Home>diy>Building & Construction>How Do Apartment Building Boilers Work


Building & Construction
How Do Apartment Building Boilers Work
Modified: December 7, 2023
Learn how apartment building boilers work in this informative guide. Explore the key components and processes involved in building-construction heating systems.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Welcome to the world of apartment building boilers! If you have ever lived in a multi-unit residential building, you have probably benefitted from the central heating system powered by a boiler. These marvels of modern engineering work tirelessly behind the scenes to keep your living space warm and comfortable during the chilly winter months.
In this article, we will take a closer look at how apartment building boilers work. We will explore the various components of a boiler system, delve into the fuel source and combustion process, examine heat transfer and distribution, discuss boiler controls and safety measures, and touch on maintenance and troubleshooting.
By gaining a better understanding of apartment building boilers, you will be equipped with valuable knowledge about the inner workings of these systems, enabling you to appreciate the effort and expertise that goes into providing reliable heating for multiple units.
So, let us dive into the world of apartment building boilers and unravel the mysteries behind their functionality!
Key Takeaways:
- Apartment building boilers are intricate systems comprising components like boilers, piping networks, and control panels. Understanding their inner workings and maintenance is crucial for reliable heating in multi-unit residential buildings.
- Efficient combustion, heat transfer, and robust safety measures are essential for safe and cost-effective operation of apartment building boilers. Regular maintenance and troubleshooting by qualified professionals ensure uninterrupted comfort for residents.
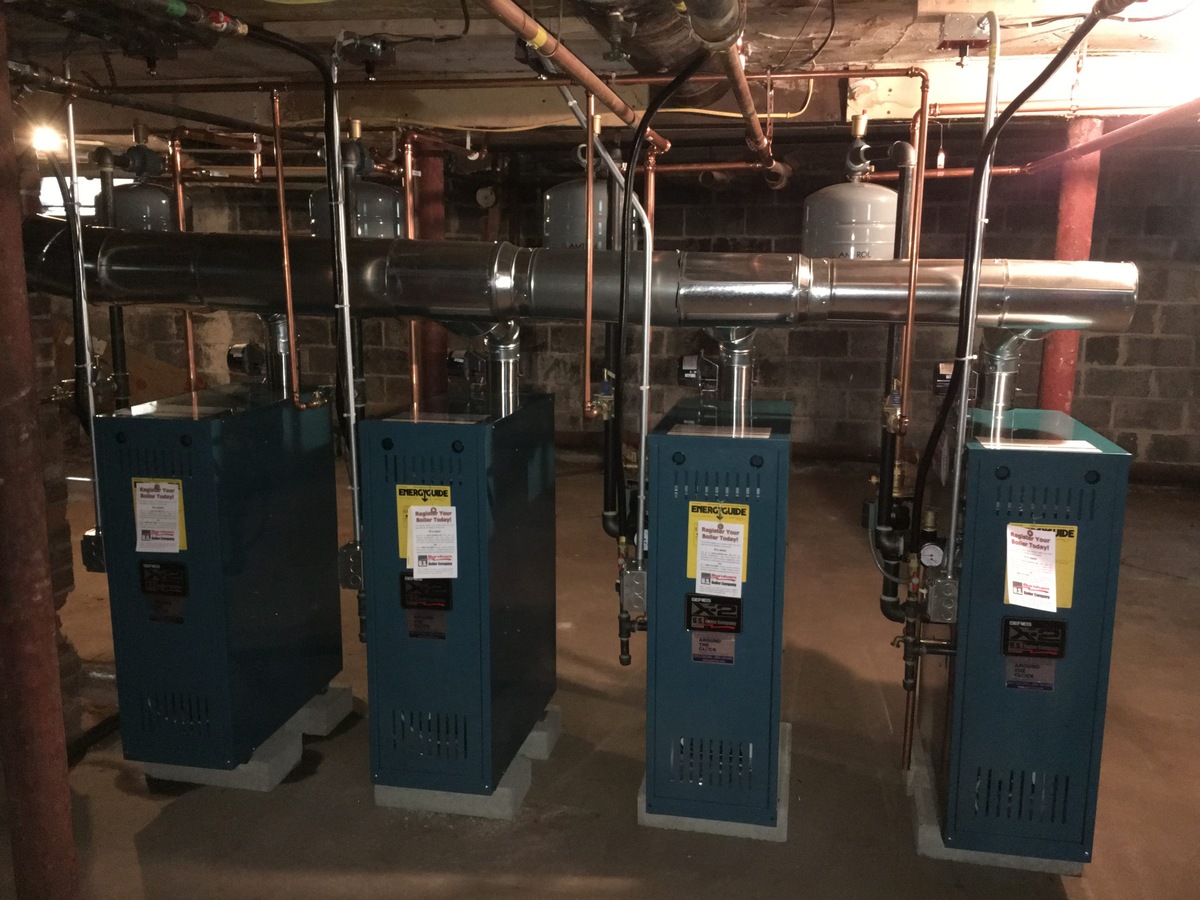
Components of an Apartment Building Boiler System
An apartment building boiler system consists of several key components that work together to provide efficient heating to multiple units. Let’s explore each component in detail:
- Boiler: The heart of the system, the boiler generates heat by burning a fuel source. It is usually located in a dedicated boiler room within the building. Boilers come in various types such as gas, oil, electric, or biomass, depending on the available fuel and the specific requirements of the building.
