

Articles
Who Invented The Electric Motor
Modified: January 6, 2024
Learn about the fascinating history of electric motors with our informative articles. Discover the inventors and their contributions to this groundbreaking technology.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
The invention of the electric motor revolutionized the world, paving the way for countless technological advancements and shaping the modern way of life. Electric motors are used in various applications, from powering appliances and vehicles to driving industrial machinery. But who can be credited with the invention of this remarkable device?
The development of electric motors can be traced back to the early discoveries in electromagnetism that laid the foundation for understanding the principles behind their functioning. This article takes a journey through history to explore the origins of the electric motor and the key figures who contributed to its invention.
Key Takeaways:
- The invention of the electric motor was a result of groundbreaking discoveries in electromagnetism by figures like Ørsted, Ampère, Henry, and Faraday, laying the foundation for the transformative technology that powers our modern world.
- Thomas Davenport’s pioneering work led to the creation of the first practical electric motor, sparking a wave of innovations by inventors like Edison and Tesla, shaping the electrified world we live in today.
Read more: Who Invented The Ac Electric Motor
Early Developments in Electromagnetism
The roots of the electric motor lie in the discoveries made in the field of electromagnetism. In the early 19th century, scientists began experimenting with the relationship between electricity and magnetism, laying the groundwork for the development of electric motors.
One of the key figures in these early developments was Hans Christian Ørsted, a Danish physicist who, in 1820, observed that an electric current flowing through a wire caused a nearby compass needle to move. This accidental discovery demonstrated the connection between electricity and magnetism, and set the stage for further exploration in this field.
Building on Ørsted’s work, André-Marie Ampère, a French physicist and mathematician, formulated Ampère’s Law in 1826, which stated that a current-carrying conductor produces a magnetic field around it. This breakthrough deepened the understanding of the relationship between electricity and magnetism, setting the stage for further advancements in the field.
In the early 1830s, another significant breakthrough came from Joseph Henry, an American physicist. Henry discovered that by winding multiple turns of wire around a soft iron core, he could increase the strength of the magnetic field produced by an electric current. This coil arrangement, known as an electromagnet, became a fundamental component in the development of electric motors.
These early developments in electromagnetism paved the way for the discovery of electromagnetic induction, which played a crucial role in the invention of the electric motor.
Discovery of Electromagnetic Induction
One of the most significant breakthroughs in the path to inventing the electric motor was the discovery of electromagnetic induction. This discovery, made independently by Michael Faraday and Joseph Henry in the early 1830s, laid the foundation for the practical implementation of electric motors.
Michael Faraday, an English scientist, was conducting experiments on electromagnetism when he made a crucial discovery. He observed that when a magnet was moved in and out of a coil of wire, it induced an electric current in the wire. This phenomenon, known as electromagnetic induction, demonstrated the conversion of mechanical energy into electrical energy.
Joseph Henry, an American scientist, made similar discoveries around the same time. He also observed that the movement of a magnet relative to a coil of wire induced an electric current. Henry further explored the concept of self-induction, where a change in the current flowing through a coil induced a voltage in the same coil.
The discovery of electromagnetic induction by Faraday and Henry was a critical step towards harnessing the power of electricity for practical applications. It provided the theoretical basis for the development of electric motors.
The next challenge was to design a practical electric motor that could efficiently convert electrical energy into mechanical energy. This task was accomplished by Thomas Davenport, an American blacksmith and inventor, who is credited with building the first practical electric motor.
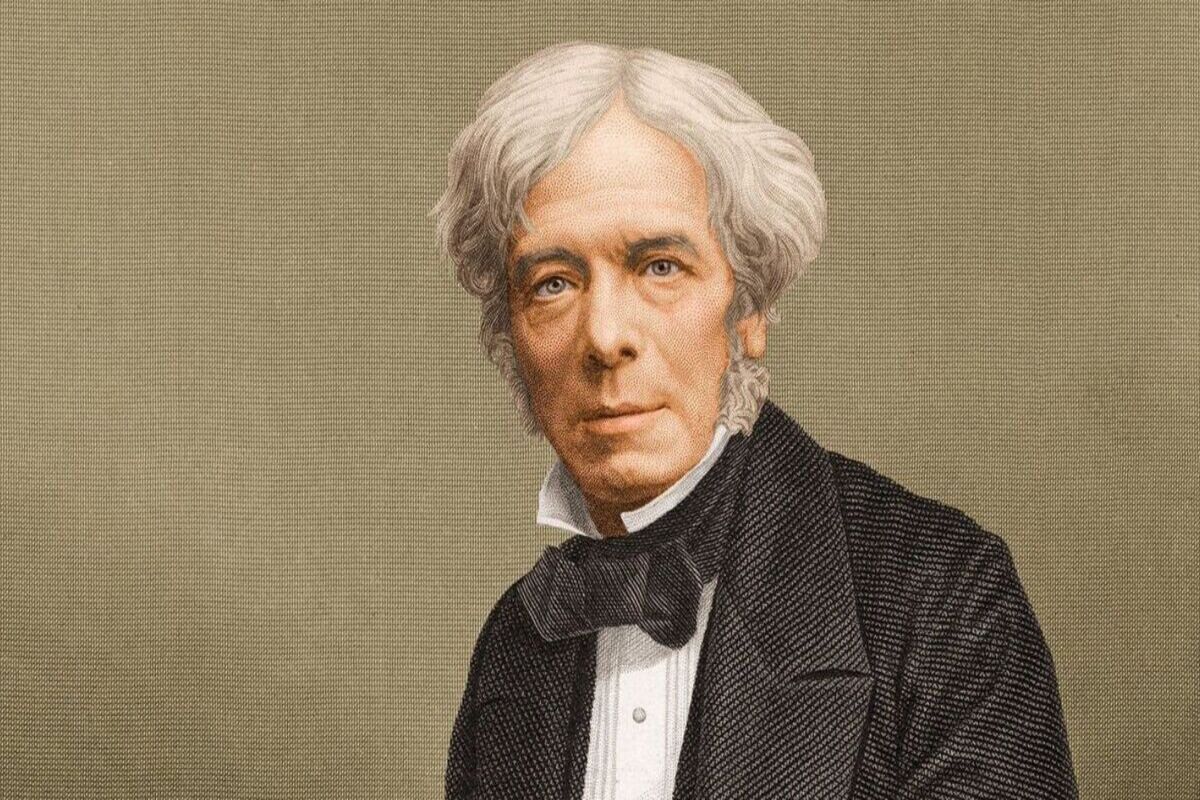
Foundational Work by Michael Faraday
Michael Faraday, often referred to as the “father of electromagnetism,” made significant contributions to the understanding of electric and magnetic phenomena. His work laid the foundation for the development of the electric motor.
