Home>diy>Building & Construction>What Does SWPPP Stand For In Construction


Building & Construction
What Does SWPPP Stand For In Construction
Modified: December 7, 2023
Discover the meaning of SWPPP in construction and how it impacts building-construction projects. Learn about stormwater management practices and compliance guidelines.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
When embarking on a construction project, there are numerous factors to consider to ensure its success. From hiring skilled workers to sourcing high-quality materials, every aspect requires careful planning and execution. However, one area that should not be overlooked is stormwater management, which plays a crucial role in maintaining the environmental integrity of construction sites.
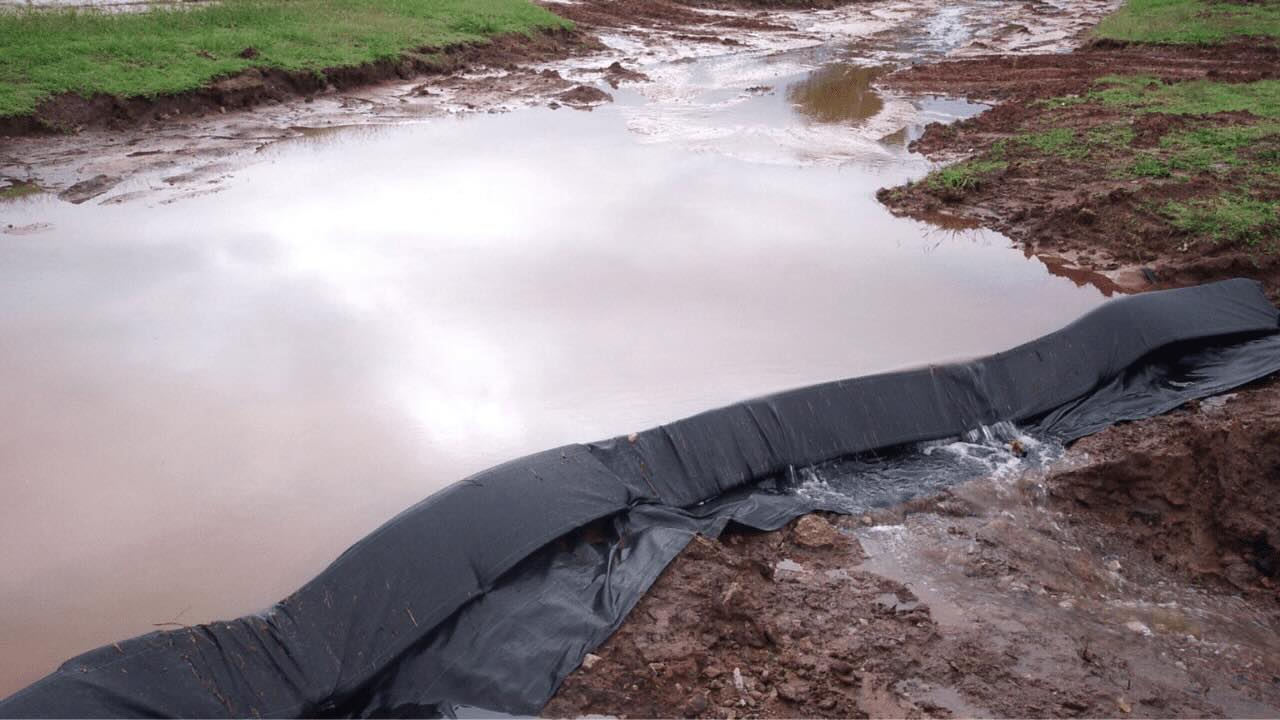
Stormwater runoff from construction sites can pose a significant threat to nearby water bodies and ecosystems. Sediments, chemicals, and pollutants can be carried by stormwater runoff, causing water pollution and degradation of aquatic habitats. To combat these issues, construction projects implement a Stormwater Pollution Prevention Plan (SWPPP).
Definition of SWPPP:
A SWPPP, which stands for Stormwater Pollution Prevention Plan, is a comprehensive strategy that outlines the measures and practices employed to manage and control stormwater runoff from construction sites. It is a crucial document required by regulatory bodies to ensure compliance with environmental regulations.
