Home>Articles>What Is The Minimum Bend Radius For An Electrical Wire Bundle?


Articles
What Is The Minimum Bend Radius For An Electrical Wire Bundle?
Modified: January 19, 2024
Find out the minimum bend radius for electrical wire bundles with our informative articles. Learn how to protect your wiring from damage and ensure proper installation.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
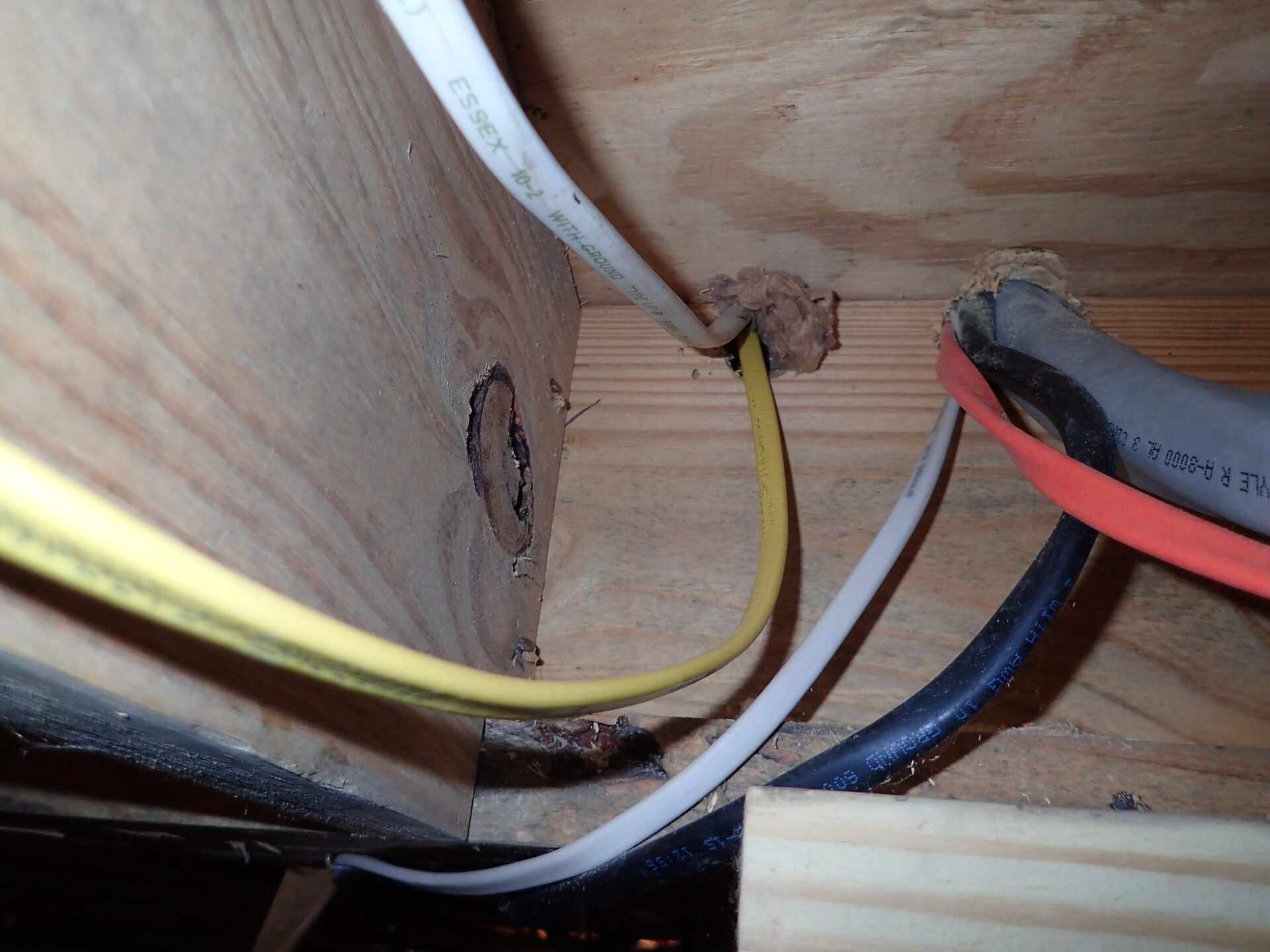
Electrical wire bundles are an essential component of various systems and devices, carrying electricity to power everything from household appliances to industrial machinery. While the performance and safety of electrical wires are crucial, their physical handling and installation are equally important. One critical aspect that must be taken into consideration when working with electrical wire bundles is the minimum bend radius.
