

Articles
What Type Of Pump Is A Typical Water Pump?
Modified: October 20, 2024
Find informative articles about different types of water pumps, including centrifugal, submersible, and booster pumps. Learn about the functions and uses of each pump to help you choose the right one for your needs.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Water pumps are essential devices used to move water from one location to another. They are commonly found in various applications, including residential, commercial, and industrial settings. Whether it’s for irrigation, household water supply, or dewatering purposes, a water pump plays a crucial role in ensuring the smooth flow and distribution of water.
In this article, we will explore the different types of water pumps commonly used today. Understanding the different pump types can aid in selecting the appropriate pump for a specific application, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency.
From centrifugal pumps to positive displacement pumps, submersible pumps, and jet pumps, each type has its own unique features and applications. By exploring their characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages, you will gain insight into choosing the most suitable pump for your water pumping needs. So, let’s dive into the world of water pumps and discover their fascinating functionalities.
Key Takeaways:
- Centrifugal pumps are ideal for high flow rate applications like water distribution and irrigation, while positive displacement pumps excel at maintaining a steady flow rate, making them perfect for pumping viscous or thick liquids.
- Submersible pumps are efficient, quiet, and capable of handling high pressures, making them an ideal choice for pumping water from wells or underground sources. Jet pumps provide a cost-effective solution for residential water supply needs from shallow water sources or wells.
Overview of Water Pumps
Water pumps are mechanical devices designed to move water from one location to another. They are primarily powered by electricity, fuel, or even manual operation. Water pumps can be categorized into different types based on their working principles and applications.
The most common types of water pumps include centrifugal pumps, positive displacement pumps, submersible pumps, and jet pumps. Each type has its own unique features and benefits, making them suitable for specific water pumping scenarios.
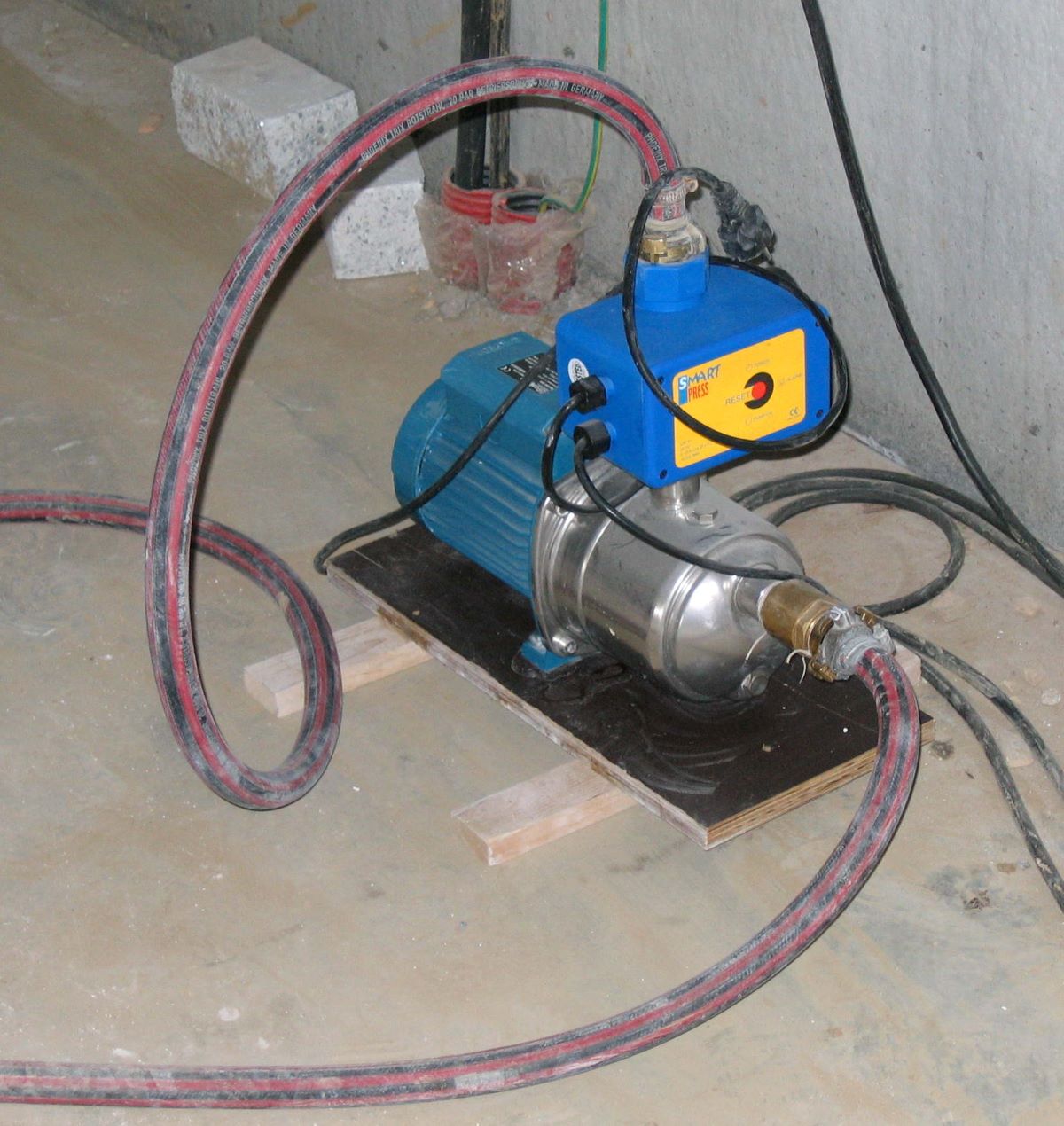
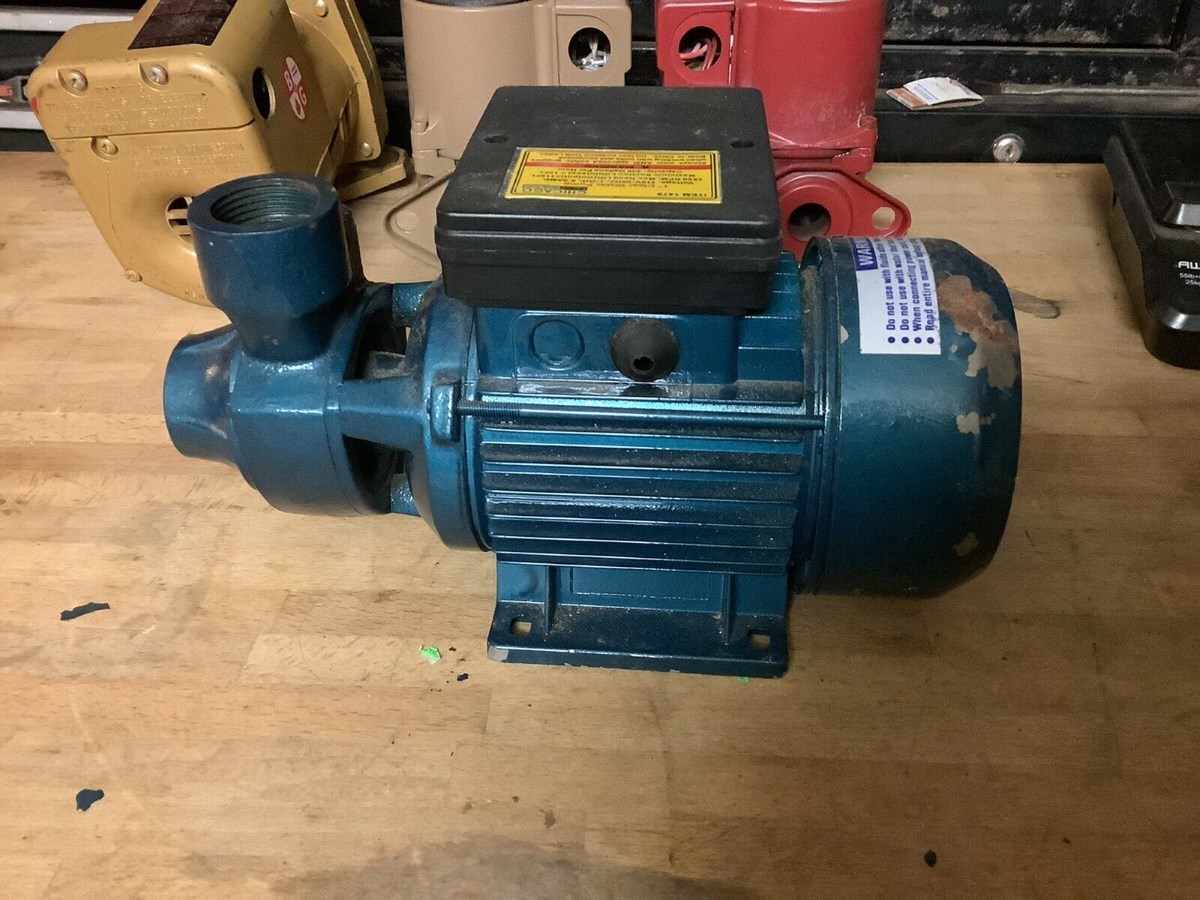
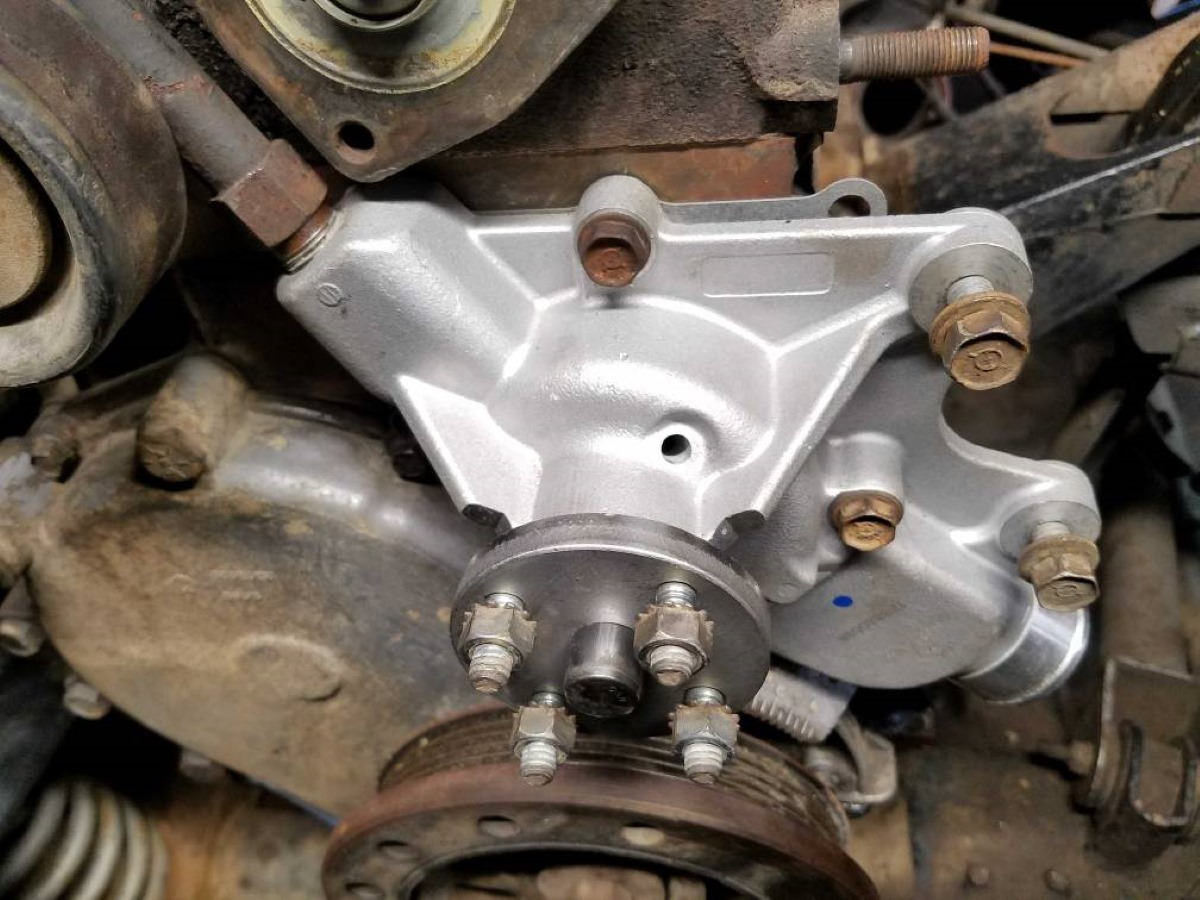