Key Takeaways:
- SWPPPs are vital for construction projects to prevent water pollution, protect the environment, and ensure compliance with regulations. They promote sustainable practices and enhance operational efficiency while safeguarding public health and safety.
- Despite challenges, implementing SWPPPs offers numerous benefits, including environmental protection, cost savings, and positive public image. Proactive planning, ongoing training, and collaboration are essential for successful SWPPP implementation.
Read more: What Does BIM Stand For In Construction
Definition of SWPPP
A SWPPP, which stands for Stormwater Pollution Prevention Plan, is a comprehensive strategy that outlines the measures and practices employed to manage and control stormwater runoff from construction sites. It is a crucial document required by regulatory bodies to ensure compliance with environmental regulations.
The primary purpose of a SWPPP is to minimize the impact of construction activities on water quality. It serves as a blueprint for construction companies to prevent pollutants from entering storm drains or nearby water bodies, such as rivers, lakes, and streams.
SWPPPs are designed to identify potential sources of pollution on construction sites and to implement effective management practices to reduce or eliminate those sources. By utilizing best management practices (BMPs) and sustainable stormwater management techniques, construction projects can minimize erosion, control sedimentation, and prevent the release of harmful substances into the environment.
The development of a SWPPP involves a thorough analysis of the construction site, including a comprehensive assessment of potential pollution sources and the implementation of erosion and sediment control measures. It also includes provisions for spill prevention, waste management, and proper handling of construction materials to prevent contamination of stormwater runoff.
Furthermore, a SWPPP should address the potential impact of heavy rain events and design appropriate stormwater management systems, such as sediment basins, silt fences, and stormwater ponds, to capture and treat runoff before it reaches water bodies.
It is important to note that a SWPPP is not a static document. It should be regularly reviewed and updated throughout the course of the construction project to address any changes or new potential pollution sources that may arise.
Purpose of SWPPP in Construction
The purpose of a SWPPP in construction is multifaceted and goes beyond mere compliance with environmental regulations. It serves as a crucial tool to protect water quality, preserve natural habitats, and mitigate the potential negative impacts of construction activities on the environment.
Here are the primary purposes of implementing a SWPPP in construction:
- Prevention of water pollution: Construction sites often generate large amounts of sediment, chemicals, and other pollutants that can be washed into nearby water bodies during rainfall events. A SWPPP aims to minimize the transport of these pollutants by implementing effective erosion and sediment control measures.
- Protection of aquatic ecosystems: Stormwater runoff contaminated with sediments, chemicals, or pollutants can have detrimental effects on aquatic life, including fish, amphibians, and various other species that rely on clean water habitats. By implementing a SWPPP, construction projects can minimize the adverse impacts on aquatic ecosystems and safeguard their biodiversity.
- Mitigation of downstream flooding: Uncontrolled stormwater runoff from construction sites can contribute to increased runoff volumes and accelerated flow rates, leading to downstream flooding. Proper stormwater management measures outlined in the SWPPP can help minimize runoff and reduce the risk of flooding in surrounding areas.
- Compliance with regulations: Regulatory authorities at the local, state, and federal levels require construction projects to develop and implement SWPPPs to ensure compliance with environmental regulations. Failure to adhere to these regulations can result in fines, penalties, or delays in project completion.
- Preservation of public health and safety: By implementing proper erosion control measures and preventing the discharge of pollutants into storm drains, SWPPPs contribute to maintaining a safe and healthy environment for workers, neighboring communities, and the public at large.
- Maintaining a positive public image: In today’s environmentally conscious society, construction companies that prioritize sustainable practices and environmental stewardship often gain a favorable reputation. By implementing a SWPPP, construction projects showcase their commitment to responsible construction practices and demonstrate their dedication to protecting the environment.
Overall, the purpose of a SWPPP in construction is to mitigate the potential adverse impacts of construction activities on water quality, promote sustainable stormwater management practices, and ensure compliance with environmental regulations. By doing so, construction projects can protect the environment, preserve natural resources, and uphold their social and environmental responsibilities.