In addition to his discovery of electromagnetic induction, Faraday conducted extensive experiments and research on the relationship between electricity and magnetism. He formulated Faraday’s laws of electrolysis, which described the quantitative relationship between the amount of electricity passed through a solution and the amount of chemical reaction occurring.
Faraday also introduced the concept of lines of force, visualizing the existence of invisible lines surrounding magnets and conductors through which the forces of attraction or repulsion acted. This concept helped explain the behavior of magnets and the interaction between electric currents and magnetic fields.
Furthermore, Faraday invented the homopolar generator, a device that produced electrical current through the rotation of a conductive disc in a magnetic field. While the homopolar generator was not a practical electric motor, it demonstrated the principles of magnetic field and rotary motion, laying the groundwork for the development of electric motors.
Faraday’s extensive research and experimentation on electromagnetism provided the essential knowledge and insights that later inventors would build upon to create practical electric motors. His contributions to the understanding of the relationship between electricity and magnetism were fundamental in shaping the field of electrical engineering.
With the foundational work of Faraday and others, the stage was set for inventors like Thomas Davenport to bring the electric motor into practical use and pave the way for further advancements in this revolutionary technology.
The electric motor was invented by Michael Faraday in 1821. He discovered that passing a current through a wire caused it to rotate around a magnet, laying the foundation for the modern electric motor.
Thomas Davenport and the First Practical Electric Motor
In the early 19th century, Thomas Davenport, an American blacksmith and inventor, made significant strides towards the development of the first practical electric motor.
Davenport’s interest in electricity and magnetism led him to experiment with electromagnetism and its potential applications. In 1834, he successfully built a small model electric motor that utilized electromagnetism to produce rotary motion. This marked a significant breakthrough in the history of electric motors.
His motor design consisted of a battery, a commutator, electromagnets, and a rotating armature. The electromagnets generated a magnetic field when an electric current flowed through them, while the commutator provided a unidirectional current flow to the electromagnets, allowing for continuous rotary movement of the armature.
Although Davenport’s electric motor was initially limited in its power and practical applications, it demonstrated the concept of converting electrical energy into mechanical motion. It laid the foundation for further innovations and improvements in electric motor technology.
Despite his groundbreaking achievement, Davenport faced challenges in commercializing his invention. He struggled to attract investors and faced skepticism from the public, who were unfamiliar with the potential applications and benefits of electric motors at that time.
However, Davenport’s work caught the attention of other inventors and engineers, who further refined and improved upon his designs. Building upon Davenport’s foundation, inventors like Thomas Edison and Nikola Tesla would make significant strides in advancing electric motor technology.
Thomas Davenport’s contribution as the inventor of the first practical electric motor cannot be overstated. His innovative design paved the way for the practical implementation of electric motors in various industries, revolutionizing transportation, manufacturing, and countless other fields.
Ultimately, Davenport’s perseverance and groundbreaking invention laid the groundwork for the electrified world we live in today, where electric motors power our machines and devices, making our lives easier and more efficient.
Read more: Who Invented The Electric Lamp
Further Innovations and Advancements
Following Thomas Davenport’s pioneering work in electric motor development, inventors and engineers continued to make significant innovations and advancements in the field. These breakthroughs propelled electric motors into a wide range of practical applications.
One notable figure in the advancement of electric motors was Thomas Edison, who improved upon Davenport’s designs and made crucial contributions to their efficiency and reliability. Edison’s innovations included the development of a more practical and efficient commutator design, as well as advancements in the materials used for the construction of the motor.