Centrifugal pumps are widely used in varied industries and applications. They work by converting rotational energy into kinetic energy, which is used to move the water. These pumps are known for their high flow rates and low-pressure capabilities. The impeller, which rotates within the pump, generates centrifugal force that propels the water outwards, creating suction. Centrifugal pumps are efficient, reliable, and easy to maintain, making them a popular choice for water distribution systems, irrigation, and HVAC systems.
On the other hand, positive displacement pumps operate differently. Instead of creating centrifugal force, these pumps use mechanical components to trap and transport water from the inlet to the outlet. Positive displacement pumps are suitable for pumping viscous liquids or when a steady flow rate is required. They are commonly used for applications such as pumping sewage, oil, or other thick fluids.
Submersible pumps are designed to be fully submerged in water and are often used for pumping water from wells or underground sources. These pumps are hermetically sealed to prevent water from entering the motor, ensuring safe and reliable operation. Submersible pumps are efficient and able to deliver water at high pressures, making them ideal for residential, commercial, and agricultural applications.
Lastly, jet pumps utilize a combination of centrifugal force and suction to move water. They are typically installed above ground and work by creating a vacuum that draws water through a pipe. Jet pumps are commonly used in residential applications, such as supplying water to households from wells or shallow water sources. They are easy to install and maintain, making them a cost-effective option for water pumping in domestic settings.
Understanding the different types of water pumps provides insight into their working principles and applications. This knowledge helps in selecting the most suitable pump for specific water pumping needs, ensuring efficient and reliable water transfer. In the following sections, we will explore each type of water pump in more detail to gain a deeper understanding of their functionalities and features.
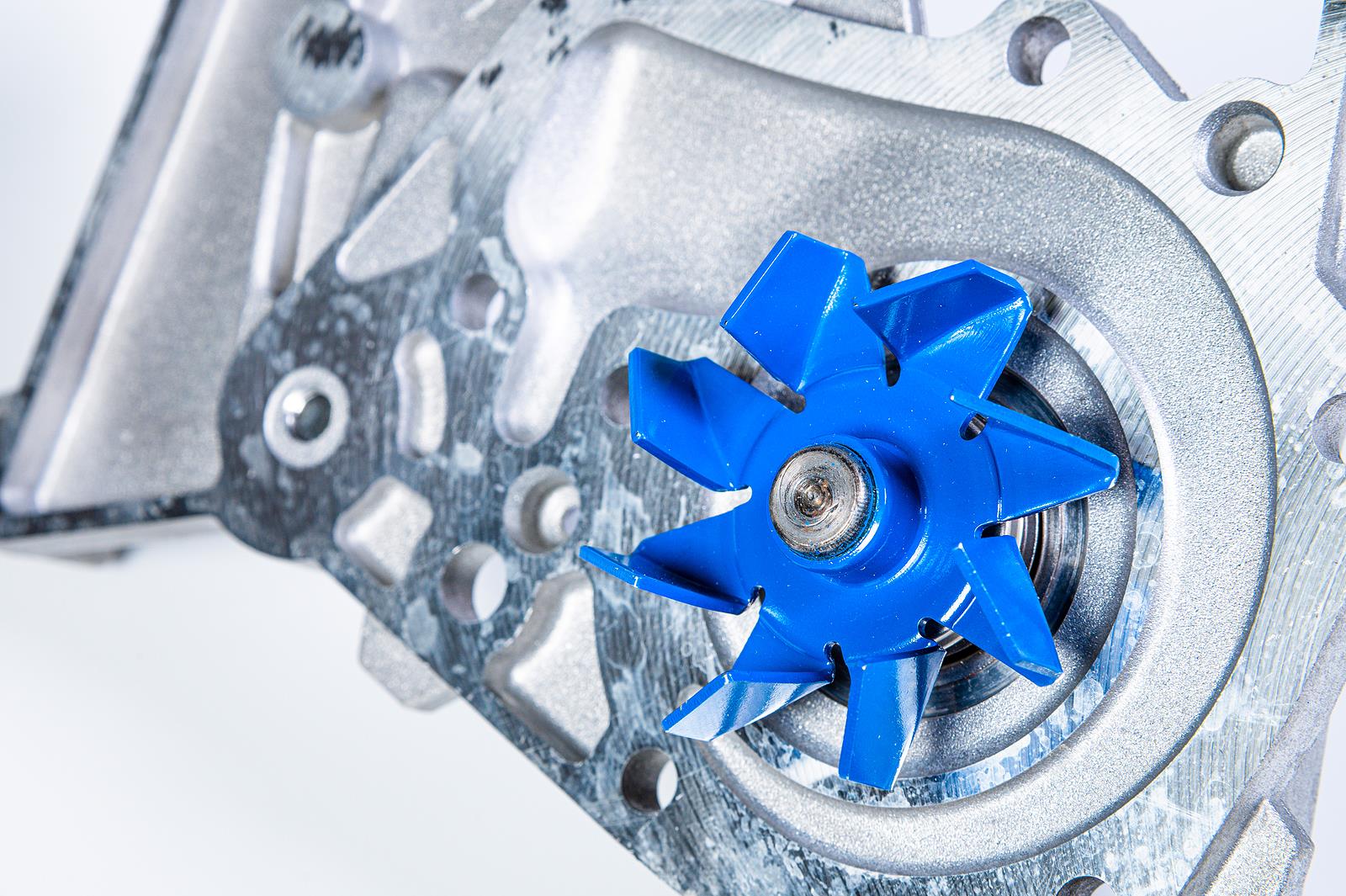
Centrifugal Water Pumps
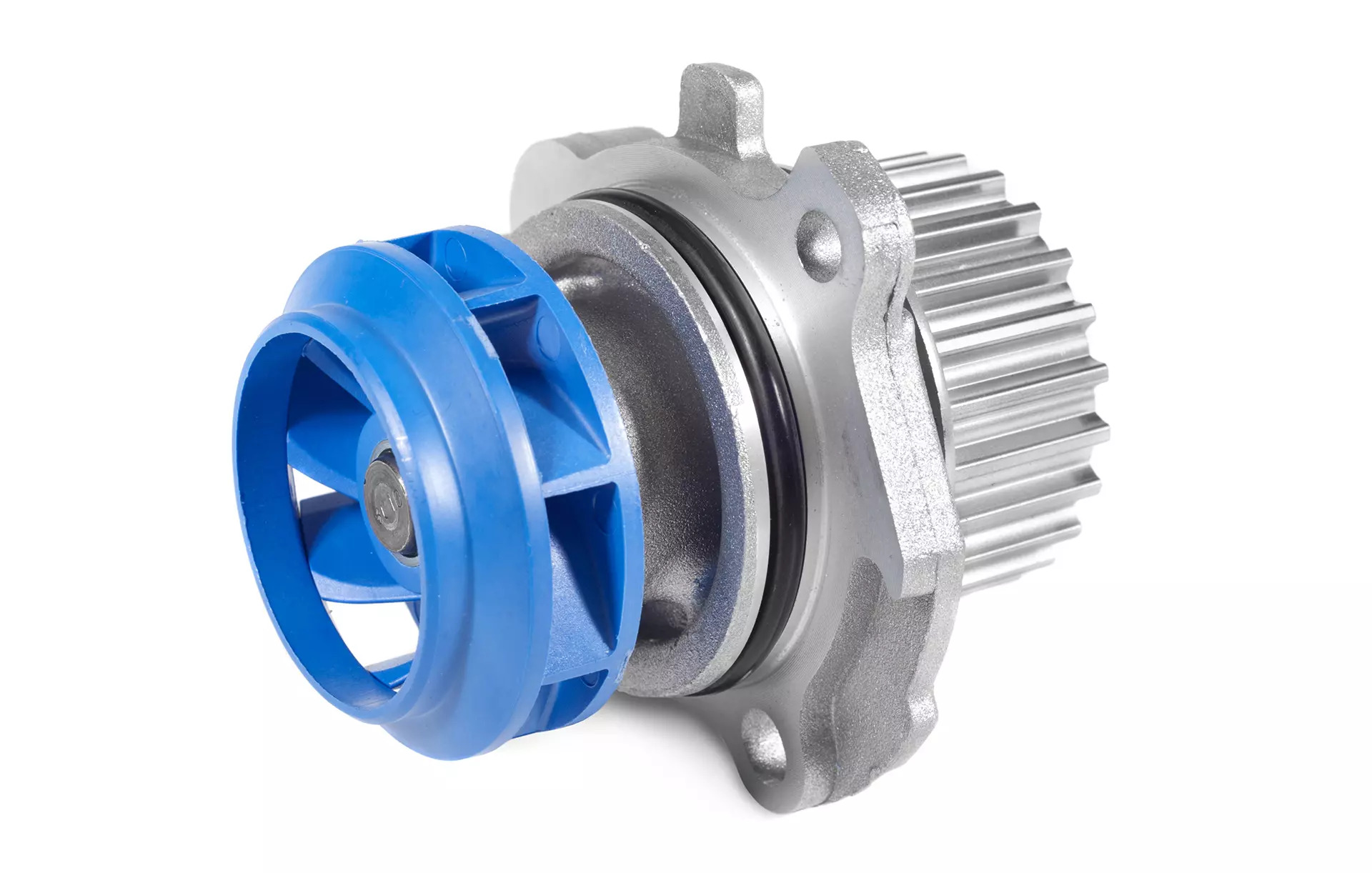
Centrifugal water pumps are one of the most common types of pumps used for water transfer due to their efficiency, simplicity, and wide range of applications. They work on the principle of converting rotational energy into kinetic energy to move water from one location to another.
