Home>diy>Architecture & Design>What Are The Advantages Of A Ventilated Façade?


Architecture & Design
What Are The Advantages Of A Ventilated Façade?
Modified: January 6, 2024
Discover the benefits of a ventilated façade in architectural design. Improve energy efficiency, reduce maintenance costs, and enhance building aesthetics.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
There is no denying the importance of a well-designed and efficient building facade. Not only does it contribute to the aesthetic appeal of a structure, but it also plays a crucial role in energy efficiency, indoor comfort, and overall durability. When it comes to designing a high-performance facade, a ventilated facade stands out as one of the most effective solutions.
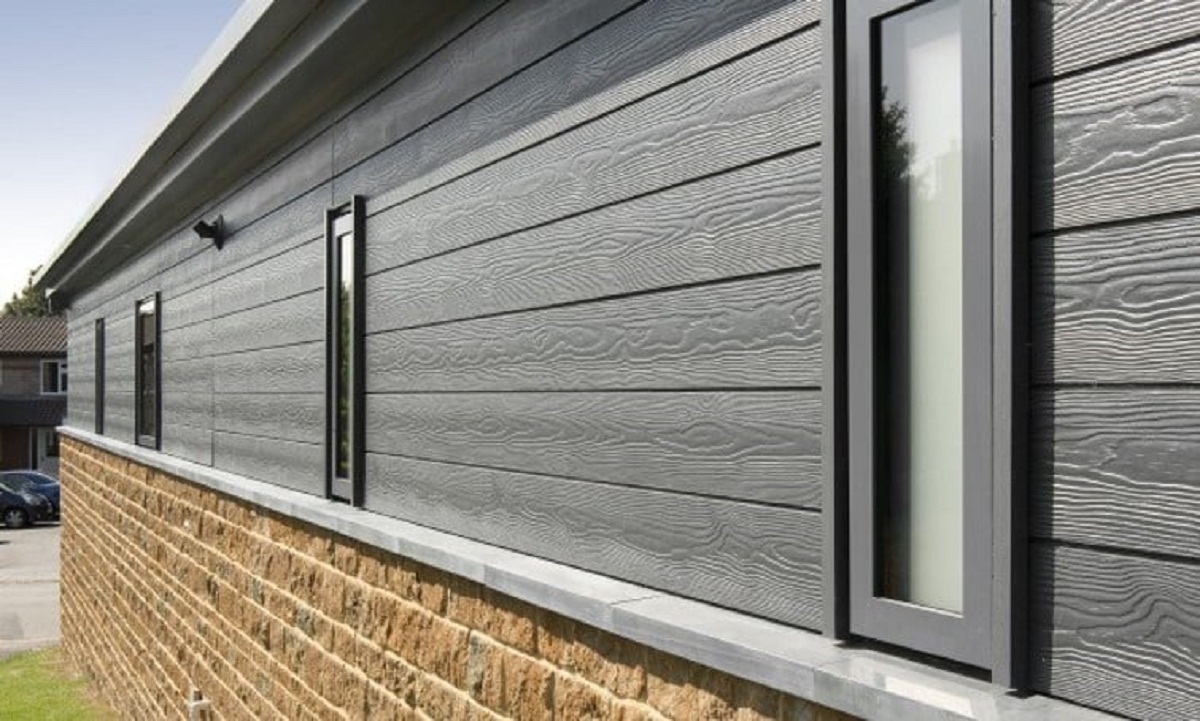
A ventilated facade, also known as a ventilated curtain wall or a rainscreen facade, is a system that is designed to create an air cavity between the building envelope and the external cladding. This cavity allows for controlled air circulation, which brings a range of advantages to both commercial and residential buildings.
In this article, we will explore the numerous advantages of a ventilated facade and why it is becoming increasingly popular in architectural designs.
Key Takeaways:
- Ventilated facades offer improved thermal insulation, energy efficiency, fire safety, indoor air quality, durability, and sound insulation. They provide a holistic solution for sustainable and comfortable building design, enhancing comfort, efficiency, and aesthetics.
- The design flexibility of ventilated facades allows for creative freedom, enabling architects to create visually striking and unique buildings. Additionally, they offer reduced maintenance and repair costs, making them an economically viable and valuable investment for any building.
Definition of a Ventilated Façade
A ventilated façade is a system that consists of an outer cladding layer, an air cavity, and an inner layer that forms the primary waterproof barrier of a building. This system creates a gap or cavity between the building structure and the cladding material, allowing for air to flow freely. The air circulation helps regulate temperature, manage moisture, and enhance the overall performance of the building envelope.
