Home>diy>Building & Construction>How Does The Construction Of Dams Positively Affect Natural Resources


Building & Construction
How Does The Construction Of Dams Positively Affect Natural Resources
Modified: December 7, 2023
Discover how the construction of dams can benefit natural resources, including the preservation of water, generation of clean energy, and promotion of wildlife habitats. Explore the impacts of building-construction on our environment.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
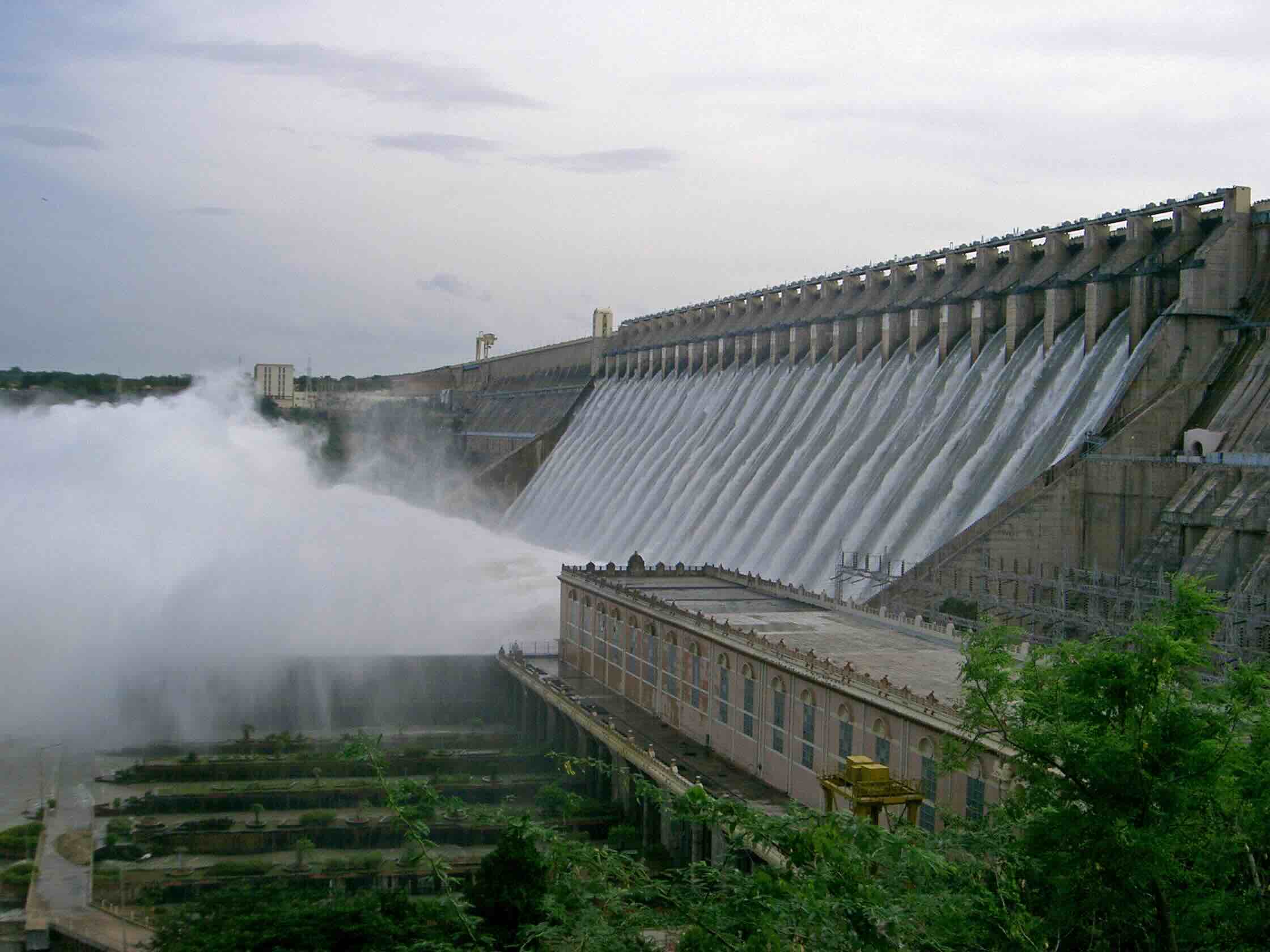
Construction of dams has had a significant impact on our natural resources, providing a wide range of benefits to both humans and the environment. Dams are large structures built across rivers or streams to store water, regulate its flow, and generate electricity. They play a crucial role in water management, energy production, flood control, and irrigation. In addition, dams provide habitat for various aquatic species and contribute to the development of recreational and tourist activities.