The minimum bend radius refers to the smallest radius that an electrical wire can safely bend without causing damage to its insulation or conductive properties. This radius is determined by factors such as the wire size, type of insulation, and the materials used in the wire’s construction. Understanding and adhering to the minimum bend radius is crucial to ensure the longevity and reliability of electrical wire bundles.
In this article, we will explore the definition of the minimum bend radius, its importance, factors affecting it, standard guidelines, methods to calculate it, examples for different wire sizes, and the consequences of not correctly following the minimum bend radius.
By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of the minimum bend radius and its significance when working with electrical wire bundles.
Key Takeaways:
- Adhering to the minimum bend radius guidelines is crucial for maintaining the durability, reliability, and safety of electrical systems. Understanding and respecting these guidelines ensures safe and reliable operation of electrical wire bundles.
- Failure to properly follow the minimum bend radius can result in various consequences, including insulation damage, conductor issues, degraded electrical performance, increased wear and tear, reduced wire lifespan, and safety hazards. Adhering to the minimum bend radius guidelines is essential for the longevity and reliability of electrical wire bundles.
Read more: How To Bend An Electrical Conduit
Definition of Minimum Bend Radius
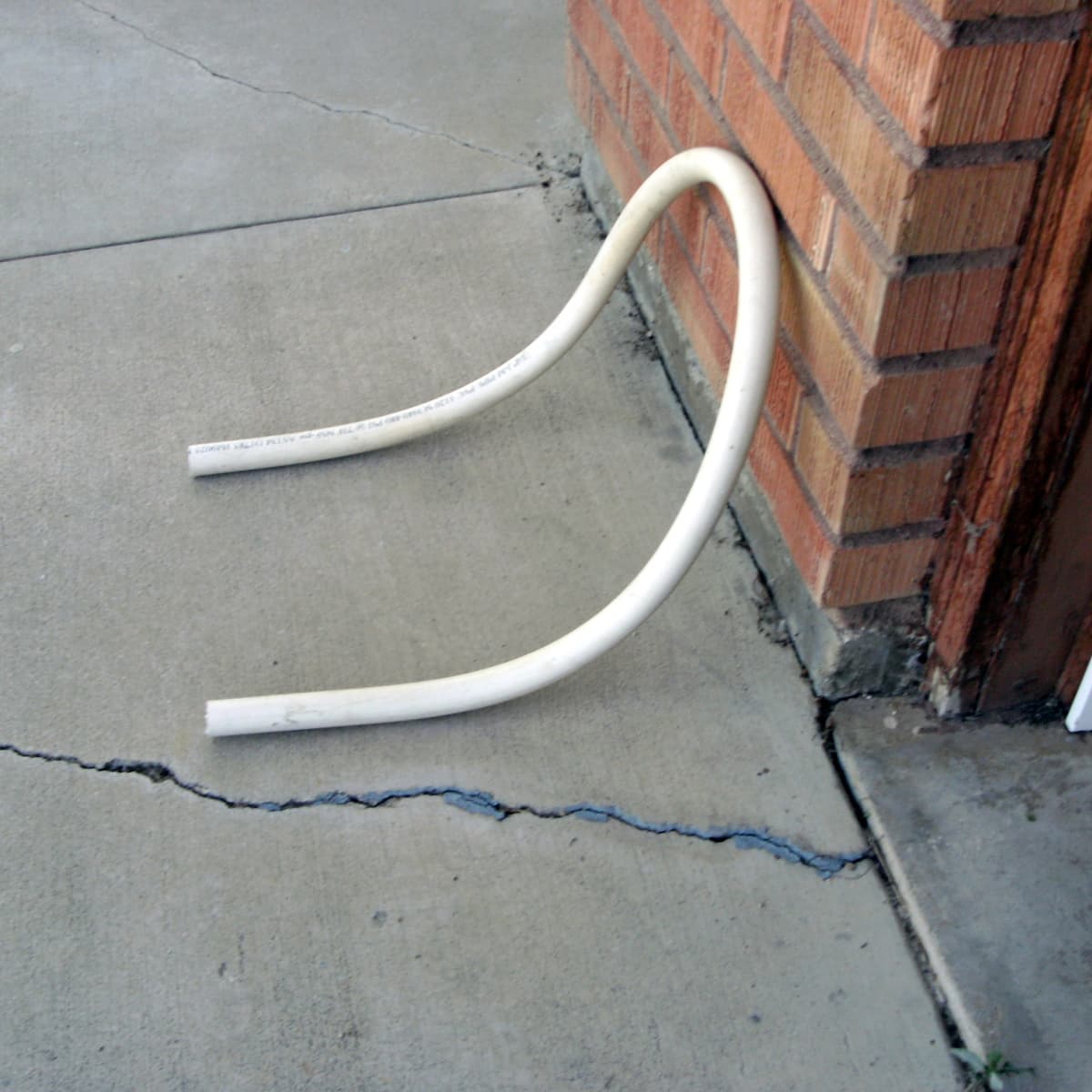
The minimum bend radius, also known as the minimum bending radius or minimum radius of curvature, refers to the minimum radius that an electrical wire can safely be bent without causing damage to its structure or compromising its electrical performance. It is the radius of the imaginary circle that the wire would form if it were bent into a curve.
The concept of the minimum bend radius is crucial because electrical wires are designed to have a specific level of flexibility to fit into various installations and configurations. However, excessive bending or bending beyond the minimum radius can result in significant issues, including damage to the wire’s insulation or conductor, increased electrical resistance, and even the possibility of wire breakage.