The outer layer of a ventilated façade is typically composed of durable materials such as stone, metal panels, terracotta, or fiber cement. These cladding materials offer aesthetic appeal, durability, and weather resistance. Behind the cladding, an air cavity is created, which acts as a buffer zone for ventilation and insulation purposes. The cavity is usually created through the use of ventilation channels or a grid system that allows air to circulate freely.
The inner layer of the ventilated façade provides the necessary insulation and waterproofing for the building. This layer serves as a barrier, protecting the structure from water infiltration and providing thermal insulation. It is often made up of materials like mineral wool, foam insulation, or a combination of both.
By creating this ventilated air gap, the façade can effectively manage heat and moisture transfer, resulting in improved energy efficiency, durability, and indoor comfort.
It is important to note that a ventilated façade is not solely limited to the external walls of a building. It can also be applied to other parts of a structure, such as roofs or balconies, to enhance their performance and functionality.
Improved Thermal Insulation
One of the key advantages of a ventilated façade is its ability to enhance thermal insulation in a building. The air cavity created between the outer cladding and the building structure acts as a barrier, reducing the transfer of heat between the interior and exterior of the building.
During hot summer months, the ventilated air gap allows for the dissipation of heat and helps prevent the transfer of external heat to the building. This reduces the reliance on air conditioning systems and keeps the interior cooler, resulting in energy savings and improved comfort for occupants.
Conversely, during colder seasons, the ventilated façade helps in maintaining a warmer interior by reducing heat loss. The air cavity acts as an additional layer of insulation, preventing cold air from penetrating into the building. This leads to reduced energy consumption and lower heating costs.
The use of insulation materials within the ventilated façade system further enhances its thermal performance. Materials such as mineral wool or foam insulation are commonly used to provide additional insulation properties, effectively reducing thermal bridging and heat transfer.
Overall, the improved thermal insulation offered by a ventilated façade contributes to a more energy-efficient building, lowers energy consumption, and improves occupant comfort by maintaining a stable indoor temperature throughout the year.
Enhanced Energy Efficiency
Beyond improved thermal insulation, a ventilated façade offers significant energy-saving benefits, making it a sustainable choice for buildings of various types. The combination of the air cavity and insulation materials helps to create a more energy-efficient envelope.
Due to the thermal barrier provided by the ventilated air gap, the building’s heating and cooling systems can operate more efficiently. With reduced heat transfer, less energy is required to maintain a comfortable indoor temperature, resulting in lower energy consumption and reduced utility costs.
In addition, the natural ventilation created by the air cavity helps to regulate the temperature inside the building. In warmer weather, the movement of air through the ventilated façade assists in dissipating heat, reducing the need for excessive air conditioning. This naturally cools the building, leading to energy savings and a more environmentally friendly approach.
Furthermore, the ventilated façade can be integrated with renewable energy systems, such as solar panels or solar thermal collectors. By combining these technologies, buildings can generate clean energy while benefiting from the enhanced insulation properties of the façade. This integration promotes a more sustainable and self-sufficient approach to energy usage.
Overall, the enhanced energy efficiency provided by a ventilated façade contributes to sustainable building practices by reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting energy conservation.
Increased Fire Safety
Fire safety is a critical consideration in building design, and a ventilated façade can significantly enhance the fire resistance of a structure. The air cavity created by the façade acts as a buffer zone, helping to prevent the spread of fire and limiting its impact on the building.
In the event of a fire, the air cavity acts as a barrier, preventing flames from directly reaching the building’s structure. This delayed exposure to heat provides occupants with more time to evacuate safely and gives firefighters added time to respond and extinguish the fire.
Furthermore, the materials used in the construction of a ventilated façade can contribute to fire safety. Non-combustible cladding materials, such as metal panels or fiber cement, are commonly used, reducing the risk of fire propagation. These materials have a higher resistance to fire, minimizing the potential for flames to ignite or spread.
The installation of fire-resistant insulation materials within the ventilated cavity further enhances fire safety. Mineral wool or other fire-resistant insulation materials are commonly used to limit the spread of flames within the façade system.
In addition, the air cavity can also serve as a smoke extraction route, drawing smoke away from the building and improving the visibility for evacuation and firefighting efforts. The improved control and management of smoke can play a critical role in saving lives during emergency situations.
