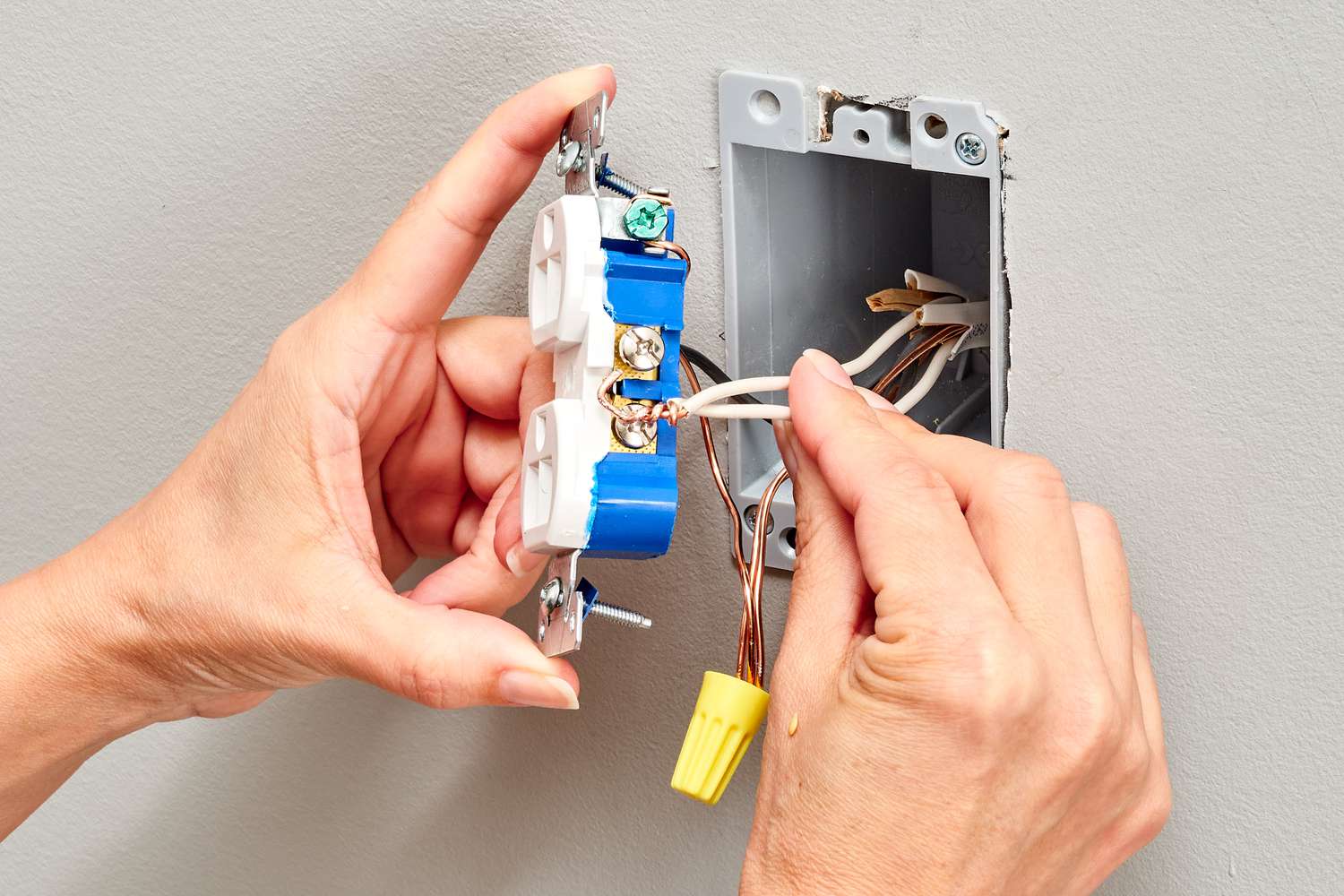


Articles
How To Ground Electrical Wires
Modified: January 9, 2024
Learn how to ground electrical wires safely and efficiently with our informative articles. Explore various techniques and tips to ensure proper grounding and electrical safety.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Welcome to the world of electrical wiring! Whether you are a seasoned DIY enthusiast or a newbie looking to learn more about the intricacies of electrical work, understanding how to ground electrical wires is an essential skill to have. Grounding plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety and functionality of electrical systems in your home or workplace.
Grounding is the process of providing a direct connection between electrical equipment and the earth. It involves creating a low-resistance path for electrical current to flow in the event of a fault or overload. This is achieved by connecting electrical devices and appliances to a grounding system, which includes ground wires, grounding rods, and grounding electrodes.
In this article, we will delve into the importance of grounding electrical wires, the safety precautions you need to take, the tools and materials required, and the step-by-step process of grounding electrical wires. We will also cover how to test the grounding system and troubleshoot grounding issues.
So, whether you are looking to install new electrical outlets, upgrade your electrical panel, or simply want to have a better understanding of electrical safety, read on to discover the ins and outs of grounding electrical wires.
Key Takeaways:
- Grounding electrical wires is crucial for safety, stability, and compliance with electrical codes. It protects against shocks, stabilizes the system, and safeguards against power surges, making it an essential skill for anyone working with electricity.
- Prioritize safety when grounding electrical wires by following safety precautions, using the right tools and materials, and testing the grounding system. Troubleshoot any issues promptly and seek professional assistance when needed.