This article will explore how the construction of dams positively affects natural resources, highlighting their impact on water resources, energy generation, agriculture, wildlife and biodiversity, flood control, and recreation and tourism.
By understanding the multi-faceted benefits of dam construction, we can appreciate how these structures contribute to sustainable development and the preservation of our natural environment.
Key Takeaways:
- Dams positively impact natural resources by regulating water flow, generating clean energy, supporting agriculture, preserving wildlife, controlling floods, and offering recreational opportunities, contributing to sustainable development.
- The construction of dams has a profound and wide-ranging impact on our natural resources, providing a reliable water supply, clean energy, agricultural support, biodiversity preservation, flood control, and recreational opportunities.
Read more: How Does Rain Affect Construction
Dams and Natural Resources
Dams play a crucial role in managing and conserving our natural resources, particularly water. By impounding water in reservoirs, dams help regulate the flow of rivers and streams, ensuring a consistent supply of water for various purposes. This is particularly important in regions experiencing water scarcity or seasonal fluctuations in water availability.
One of the key benefits of dam construction is its impact on water resources. Reservoirs created by dams act as storage units, storing water during periods of excess rainfall or snowmelt, and releasing it during times of drought or increased water demand. This ensures a reliable water supply for drinking, irrigation, and industrial use.
Furthermore, dams facilitate the generation of hydroelectric power by harnessing the force of flowing water. As water is released from the reservoir, it passes through turbines, which convert the kinetic energy of the flowing water into electricity. Hydroelectric power is a clean and renewable energy source, reducing our dependence on fossil fuels and mitigating the impacts of climate change.
In addition to water management and energy generation, dams also have a significant impact on agriculture. By providing a regulated water supply, dams support irrigation systems, enabling farmers to cultivate crops even in arid regions. Irrigation from dam reservoirs increases crop yield and extends the growing season, ultimately contributing to food security.
Dams also help maintain ecological balance by creating habitat for various wildlife species. The reservoirs formed behind the dams create new aquatic environments, providing suitable habitats for fish, mammals, and other aquatic organisms. These reservoirs often become prime fishing spots, supporting local fishing industries and recreational fishing activities.
Overall, the construction of dams has a profound positive impact on natural resources. By effectively managing water, generating clean energy, supporting agriculture, and providing habitat for wildlife, dams play a critical role in the sustainable development and conservation of our natural environment.
Impact of Dams on Water Resources
The construction of dams has a significant impact on water resources, providing a wide range of benefits for both humans and the environment.
Firstly, dams help regulate the flow of rivers and streams by impounding water in reservoirs. This regulation ensures a consistent supply of water throughout the year, even during periods of low rainfall or drought. By storing excess water during rainy seasons and releasing it during dry spells, dams act as natural buffers, ensuring a reliable water supply for drinking, irrigation, and industrial use.
Furthermore, dam reservoirs provide a valuable source of stored water for irrigation. Water released from the reservoir can be channeled through canals and pipelines to irrigate farmland, supporting agricultural activities. This is particularly beneficial in regions where rainfall is insufficient or unreliable, allowing farmers to grow crops and increase agricultural productivity.
In addition to irrigation, dams also facilitate the supply of drinking water to communities. The reservoirs created by dams serve as water storage facilities, ensuring a sufficient supply of clean drinking water. This is particularly crucial in areas facing water scarcity or contamination issues.
Moreover, dams contribute to the management of flood control. By regulating the flow of water, dams can store excess water during heavy rainfall events and release it gradually, preventing downstream flooding. This is particularly important along rivers prone to flooding, protecting communities and reducing property damage.
Dams also play a crucial role in water-based recreational activities. The reservoirs formed by dams often provide excellent opportunities for boating, fishing, swimming, and other water sports. These activities not only provide enjoyment for tourists and locals but also support local economies through tourism and associated industries.
However, it’s important to note that the construction of dams can also have negative impacts on water resources. It can lead to the displacement of communities, loss of habitat for aquatic species, and alteration of natural river ecosystems. These environmental concerns must be carefully considered and addressed during the planning and construction stages of dam projects.
In summary, dams have a significant positive impact on water resources. They regulate water flow, provide a reliable water supply for irrigation and drinking water, contribute to flood control, and offer recreational opportunities. However, it is crucial to balance these benefits with the careful management and conservation of natural river ecosystems.
