Home>diy>Planning & Engineering>What Is Chainage In Civil Engineering


Planning & Engineering
What Is Chainage In Civil Engineering
Modified: January 4, 2024
Learn about chainage in civil engineering and its importance in planning and engineering. Explore the concept, uses, and benefits of chainage for efficient project management.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Welcome to the world of civil engineering, where precision and accuracy are paramount. In the realm of civil engineering, one term that holds great significance is chainage. Chainage plays a vital role in various aspects of civil engineering, particularly in road construction and design. It serves as a reference point for engineers and surveyors to determine the location, measurements, and alignment of features along a road or highway.
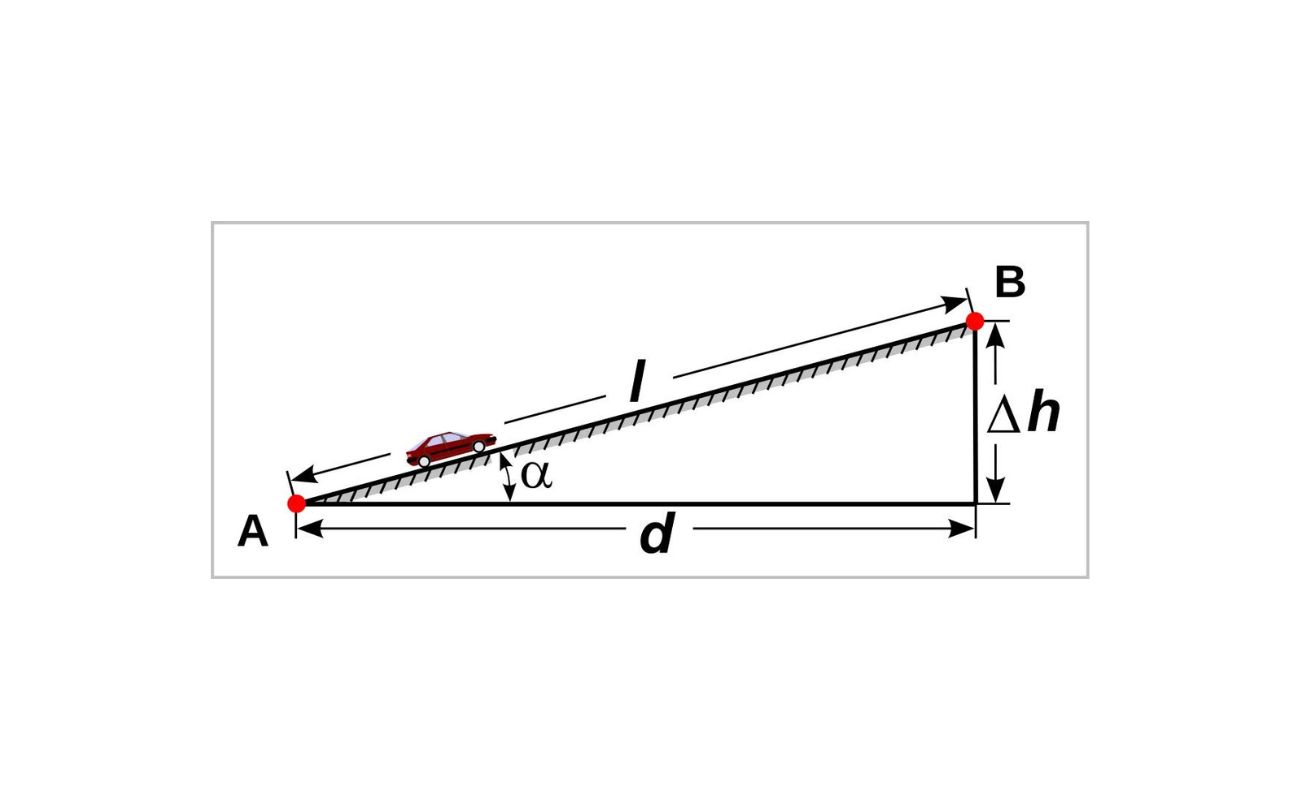
In simple terms, chainage refers to the linear distance measurement along a road or any linear infrastructure project. It provides a systematic way to measure and locate specific points such as intersections, curves, gradients, and structures.