- Piping Network: A network of pipes connects the boiler to the different units in the building. These pipes carry hot water or steam, depending on the system type, to the radiators or heat exchangers in each unit, providing the necessary heat.
- Radiators or Heat Exchangers: Radiators are typically used in older buildings, while heat exchangers are common in newer constructions. These devices transfer heat from the hot water or steam to the surrounding air, effectively warming up the living spaces.
- Pumps and Valves: Pumps circulate the hot water or steam through the piping network, ensuring a consistent flow of heat to each unit. Valves control the flow and distribution of hot water or steam to different areas of the building, allowing for temperature regulation and zone heating.
- Expansion Tank: This component helps maintain system pressure by accommodating the expansion and contraction of the heated water or steam. It prevents excessive pressure build-up, ensuring safe and efficient operation of the boiler system.
- Control Panel: The control panel houses the controls and sensors that monitor and regulate the boiler system. It allows for temperature adjustments, enables automatic operation, and ensures safety by detecting any malfunctions or irregularities.
- Ventilation System: Since the combustion process produces exhaust gases, a ventilation system is essential to safely remove these gases from the building. It typically includes flues, chimneys, draft regulators, and exhaust fans to maintain proper air quality.
- Expansion Joints and Isolation Valves: Expansion joints help absorb the stress caused by temperature fluctuations and prevent damage to the piping system. Isolation valves allow for maintenance or repair work, enabling specific sections of the system to be shut off without affecting the entire building.
Each of these components plays a crucial role in the functioning of an apartment building boiler system. The combination of these elements ensures the reliable delivery of heat to each unit, creating a comfortable living environment for all residents.
Fuel Source and Combustion Process
The fuel source and combustion process are fundamental to the operation of an apartment building boiler system. The choice of fuel and the efficiency of its combustion directly impact the system’s performance. Let’s explore this aspect in more detail:
Fuel Source: Apartment building boilers can be powered by various fuel sources, including natural gas, heating oil, electricity, and even renewable biomass. The selection of the fuel source depends on factors such as availability, cost, environmental considerations, and building regulations. Natural gas is a popular choice due to its affordability, cleanliness, and wide availability in many urban areas.
Combustion Process: Once the fuel source is determined, the combustion process begins. In a gas-fired system, natural gas is mixed with air in the burner, creating a combustible mixture. The burner then ignites this mixture to produce a flame. In an oil-fired system, heating oil is atomized into a fine mist and injected into the burner, where it is ignited by an electric spark.
During combustion, the fuel undergoes a chemical reaction that releases heat energy. This heat energy is transferred to the water in the boiler, raising its temperature. For steam systems, the heat energy generated by combustion converts the water into steam.
Efficient combustion is vital for maximizing the heat output and minimizing fuel consumption. Factors such as proper air-to-fuel ratio, sufficient oxygen supply, and consistent flame stability contribute to efficient combustion. Monitoring devices and sensors in the control panel ensure optimal combustion by adjusting the fuel flow and air intake as necessary.
It is worth mentioning that advancements in technology have led to the development of high-efficiency boilers that extract more heat from the fuel, resulting in lower energy consumption and reduced emissions. These boilers employ condensing technology, which captures and utilizes the latent heat in the flue gases, further increasing efficiency.