Read more: How To Wire A Chandelier With A Ground Wire
Importance of Grounding Electrical Wires
Grounding electrical wires is vital for several reasons. Let’s explore the importance of grounding and why it should never be overlooked:
- Safety: Safety is the number one reason to ensure proper grounding of electrical wires. In the event of a fault, such as a short circuit or electrical surge, grounding provides a safe pathway for excess electrical current to flow to the earth, preventing electrocution or electrical fires. By creating a low-resistance path, grounding protects both people and the electrical system itself.
- Protection against electrical shocks: Grounding helps protect against electrical shocks by redirecting the flow of electrical current. In a properly grounded system, if an electrical appliance becomes faulty and the metal casing becomes live, the ground wire will carry the current directly to the earth, eliminating the risk of electric shock to anyone touching the appliance.
- Stability of electrical system: Grounding also helps maintain the stability of the electrical system. By providing a stable reference point, grounding ensures that voltage levels are consistent and prevents fluctuations that could damage sensitive electronic devices or cause interruptions in power supply.
- Surge protection: Grounding helps protect electrical equipment from power surges, such as those caused by lightning strikes or sudden voltage spikes. When a surge occurs, the excess electrical energy is diverted to the ground, preventing it from damaging appliances and electronics connected to the electrical system.
- Compliance with electrical codes: Proper grounding is not only good practice for safety, but it is also a requirement in most electrical codes and regulations. By following the prescribed grounding guidelines, you ensure that your electrical system meets the necessary standards and is up to code.
Overall, grounding electrical wires is an integral part of electrical system design and installation. It provides safety, protects against electrical shocks, stabilizes the electrical system, and safeguards against power surges. Understanding and implementing proper grounding techniques is essential for the security and functionality of your electrical infrastructure.
Safety Precautions
Working with electrical wires can be hazardous if proper safety precautions are not taken. Before you begin grounding electrical wires, consider the following safety guidelines:
- Turn off the power: Before starting any electrical work, always turn off the power to the circuit you will be working on. This can be done by switching off the corresponding circuit breaker in the electrical panel. Use a voltage tester to ensure that no electricity is flowing to the wires you will be working with.
- Wear protective gear: Protect yourself by wearing appropriate safety gear, such as safety glasses, gloves, and non-conductive footwear. Avoid loose clothing or jewelry that can get caught in tools or equipment.