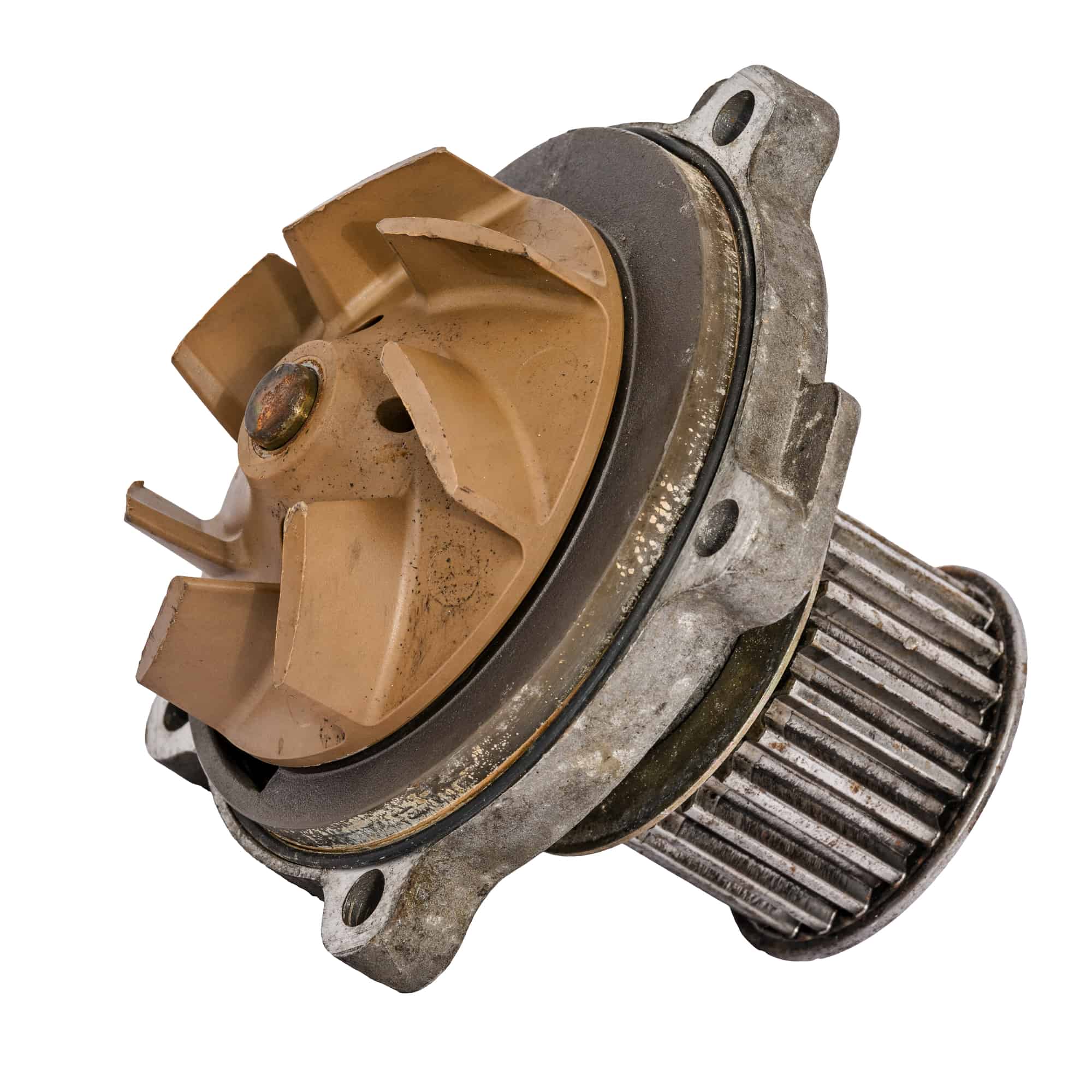
The main component of a centrifugal pump is the impeller, which is a rotating disk with curved blades. When the pump is activated, the impeller spins rapidly, creating centrifugal force. This force pushes the water outward from the center of the impeller, creating a low-pressure area near the inlet. As a result, water is drawn into the pump through the inlet and forced out through the outlet.
Centrifugal pumps are known for their high flow rates and relatively low pressure capabilities. They are commonly used in applications that require the transfer of large volumes of water, such as water distribution systems, irrigation, fire suppression, and HVAC systems.
One of the advantages of centrifugal pumps is their simplicity. They have fewer moving parts compared to other types of pumps, making them easier to maintain and repair. Additionally, they are generally more cost-effective and energy-efficient compared to positive displacement pumps, especially when dealing with large volumes of water.
There are different subtypes of centrifugal pumps, including end-suction pumps, split-case pumps, and multi-stage pumps. End-suction pumps are the most common type, with the suction and discharge ports located at opposite ends of the pump. Split-case pumps feature a casing that can be opened to access the impeller, facilitating easier maintenance. Multi-stage pumps consist of multiple impellers stacked together, allowing for higher pressure generation.