The minimum bend radius varies depending on various factors, including the wire size, type of insulation or jacketing, and the material composition of the wire. It is typically specified by the wire manufacturer or governed by industry standards to ensure the safe handling and installation of electrical wire bundles.
It is essential to note that the minimum bend radius is not a fixed value for all wires. Different wire sizes and types have their own unique minimum bend radius requirements. It is crucial to consult the manufacturer’s documentation or applicable standards to determine the specific minimum bend radius for a particular wire.
Overall, the minimum bend radius defines the limits within which an electrical wire can be bent without compromising its structural integrity and electrical performance. Adhering to the minimum bend radius guidelines is essential to ensure safe and reliable operation of electrical wire bundles.
Importance of Minimum Bend Radius for Electrical Wire Bundles
The minimum bend radius plays a crucial role in maintaining the performance, durability, and safety of electrical wire bundles. Understanding and adhering to the minimum bend radius guidelines is essential for the following reasons:
- Preserves Insulation Integrity: Electrical wires are typically insulated to protect the conductors and prevent electrical leakage or short circuits. Bending the wire beyond its minimum bend radius can strain the insulation, leading to cracks, pinholes, or even complete failure of the insulation. This damage can result in electrical faults, safety hazards, and decreased wire lifespan.
- Prevents Signal Interference: In applications where electrical wires carry signals, such as data transmission or communication systems, maintaining the integrity of the signal is critical. Excessive bending can cause signal degradation, cross-talk, or electromagnetic interference, affecting the accuracy and reliability of the transmitted data.
- Avoids Conductor Damage: The conductors inside electrical wires are responsible for carrying the current. Excessive bending can strain the conductors, causing stretching, microcracks, or even breakage. This can result in increased electrical resistance, voltage drop, and ultimately lead to system malfunctions or failures.