- Work in a dry environment: Ensure that the area where you will be working is dry. Avoid working in wet or damp conditions, as water can conduct electricity and increase the risk of electrical shock.
- Use insulated tools: When working with electrical wires, always use insulated tools specifically designed for electrical work. These tools have non-conductive handles and minimize the risk of electrical conductivity.
- Avoid overloading circuits: Ensure that the circuit you are grounding is not overloaded. Overloading a circuit can cause overheating and increase the risk of electrical fires. Distribute the electrical load evenly across multiple circuits if needed.
- Properly secure wires: When connecting wires, make sure they are properly secured and free from any tension or strain. This helps prevent accidental disconnection or fraying of the wires.
- Follow local electrical codes: Familiarize yourself with the electrical codes and regulations specific to your area. Ensure that you follow all guidelines and requirements regarding grounding methods and materials.
- Seek professional assistance if unsure: If you are unsure about any aspect of grounding electrical wires or feel uncomfortable with the task, it is best to seek the help of a licensed electrician. They have the knowledge and experience to complete the job safely and accurately.
Remember, safety should always be the top priority when working with electricity. By following these safety precautions, you can minimize the risk of accidents and ensure a safe working environment when grounding electrical wires.
Tools and Materials Required
Before you begin grounding electrical wires, gather the following tools and materials to ensure a smooth and efficient process:
Tools:
- Insulated screwdrivers: These are essential for connecting wires and tightening screws.
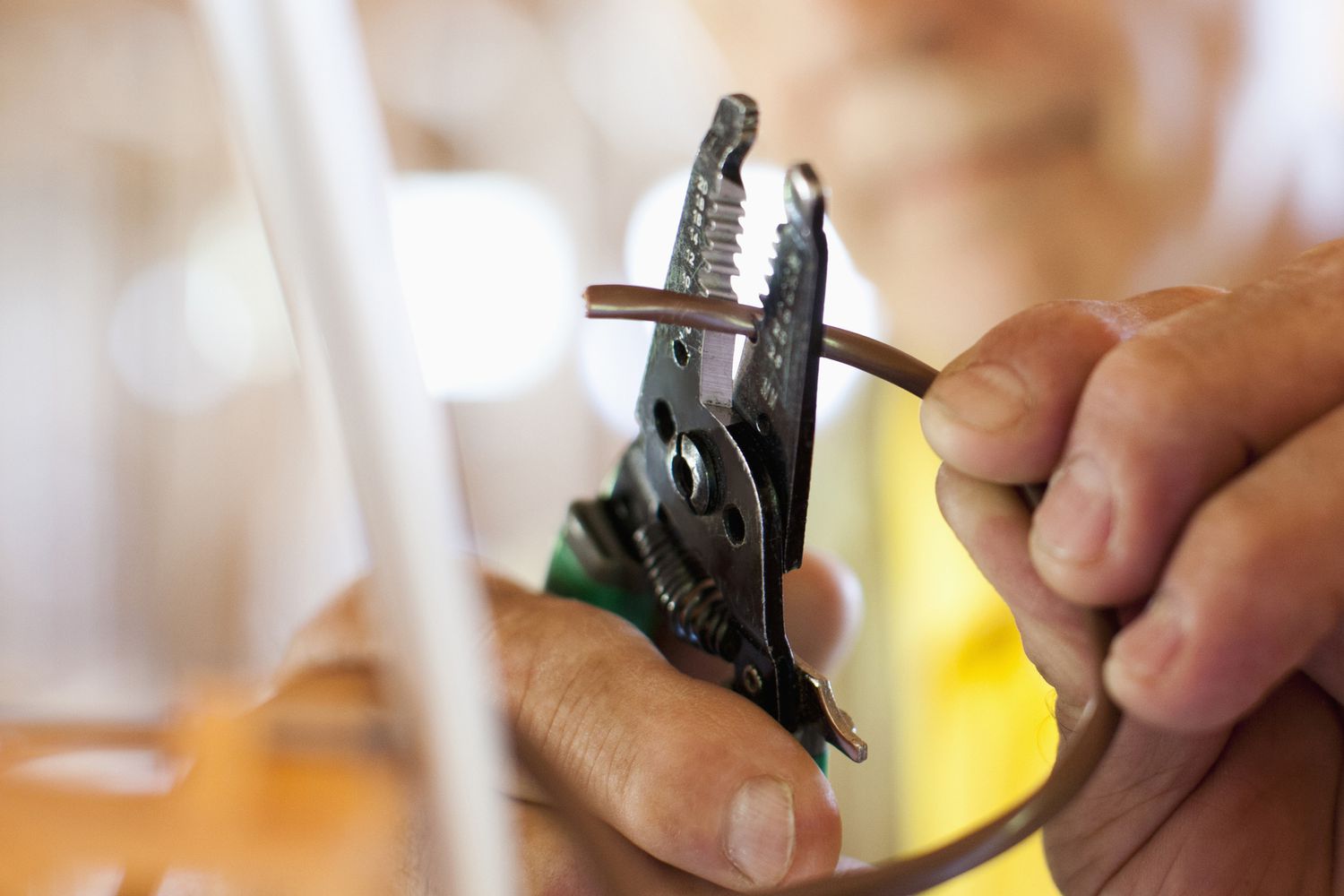
- Wire strippers: Used to strip off the insulation from the ends of the wires.
- Wire cutters: Used to cut wires to the desired lengths.
- Needle-nose pliers: Useful for bending and shaping wires.
- Circuit tester: Used to check if the power is turned off before starting work.
- Drill with masonry bit: Required for drilling holes in concrete surfaces for grounding electrodes.
- Hammer: Used when installing grounding rods or driving ground clamps.
- Measuring tape: Useful for taking measurements accurately.
Materials:
- GFCI (Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter) outlets: These outlets are designed to protect against ground faults and should be used in areas where water may be present, such as kitchens and bathrooms.
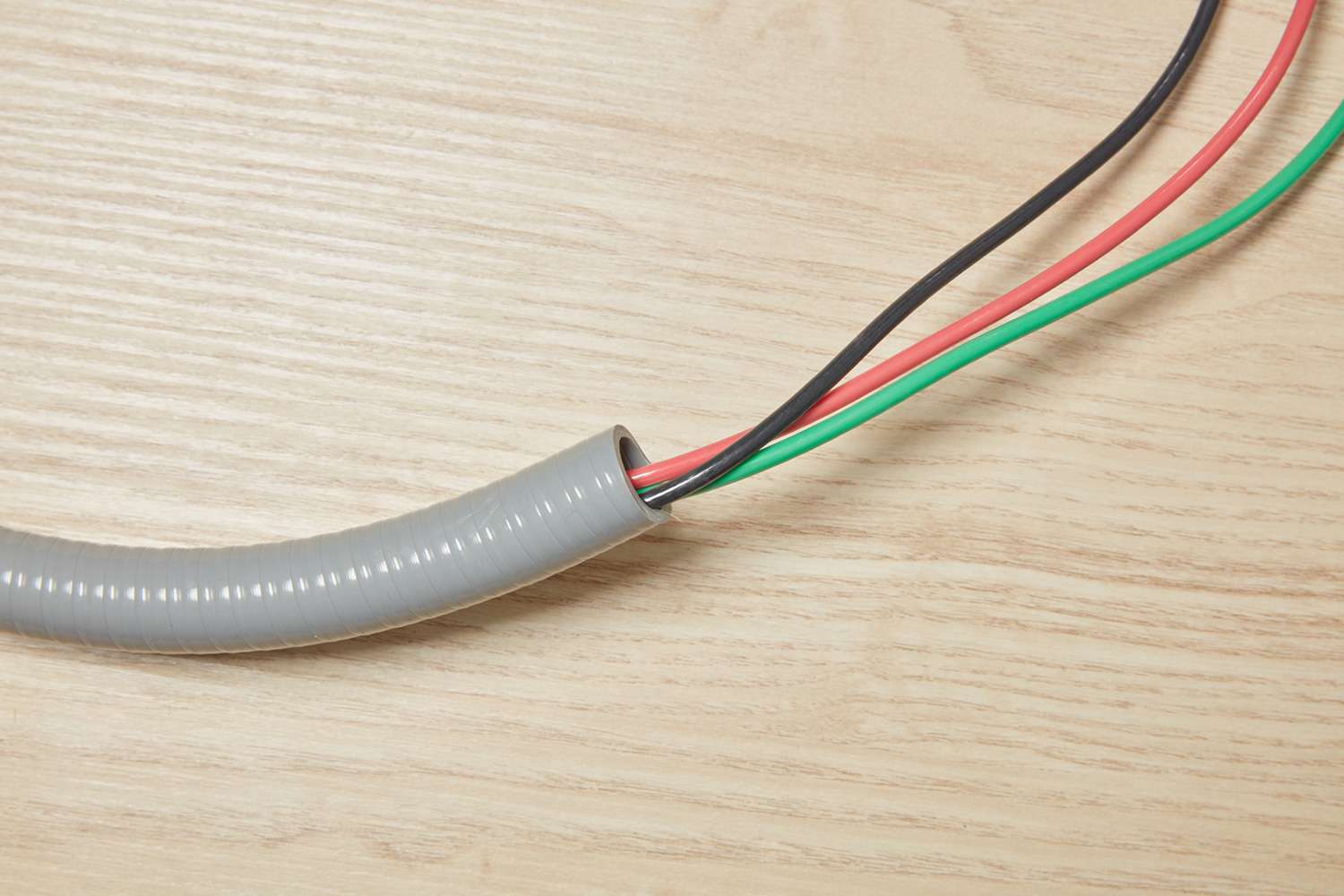
- Grounding wire: Also known as grounding conductor, this wire is typically copper or aluminum and connects electrical equipment to the grounding system.