Components of SWPPP
A well-developed SWPPP consists of several key components that work together to effectively manage stormwater runoff and prevent pollution. These components are tailored to the specific needs and characteristics of each construction site, but they generally include the following:
- Site Description and Project Information: This section provides an overview of the construction site, including its location, size, and a description of the project activities. It also includes information on the construction schedule, anticipated duration, and the expected number of workers on-site.
- Potential Pollution Sources: Here, all potential pollution sources on the construction site are identified and assessed. This includes sources such as stockpiles of construction materials, fueling areas, equipment maintenance areas, and areas where runoff can occur. Identifying these sources helps determine the necessary measures to prevent pollution.
- Erosion and Sediment Control Measures: This component outlines the specific erosion and sediment control measures that will be implemented to minimize soil erosion and the transport of sediment in stormwater runoff. Examples of such measures include slope stabilization, vegetative buffers, erosion control blankets, and sediment basins.
- Stormwater Management Practices: This section details the stormwater management practices that will be employed on the construction site. It includes the design and installation of stormwater control devices such as sediment ponds, filter systems, and bioswales, which are used to capture, treat, and manage stormwater runoff.
- Spill Prevention and Control: Construction sites often have the potential for accidental spills of hazardous substances, fuel, or chemicals. This part of the SWPPP outlines spill prevention and control measures, including proper storage, labeling, and handling of hazardous materials, as well as spill response protocols to minimize the impact of spills on water quality.
- Waste Management: Construction activities generate various types of waste, including construction debris, excess materials, and potentially hazardous substances. The SWPPP includes provisions for proper waste management, including recycling, disposal, and recycling procedures, to prevent waste from entering stormwater runoff.
- Inspection and Maintenance: Regular inspections and maintenance are crucial to ensure the effectiveness of erosion control and stormwater management practices. This component outlines the frequency and procedures for site inspections, as well as the maintenance activities required to keep erosion control measures and stormwater management devices in good working condition.
- Employee Training: Adequate training and education are essential to ensure that all construction site workers are aware of their responsibilities regarding stormwater management and pollution prevention. This component describes the training programs that will be provided to workers, emphasizing Best Management Practices (BMPs) and procedures to minimize pollution.
- Record Keeping: The SWPPP requires proper documentation of all activities related to erosion and sediment control, stormwater management, inspections, maintenance, spill prevention, and employee training. This component details the types of records to be maintained and the duration for which they should be retained.
- Contingency Plans: In case of unexpected weather events or other emergencies, contingency plans are developed to address potential risks to water quality. These plans outline the steps to be taken in the event of heavy rainfall, flooding, or other scenarios that may require adjustments to the SWPPP or immediate action to prevent pollution.
By incorporating these essential components, a SWPPP provides a comprehensive framework for effective stormwater management and pollution prevention on construction sites.
Planning and Implementation of SWPPP
The planning and implementation of a SWPPP involves a systematic approach to address stormwater management and pollution prevention throughout the duration of a construction project. It requires collaboration between project managers, engineers, environmental consultants, and construction site personnel. Here are the key steps involved in the planning and implementation of a SWPPP:
- Site Assessment: The first step is to conduct a thorough assessment of the construction site to identify potential pollution sources and evaluate the site’s characteristics. This includes assessing slope gradients, soil types, drainage patterns, and nearby water bodies. The assessment helps determine the appropriate erosion control measures and stormwater management practices to be implemented.
- Regulatory Compliance: Familiarize yourself with the environmental regulations and permit requirements specific to your construction site. This includes understanding the applicable stormwater regulations, obtaining necessary permits, and ensuring compliance with local, state, and federal guidelines.
- Development of SWPPP: Based on the site assessment and regulatory requirements, develop a comprehensive SWPPP that addresses all components outlined in the previous section. Consider the unique characteristics of the construction site, such as the magnitude of the project, duration, size, and potential environmental impacts.
- Communication and Training: It is crucial to communicate the SWPPP requirements and objectives to construction site personnel, subcontractors, and other stakeholders. Conduct training sessions to ensure everyone understands their roles in implementing erosion control measures, stormwater management practices, and pollution prevention strategies.