Choosing the right fuel source and ensuring efficient combustion are essential for maintaining a cost-effective and environmentally friendly apartment building boiler system. By optimizing these factors, building owners can reduce energy expenses and contribute to a greener future.
Heat Transfer and Distribution
Once the boiler generates heat through the combustion process, the next step is to transfer and distribute that heat throughout the apartment building. This ensures that each unit receives the desired level of warmth. Let’s explore the heat transfer and distribution mechanisms in an apartment building boiler system:
Heat Transfer: In a hot water-based heating system, heat is transferred from the boiler to the water through a process called conduction. The hot water flows through the pipes that are strategically routed throughout the building. As the hot water circulates, it gradually loses heat to the surrounding pipes and radiators/heat exchangers.
For steam-based heating systems, the heat transfer occurs through a combination of conduction and condensation. Steam, which is high in latent heat, is distributed through the pipes to the radiators/heat exchangers. As the steam comes into contact with the cooler surfaces of the radiators/heat exchangers, it condenses into water, releasing its latent heat and warming up the surrounding air.
Heat Distribution: In an apartment building, heat distribution is typically achieved through a system of radiators or heat exchangers located in each unit. These devices are strategically placed in the living spaces, such as bedrooms and living rooms, to ensure even heat distribution. The heated water or steam enters the radiators/heat exchangers through the pipes, warming up the metal surfaces.
As the metal surfaces heat up, they transfer thermal energy to the surrounding air through a process known as convection. The warm air rises, creating a natural circulation pattern and spreading the heat throughout the room. This process continues until the desired temperature is reached, at which point the thermostat signals the boiler to regulate the heat output.
Some modern apartment buildings employ a zoning system, allowing for individual temperature control in different areas of the building. This is achieved by installing zone valves or separate control units that regulate the flow of hot water or steam to specific zones or units.
In summary, heat transfer and distribution are essential mechanisms in apartment building boiler systems. These processes ensure that the heat generated by the boiler is effectively delivered to each unit, providing a comfortable and cozy living environment for all residents.
Regular maintenance of apartment building boilers is essential to ensure efficient and safe operation. This includes checking for leaks, inspecting and cleaning burners, and testing safety controls.
Boiler Controls and Safety Measures
Boiler controls and safety measures are critical components of an apartment building boiler system. They ensure safe and efficient operation, preventing potential hazards and malfunctions. Let’s explore some of the key controls and safety features commonly found in these systems:
Thermostat: The thermostat is the primary control device that regulates the temperature within each unit. Occupants can adjust the desired temperature using the thermostat, which sends signals to the boiler to increase or decrease the heat output accordingly. This enables precise temperature control and helps maintain a comfortable living environment.
Pressure Relief Valve: The pressure relief valve is a vital safety feature that protects the boiler from excessive pressure buildup. It automatically releases water or steam if the pressure within the boiler exceeds a safe level, preventing potential damage or explosions.
High-Limit Control: The high-limit control is another safety device that monitors the temperature within the boiler. If the temperature rises above a predetermined threshold, the high-limit control shuts off the burner to prevent overheating and potential equipment damage.
Flow Control Valve: The flow control valve regulates the flow of hot water or steam within the system. It ensures that the proper amount of heat is distributed to each unit, preventing overheating or underheating. The flow control valve works in conjunction with the thermostat to maintain consistent and desired temperature levels.
Flame Safeguard System: For gas- or oil-fired boilers, a flame safeguard system is installed to ensure proper flame ignition and continuous burning. This system consists of flame sensors and safety controls that monitor the presence and stability of the flame. If any irregularities are detected, the system automatically shuts off the fuel supply to prevent dangerous situations.
Water Level Control: In water-based boiler systems, maintaining the proper water level is essential for safe and efficient operation. Water level control devices, such as probes or float switches, monitor the water level within the boiler. If the water level drops too low or rises too high, these controls activate mechanisms to add or drain water as needed.
Gas Leak Detection: Gas-fired boiler systems incorporate gas leak detection sensors to ensure the safety of the occupants. These sensors continuously monitor the presence of gas and alert the system if any leaks are detected. This precautionary measure helps prevent gas-related accidents and ensures the well-being of the building’s occupants.
Emergency Shutdown Switch: An emergency shutdown switch is installed in a readily accessible location to allow for immediate boiler shutdown in case of emergencies or maintenance needs. This switch quickly cuts off the fuel supply and shuts down the entire system, minimizing potential risks.