- Grounding clamps: Used to securely attach the grounding wire to metal pipes, grounding rods, or other grounding surfaces.
- Grounding rods: These are metal rods, usually made of copper or galvanized steel, that are driven into the ground to provide an effective grounding system.
- Grounding electrodes: These are metal plates or conductive rods that are connected to grounding wires and buried in the ground to enhance the grounding system.
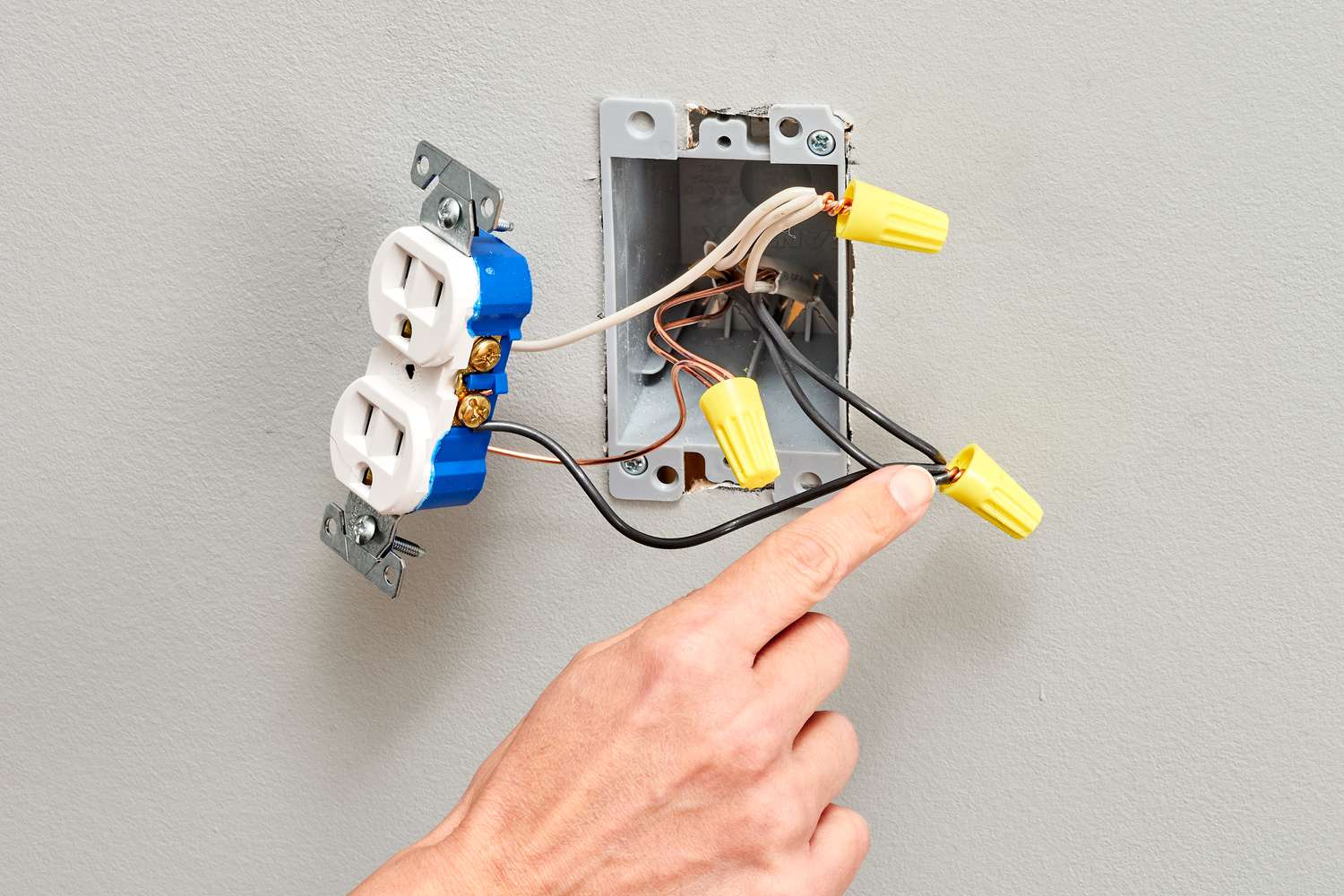
- Wire connectors: Used to join wires together securely.
- Electrical tape: Used to insulate wire connections and provide added protection.
- Markers or labels: Helpful for identifying and labeling wires for future reference.
Having these tools and materials readily available will make the grounding process easier and more efficient. It’s important to use high-quality materials to ensure a reliable and effective grounding system.