- Implementation of BMPs: Implement Best Management Practices (BMPs) as outlined in the SWPPP to control erosion, manage stormwater runoff, and prevent pollution. This may include installing erosion control measures, constructing sediment basins, establishing vegetative buffer zones, and using engineered stormwater management systems.
- Regular Inspections: Conduct regular inspections of the construction site to assess the effectiveness of erosion control and stormwater management measures. Identify any potential issues or areas of improvement and take corrective actions promptly. Document all inspections and maintain records as required.
- Maintenance and Monitoring: Proper maintenance of erosion control measures and stormwater management systems is essential for their long-term effectiveness. Regularly monitor and maintain sediment basins, filter systems, and other stormwater control devices. Keep records of maintenance activities to demonstrate compliance with the SWPPP.
- Record Keeping and Reporting: Maintain accurate and up-to-date records of all activities related to erosion control, stormwater management, inspections, maintenance, and employee training. This includes documenting any changes or modifications to the SWPPP. Prepare any necessary reports required by regulatory agencies.
- Contingency Planning: Develop contingency plans to address potential risks to water quality in case of unexpected weather events or emergencies. Outline actions to be taken during heavy rainfall, floods, or other situations that may require adjustments to the SWPPP or immediate response to prevent pollution.
Regularly review and update the SWPPP throughout the construction project as necessary. Ensure that all personnel involved in the project are aware of the SWPPP requirements and their responsibilities to maintain a safe and environmentally responsible construction site.
By following a well-planned and implemented SWPPP, construction projects can effectively manage stormwater runoff, minimize erosion, and prevent pollution, thereby protecting water quality and maintaining environmental compliance.
SWPPP stands for Stormwater Pollution Prevention Plan. It is a requirement for construction sites to prevent stormwater pollution by implementing best management practices.
Read more: What Does SD Stand For In Construction
Importance of SWPPP in Construction Projects
A Stormwater Pollution Prevention Plan (SWPPP) is of utmost importance in construction projects for several reasons. It not only ensures compliance with environmental regulations but also plays a crucial role in protecting the environment, safeguarding public health, and promoting sustainable construction practices. Here are the key reasons why a SWPPP is essential:
- Environmental Protection: Construction activities have the potential to generate significant amounts of sediment, pollutants, and chemicals that can negatively impact nearby water bodies and ecosystems. A SWPPP helps minimize the release of pollutants into stormwater runoff, protecting water quality, preserving aquatic habitats, and reducing the overall ecological footprint of construction projects.
- Compliance with Regulations: Regulatory agencies at the local, state, and federal levels have established strict guidelines for stormwater management in construction projects. Implementing a SWPPP ensures compliance with these regulations. Failure to comply can result in penalties, fines, and delays in project completion, which can be costly for construction companies.
- Prevention of Water Pollution: By implementing erosion and sediment control measures, practices to prevent spills, and proper management of construction waste, a SWPPP helps prevent water pollution. It minimizes the transport of sediments, chemicals, and contaminants into storm drains and nearby water bodies, reducing the risk of pollution and degradation of aquatic ecosystems.
- Protection of Public Health and Safety: Polluted stormwater runoff can pose health risks to nearby communities, particularly if it contaminates drinking water sources or recreational areas. By managing stormwater runoff and preventing the release of pollutants, a SWPPP helps protect public health and ensures the safety of workers, residents, and visitors in the vicinity of construction sites.
- Sustainable Construction Practices: SWPPPs promote the adoption of sustainable construction practices, such as the use of Best Management Practices (BMPs), efficient stormwater management systems, and responsible waste management. By incorporating these practices, construction projects minimize resource depletion, reduce their carbon footprint, and contribute to the overall sustainability of the built environment.
- Positive Public Image: A construction project that demonstrates a commitment to environmental stewardship and responsible construction practices can enhance its reputation and attract potential clients and investors. By implementing a SWPPP and effectively managing stormwater runoff, construction companies showcase their dedication to sustainability and contribute to the preservation of natural resources, which resonates positively with the public.
- Long-Term Cost Savings: Implementing a SWPPP from the early stages of a construction project can help mitigate potential risks and prevent costly issues related to erosion, sedimentation, and water pollution. By investing in erosion control measures and effective stormwater management, construction companies can avoid potential fines, delays, and costly remediation efforts, resulting in long-term cost savings.