Impact of Dams on Energy Generation
The construction of dams has a profound impact on energy generation, particularly through the production of hydroelectric power. Dams harness the force of flowing water to generate clean, renewable energy, reducing our dependence on fossil fuels and mitigating the impact on the environment.
Hydroelectric power is generated as water stored in a dam’s reservoir is released and allowed to flow through turbines. The force of the flowing water drives the turbines, which then rotate a generator to produce electricity. This process is known as hydroelectric power generation.
One of the primary advantages of hydroelectric power is its renewable nature. Water is a constantly replenished resource, making hydroelectric power a sustainable and reliable energy source. Unlike fossil fuels, which require extraction and combustion, hydroelectric power production does not result in greenhouse gas emissions or air pollution.
Dams also offer a high level of flexibility in generating electricity. By controlling the release of water from the reservoir, dam operators can adjust the output of the hydroelectric power plant. This allows for immediate response to changes in energy demand, making hydroelectric power an essential component in maintaining a stable and reliable electric grid.
Furthermore, hydroelectric power plants have a long operational lifespan. With proper maintenance and regular upgrades, a well-designed dam and power plant can continue to generate electricity for several decades. This longevity makes hydroelectric power a cost-effective and sustainable energy solution in the long run.
Large-scale hydroelectric projects can generate significant amounts of electricity. Mega-dams, such as Three Gorges Dam in China or the Itaipu Dam in Brazil and Paraguay, have enormous capacities and can produce thousands of megawatts of electricity. This scale of electricity generation can be crucial in meeting the energy needs of highly populated areas or supporting industrial and commercial sectors.
Furthermore, hydroelectric power plants can help with energy storage and grid stability. During periods of low energy demand, excess electricity generated by hydroelectric power plants can be used to pump water back into the reservoir for future use. This pumped-storage technology allows for the efficient use of surplus energy and provides grid stability by balancing the supply and demand of electricity.
Overall, the construction of dams has a significant positive impact on energy generation by harnessing the power of flowing water to produce clean and renewable hydroelectric power. This form of energy not only reduces greenhouse gas emissions but also offers flexibility, longevity, and the ability to support large-scale energy needs.
Impact of Dams on Agriculture
The construction of dams has a transformative impact on agriculture, providing a reliable water supply for irrigation and improving agricultural productivity. Dams play a crucial role in water management, ensuring that water is available when and where it is needed for crop cultivation.
One of the key benefits of dams in agriculture is their role in irrigation. The reservoirs created by dams act as water storage units, allowing water to be released in controlled amounts for crop irrigation. This is particularly important in regions where rainfall is limited or unreliable. By providing a consistent water supply, dams support agricultural activities, enabling farmers to cultivate crops even during dry seasons or in arid environments.
Irrigation from dams offers several advantages for agriculture. Firstly, it extends the growing season by supplementing rainfall with irrigation water. This allows farmers to cultivate crops throughout the year, maximizing their yield and increasing food production. Additionally, irrigation water from dams can be precisely allocated, ensuring that crops receive the optimal amount of water required for their growth and development.
Moreover, dams help to mitigate the impact of droughts on agriculture. During periods of drought, when natural water sources may be depleted, dams can provide a lifeline for farmers by supplying water for irrigation. This helps to maintain crop production and reduce the vulnerability of agriculture to climate-related challenges.
Dams also contribute to the efficient use of water in agriculture. Through the controlled release of water from reservoirs, dams help to reduce water wastage and prevent excessive water runoff. This not only conserves water resources but also minimizes the impact on downstream ecosystems.
Furthermore, the use of dam water for irrigation can enhance soil fertility and productivity. The controlled distribution of water allows for better nutrient absorption by plants and can help to flush out soil salinity, improving crop health and yield.
In addition to irrigation, dams can support agricultural activities by providing hydroelectric power for agricultural machinery and equipment. Reliable access to electricity enables farmers to use modern irrigation systems, such as sprinklers or drip irrigation, which are more efficient and effective in delivering water to crops. This enhances overall agricultural productivity and promotes sustainable farming practices.
Overall, dams have a significant positive impact on agriculture by providing a reliable water supply for irrigation, extending the growing season, mitigating the impact of droughts, promoting efficient water use, and supporting the use of modern agricultural technologies. By enhancing agricultural productivity, dams contribute to food security and the economic well-being of farming communities.
Dams can positively affect natural resources by providing water for irrigation, hydroelectric power, and flood control. This can lead to increased agricultural productivity, renewable energy generation, and reduced risk of flooding.