Steps to Ground Electrical Wires
Grounding electrical wires involves a series of steps to ensure a proper and effective connection to the earth. Follow these steps to ground electrical wires safely and accurately:
- Turn off the power: Start by turning off the power to the circuit you will be working on. Locate the circuit breaker in the electrical panel and switch it off.
- Prepare the grounding wire: Cut the grounding wire to the required length, ensuring it is long enough to reach the grounding point with some extra length for flexibility.
- Strip the wire ends: Use wire strippers to remove the insulation from both ends of the grounding wire. Strip off around ¾ inch of insulation from each end.
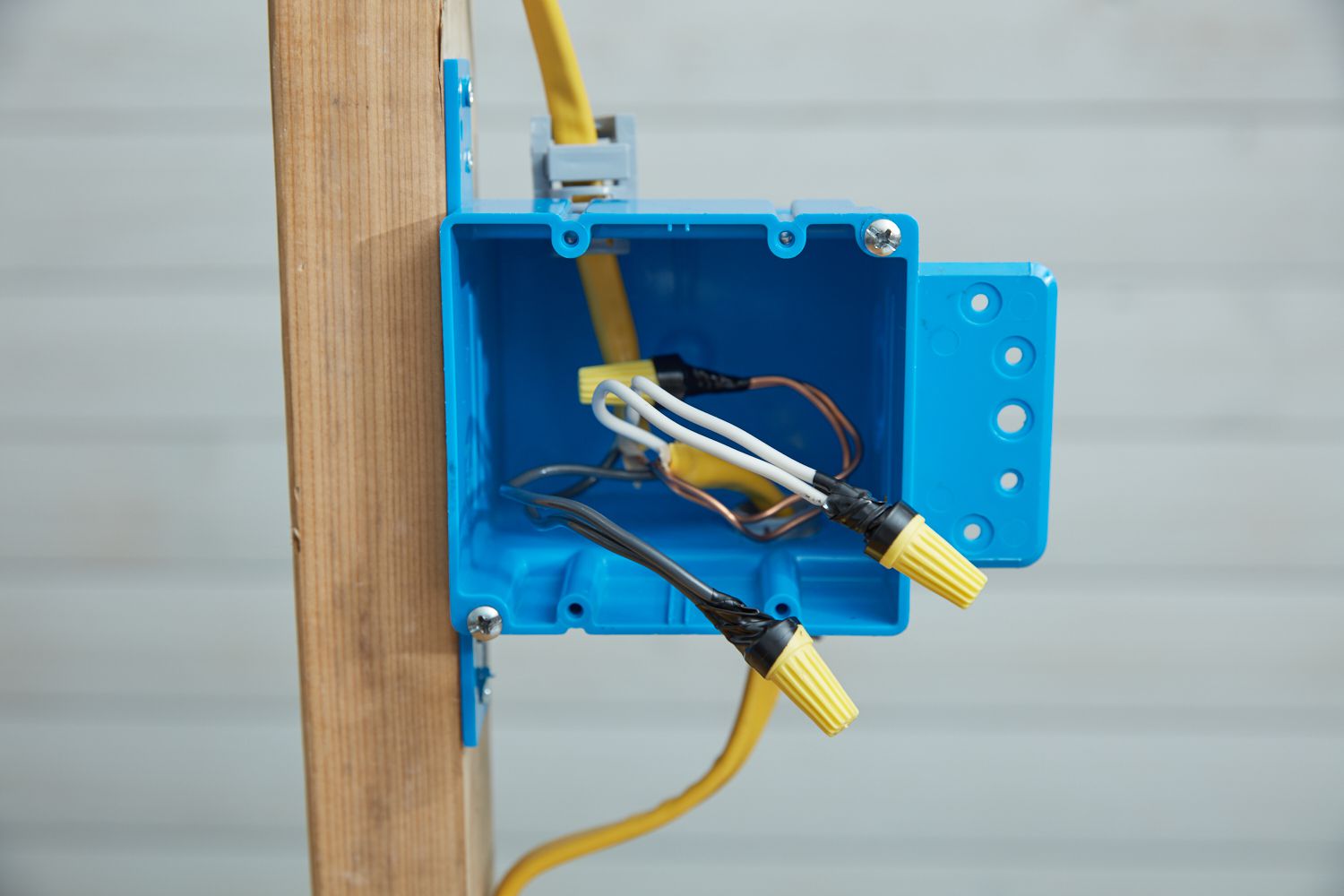
- Connect the wire to the grounding point: Attach one end of the grounding wire to the grounding point, such as a metal water pipe or grounding rod, using a grounding clamp. Ensure the connection is secure and tight.
- Connect the wire to the electrical panel: Locate the grounding bar in the electrical panel and attach the other end of the grounding wire to it using another grounding clamp. Again, ensure the connection is secure and tight.
- Secure any loose connections: Check all wire connections and make sure they are secure and properly tightened. Use a screwdriver to tighten any loose screws or connections.
- Label the grounding wire: Use markers or labels to clearly identify the grounding wire. This will be useful for future reference or troubleshooting.
- Restore the power: Once you have completed the grounding process and ensured all connections are secure, you can turn the power back on. Test the circuit to ensure everything is functioning properly.
It’s important to note that the specific steps may vary depending on the electrical system and the grounding requirements of your specific project. Always refer to the manufacturer’s instructions and follow local electrical codes to ensure compliance and safety.
Remember, if you are unsure about any step or aspect of grounding electrical wires, it is best to consult a licensed electrician for guidance or assistance.