Overall, a ventilated façade contributes to increased fire safety by providing a protective layer, delaying the spread of fire, and incorporating fire-resistant materials and insulation systems to minimize potential damage and risks to occupants.
Improved Indoor Air Quality
Indoor air quality is a crucial factor in creating a healthy and comfortable living or working environment. A ventilated façade plays a significant role in improving indoor air quality by promoting proper air circulation and mitigating the buildup of pollutants.
The air cavity created by the façade allows for the circulation of fresh air throughout the building. As external air enters the cavity, it helps to flush out stale indoor air that may be contaminated with pollutants, odors, or allergens. This continuous exchange of air reduces the concentration of pollutants, creating a healthier indoor environment.
In addition to the natural ventilation provided by the air cavity, mechanical ventilation systems can be integrated into the façade design. These systems enhance indoor air quality by actively bringing in fresh air from outside and expelling stale air, ensuring a constant supply of clean, oxygen-rich air.
Furthermore, the use of high-quality insulation materials within the ventilated façade helps to reduce the infiltration of outdoor pollutants, such as dust, pollen, and environmental toxins. The insulation acts as a barrier, preventing the entry of unwanted particles and allergens into the building, contributing to a cleaner and healthier indoor environment.
Improved indoor air quality has numerous benefits, including reducing the risk of respiratory illnesses, improving occupant productivity and comfort, and creating a more pleasant and inviting atmosphere. By implementing a ventilated façade, building owners and occupants can enjoy the advantages of improved indoor air quality and a healthier living or working environment.
When considering a ventilated façade, keep in mind that it can improve energy efficiency, provide better insulation, reduce maintenance costs, and enhance the overall aesthetics of a building.
Enhanced Durability and Weather Resistance
A ventilated façade offers enhanced durability and weather resistance, protecting the building from the harsh elements and ensuring its longevity.
The outer cladding materials used in a ventilated façade are carefully selected for their durability and ability to withstand various weather conditions. Whether it is extreme heat, heavy rain, or strong winds, the cladding acts as a protective layer, shielding the building from potential damage.
Additionally, the air cavity in a ventilated façade acts as a buffer zone, preventing direct contact between the cladding and the building structure. This separation helps to reduce the impact of thermal expansion and contraction caused by temperature fluctuations. By minimizing the stress on the building materials, the façade system improves its resistance to cracks and structural damage.
The ventilated façade also helps to manage moisture effectively. Rainwater that penetrates the outer cladding is drained away through the air cavity and ventilation channels, preventing water from saturating the building’s structure. This controlled moisture management helps to prevent the growth of mold, rot, and other moisture-related issues that can compromise the durability of the building.
Furthermore, the incorporation of insulation materials within the ventilated cavity helps to regulate the temperature and moisture levels inside the building. This balance helps to prevent condensation, which can lead to dampness and damage to the building materials over time.
By providing durability and weather resistance, a ventilated façade extends the lifespan of the building, reducing the need for costly repairs and maintenance. This not only safeguards the investment but also ensures the long-term functionality and aesthetic appeal of the structure.
Sound Insulation
Sound insulation is an often overlooked but essential aspect of building design. A ventilated façade can contribute significantly to reducing noise pollution and creating a quieter and more peaceful indoor environment.
The air cavity created by the ventilated façade acts as a sound buffer, helping to absorb and attenuate external noises before they reach the interior of the building. This means that sounds from traffic, construction sites, or other sources of noise pollution are significantly reduced, promoting a more serene and comfortable indoor atmosphere.
The insulation materials used within the ventilated cavity further enhance sound insulation. Materials like mineral wool have excellent acoustical properties, effectively absorbing and dampening noise vibrations. With the combination of the air cavity and insulation, the façade system acts as a sound barrier, protecting the interior from unwanted noise disturbances.
In addition to reducing exterior noise, a ventilated façade can also offer improved sound insulation between different areas within the building. By creating separate compartments and reducing sound transmission paths, the façade system helps to maintain privacy and minimize disturbances between adjacent rooms or different floors.
Whether in residential buildings, offices, or educational institutions, the benefits of sound insulation provided by a ventilated façade contribute to a more comfortable and productive indoor environment. Occupants can enjoy a quieter space, free from unwanted noise distractions, leading to improved concentration, sleep quality, and overall well-being.
Design Flexibility
A ventilated façade offers a high level of design flexibility, allowing architects and designers to create visually striking and unique buildings that meet specific aesthetic requirements.