Read more: How Does Construction Affect Wildlife
Impact of Dams on Wildlife and Biodiversity
The construction of dams can have both positive and negative impacts on wildlife and biodiversity. While dams create new habitats and support the growth of certain species, they can also disrupt natural ecosystems and lead to the loss of biodiversity.
One of the positive impacts of dams on wildlife is the creation of reservoirs, which provide new aquatic habitats. These reservoirs become home to various species of fish, amphibians, and aquatic plants. The presence of these habitats can increase overall biodiversity and provide opportunities for recreational fishing, thereby supporting local economies and tourism.
Dams can also regulate the flow of rivers, creating conditions that are favorable for certain species. For example, the controlled release of water downstream can simulate natural flooding cycles, benefiting the breeding and migration patterns of fish and waterbird species.
Many dams also include fish ladders or bypass channels, allowing fish to bypass the dam and continue their upstream migrations. These structures help maintain fish populations and preserve the ecological balance of river systems.
However, it’s important to consider the negative impacts of dams on wildlife and biodiversity as well. The construction of dams can disrupt natural river habitats and lead to the loss of species that are unable to adapt to the changes in their environment.
Large-scale dams can result in the flooding of vast areas of land. This submergence can lead to the loss of terrestrial habitats, including forests and grasslands, which are important for various animal species. Additionally, the fragmentation of rivers caused by dam construction can isolate populations of certain species, reducing their genetic diversity and making them more vulnerable to extinction.
Furthermore, dams can alter the natural flow and temperature of rivers, affecting the reproductive cycles of aquatic species. Changes in the flow regime can impact the availability of food, breeding grounds, and migration routes for fish and other aquatic organisms.
To mitigate the negative impacts on wildlife and biodiversity, environmental considerations and mitigation measures are crucial during the planning and construction of dam projects. This may include the creation of wildlife corridors, the implementation of fish passage systems, and the preservation of critical habitats in the dam’s vicinity.
In summary, dams can have both positive and negative impacts on wildlife and biodiversity. While they create new aquatic habitats and support certain species, they can also disrupt natural ecosystems and lead to the loss of biodiversity. By implementing proper environmental management practices and mitigation measures, the negative impacts can be minimized, allowing dams to coexist with wildlife and contribute to the preservation of biodiversity.
Impact of Dams on Flood Control
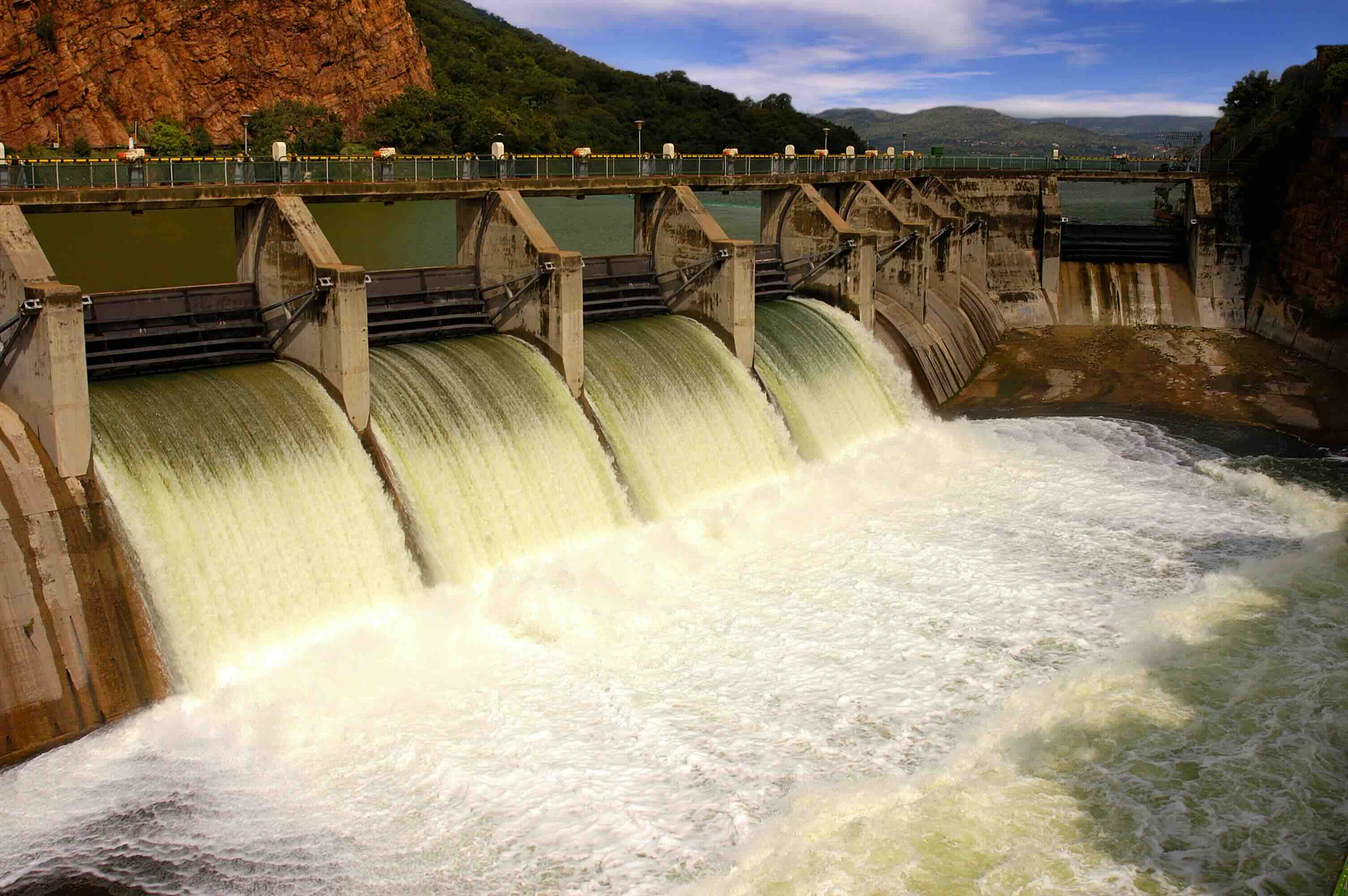
The construction of dams has a significant impact on flood control, providing a crucial mechanism to manage and mitigate the destructive effects of flooding. Dams act as barriers, regulating the flow of water and reducing the risk of downstream flooding during periods of heavy rainfall or snowmelt.