Chainage is also referred to as stationing or mileposting in some regions. Regardless of the terminology, the underlying purpose remains the same – to establish a consistent point of reference that aids in construction, maintenance, and management of road networks.
In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the definition of chainage, its importance in civil engineering, methods of determining chainage, its application in road construction, as well as the challenges and considerations associated with chainage calculation.
Key Takeaways:
- Chainage is a crucial reference point in civil engineering, aiding in precise location, design, and construction of road features. It ensures efficient collaboration and accurate measurement for successful road projects.
- Determining chainage involves various modern methods such as GPS, LiDAR, and aerial surveys, enhancing accuracy and efficiency in civil engineering projects. These advanced techniques contribute to seamless road construction and maintenance.
Read more: What Is Civil Engineering Major
Definition of Chainage
Chainage is a linear measurement system used in civil engineering to determine the position of various features and structures along a road or linear infrastructure project. It involves measuring the distance from a fixed reference point, typically the starting point or baseline of the project. Chainage is usually measured in meters, kilometers, miles, or other standard units of length.
In practical terms, chainage provides a means to locate and identify specific points along a road, such as intersections, curves, bridges, culverts, and any other significant features. These points are marked with corresponding chainage values, which serve as a unique identifier for their position along the road.
Chainage is typically represented as a continuous sequence of numbers, starting from zero or any other chosen reference point. For example, if a road is 10 kilometers long, the chainage values will range from 0 to 10 kilometers. Intermediate points are assigned chainage values proportionate to their distance from the reference point.
Chainage can be measured and marked directly on the ground using physical markers or through surveying techniques such as total station, GPS, or LiDAR. These measurements are then documented in engineering plans, maps, and drawings for reference during construction, maintenance, and management of the road.
It is important to note that chainage is a linear measurement system and should not be confused with coordinate systems such as latitude and longitude or Cartesian coordinates. While coordinates provide a two-dimensional representation of a location on the Earth’s surface, chainage focuses solely on the linear distance along a road or infrastructure project.
Importance of Chainage in Civil Engineering
Chainage plays a crucial role in civil engineering, especially in the field of road construction and design. It provides engineers, surveyors, and construction teams with a common reference point for various tasks and activities. Here are some key reasons why chainage is important in civil engineering:
- Location and Alignment: Chainage helps in accurately locating and aligning different features along a road, such as intersections, curves, and structures. By referencing chainage values, engineers can easily identify the precise position of these features, ensuring proper design and construction.
- Efficient Construction: Chainage facilitates the efficient execution of road construction projects. Contractors and construction teams can use chainage values to set out the alignment, grade, and dimensions of the road, ensuring uniformity and compliance with design specifications.
- Measurement and Quantity Estimation: The linear nature of chainage allows for accurate measurement of distances and quantities. Engineers can calculate the length of road sections, the amount of materials required, and quantities of asphalt, concrete, or other construction materials needed for a particular chainage interval.
- Monitoring and Maintenance: Chainage provides a systematic way to monitor and maintain road networks. By dividing the road into chainage intervals, engineers can easily identify and track changes or damages along specific sections, enabling timely repairs and maintenance.
- Asset Management: Chainage values serve as a vital component of asset management systems for road networks. By associating specific features and structures with their corresponding chainage values, it becomes easier to track and manage road assets such as bridges, culverts, signs, and barriers.
- Collaboration and Communication: Chainage acts as a common reference point for all stakeholders involved in a road project. Engineers, surveyors, contractors, and government authorities can communicate and collaborate effectively by using chainage values to refer to specific locations along the road.
In summary, chainage is essential in civil engineering as it provides a consistent and standardized measurement system for locating, designing, constructing, and maintaining roads. Its importance extends beyond construction and into the management and operation of road networks, making it a fundamental aspect of civil engineering planning and execution.