Overall, the importance of a SWPPP in construction projects cannot be overstated. It ensures compliance with environmental regulations, protects water quality and ecosystems, promotes sustainable construction practices, safeguards public health and safety, enhances reputation, and helps achieve long-term cost savings. By prioritizing stormwater management and pollution prevention, construction projects can successfully balance their operational needs with their environmental responsibilities.
Compliance and Enforcement of SWPPP Regulations
Compliance with Stormwater Pollution Prevention Plan (SWPPP) regulations is essential to ensure the effective management of stormwater runoff and prevent pollution from construction sites. Regulatory agencies at the local, state, and federal levels have established guidelines and standards for SWPPP implementation, with enforcement mechanisms in place to ensure compliance. Here’s an overview of compliance and enforcement aspects of SWPPP regulations:
Permitting and Approval:
Construction projects typically require permits from regulatory agencies to operate legally. These permits, such as National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System (NPDES) permits in the United States, often include specific requirements related to stormwater management and pollution prevention. The SWPPP serves as the documentation of compliance with these requirements and must be submitted for approval before commencing construction activities.
Inspections and Audits:
Regulatory agencies conduct routine inspections and audits of construction sites to assess compliance with SWPPP regulations. These inspections may be scheduled or unscheduled, and they involve evaluating the implementation of erosion control measures, stormwater management practices, and pollution prevention strategies outlined in the SWPPP. Inspection findings are documented, and remedial actions may be required for any identified deficiencies or non-compliance.
Enforcement Actions:
If non-compliance with SWPPP regulations is identified during inspections or audits, regulatory agencies have the authority to take enforcement actions. These actions may include issuing warning letters, imposing fines and penalties, requiring corrective actions, or even halting construction activities until compliance is achieved. The severity of the enforcement action depends on the nature and extent of the non-compliance and the regulatory authority’s enforcement policy.
Public Reporting and Complaints:
In some jurisdictions, regulatory agencies provide channels for the public to report non-compliance with SWPPP regulations. These agencies may investigate complaints and take appropriate enforcement actions if violations are substantiated. The inclusion of public reporting mechanisms helps ensure transparency and accountability within the construction industry, as concerned citizens can play a crucial role in identifying instances of non-compliance.
Record Keeping and Reporting:
Construction projects are typically required to maintain records related to SWPPP implementation, inspections, and maintenance activities. These records serve as evidence of compliance and must be made available to regulatory authorities upon request. Additionally, construction projects may be required to submit periodic reports detailing their progress in implementing the SWPPP and their adherence to regulations.
Education and Training:
Regulatory agencies often provide educational resources and training programs to construction industry professionals to enhance understanding and compliance with SWPPP regulations. These educational initiatives aim to ensure that construction site personnel are aware of their responsibilities, understand best practices for erosion control and stormwater management, and are equipped with the knowledge and skills to implement effective pollution prevention measures.
Collaboration with Contractors and Industry Organizations:
Regulatory agencies collaborate with contractors, trade associations, and industry organizations to promote compliance with SWPPP regulations. This collaboration includes disseminating guidance materials, organizing training workshops, and fostering a cooperative relationship between regulatory authorities and construction industry stakeholders. Such collaborations help facilitate effective implementation of SWPPPs and create a culture of compliance within the construction industry.
Continuous Improvement and Adaptation:
SWPPP regulations and enforcement mechanisms are subject to continuous improvement and adaptation to address emerging challenges and reflect advancements in stormwater management practices. Regulatory agencies regularly review regulations to ensure that they remain effective, relevant, and adaptable to changing circumstances. Construction companies should stay informed about any updates or revisions to SWPPP regulations to maintain compliance.
Compliance with SWPPP regulations is essential to protect water quality, preserve natural resources, and ensure the sustainability of construction projects. By adhering to these regulations, construction companies contribute to creating a safer and healthier environment for workers, neighboring communities, and the public at large, while avoiding potential penalties and maintaining a positive reputation within the industry.