The outer cladding materials used in a ventilated façade come in a wide range of options, including stone, metal panels, terracotta, glass, and fiber cement. This variety of materials offers endless possibilities for creating different textures, colors, and patterns, allowing architects to achieve the desired aesthetic effect.
In addition to material options, the ventilated façade system allows for creative freedom in terms of cladding layout and design. Architects can experiment with different panel sizes, shapes, and configurations to create visually interesting facades with depth and dimension. Building facades can be modular, asymmetrical, or incorporate artistic elements, bringing a unique character to the structure.
The design flexibility of a ventilated façade also extends to integration with other architectural elements. The system can seamlessly incorporate windows, doors, balconies, or other features, maintaining a cohesive and harmonious appearance.
Given the wide range of design options available, ventilated façades are particularly suitable for modern and contemporary architectural styles. However, they can also be adapted to complement traditional or historic designs, seamlessly blending the building’s facade with its surroundings.
Overall, the design flexibility of a ventilated façade provides architects and designers with the freedom to create visually striking buildings while ensuring optimal performance and functionality.
Reduced Maintenance and Repair Costs
A ventilated façade offers significant advantages when it comes to maintenance and repair, contributing to cost savings over the long term.
The outer cladding materials used in a ventilated façade are selected for their durability and weather resistance, requiring minimal maintenance. These materials are designed to withstand the elements and maintain their appearance over time, reducing the need for frequent cleaning or repairs due to wear and tear.
The air cavity within the ventilated façade serves as a protective layer, preventing direct exposure of the building structure to external elements. This helps to minimize the risk of damage to the primary waterproof barrier or insulation materials, which are typically located within the cavity. As a result, the need for repairs and replacements to these components is significantly reduced.
Furthermore, the ventilation provided by the air cavity helps to manage moisture effectively, preventing the accumulation of water and potential damage to the building structure. By minimizing the risk of moisture-related issues such as mold growth or rot, the frequency of maintenance and repairs is greatly reduced.
In the event that repairs are necessary, the modular design of a ventilated façade simplifies the process. The cladding panels can be individually removed and replaced, allowing targeted repairs without the need to dismantle the entire façade. This modularity results in cost savings, as only the affected area needs to be addressed rather than replacing the entire facade.
The integration of high-quality insulation materials within the ventilated cavity further contributes to reduced maintenance costs. These materials are designed to be durable and resistant to moisture, reducing the risk of degradation over time and the need for frequent replacements.
In summary, a ventilated façade offers reduced maintenance and repair costs due to the durable cladding materials, moisture management, and modular design. These cost savings can significantly impact the long-term maintenance budget of a building, making it an attractive choice for developers and property owners.
Conclusion
A ventilated façade offers numerous advantages that make it an attractive choice for architects, designers, and building owners. The benefits of improved thermal insulation, enhanced energy efficiency, increased fire safety, improved indoor air quality, enhanced durability and weather resistance, sound insulation, design flexibility, and reduced maintenance and repair costs all contribute to creating sustainable and comfortable buildings.
The thermal insulation provided by a ventilated façade helps to regulate indoor temperatures, leading to energy savings and improved occupant comfort. The enhanced energy efficiency contributes to sustainable building practices and reduces carbon emissions.
The increased fire safety offered by a ventilated façade provides a protective barrier, delaying the spread of flames and protecting the occupants and the structure. This feature plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety of building occupants during emergencies.
Improved indoor air quality is essential for a healthy and comfortable living or working environment. The ventilated façade promotes fresh air circulation, reducing the concentration of pollutants and improving occupant well-being.
Enhanced durability and weather resistance ensure the longevity of the building, reducing maintenance costs and the need for frequent repairs. The façade system protects the building from moisture damage and harsh weather conditions.
Sound insulation provided by a ventilated façade creates a quieter indoor environment, free from external noise pollution, improving occupant concentration and overall well-being.
The design flexibility of a ventilated façade allows for creative freedom, enabling architects to design visually appealing and unique buildings that meet specific aesthetic requirements.
Furthermore, the reduced maintenance and repair costs associated with a ventilated façade result in long-term cost savings, making it an economically viable option.
In conclusion, a ventilated façade offers a comprehensive solution to address various architectural, performance, and sustainability needs. It combines functionality, energy efficiency, and aesthetics, providing a holistic approach to building design. With its wide range of benefits, a ventilated façade is a valuable investment that enhances the comfort, efficiency, and durability of any building.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Are The Advantages Of A Ventilated Façade?
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.












0 thoughts on “What Are The Advantages Of A Ventilated Façade?”