- Ensures Proper Installation: Adhering to the minimum bend radius is vital during the installation process. It ensures that wires are properly routed, secured, and bent without exceeding their bending limits. Improper installation can cause stress on the wire bundle, increasing the risk of mechanical damage, abrasion, or accidental contact with other conductive elements.
- Guarantees Longevity and Reliability: Wires that are bent within their specified minimum bend radius are more likely to maintain their electrical properties and structural integrity over time. By following the minimum bend radius guidelines, wire bundles can withstand the rigors of daily use, vibrations, temperature changes, and other environmental factors, ensuring long-term reliability and reducing the need for frequent replacements.
Adhering to the minimum bend radius is, therefore, critical for maintaining the overall performance, safety, and lifespan of electrical wire bundles. By understanding and respecting these guidelines, professionals can ensure that electrical systems operate optimally with minimal risk of damage or failure.
Factors Affecting the Minimum Bend Radius
The minimum bend radius of an electrical wire is influenced by several factors that determine its flexibility and ability to withstand bending without damage. Understanding these factors is essential when working with wire bundles. The key factors affecting the minimum bend radius are as follows:
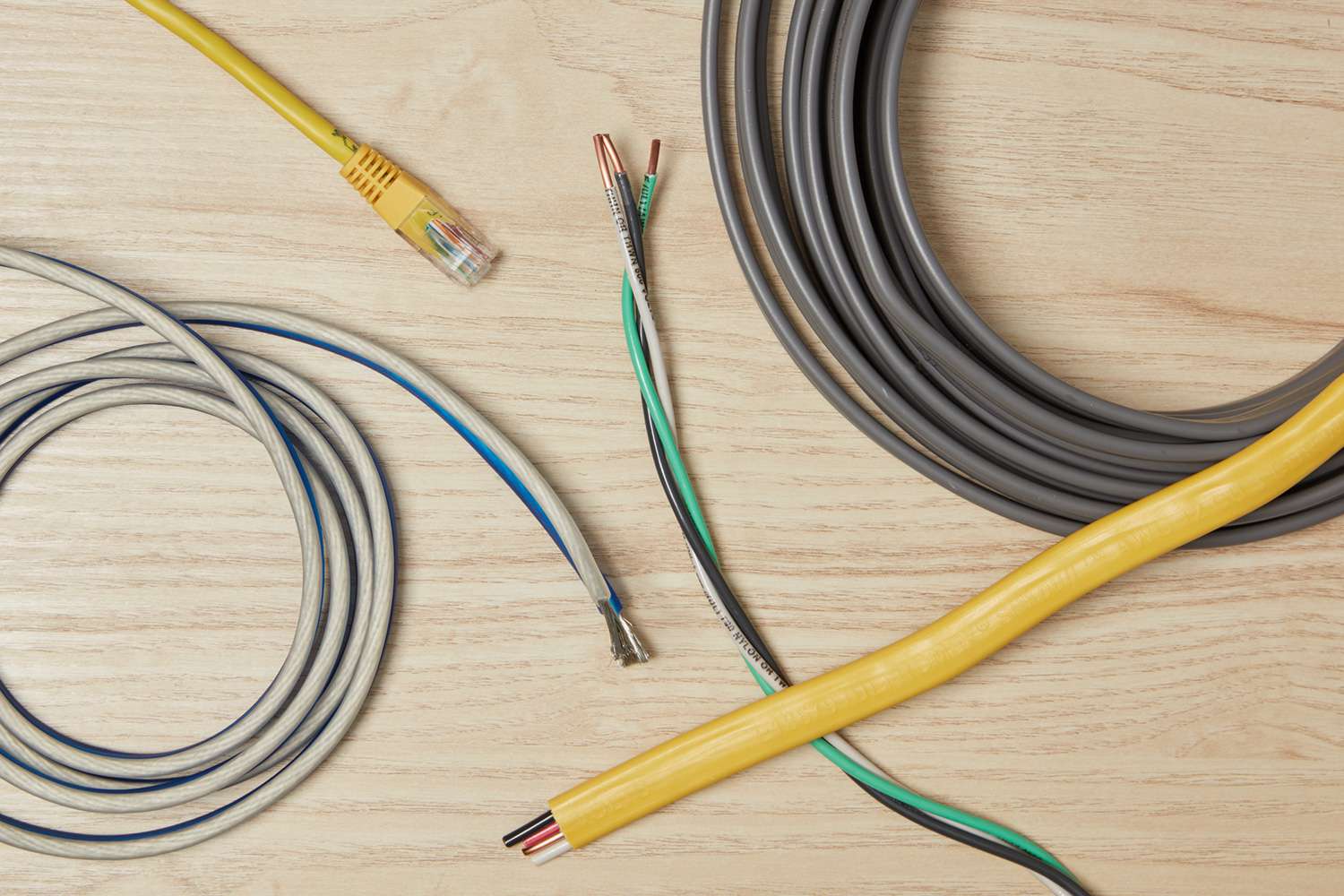
- Wire Size: The size or gauge of the wire plays a significant role in determining the minimum bend radius. Generally, smaller gauge wires have a smaller minimum bend radius compared to larger gauge wires. This is because smaller wires have less material to withstand the bending stress.
- Insulation Type: Different types of insulation used on electrical wires have different flexibility characteristics. Some insulation materials are more flexible and can tolerate tighter bends, while others are more rigid and require a larger minimum bend radius. The flexibility of the insulation impacts the overall flexibility of the wire bundle.
- Conductor Material: The material used in the conductors can affect the minimum bend radius. For example, copper conductors are more flexible than aluminum conductors, allowing for smaller minimum bend radii.
- Temperature: The temperature at which the wire operates can influence its flexibility and minimum bend radius. Extreme temperatures, whether hot or cold, can cause the wire to become more rigid, reducing its ability to bend. Therefore, it is important to consider the temperature range of the wire when determining the minimum bend radius.