Benefits of Implementing SWPPP in Construction Projects
Implementing a Stormwater Pollution Prevention Plan (SWPPP) in construction projects offers a wide range of benefits, both in terms of environmental protection and operational efficiency. By prioritizing stormwater management and pollution prevention, construction companies can achieve the following advantages:
- Environmental Protection: The primary benefit of implementing a SWPPP is the protection of the environment, particularly water bodies and ecosystems. By effectively managing stormwater runoff, controlling erosion, and preventing the release of pollutants, construction projects significantly reduce their environmental impact, protect water quality, and preserve natural habitats.
- Compliance with Regulations: Compliance with environmental regulations, including SWPPP requirements, is crucial to avoid fines, penalties, and delays in construction projects. By implementing a SWPPP, construction companies ensure adherence to local, state, and federal regulations, effectively demonstrating their commitment to environmental responsibility.
- Prevention of Water Pollution: Implementing erosion and sediment control measures, as well as pollution prevention practices outlined in the SWPPP, minimizes the transport of sediments, chemicals, and pollutants into storm drains and nearby water bodies. This helps prevent water pollution, preserves aquatic ecosystems, and safeguards public health.
- Enhanced Risk Management: By addressing potential sources of pollution and implementing effective stormwater management practices, construction projects reduce the risk of environmental incidents and associated liabilities. Proactive risk management through the SWPPP ensures that potential issues are identified and mitigated, minimizing financial and reputational risks.
- Improved Operational Efficiency: Implementing a SWPPP promotes efficient construction site management and minimizes disruptions due to environmental issues. Proactive erosion control measures, proper handling of construction waste, and effective stormwater management systems contribute to smoother project execution, minimizing delays, and enhancing overall operational efficiency.
- Positive Public Image: Construction companies that prioritize environmental stewardship and sustainable practices gain a positive reputation within their industry and among stakeholders. Implementing a SWPPP showcases a commitment to responsible construction practices, promoting a favorable public image and enhancing trust with clients, investors, and the community.
- Cost Savings: While implementing a SWPPP requires upfront investment, it can lead to long-term cost savings. Effective erosion control measures and stormwater management practices reduce the potential for environmental incidents, costly fines, and expensive remediation efforts. By preventing issues and avoiding project disruptions, construction projects can achieve significant cost savings.
- Adaptability and Resilience: SWPPPs encourage construction companies to consider the potential impacts of heavy rainfall events, changing weather patterns, and other environmental factors. By incorporating resilience features into the SWPPP, such as storage ponds, green infrastructure, and adaptable drainage systems, construction projects become better equipped to handle changing conditions and potential climate-related challenges.
- Professional Growth and Collaboration: Implementing SWPPPs encourages construction companies to stay updated with the latest stormwater management practices, environmental regulations, and industry standards. Engaging in professional growth and fostering collaborations with environmental consultants, contractors, and regulatory authorities leads to the exchange of knowledge and best practices, ultimately improving the construction industry as a whole.
By recognizing and reaping the benefits of implementing a SWPPP, construction projects enhance their environmental performance, ensure compliance with regulations, and improve operational efficiency. Furthermore, the positive impact on public perception, risk management, and cost savings solidifies the importance of integrating SWPPPs into construction projects to achieve sustainable and responsible outcomes.
Challenges and Limitations of SWPPP
While Stormwater Pollution Prevention Plans (SWPPPs) are crucial for effective stormwater management and pollution prevention in construction projects, there are several challenges and limitations that need to be considered. These challenges arise from various factors, including site conditions, resources, and regulatory constraints. Understanding these limitations is essential to address them effectively and optimize the outcomes of SWPPP implementation:
- Site-Specific Challenges: Each construction site presents unique challenges in terms of topography, soil types, drainage patterns, and proximity to water bodies. These site-specific factors can impact SWPPP implementation and effectiveness. For example, sites with steep slopes or unstable soils may require more extensive erosion and sediment control measures to mitigate erosion and prevent sediment transport.
- Changing Weather Conditions: Construction projects are often exposed to changing weather patterns, including heavy rainfall events and storms. These weather conditions can strain the effectiveness of erosion control measures and stormwater management systems outlined in the SWPPP. Flexibility and adaptability in responding to these weather events are crucial to ensure continued pollution prevention and stormwater management.