While centrifugal pumps have many advantages, they do have some limitations. They are not suitable for pumping viscous fluids or handling abrasive particles, as these can cause damage to the impeller. Additionally, centrifugal pumps may experience cavitation, which is the formation of vapor bubbles due to low pressure, leading to reduced pump efficiency and potential damage.
Overall, centrifugal water pumps are versatile and efficient devices used for various water transfer applications. Their simplicity, high flow rates, and relatively low cost make them a popular choice in both residential and industrial settings. By understanding the working principles and limitations of centrifugal pumps, you can make informed decisions when it comes to choosing the right pump for your specific water pumping needs.
Positive Displacement Water Pumps
Positive displacement water pumps are a type of pump that uses mechanical components to move water by trapping and displacing it from the inlet to the outlet in a continuous flow. Unlike centrifugal pumps, which generate pressure through rotational force, positive displacement pumps create flow by physically pushing or pulling the water through the pump chamber.
One of the key advantages of positive displacement pumps is their ability to maintain a steady flow rate regardless of the pressure or viscosity of the fluid being pumped. This makes them particularly well-suited for applications where a consistent flow is required, such as pumping thick liquids or handling variable backpressures.
Positive displacement pumps come in various designs, including piston pumps, diaphragm pumps, and rotary pumps.
Piston pumps use a reciprocating motion of pistons within cylinder sleeves to create a pumping action. As the piston moves back and forth, it draws water into the cylinder on the suction stroke and then pushes it out during the compression stroke. Piston pumps are commonly used for high-pressure applications, such as in hydraulic systems or where precise control of flow rates is necessary.
Diaphragm pumps utilize a flexible diaphragm that moves back and forth, creating a suction on one side and a pressure on the other. The diaphragm is typically made of rubber or thermoplastic material, and it helps to separate the fluid being pumped from the moving parts of the pump, making it suitable for pumping corrosive or abrasive fluids.
Rotary pumps, on the other hand, rely on rotating mechanisms to displace water. They can be further divided into different types, such as gear pumps, vane pumps, and screw pumps. Gear pumps utilize interlocking gears to trap and move the fluid, while vane pumps use rotating vanes to create the pumping action. Screw pumps have helical screws that rotate to move water through the pump chamber. Rotary pumps are often used for applications involving high-viscosity liquids or where a smooth and continuous flow is required.
Positive displacement pumps have several advantages over centrifugal pumps. They can handle a wide range of viscosities, including thick or viscous liquids. Additionally, they are less prone to cavitation, as they do not rely on high speeds to generate pressure. Positive displacement pumps are also suitable for applications where accurate dosing or control of flow rates is necessary.
However, positive displacement pumps do have some limitations. They can be more expensive compared to centrifugal pumps and may require regular maintenance due to their intricate design and moving parts. The selection of the right positive displacement pump depends on factors such as the type of fluid being pumped, desired flow rate, and level of accuracy needed in control.