Another key figure in electric motor development was Nikola Tesla. Tesla’s contributions were revolutionary and shaped the future of electric motor technology. He pioneered the development of alternating current (AC) motors, which offered numerous advantages over direct current (DC) motors, such as higher efficiency, longer lifespan, and the ability to transmit electricity over longer distances.
Tesla’s invention of the induction motor, which used rotating magnetic fields to generate motion, became widely adopted and formed the basis for modern electric motors. His work on AC power systems and motor design transformed the field of electrical engineering and laid the groundwork for the widespread use of electric motors in various applications.
In the 20th century, electric motors became integral components in transportation, manufacturing, and household appliances. They powered electric trains, automobiles, industrial machinery, and countless household devices, making everyday life more convenient and efficient.
Advancements in motor technology continue to this day, with a focus on increasing efficiency, reducing environmental impact, and exploring new applications. Electric motors have become an essential component in renewable energy systems, such as wind turbines and electric vehicles, further contributing to a more sustainable future.
With ongoing research and development, electric motor technology will continue to evolve, enabling new possibilities in various sectors. From robotics and automation to renewable energy systems and beyond, electric motors remain at the forefront of innovation, driving progress and shaping our modern world.
Contributions by Nikola Tesla
Nikola Tesla, a renowned Serbian-American inventor, electrical engineer, and physicist, made groundbreaking contributions to the field of electric motors and power systems. His inventions and discoveries revolutionized the way electric motors were designed and utilized.
One of Tesla’s most notable contributions was the development of the induction motor, also known as the Tesla coil. This motor utilized alternating current (AC) and rotating magnetic fields to generate motion. Tesla’s design solved many of the limitations of earlier electric motors and became the standard for modern motor technology.
The induction motor offered several advantages over direct current (DC) motors, including higher efficiency, lower maintenance requirements, and the ability to operate over long distances. Tesla’s innovation in AC motors played a pivotal role in the development of electrification systems, powering industries, transportation, and households worldwide.
Tesla’s contributions went beyond motor technology. He played a crucial role in the development of AC power systems, including the design of power distribution networks, transformers, and generators.
Among his numerous patents, Tesla’s inventions also included the Tesla turbine and the Tesla coil. The Tesla turbine was a novel type of turbine that used a series of smooth, closely spaced disks to harness the energy of a fluid or gas flow. The Tesla coil, on the other hand, was a high-voltage resonant transformer that produced high-frequency, high-voltage electricity.
Tesla’s innovations demonstrated his deep understanding of electrical engineering principles and his visionary approach to power systems. His inventions laid the foundation for the modern electrical grid and formed the basis for many of the technologies we rely on today.
Despite his significant contributions, Tesla’s work often went underappreciated during his lifetime. Nevertheless, his ideas and inventions continue to inspire researchers and engineers, fueling advancements in electric motor design, power systems, and renewable energy.
Nikola Tesla’s relentless pursuit of knowledge and his indelible contributions to electric motor technology and power systems have solidified his place as one of the greatest inventors in history. His work continues to influence and shape our modern world, providing the foundation for a sustainable and electrified future.
Conclusion
The invention of the electric motor has had a profound impact on the world, driving technological advancements and transforming the way we live, work, and communicate. Throughout history, numerous individuals have made significant contributions to the development of electric motors, shaping the field of electromagnetism and propelling society into the age of electricity.
The early developments in electromagnetism by scientists such as Hans Christian Ørsted, André-Marie Ampère, and Joseph Henry laid the groundwork for the discovery of electromagnetic induction, a crucial principle in the functioning of electric motors.
Michael Faraday’s foundational work on electromagnetic induction and understanding the relationship between electricity and magnetism provided the essential knowledge that paved the way for the creation of electric motors. His conceptualization of lines of force and his invention of the homopolar generator contributed greatly to the field.
Thomas Davenport’s invention of the first practical electric motor demonstrated the feasibility of converting electrical energy into mechanical motion. His design became the springboard for future inventors and engineers to refine and improve upon.
Notable figures like Thomas Edison and Nikola Tesla made significant advancements in electric motor technology, with Tesla revolutionizing the field by his pioneering work on AC power systems and the induction motor, which became the industry standard.
Further innovations and advancements in electric motor technology have continued to this day, with a focus on increasing efficiency, reducing environmental impact, and exploring new applications in various industries.
The contributions of these inventors and engineers have shaped the world we live in today. Electric motors power our homes, industries, transportation systems, and renewable energy sources, enabling a more efficient and sustainable future.
The journey towards the invention of the electric motor is a testament to human curiosity, innovation, and perseverance. It is a reminder of the transformative power of science and engineering in propelling society forward.
In conclusion, the invention of the electric motor has revolutionized our world, and its impact will continue to shape our future. As technology continues to advance, electric motor technology will inevitably evolve, powering the next wave of progress and paving the way for new possibilities.
Frequently Asked Questions about Who Invented The Electric Motor
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.














0 thoughts on “Who Invented The Electric Motor”