- Resource Limitations: Implementing an effective SWPPP requires financial resources, skilled personnel, and access to appropriate materials and equipment. Smaller construction companies or projects with limited budgets may face challenges in allocating sufficient resources to develop and execute comprehensive SWPPPs.
- Education and Training: Proper training and education are critical for the successful implementation of SWPPPs. It can be a challenge to ensure that all workers, subcontractors, and personnel involved in the construction project have the necessary knowledge and skills to implement erosion control measures, stormwater management practices, and pollution prevention strategies outlined in the SWPPP. Ongoing training and awareness programs are essential to overcome this challenge.
- Compliance Monitoring: Ensuring ongoing compliance with SWPPP requirements can be a challenging task, particularly on large construction sites with multiple subcontractors. Regular inspections and monitoring are necessary to assess and address potential non-compliance issues promptly. However, resource limitations and the dynamic nature of construction projects can pose challenges in maintaining consistent compliance monitoring protocols.
- Long-Term Maintenance: Proper maintenance of erosion control measures and stormwater management systems is vital for their long-term effectiveness. However, ensuring regular inspections, maintenance activities, and record keeping can be challenging, particularly for long-duration construction projects. This challenge may be compounded by turnover of construction site personnel and changes in project management over time.
- Regulatory Changes: SWPPPs must adhere to local, state, and federal regulations, which can be subject to changes and updates. Keeping up with these changes can be challenging for construction companies, requiring continuous monitoring and adjustment of SWPPPs to ensure compliance. Failure to stay updated with regulatory changes can result in non-compliance and potential penalties.
- Communication and Coordination: Effective communication and coordination among project stakeholders, including contractors, site managers, regulatory authorities, and consultants, are essential for successful SWPPP implementation. Challenges may arise when multiple entities are involved in a project, leading to potential miscommunications, delays in decision-making, and inconsistencies in implementing SWPPP measures.
- Limitations of Technology and Resources: While advancements in erosion control products, stormwater management technologies, and monitoring tools have improved SWPPP implementation, certain site conditions and constraints may limit the effectiveness of available resources. For example, steep slopes or limited space may restrict the application of certain erosion control measures or stormwater management systems.
Overcoming these challenges and limitations requires proactive planning, effective communication, continuous training, and adaptability. Working closely with environmental consultants, regulators, and industry stakeholders can help address these challenges and optimize the effectiveness of SWPPP implementation in construction projects.
Read more: What Does PR Stand For In Construction
Conclusion
Implementing a Stormwater Pollution Prevention Plan (SWPPP) is essential for construction projects to manage stormwater runoff, prevent water pollution, and protect the environment. SWPPPs play a crucial role in ensuring compliance with environmental regulations, preserving water quality, and promoting sustainable construction practices.
A well-developed SWPPP addresses potential pollution sources, incorporates erosion and sediment control measures, and implements effective stormwater management practices. It provides a comprehensive roadmap for construction companies to prevent the release of pollutants into storm drains and nearby water bodies.
The benefits of implementing a SWPPP are far-reaching. Environmental protection, compliance with regulations, prevention of water pollution, and enhanced risk management are some of the key advantages. SWPPPs also improve operational efficiency, promote a positive public image, and often result in long-term cost savings for construction projects.
Despite the challenges and limitations that may arise, such as site-specific constraints, resource limitations, and changing weather conditions, proactive planning, ongoing training, and continuous monitoring can help overcome these hurdles. Effective communication, collaboration, and staying informed about regulatory changes are crucial for successful SWPPP implementation.
In conclusion, by prioritizing stormwater management and pollution prevention through the development and implementation of SWPPPs, construction projects can align with environmental best practices, protect water resources, and contribute to the sustainability of the built environment. SWPPPs enable construction companies to fulfill their responsibilities to the environment, the community, and future generations, ultimately creating a safer, cleaner, and more sustainable construction industry.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Does SWPPP Stand For In Construction
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.













0 thoughts on “What Does SWPPP Stand For In Construction”