- Wire Construction: The construction of the wire, including the number of conductors and the overall design, can impact the minimum bend radius. Multi-conductor wires or cables may have specific bending requirements to maintain the integrity of each individual conductor within the bundle.
- Wire Flexibility: The inherent flexibility of the wire itself is also a factor in determining the minimum bend radius. Some wires are designed to be more flexible, allowing for tighter bends, while others are stiffer and require larger bend radii to prevent damage.
It is important to consider all these factors collectively when determining the appropriate minimum bend radius for a specific wire bundle. Manufacturers and industry standards often provide guidelines and specifications based on these factors to ensure the safe and proper handling of electrical wire bundles.
Standard Guidelines for Minimum Bend Radius
Standard guidelines for the minimum bend radius of electrical wire bundles are established by various industry organizations and manufacturers to ensure safe and reliable operation. These guidelines provide a reference for professionals working with electrical wires. While specific guidelines may vary depending on the application and wire type, the following are common practices:
- National Electrical Code (NEC): The NEC, published by the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), is one of the most widely adopted electrical codes. It provides guidelines for electrical installations, including recommendations for the minimum bend radius of wires. The NEC specifies the minimum bend radius for different wire sizes and types based on safety and performance considerations.
- Wire Manufacturer’s Documentation: Wire manufacturers generally provide technical documentation that includes specific guidelines for minimum bend radius. This documentation is based on extensive testing and evaluation of their products. It is essential to consult the manufacturer’s documentation to ensure that the wire bundle is handled and installed correctly.
- Industry Standards: Various industry standards organizations, such as the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) and the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), define minimum bend radius requirements for specific applications. These standards are designed to ensure compatibility, safety, and reliability across different systems and installations.
- Equipment Manufacturer Specifications: Equipment manufacturers often provide minimum bend radius requirements for the wires that connect to their specific devices. These specifications are critical to ensure proper functioning and longevity of the equipment. It is important to follow these guidelines when installing and routing wires within the equipment.