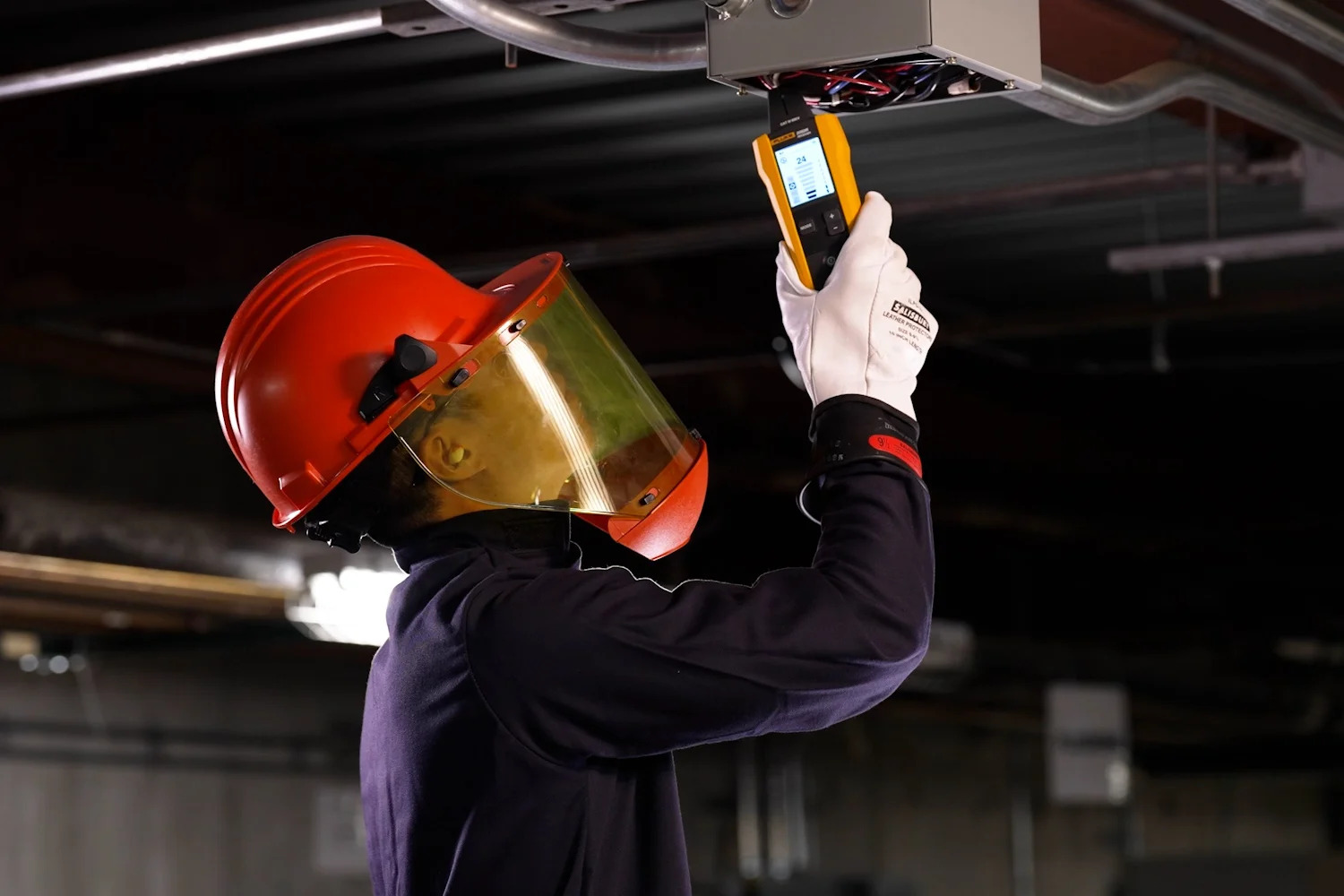
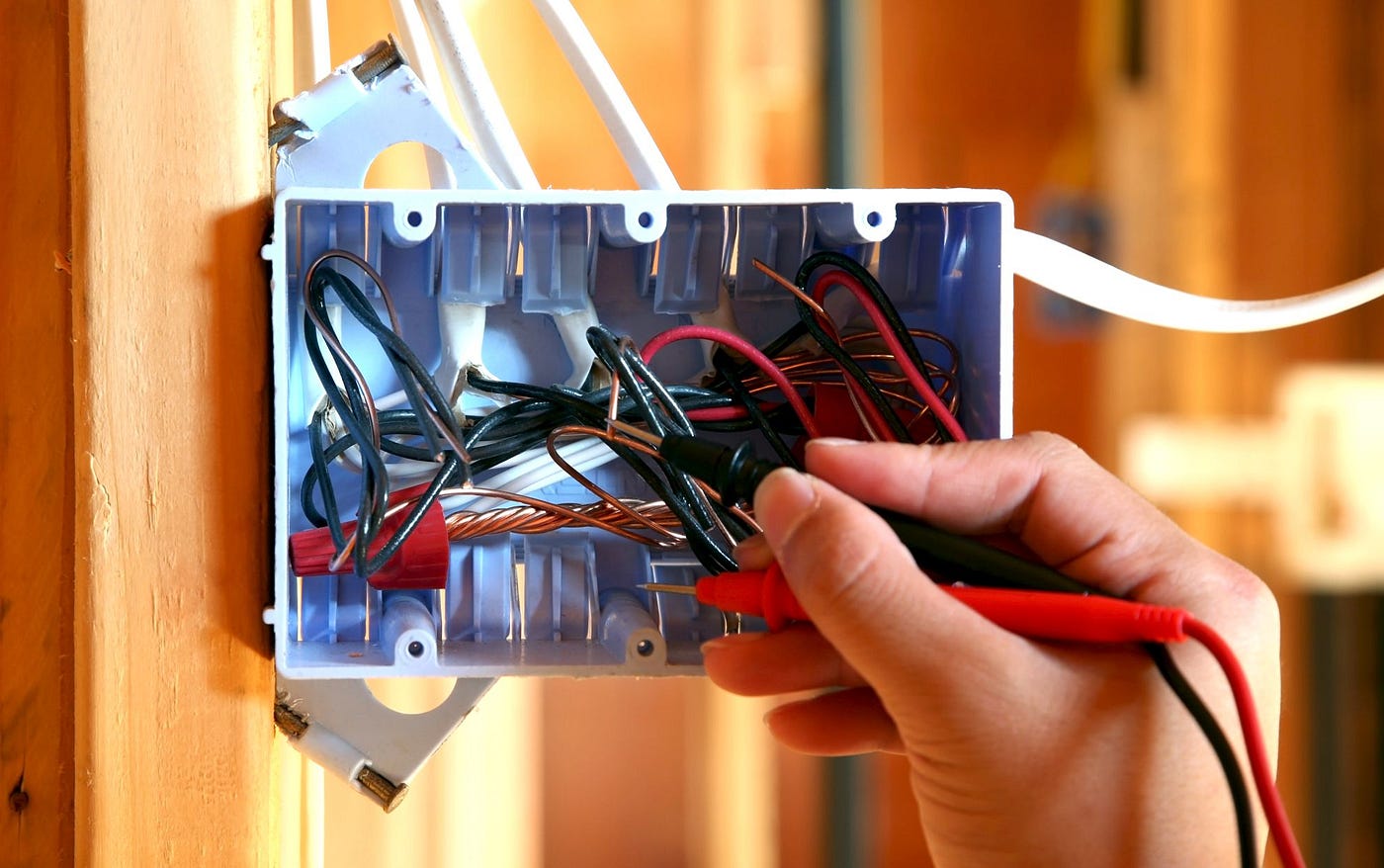
Testing the Grounding System
Testing the grounding system is a crucial step to ensure its effectiveness and safety. Here are the steps to test the grounding system:
- Turn off the power: Before conducting any testing, turn off the power to the circuit or electrical equipment you are working with. This ensures your safety during the testing process.
- Use a multimeter or ground tester: Obtain a multimeter or a ground tester designed specifically to test the grounding system. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions on how to use the device properly.
- Select the appropriate testing method: There are multiple ways to test the grounding system, including the three-point test or the fall-of-potential test. Choose the method that aligns with your equipment and preferences. Consult a professional if you are unsure about the testing method.
- Conduct the testing: Follow the instructions for the selected testing method to perform the test. This may involve connecting the test device to the grounding system and measuring the resistance or voltage levels.
- Interpret the test results: Compare the measured values to the acceptable limits defined in electrical codes and standards. If the measured values fall within the acceptable range, it indicates that the grounding system is functioning properly. However, if the values are outside the acceptable range, further investigation or adjustment may be necessary.
- Maintain records: Document the test results and keep them in your records for future reference. This will help you track the history of the grounding system and monitor any changes or improvements over time.
Regular testing of the grounding system is recommended to ensure its continued effectiveness. It can help detect any faults or deficiencies in the system and allow for prompt corrective actions. If you are unsure about the testing process or need assistance, it is best to consult a qualified electrician or an electrical engineer who can provide specialized knowledge and equipment for comprehensive testing.
Remember, proper testing of the grounding system is essential for maintaining electrical safety and system performance. Don’t skip this crucial step in your electrical maintenance routine.
