the National Electrical Code (NEC) or consult industry standards and manufacturer guidelines.
3. Identify Conduit Fill Capacity: Determine the maximum conduit fill capacity for the chosen conduit size. This information can be found in the NEC or other applicable codes and standards. Conduit fill percentages range from 25% to 60%, depending on factors such as the size and type of conductors, conduit material, and specific application requirements.
4. Calculate Conductor Fill Area: Calculate the fill area of each conductor being installed within the conduit. This is done by using the appropriate formula or table provided by the NEC or manufacturer specifications. The fill area is typically expressed in square inches.
5. Calculate Total Fill Area: Add up the fill areas of all the conductors that will be installed within the conduit. This will give you the total fill area occupied by the conductors.
6. Compare with Conduit Fill Capacity: Compare the total fill area with the maximum conduit fill capacity for the chosen conduit size. Ensure that the total fill area does not exceed the maximum fill capacity to maintain compliance with safety standards. If the total fill area exceeds the maximum capacity, it will be necessary to choose a larger conduit or make adjustments to the conductor size or arrangement.
7. Allow for Fillers, Spacers, and Fittings: If fillers, spacers, or fittings are present within the conduit system, ensure that their space requirements are also considered in the calculation. Deduct the fill area occupied by these components from the total fill area before comparing it with the maximum fill capacity of the conduit.
By following these steps and accurately calculating conduit fill, electricians and engineers can ensure the safe and efficient installation of electrical conductors within a conduit system. It is important to consult the NEC and other applicable regulations, as well as seek professional advice, to ensure accurate calculations and compliance with safety standards.
Maximum Conduit Fill Guidelines
Maximum conduit fill guidelines provide specific recommendations on the maximum allowable percentage of conduit space that can be occupied by electrical conductors. Adhering to these guidelines is crucial to ensure the safe and efficient installation of wiring within a conduit system. Let’s explore some key guidelines to keep in mind:
1. National Electrical Code (NEC): The NEC, developed by the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), provides comprehensive guidelines for electrical installations in the United States. The NEC outlines the maximum conduit fill percentages based on factors such as conduit size, conductor size, and insulation type. It is important to consult the NEC and any local amendments or modifications that may apply in your jurisdiction.
2. Different Conduit Types: Various types of conduits have their own specific maximum fill percentages. For example, PVC (polyvinyl chloride) conduits typically have higher fill percentages compared to metal conduits. Be sure to refer to the appropriate standards and guidelines for the specific type of conduit being used in your installation.
3. Conductor Size and Type: The size and type of conductors being installed within the conduit also impact the maximum fill allowable. Different conductor sizes and insulation types have varying dimensions, which can affect the available space within the conduit. Ensure that the conductor sizes and types conform to the NEC requirements and any specific manufacturer guidelines.
4. Load Calculation: The electrical load calculation is crucial in determining the appropriate conductor size and the maximum fill within the conduit. By accurately calculating the load requirements of the circuit, you can ensure that the conductors have the necessary capacity and determine the appropriate conduit size and fill percentages.
5. Derating Factors: In certain situations, derating factors must be applied to the maximum conduit fill percentages. Factors such as ambient temperature, the number of current-carrying conductors, and conductor bundling can affect the conductor’s ampacity and, therefore, impact the maximum fill. It is essential to consider these derating factors to ensure the safe and efficient operation of the electrical system.
6. Professional Advice: It is highly recommended to consult with qualified electricians or engineers who have expertise in conduit fill calculations. Their knowledge and experience can provide valuable insights and ensure accurate adherence to maximum conduit fill guidelines.
By following these maximum conduit fill guidelines, you can ensure the safe and efficient installation of electrical conductors within a conduit system. Adhering to these guidelines not only ensures compliance with safety standards but also helps prevent issues such as overheating, voltage drops, and difficulty in future maintenance and repairs. Remember to consult the NEC and other applicable codes and standards to stay up to date with the latest requirements.
Consequences of Exceeding Maximum Conduit Fill
Exceeding the maximum conduit fill can have serious consequences for the safety and performance of an electrical installation. It is essential to adhere to the recommended fill percentages to avoid potential issues. Let’s explore some of the consequences that can arise from exceeding maximum conduit fill:
1. Overheating: Overcrowding cables within a conduit can lead to overheating. When conductors are tightly packed, their ability to dissipate heat is compromised. This can result in increased resistance, insulation deterioration, and ultimately, potential fire hazards. Overheating poses a significant risk to the safety of the electrical system and the surrounding environment.
2. Voltage Drop: Another consequence of exceeding the maximum conduit fill is increased voltage drop. Voltage drop refers to the decrease in voltage experienced along the length of a conductor. When conductors are crowded within a conduit, it can increase resistance and lead to higher voltage drops. Excessive voltage drop can affect the performance and efficiency of electrical circuits, particularly those sensitive to voltage variations.
3. Difficult Maintenance and Repairs: Excessive conduit fill can make future maintenance and repairs more challenging. Lack of adequate space within the conduit system makes it difficult to add or remove wires, troubleshoot faults, and perform necessary upgrades or modifications. It may require significant labor and time to navigate through crowded conduits, resulting in increased costs and potential damage to existing conductors.
4. Non-compliance with Regulations: Exceeding the maximum conduit fill violates regulations and safety standards, such as those outlined in the National Electrical Code (NEC) or applicable local codes. Non-compliance can lead to problems during inspections, potential fines or penalties, and legal consequences. Compliance with regulations is crucial to ensure the reliability and safety of electrical installations.