When working with wire bundles, it is crucial to consult the relevant guidelines and standards to determine the appropriate minimum bend radius for a specific wire size, type, and application. Failure to adhere to these guidelines can result in damaged wires, compromised performance, and potential safety hazards.
Additionally, it is essential to understand that the minimum bend radius is just one of the considerations for safe wire installation. Other factors, such as maximum pull tension, proper support, and protection against environmental hazards, should be taken into account to ensure a robust and reliable electrical system.
The minimum bend radius for an electrical wire bundle is typically 10 times the outside diameter of the largest wire in the bundle. This helps prevent damage to the wires and ensures proper electrical performance.
Read more: What Is 4 Wire Electrical Wire
Calculating the Minimum Bend Radius
Calculating the minimum bend radius for an electrical wire involves considering various factors, such as wire size, insulation type, and the specific guidelines provided by manufacturers or industry standards. While specific calculations may vary depending on the wire type and application, the following general steps can be followed:
- Refer to Manufacturer’s Documentation: Start by consulting the manufacturer’s documentation for the wire in question. The manufacturer may provide specific guidelines or a table that correlates the wire size and insulation type with the corresponding minimum bend radius.
- Consider Specific Requirements: Take into account any specific requirements or limitations mentioned in the documentation. These could include special instructions for high-temperature environments, tight installations, or specific wire constructions.
- Determine Wire Size: Identify the gauge or size of the wire. This information is typically specified in the wire markings or can be measured using a wire gauge tool.
- Identify Insulation Type: Determine the type of insulation or jacketing used on the wire. Common insulation types include PVC, XLPE, rubber, or Teflon. Refer to the manufacturer’s documentation to ensure accuracy.
- Apply Guidelines or Standards: Use the manufacturer’s provided guidelines or industry standards to find the recommended minimum bend radius for the specific wire size and insulation type. These guidelines are designed to ensure the safe and proper handling of the wire bundle.
- Consider Additional Factors: Keep in mind any additional factors that may influence the minimum bend radius, such as temperature requirements, the flexibility of the wire, and the specific installation conditions.
- Verify with Manufacturers or Experts: If there are any uncertainties or unique situations, it is advisable to reach out to the wire manufacturer or consult with experts in the field. They can provide additional guidance and clarifications based on their expertise and experience.
Calculating the minimum bend radius is essential to ensure that the wire bundle is handled and installed correctly, reducing the risk of damage, performance issues, and safety hazards. By following these steps and considering the relevant guidelines and standards, professionals can determine the appropriate minimum bend radius for a specific wire, ensuring a reliable and long-lasting electrical system.
Examples of Minimum Bend Radius for Different Wire Sizes
The minimum bend radius for electrical wires varies depending on the wire size and insulation type. Here are some examples of minimum bend radius guidelines for different wire sizes:
- 14 Gauge Wire: For a 14 gauge wire with PVC insulation, the minimum bend radius may be around 3 times the diameter of the wire. So, if the wire diameter is approximately 0.067 inches, the minimum bend radius would be around 0.201 inches.
- 10 Gauge Wire: With a larger wire size like 10 gauge, the minimum bend radius might be greater. For instance, with a PVC insulated 10 gauge wire that has a diameter of about 0.101 inches, the minimum bend radius could be around 6 times the wire diameter, resulting in a minimum bend radius of approximately 0.606 inches.
- 6 Gauge Wire: Moving to even larger wire sizes like 6 gauge, the minimum bend radius may increase further. For a 6 gauge wire with PVC insulation and a diameter of about 0.162 inches, the minimum bend radius could be around 10 times the wire diameter, resulting in a minimum bend radius of approximately 1.62 inches.
- 2 Gauge Wire: As the wire size increases, the minimum bend radius tends to increase as well. For example, a 2 gauge wire with PVC insulation and a diameter of around 0.258 inches might require a minimum bend radius of around 15 times the wire diameter, giving an approximate minimum bend radius of 3.87 inches.