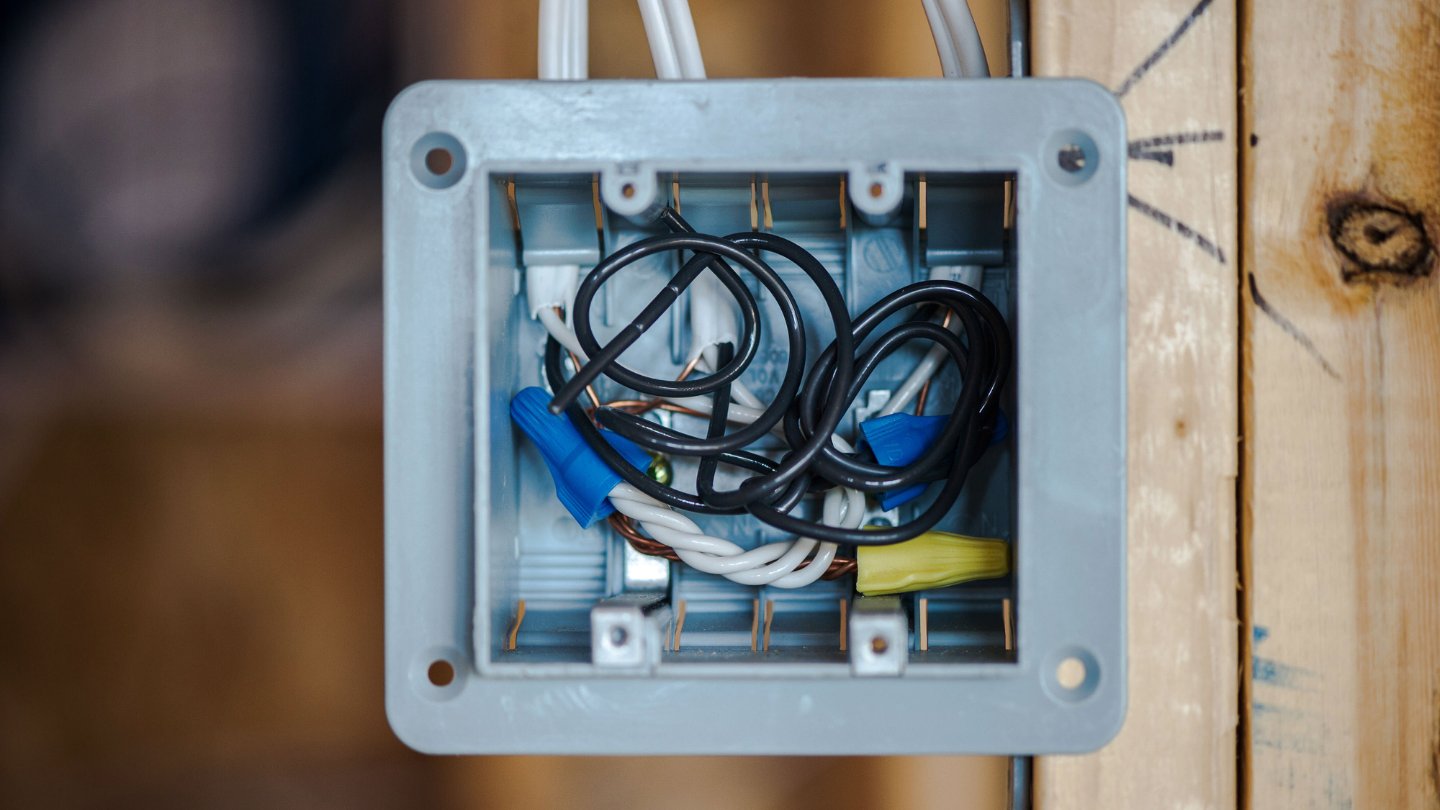
Troubleshooting Grounding Issues
While grounding electrical wires is crucial for safety and functionality, issues can sometimes arise with the grounding system. If you encounter any problems, it’s important to troubleshoot and address them promptly. Here are some common grounding issues and their possible solutions:
Read more: How To Ground An Electrical Box
1. Inconsistent or high resistance:
If you find that the resistance of the grounding system is too high or inconsistent, it may indicate poor connections or deterioration. Check for loose connections, corrosion, or damaged wires. Clean and tighten connections, replace corroded parts, and repair or replace damaged wires.
2. Excessive voltage on grounding system:
If you detect a voltage on the grounding system, it could be due to a wiring error or a fault in the electrical system. Identify and rectify any wiring mistakes, such as improper connections or reversed polarity. It’s also important to check for faulty appliances or equipment that may be causing the voltage leakage.
3. Inadequate grounding:
If the grounding system fails to provide adequate protection, it may be due to insufficient grounding electrodes or improper installation. Consult an electrician to assess the grounding system and determine if additional grounding rods or electrodes are needed. They can also inspect the installation and make any necessary changes to improve the grounding system.
4. Grounding system overload:
If the grounding system is subjected to excessive electrical load or power surges, it may become overwhelmed and fail to function effectively. Consider redistributing loads across multiple circuits or installing surge protectors to divert excess energy away from the grounding system.
5. Environmental factors:
Environmental factors such as moisture, extreme temperatures, and soil conditions can impact the performance of the grounding system. Ensure that grounding electrodes, rods, and wires are protected from moisture and corrosion. Consider using specialized grounding materials or consulting a professional to address specific environmental challenges.
If you encounter persistent grounding issues or are unsure about troubleshooting the problem yourself, it is always recommended to seek the help of a qualified electrician. They have the expertise and equipment to identify and resolve complex grounding issues safely and effectively.