One of the primary functions of dams in flood control is the ability to store excess water during periods of heavy precipitation. As rivers and streams swell with water, dams can retain and control the release of water, preventing it from inundating downstream areas. By storing the excess water, dams act as natural buffers, reducing the peak flow of water downstream and mitigating the risk of devastating floods.
Dams also play a crucial role in regulating water flow patterns. By controlling the release of water from reservoirs, dam operators can manage the flow downstream, ensuring a steady and gradual release that prevents sudden surges of water. This controlled release of water helps to prevent flash floods and allows downstream communities to better prepare for increased water levels.
During periods of heavy rainfall or snowmelt, dams can hold back water and release it gradually, matching the downstream water flow capacity. This prevents the overwhelming of rivers and stream channels, reducing erosion, and minimizing damage to infrastructure and property downstream.
In addition to flood control, dams contribute to the overall management of water resources, which indirectly helps in flood prevention. By providing a regulated water supply for irrigation and consumption, dams help to reduce the demand for water extraction from natural sources. This ensures that water is available for agricultural and domestic needs, reducing the need to encroach upon flood-prone areas for water supply.
Furthermore, dams can serve as reservoirs to retain floodwaters temporarily, allowing for controlled downstream release once the flood threat has passed. This strategy can help protect communities by preventing rapid and uncontrolled flooding, giving authorities the opportunity to assess and respond to the situation effectively.
It is important to note that while dams can play a crucial role in flood control, they are just one part of a comprehensive flood management system. Effective flood management requires a combination of measures including proper land-use planning, flood forecasting and warning systems, floodplain zoning, and community preparedness.
In summary, dams have a significant impact on flood control by providing the ability to store excess water, regulate the release of water downstream, and maintain a steady flow. By acting as buffers and managing water resources, dams help to mitigate the risk of flooding, protect downstream communities, and contribute to overall flood management strategies.
Impact of Dams on Recreation and Tourism
The construction of dams has a notable impact on recreation and tourism, creating new opportunities for outdoor activities and attracting visitors to these man-made reservoirs and their surrounding areas.
One of the primary benefits of dams in terms of recreation is the creation of reservoirs. These reservoirs transform the landscape, forming large bodies of water that provide opportunities for boating, kayaking, canoeing, and other water-based activities. These recreational activities attract enthusiasts and visitors seeking outdoor adventures and leisurely pursuits.