It is important to note that these examples are general guidelines and actual minimum bend radius requirements may vary depending on the specific wire manufacturer, insulation type, and industry standards. Always consult the manufacturer’s documentation or applicable guidelines to determine the precise minimum bend radius for a given wire size and insulation type.
By following the appropriate minimum bend radius guidelines, professionals can ensure the safe handling and installation of electrical wire bundles, promoting reliability, performance, and longevity.
Consequences of Not Properly Following the Minimum Bend Radius
Failure to adhere to the minimum bend radius guidelines when handling electrical wire bundles can have several negative consequences, ranging from immediate damage to long-term performance issues. Here are some potential consequences of not properly following the minimum bend radius:
- Insulation Damage: Bending the wire beyond its minimum bend radius can cause stress on the insulation, leading to cracks, cuts, or punctures. This damage compromises the insulation’s ability to protect the conductor, increasing the risk of short circuits, electrical leakage, and potential hazards.
- Conductor Damage: Excessive bending can strain the conductors, resulting in stretching, deformation, or even breakage. Damaged conductors lead to increased electrical resistance, voltage drop, and potential system malfunctions or failures.
- Electrical Performance Degradation: Bending the wire beyond the minimum bend radius can alter its electrical characteristics. It can cause impedance variations, signal degradation, or electromagnetic interference, impacting the overall performance and reliability of electrical circuits.
- Increased Wear and Tear: When wires are subjected to excessive bending or tight bends, they may experience increased friction, rubbing against other components, or abrasion against rough surfaces. This can lead to insulation wear, conductor exposure, and potential short circuits or ground faults.
- Reduced Wire Lifespan: Continuous bending of wires beyond their minimum bend radius can shorten their overall lifespan. The repeated stress and strain on the wire can weaken the materials, making them more susceptible to failure over time. This increases the likelihood of premature wire replacement and maintenance costs.
- Safety Hazards: Improperly bent wires pose a safety risk, as compromised insulation or conductors can increase the chance of electrical shocks, fires, or other electrical accidents. These hazards can harm individuals and cause damage to equipment, property, and infrastructure.
It is crucial to understand that the consequences of not following the minimum bend radius may not be immediately apparent. The damage caused by excessive bending can accumulate over time and result in unexpected failures or performance issues.
By strictly adhering to the minimum bend radius guidelines, professionals ensure the integrity and reliability of electrical wire bundles. Proper handling and installation can prevent damage, maintain electrical performance, and contribute to the overall safety and longevity of electrical systems.
Conclusion
The minimum bend radius is a critical factor to consider when working with electrical wire bundles. It defines the smallest radius that an electrical wire can safely bend without causing damage to its insulation, conductors, or overall performance. Adhering to the minimum bend radius guidelines is crucial for maintaining the durability, reliability, and safety of electrical systems.
By understanding the factors that influence the minimum bend radius, such as wire size, insulation type, and specific requirements from manufacturers or industry standards, professionals can accurately determine the appropriate minimum bend radius for a given wire bundle.
Failure to properly follow the minimum bend radius can result in various consequences, including insulation damage, conductor issues, degraded electrical performance, increased wear and tear, reduced wire lifespan, and safety hazards. These consequences can lead to system malfunctions, failures, and potential dangers to personnel and equipment.
To ensure the proper handling and installation of electrical wire bundles, it is essential to consult the manufacturer’s documentation, industry guidelines, and applicable standards. Carefully calculating the minimum bend radius and implementing the necessary precautions will contribute to the longevity and reliability of electrical systems.
Remember, the minimum bend radius is just one aspect of safe wire handling. It is crucial to consider other factors such as maximum pull tension, proper support, and protection against environmental hazards to ensure a robust and reliable electrical system.
By understanding and following the minimum bend radius guidelines, professionals can ensure the proper care and longevity of electrical wire bundles, promoting safety, performance, and overall efficiency in various applications and industries.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is The Minimum Bend Radius For An Electrical Wire Bundle?
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.












0 thoughts on “What Is The Minimum Bend Radius For An Electrical Wire Bundle?”