By having robust controls and safety measures in place, apartment building boiler systems can operate reliably, efficiently, and safely, providing peace of mind for both building owners and residents.
Read more: How Do You Buy An Apartment Building
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Maintenance is crucial for the smooth and efficient operation of an apartment building boiler system. Regular maintenance not only prolongs the lifespan of the equipment but also helps prevent costly breakdowns and ensures the safety of the building’s occupants. Here are some key maintenance tasks and troubleshooting measures for apartment building boilers:
Regular Inspections: Routine inspections by trained professionals are essential to identify and address any potential issues before they escalate. These inspections involve checking boiler components, controls, safety devices, and ventilation systems. Inspections also include assessing the integrity of pipes, valves, and expansion joints.
Cleaning and Servicing: Regular cleaning of boiler components, such as burners, heat exchangers, and flues, helps remove any accumulated debris or soot. This improves the efficiency of the boiler system and prevents problems caused by restricted airflow. Servicing the boiler includes tasks such as lubricating moving parts, inspecting and replacing worn-out gaskets, and calibrating controls for optimal performance.
Water Treatment: Proper water treatment is essential to prevent corrosion and scale buildup in the boiler system. Treating the water helps maintain the efficiency of heat transfer and extends the lifespan of the equipment. This involves regular testing of water quality and adding appropriate chemicals to inhibit corrosion and control mineral deposits.
Monitoring Fuel Efficiency: Monitoring fuel consumption and efficiency is important for cost control and environmental sustainability. Regularly check the fuel consumption against the heat output to ensure the system operates at optimal efficiency. This can be done by analyzing fuel bills and comparing them to the heating load and weather conditions.
Troubleshooting: In the event of malfunctions or operational issues, troubleshooting the boiler system is essential for identifying and resolving problems. Common troubleshooting measures include checking for error codes or fault indicators on the control panel, inspecting and testing safety devices, investigating abnormal noises or vibrations, and analyzing fuel supply issues.
Emergency Procedures: Having emergency procedures in place is crucial to handle unforeseen circumstances, such as leaks, pressure surges, or system failures. These procedures outline the steps to be taken in case of emergency, including shutting off the fuel supply, evacuating the building if necessary, and contacting qualified technicians for assistance.
It is important to note that maintenance and troubleshooting tasks should be carried out by qualified professionals with expertise in boiler systems. Regular maintenance contracts with reputable service providers can help ensure the proper functioning and safety of apartment building boilers.
By implementing a proactive maintenance approach and promptly addressing any troubleshooting needs, building owners can ensure the reliability, efficiency, and longevity of their apartment building boiler systems, providing uninterrupted comfort for the residents.
Conclusion
Apartment building boilers are the unsung heroes that work diligently to keep residents warm and comfortable during the colder months. From the combustion of fuel to the distribution of heat, these systems rely on an intricate network of components, controls, and safety measures to deliver reliable heating to multiple units. Understanding how these systems work and how to maintain them is essential for building owners and residents alike.
Throughout this article, we have explored the various components of an apartment building boiler system, such as the boiler itself, piping network, radiators or heat exchangers, pumps and valves, and expansion tanks. We have also learned about the fuel sources and combustion process, heat transfer and distribution mechanisms, boiler controls, safety measures, and maintenance protocols.
Maintaining and troubleshooting these systems require regular inspections, cleaning, servicing, and water treatment. Monitoring fuel efficiency, having emergency procedures in place, and promptly addressing any issues are vital for safe and efficient operation. Consulting with qualified professionals for maintenance and troubleshooting tasks is crucial to ensure the longevity and reliability of the system.
Apartment building boilers have come a long way with advancements in technology, offering high-efficiency options such as condensing boilers that contribute to energy savings and environmental sustainability. These systems not only provide heating comfort but also play a significant role in reducing energy consumption and associated costs.
In conclusion, apartment building boilers are complex systems that operate behind the scenes to provide warmth and comfort to numerous residents. Understanding their inner workings, performing regular maintenance, and addressing any troubleshooting needs are essential for the efficient and safe operation of these systems. By appreciating the effort and expertise behind apartment building boilers, we can ensure reliable heating for all occupants and contribute to a comfortable living environment in multi-unit buildings.
Frequently Asked Questions about How Do Apartment Building Boilers Work
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.














0 thoughts on “How Do Apartment Building Boilers Work”