Remember, maintaining a properly functioning grounding system is essential for electrical safety. Regular inspections, maintenance, and prompt troubleshooting can help ensure that your grounding system is always in optimal condition.
Conclusion
Grounding electrical wires is a critical aspect of electrical system safety and performance. By creating a low-resistance path to the earth, grounding protects against electric shock, stabilizes the electrical system, and prevents damage from power surges. Understanding how to ground electrical wires is essential for anyone involved in electrical work or maintenance.
In this article, we’ve explored the importance of grounding electrical wires and the safety precautions to follow when working with electricity. We’ve discussed the tools and materials needed for grounding, as well as the step-by-step process to ground electrical wires effectively. Additionally, we’ve highlighted the significance of testing the grounding system to ensure its reliability and troubleshooting common grounding issues that may arise.
Remember, safety should always be the top priority when working with electricity. Always turn off the power before starting any electrical work and wear appropriate protective gear. If you are unsure about any aspect of grounding electrical wires or encounter any issues, it’s best to consult a professional electrician for assistance.
Proper grounding of electrical wires not only ensures the safety of individuals and electrical systems but also helps comply with electrical codes and regulations. By following the guidelines outlined in this article and staying up to date with best practices, you can carry out grounding tasks with confidence and maintain a safe and efficient electrical infrastructure.
Continue to expand your knowledge of electrical work and stay informed about updates and advancements in the field. By doing so, you can enhance your skills and contribute to the electrical safety and well-being of your home or workplace.
Frequently Asked Questions about How To Ground Electrical Wires
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.







0 thoughts on “How To Ground Electrical Wires”