Overall, positive displacement water pumps are versatile devices that offer a steady flow rate and the ability to handle a wide range of fluids. With their capability to handle variable pressures and viscosity, they are suitable for applications where consistent flow and precise control are critical.
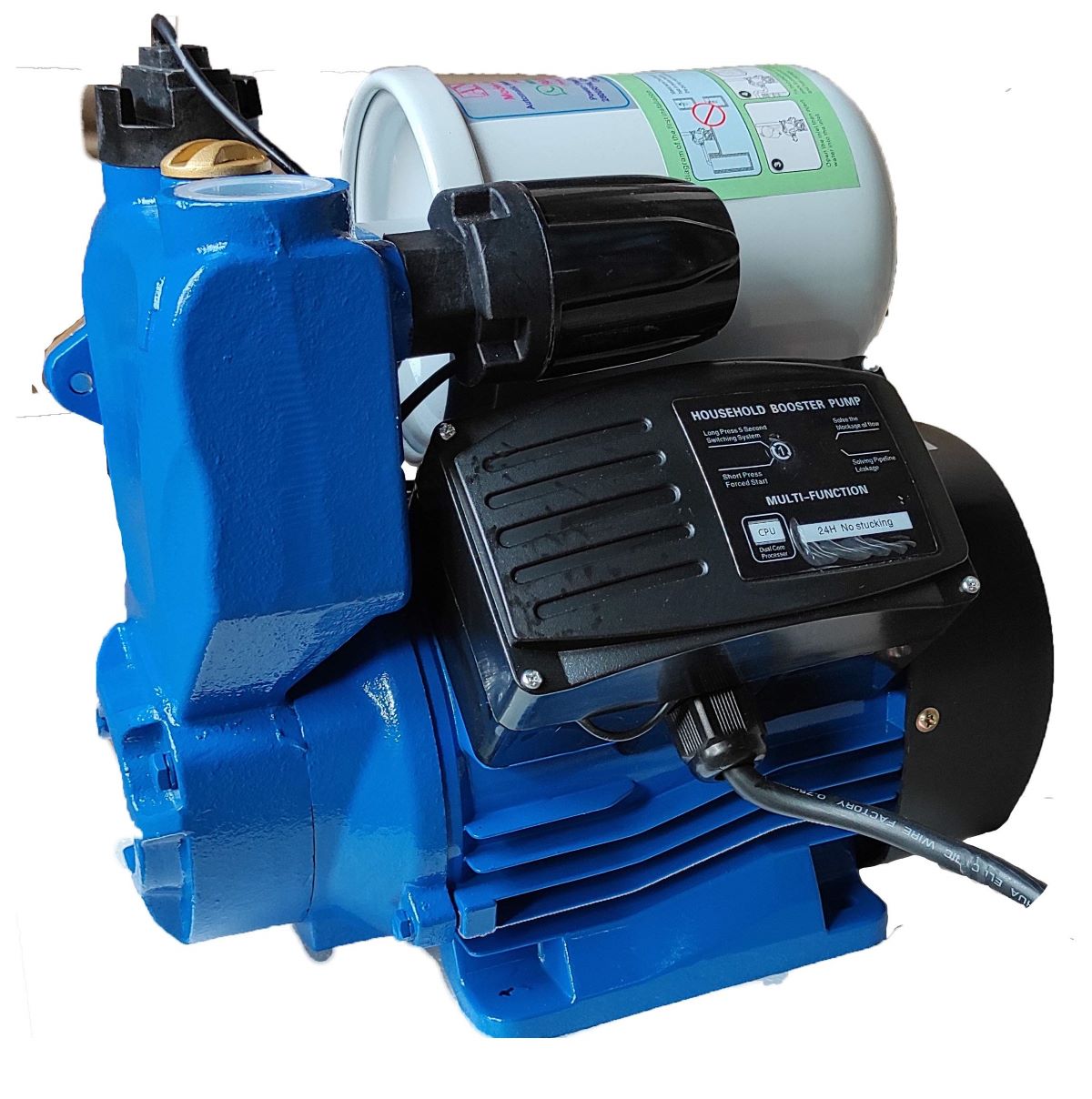
A typical water pump is a centrifugal pump, which uses an impeller to create centrifugal force and move water through the pump. It is commonly used for various applications such as irrigation, water supply, and HVAC systems.
Submersible Water Pumps
Submersible water pumps are a specialized type of pump that is designed to be fully submerged in water. They are commonly used for pumping water from wells, underground sources, or other deep water locations. Submersible pumps are highly efficient and offer several advantages over other types of pumps.
One of the key advantages of submersible pumps is their ability to operate quietly and efficiently. Being submerged in water helps to dampen the noise produced by the pump, making them ideal for residential and commercial applications where noise reduction is important.
Submersible pumps consist of a hermetically sealed motor that is protected from water ingress. The motor is designed to withstand the water pressure and operate reliably even when fully submerged. The motor is coupled with an impeller that creates the pumping action, forcing water into the pump and out through the discharge pipe.
One of the main advantages of submersible pumps is their ability to generate high pressures, making them suitable for pumping water from deep wells or underground sources. The water surrounding the pump provides additional support and cooling for the motor, allowing it to withstand high-pressure pumping applications.
Submersible pumps are available in various sizes and configurations to meet different pumping needs. They can range from small pumps used for residential water supply to larger pumps used for industrial and agricultural applications. Some submersible pumps have additional features, such as built-in sensors to detect water levels or automatic shutoff mechanisms to protect the pump from damage.
One of the key considerations when using a submersible pump is the depth of the water source. The pump should be properly sized and positioned at a depth that allows it to operate efficiently while preventing any damage to the motor or impeller. It is essential to consult the manufacturer’s guidelines and follow proper installation procedures to ensure optimal performance.
In addition to their efficiency and reliability, submersible pumps offer ease of maintenance. Since they are located underwater, they are protected from external elements that may cause damage or require frequent maintenance. However, regular inspection and cleaning of the pump, including the intake screen, is still necessary to prevent clogging and maintain optimal performance.
Overall, submersible water pumps are a reliable and efficient choice for pumping water from wells, underground sources, or other deep water locations. Their ability to operate quietly, generate high pressures, and their ease of maintenance make them ideal for various residential, commercial, and agricultural applications. When selecting a submersible pump, it is crucial to consider factors such as the desired flow rate, the depth of the water source, and the specific requirements of the application at hand.