Methods of Determining Chainage
Several methods are used to determine chainage in civil engineering projects. The choice of method depends on the specific project requirements, budget, time constraints, and available technology. Here are some commonly used methods:
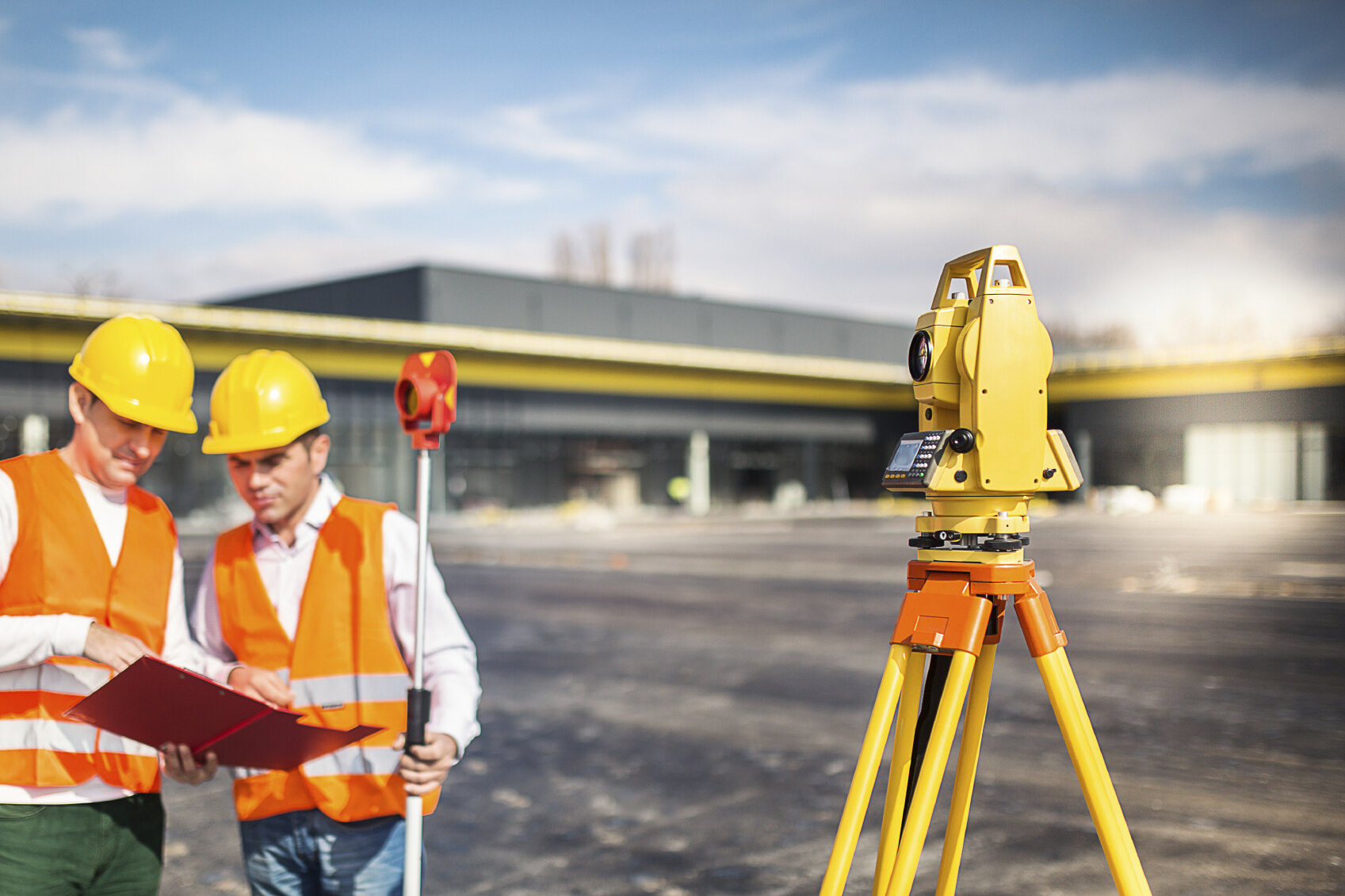
- Surveying Techniques: Traditional surveying techniques, such as the use of theodolites or total stations, can be employed to measure chainage. Surveyors set up the equipment at predetermined points and measure the distances between them. By accurately recording the distances, they can determine the chainage values at various locations along the road.