Fishing is another popular recreational activity associated with dam reservoirs. Dams create habitats that support various fish species, providing excellent fishing opportunities for both recreational and professional anglers. The stocked reservoirs become prime locations for fishing tournaments and attract anglers from all around, stimulating local economies and supporting the fishing industry.
Furthermore, the presence of dam reservoirs often leads to the development of recreational facilities such as marinas, beaches, and campgrounds. These amenities provide opportunities for picnicking, swimming, sunbathing, and camping, enhancing the overall recreational experience for visitors.
Dam reservoirs also offer opportunities for wildlife observation and birdwatching. The created habitats attract a variety of bird species, including migratory birds, waterfowl, and wading birds. Such reservoirs become popular birdwatching destinations, drawing nature enthusiasts who take pleasure in observing and documenting the diverse birdlife.
In addition to the immediate recreational opportunities around the dam reservoirs, the surrounding landscape often benefits from the increased tourism. Visitors are drawn to the scenic beauty and serenity of these areas, leading to the growth of tourism-related services and businesses. Hotels, restaurants, souvenir shops, and adventure tour companies emerge, catering to the needs and interests of the tourists.
Dam sites themselves can also become tourist attractions. Some dams are architecturally impressive and offer panoramic views, attracting tourists interested in engineering marvels and the history of dam construction. Visitors may enjoy guided tours to learn about the construction process, the technology behind the dam’s operation, and the impacts on the surrounding environment.
However, it is essential to manage recreational activities around dams sustainably to minimize negative impacts on the environment and ensure the preservation of natural resources. Monitoring the water quality, enforcing fishing regulations, and maintaining appropriate signage and facilities are essential for the sustainable development of recreational and tourism activities.
In summary, dams have a significant positive impact on recreation and tourism by creating new opportunities for water-based activities, fishing, camping, birdwatching, and wildlife observation. The emergence of recreational facilities and increased tourism benefits the local economy, while dam sites themselves can become attractions for those interested in engineering and historical significance. It is crucial to manage recreational activities responsibly to preserve the natural environment and maintain a sustainable balance between tourism and conservation.
Conclusion
The construction of dams has a profound and wide-ranging impact on our natural resources. Dams play a crucial role in managing water resources, generating clean energy, supporting agriculture, preserving wildlife and biodiversity, controlling floods, and providing recreational opportunities.
Dams are instrumental in water management, ensuring a consistent water supply for various purposes. They regulate the flow of rivers and store water during periods of plenty, releasing it during times of drought or increased demand. This reliable water supply supports irrigation, drinking water, and industrial needs, contributing to agricultural productivity and human well-being.
Hydroelectric power generation from dams offers clean, renewable energy. By harnessing the force of flowing water, dams reduce our reliance on fossil fuels and help mitigate the impacts of climate change. They provide a flexible and sustainable energy source that can meet the needs of highly populated areas and support industrial and commercial sectors.
Dams have a transformative impact on agriculture by providing a reliable water supply for irrigation. They extend the growing season, mitigate the impact of droughts, and support the efficient use of water resources. By improving agricultural productivity, dams contribute to food security and the economic well-being of farming communities.
The creation of reservoirs behind dams provides habitats for various aquatic species, expanding biodiversity and supporting recreational activities such as boating, fishing, and swimming. However, the construction of dams can also disrupt natural ecosystems and lead to the loss of habitats. Careful environmental planning and mitigation measures are necessary to minimize these negative impacts and preserve biodiversity.
Dams play a crucial role in flood control, regulating the flow of water, storing excess water, and reducing the risk of downstream flooding. By preventing flash floods and providing controlled releases, dams protect communities and infrastructure from the destructive effects of flooding.
Furthermore, dam reservoirs offer recreational opportunities such as boating, fishing, camping, birdwatching, and wildlife observation. The presence of dams attracts tourists, stimulating local economies and supporting the development of tourism-related services and businesses.
While dams bring significant benefits, it is essential to manage and balance their impacts on the environment and communities. Proper planning, environmental considerations, and mitigation measures are crucial in minimizing negative effects and preserving the natural ecosystems and resources.
In conclusion, the construction of dams positively impacts natural resources by managing water, generating clean energy, supporting agriculture, preserving wildlife, controlling floods, and offering recreational opportunities. The benefits of dams are vast, contributing to sustainable development and the conservation of our natural environment.
Frequently Asked Questions about How Does The Construction Of Dams Positively Affect Natural Resources
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.













0 thoughts on “How Does The Construction Of Dams Positively Affect Natural Resources”