Read more: What Is A Water Pump
Jet Water Pumps
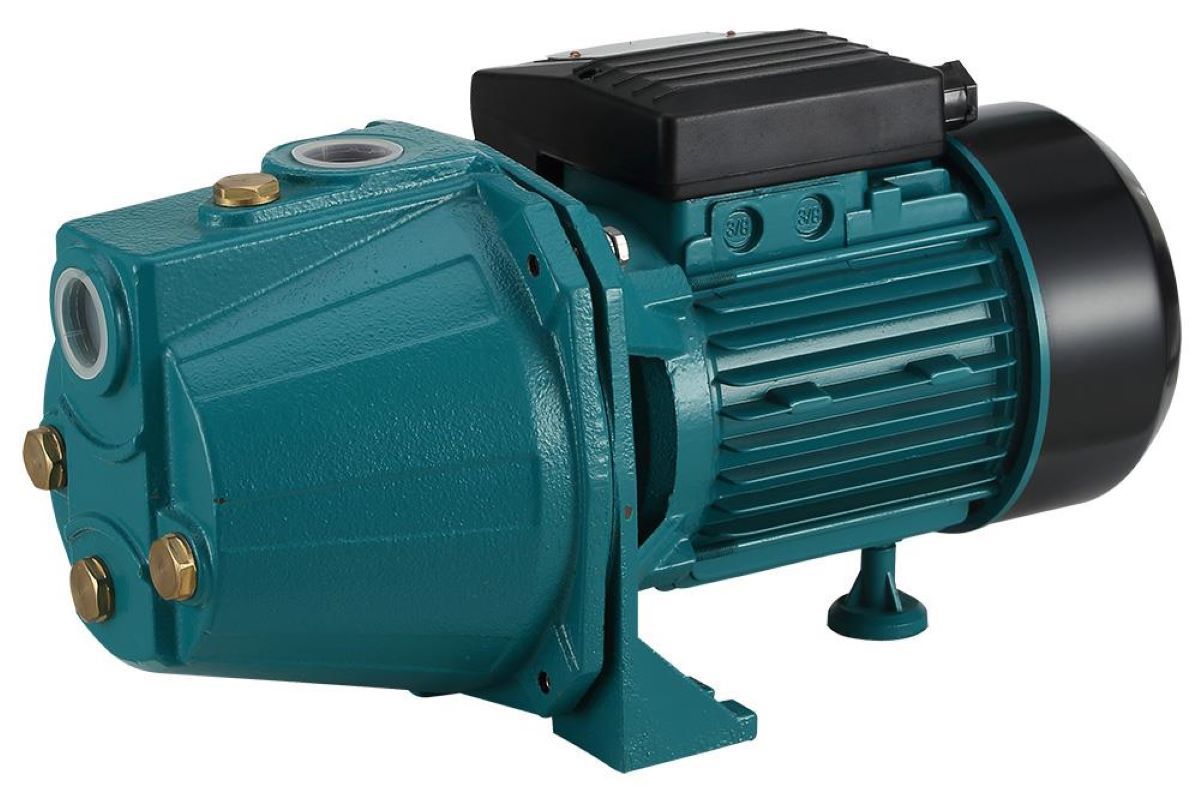
Jet water pumps, also known as ejector pumps or jet pumps, are a type of water pump commonly used for residential water supply from wells or shallow water sources. They utilize a combination of centrifugal force and suction to move water from the source to the destination.
Jet pumps are typically installed above ground and consist of a motor, an impeller, and a jet assembly. The motor provides the rotational energy to drive the impeller, which creates a centrifugal force that propels the water outward. The jet assembly, located above the impeller, generates suction by creating a pressure difference between the inlet and outlet of the pump.
One of the advantages of jet pumps is their simplicity and ease of installation. They do not require a submersible design and can be easily mounted on a stable surface. Jet pumps are commonly used in residential applications where water needs to be drawn from wells or shallow water sources, as they can effectively lift water from depths of up to 25 feet.
Jet pumps operate in a two-stage process. In the first stage, known as the suction stage, the impeller creates centrifugal force that draws water from the well or source and directs it into the jet assembly. In the second stage, known as the pressure stage, the jet assembly increases the velocity of the water and creates suction. This increased velocity and suction allow the pump to lift the water to a higher elevation and deliver it to the desired location.
One important consideration when using a jet pump is the depth of the water source. Jet pumps have limitations in terms of the lifting capacity, and they become less efficient as the depth of the water source increases. Therefore, it is crucial to select a pump that is appropriate for the depth at which the water source is located.
Jet pumps are generally reliable and easy to maintain. They have fewer moving parts compared to other types of pumps, reducing the risk of mechanical failure. However, periodic inspection and maintenance are still necessary to ensure optimal performance.
It is worth noting that jet pumps may experience some limitations. They are not ideal for applications that require high flow rates or where large volumes of water need to be pumped. Additionally, they are not suitable for pumping water from deep wells or sources located at significant depths.
Overall, jet water pumps provide a cost-effective and practical solution for residential water supply needs from shallow water sources or wells. Their simplicity, ease of installation, and reliable performance make them suitable for delivering water to households and other small-scale applications. When selecting a jet pump, it is important to consider the specific requirements of the application, including the depth of the water source and the desired flow rate.
Conclusion
Water pumps are essential devices for transferring water from one location to another, catering to various residential, commercial, and industrial applications. Understanding the different types of water pumps is crucial for selecting the most suitable pump for specific needs, ensuring efficient and reliable water transfer.
In this article, we explored four common types of water pumps: centrifugal pumps, positive displacement pumps, submersible pumps, and jet pumps. Centrifugal pumps are known for their high flow rates and low-pressure capabilities, making them suitable for water distribution systems, irrigation, and HVAC systems. Positive displacement pumps excel at maintaining a steady flow rate, making them ideal for pumping viscous or thick liquids. Submersible pumps are designed to be fully submerged and are efficient, quiet, and capable of handling high pressures. Jet pumps, on the other hand, combine centrifugal force and suction to draw water from shallow sources or wells for residential water supply.
Each type of water pump has its own unique features, benefits, and limitations. Therefore, it is crucial to consider factors such as flow rate requirements, specific pumping applications, and budget considerations when selecting a pump.
Ultimately, the choice of water pump depends on the specific water pumping needs. By understanding the working principles, advantages, and limitations of each type, individuals and businesses can make informed decisions and ensure optimal performance and efficiency in their water pumping operations.
Whether it’s transferring water for irrigation, maintaining household water supply, or pumping out water in industrial settings, selecting the right water pump is crucial. With the right pump, water can be efficiently and reliably moved, ensuring the smooth flow and distribution of this invaluable resource.
Take the time to evaluate your water pumping requirements, consider the available pump options, and make an informed decision. By doing so, you can ensure that your water pumping needs are met efficiently and effectively, meeting the demands of your specific application.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Type Of Pump Is A Typical Water Pump?
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.














0 thoughts on “What Type Of Pump Is A Typical Water Pump?”