- Global Positioning System (GPS): GPS technology has revolutionized surveying and chainage determination. By using satellite signals, GPS receivers can provide precise location information. Surveyors can collect GPS data at various points along the road, allowing them to calculate the chainage values accurately.
- Laser Scanning (LiDAR): LiDAR technology utilizes laser beams to measure distances and create highly detailed 3D models of the terrain. By capturing thousands or even millions of points, LiDAR scanners can accurately determine chainage values by measuring the distance from the reference point.
- Differential Leveling: Differential leveling involves using a leveling instrument to measure the difference in elevation between points along the road. By knowing the height differences and distances, surveyors can calculate the chainage values by considering the slope and grade of the road.
- Mobile Mapping Systems: Mobile mapping systems combine GPS and LiDAR technology with advanced sensors and cameras mounted on vehicles. These systems can capture precise location data and create detailed road maps, including chainage values. They are particularly useful for large-scale road projects.
- Aerial Surveys: Aerial surveys involve using drones or aircraft to capture high-resolution images and collect topographic data. By analyzing these images and data, surveyors can determine chainage values by measuring distances and making spatial references to specific locations along the road.
It is worth noting that advances in technology have greatly improved the efficiency and accuracy of chainage determination. Modern methods not only provide precise measurements but also offer the ability to create detailed digital models and maps, further enhancing the planning and design process in civil engineering projects.
Chainage in civil engineering refers to the linear measurement along a road, railway, or pipeline. It is used to locate and reference specific points and features along the route. It is typically measured in meters or kilometers from a fixed starting point.
Application of Chainage in Road Construction
Chainage plays a critical role in road construction projects, providing engineers and construction teams with essential information and a framework for executing various tasks. Here are some key applications of chainage in road construction:
- Alignment and Grade: Chainage serves as a reference point for establishing the alignment and grade of the road. Engineers use chainage values to determine the curvature of road sections, ensuring smooth transitions between straight sections and curves. Additionally, chainage helps in designing and implementing the desired road grade to ensure proper water drainage and efficient vehicle movement.
- Structural Elements: Chainage is crucial for identifying and locating structural elements along the road, such as bridges, culverts, retaining walls, and road signage. Engineers use chainage values to place these features accurately, ensuring they align with the overall road design and meet safety standards.
- Construction Phasing: Chainage provides a convenient way to divide the road into sections or construction phases. This allows for efficient project management, as different contractors and construction teams can work on specific chainage intervals simultaneously, thereby minimizing overlapping work and improving overall construction speed.
- Quantities and Cost Estimation: By associating chainage values with specific road sections, engineers can accurately estimate the quantities of construction materials required. This includes estimating the amount of asphalt, concrete, aggregates, and other materials needed for each chainage interval. This estimation helps in cost planning, budgeting, and procurement of materials.
- Maintenance and Repairs: Chainage is critical for conducting regular maintenance and repairs on roads. By dividing the road into chainage intervals, engineers and maintenance crews can easily identify and address issues such as potholes, cracks, and damaged road surfaces. Chainage serves as a valuable tool for creating maintenance schedules and tracking the condition of the road over time.
- Navigation and Communication: Chainage values allow for efficient navigation and communication within the road construction site. Engineers and construction teams can communicate locations, instructions, and progress updates using chainage as a common reference. This facilitates smooth coordination and reduces the chances of miscommunication.