5. Reduced Lifespan of Conductors: Overcrowding conductors within a conduit can subject them to physical stress and compression. This can damage the conductors’ insulation, leading to premature wear and shortened lifespan. Replacing damaged conductors can be time-consuming and costly, affecting the overall performance and longevity of the electrical system.
6. Increased Risk of Electrical Accidents: Excessive conduit fill creates an environment prone to electrical accidents. Overheating, insulation degradation, and voltage drops can increase the risk of electrical shocks, arcs, and fires. These accidents pose a threat to the safety of people and property, emphasizing the importance of adhering to maximum conduit fill guidelines.
To avoid these consequences, it is crucial to accurately calculate conduit fill and ensure compliance with recommended maximum fill percentages. Working with qualified electricians or engineers who have expertise in conduit fill calculations can help ensure the safety and efficiency of your electrical installation. Remember to consult the NEC or other applicable codes and standards to stay informed about the specific requirements for conduit fill in your jurisdiction.
Conduit Fill Examples
To better understand how conduit fill works in practice, let’s explore a few examples to illustrate the calculations and considerations involved:
Example 1: Residential Wiring
Suppose you are working on a residential wiring project, and you need to determine the conduit fill for a 1/2-inch PVC conduit. The installation requires three 12 AWG THHN conductors and one 12 AWG bare ground wire. You consult the NEC and find that the maximum fill percentage for a 1/2-inch PVC conduit is 53%.
To calculate the conduit fill, you start by determining the fill area for each conductor. The fill area for a 12 AWG conductor is 0.0133 square inches. Since you have four conductors (three current-carrying and one ground wire), the total fill area for the conductors is 0.0133 * 4 = 0.0532 square inches.
Next, you compare the total fill area with the maximum fill percentage for the conduit. In this case, the maximum fill percentage is 53%. Multiply the conduit size by the maximum percentage (0.5 * 53% = 0.265), and you find that the available fill area is 0.265 square inches.
Since the total fill area (0.0532 square inches) is significantly less than the maximum available fill area (0.265 square inches), you can proceed with this conduit size, ensuring compliance with the maximum conduit fill guidelines.
Example 2: Commercial Building
Now, let’s consider a commercial building project with a larger conduit size. You are installing a 2-inch EMT conduit in a commercial building. The installation requires twelve 10 AWG THHN conductors and two 10 AWG bare ground wires. The maximum allowable fill percentage for a 2-inch EMT conduit, according to the NEC, is 40%.
To calculate the conduit fill, you determine the fill area for each conductor. The fill area for a 10 AWG conductor is 0.0397 square inches. With fourteen conductors (twelve current-carrying and two ground wires), the total fill area for the conductors is 0.0397 * 14 = 0.5558 square inches.
Comparing this total fill area to the maximum allowable fill percentage (40% of the conduit size), you multiply the conduit size by the maximum percentage (2 * 40% = 0.8) to find the available fill area. In this case, the available fill area is 0.8 square inches.
Since the total fill area (0.5558 square inches) is less than the available fill area (0.8 square inches), you can proceed with this conduit size, ensuring compliance with the maximum conduit fill guidelines for a 2-inch EMT conduit.
These examples demonstrate the importance of accurate conduit fill calculations to ensure compliance with maximum fill guidelines. Proper calculations help prevent issues such as overheating, voltage drops, and difficulty with future maintenance or repairs. Always consult the NEC and any applicable standards to ensure compliance and safety in your specific electrical installation.
Read more: What To Fill Outdoor Planters With
Conclusion
Conduit fill is a fundamental aspect of electrical installations that plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety, performance, and efficiency of the electrical system. By understanding and adhering to conduit fill guidelines, electricians and engineers can prevent potential issues such as overheating, voltage drops, and challenges with future maintenance or repairs.
Throughout this article, we have explored various components related to conduit fill, including its definition, importance, regulations, factors affecting conduit fill, calculating conduit fill, maximum conduit fill guidelines, consequences of exceeding maximum fill, and provided examples to illustrate these concepts.
Accurate conduit fill calculations involve considering factors such as wire size, conduit size, type of conductors, insulation type, fillers, spacers, fittings, bend radius, and load requirements. Taking these factors into account ensures that the wires are properly spaced, heat dissipation is adequate, and compliance with safety standards is maintained.
Furthermore, consulting the National Electrical Code (NEC) and other applicable codes and standards is essential to stay up to date with the latest requirements and recommendations. Collaboration with qualified professionals in the field can provide valuable insights and ensure accurate calculations for conduit fill.
Exceeding the maximum conduit fill can have severe consequences, including overheating, voltage drops, difficulties with future maintenance and repairs, non-compliance with regulations, and increased risks of electrical accidents. Adhering to maximum conduit fill guidelines mitigates these risks and ensures the longevity and performance of the electrical system.
By following proper conduit fill practices, electricians and engineers demonstrate their commitment to safety, professionalism, and responsible electrical practices. They can create reliable, efficient, and safe electrical installations that meet regulatory requirements and provide sustainable solutions for long-term use.
In conclusion, understanding and implementing conduit fill guidelines are vital for the successful design and installation of electrical systems. By prioritizing safety, efficiency, and compliance with regulations, electricians and engineers can ensure that electrical installations operate smoothly and reliably, minimizing risks and maximizing the lifespan of the system.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is The Maximum Conduit Fill
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.














0 thoughts on “What Is The Maximum Conduit Fill”