Overall, chainage is a fundamental aspect of road construction, assisting engineers and construction teams in various tasks, including alignment design, structure placement, construction phasing, cost estimation, maintenance planning, and communication. It provides a systematic framework for efficient execution and ensures the successful completion of road construction projects.
Read more: What Is A Civil Engineering Technician
Challenges and Considerations in Chainage Calculation
While chainage calculation is a crucial aspect of civil engineering, it comes with its own set of challenges and considerations. Here are some key factors to consider when undertaking chainage calculation:
- Accuracy and Precision: Achieving accurate and precise chainage measurements is essential for ensuring the integrity and reliability of the road project. Factors such as instrument calibration, surveying techniques, and data processing must be carefully considered to minimize errors and discrepancies in chainage calculation.
- Terrain and Topography: The type of terrain and topography can significantly impact chainage calculation. In hilly or mountainous areas, changes in elevation and steep slopes require additional considerations to accurately determine chainage, as simple linear measurements may not suffice. Differential leveling and appropriate surveying techniques should be employed to account for these variations.
- Cross-Sections and Curves: Chainage calculation becomes more complex when dealing with curves, intersections, and other irregularities in the road alignment. Special techniques, such as spiral or transition curves, may need to be implemented to ensure smooth transitions and accurate chainage values along these sections.
- Data Collection and Processing: The collection and processing of survey data play a vital role in chainage calculation. Proper field procedures, data management, and quality control measures should be implemented to ensure the accuracy and consistency of the collected data. Advanced software and algorithms can aid in processing the data and calculating chainage values efficiently.
- Changes and Adjustments: Throughout the project lifecycle, changes and adjustments to the road design or alignment may occur. These alterations can impact the chainage calculation, requiring careful adjustment and integration of new chainage values into the existing system. Proper documentation and communication are crucial to ensure all stakeholders are aware of the changes and adjust their plans accordingly.
- Maintenance and Updates: Chainage values should be regularly maintained and updated to reflect any modifications or improvements made to the road. This includes incorporating changes due to maintenance works, alterations in the road layout, or the addition of new structures or features. Regular surveys and inspections should be conducted to validate the chainage values and keep the records up to date.
- Standardization and Consistency: It is important to follow established standards and guidelines for chainage calculation to ensure consistency across different projects and regions. Standardizing practices and maintaining consistent measurement techniques can help eliminate confusion and facilitate seamless collaboration between different stakeholders involved in road construction projects.
By considering these challenges and taking appropriate measures, engineers and surveyors can overcome hurdles in chainage calculation and ensure accurate, reliable, and consistent results. This will contribute to the successful execution and management of road projects.
Conclusion
Chainage is a fundamental concept in civil engineering, particularly in road construction and design. It serves as a vital reference point for locating, measuring, and managing various features along a road or linear infrastructure project. By providing a systematic measurement system, chainage enables engineers, surveyors, and construction teams to accurately plan, construct, maintain, and manage roads.
In this article, we explored the definition of chainage and its importance in civil engineering. We discussed the various methods used to determine chainage, including traditional surveying techniques, GPS, LiDAR, and aerial surveys. We also examined the practical applications of chainage in road construction, such as alignment and grade determination, structural element placement, construction phasing, and maintenance planning.
Additionally, we highlighted the challenges and considerations involved in chainage calculation, such as accuracy and precision, terrain and topography, curves and intersections, data collection, and changes in road design. By addressing these challenges and adhering to established standards, engineers and surveyors can overcome obstacles and ensure the reliability and consistency of chainage values.
Overall, chainage is a valuable tool that enhances the efficiency, accuracy, and effectiveness of road construction projects. It enables precise measurement, effective communication, and seamless collaboration among stakeholders involved in the planning, design, construction, and maintenance of roads. By incorporating chainage as a key aspect of civil engineering practices, we can continue to build safe, well-aligned, and robust road networks that support the movement of people and goods, while ensuring the sustainable development and growth of our communities.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is Chainage In Civil Engineering
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.














0 thoughts on “What Is Chainage In Civil Engineering”