Home>diy>Planning & Engineering>What Are The Different Types Of Civil Engineering


Planning & Engineering
What Are The Different Types Of Civil Engineering
Modified: January 4, 2024
Learn about the various types of civil engineering, including planning engineering, and how they play a crucial role in designing and constructing our modern infrastructure.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Civil engineering is a diverse and critically important field that encompasses the design, construction, and maintenance of infrastructure projects essential for modern society. It plays a crucial role in shaping our cities, improving transportation systems, and ensuring the safety and functionality of buildings and structures.
In this article, we will explore the different types of civil engineering disciplines and their unique contributions to the built environment. Whether you are considering a career in civil engineering or simply curious about the field, understanding these specialties will give you insight into the wide range of opportunities available within this profession.
From structural engineering to transportation engineering, each discipline within civil engineering focuses on specific aspects of infrastructure development and management. Let us delve into the fascinating world of civil engineering and explore these different areas of specialization.
Key Takeaways:
- Civil engineering encompasses diverse disciplines such as structural, transportation, and environmental engineering, working together to create safe, sustainable, and efficient infrastructure systems that shape our modern world.
- Urban planning integrates economic, social, and environmental factors to create vibrant and functional cities that meet the needs of present and future generations, fostering healthy and thriving communities.
Structural Engineering
Structural engineering is a branch of civil engineering that deals with the design, analysis, and construction of structures such as buildings, bridges, dams, and towers. It ensures that these structures are safe, stable, and capable of withstanding the forces they will encounter over their lifespan.
Structural engineers are responsible for determining the appropriate materials, dimensions, and configurations needed to support the intended purpose of a structure. They utilize principles of physics and mathematics to calculate the stresses and loads that a structure will undergo and design the framework accordingly.
The role of a structural engineer extends beyond the initial design phase. They are involved in every stage of a project, from feasibility studies and conceptual design to construction oversight and quality assurance. They work closely with architects, contractors, and other professionals to ensure that the structure meets safety standards and is built to withstand environmental factors such as earthquakes, wind, and snow loads.
Advancements in technology have revolutionized the field of structural engineering. Computer-aided design (CAD) software, finite element analysis (FEA), and building information modeling (BIM) tools are now commonly used to create detailed models, simulate structural behavior, and optimize designs.
Structural engineering is a rewarding career for those who enjoy problem-solving, creativity, and working with numbers. It offers opportunities to work on iconic projects and make a lasting impact on the built environment. Whether it is designing skyscrapers that pierce the skyline or structurally retrofitting historical buildings, structural engineers play a crucial role in ensuring the safety, functionality, and longevity of structures that shape our world.
Geotechnical Engineering
Geotechnical engineering is a branch of civil engineering that focuses on the behavior of earth materials, including soil and rock, and their interaction with structures and the environment. It is concerned with assessing and managing the geological and geotechnical risks associated with construction projects.
Geotechnical engineers investigate the properties and characteristics of soils and rocks at a construction site and analyze how these materials will respond to the applied loads. They assess factors such as soil composition, strength, and permeability to determine the stability and suitability of a site for building foundations, embankments, and other structures.
One of the key tasks of a geotechnical engineer is conducting site investigations and performing geotechnical testing to gather data about the soil and rock conditions. This information is crucial for designing safe and reliable foundations and earth structures. Additionally, geotechnical engineers provide recommendations for reducing potential risks, such as slope stability analysis to prevent landslides or designing retaining walls to support excavations.
With the growing demand for sustainable construction practices, geotechnical engineers are also involved in geotechnical considerations for infrastructure projects in environmentally sensitive areas. This includes designing techniques to minimize soil erosion, implementing measures for groundwater protection, and evaluating the impact of construction on local ecosystems.
Geotechnical engineering requires a solid understanding of soil mechanics, foundation engineering, and geology. Mathematical modeling and computer simulations are used extensively to analyze complex soil-structure interactions and predict potential ground movements.
Overall, geotechnical engineering plays a crucial role in ensuring the stability and longevity of construction projects. By carefully evaluating the geological and geotechnical aspects of a site, geotechnical engineers help minimize risks and ensure the safety and sustainability of infrastructure in various types of soil and rock conditions.
Transportation Engineering
Transportation engineering is a specialized branch of civil engineering that focuses on planning, design, operation, and management of transportation systems. It involves the analysis and optimization of various modes of transportation including roadways, railways, airports, and waterways to ensure efficient movement of people and goods.
Transportation engineers work on a wide range of projects, from designing road networks and traffic signal systems to planning public transit routes and optimizing transportation infrastructure. The goal is to improve the safety, capacity, and sustainability of transportation systems while minimizing travel times and environmental impact.
One of the key responsibilities of transportation engineers is to analyze and design transportation facilities and networks to accommodate the projected demand. This includes determining the optimal placement and capacity of roads, highways, and intersections. They also consider factors such as traffic flow, safety, and accessibility for different modes of transportation, including pedestrians and cyclists.
To support their analysis and decision-making processes, transportation engineers employ various tools and techniques such as traffic modeling, computer simulation, and geographic information systems (GIS). These technologies help them evaluate different scenarios, predict traffic patterns, and assess the performance of transportation systems under different conditions.
Additionally, transportation engineers play a critical role in promoting sustainable transportation solutions. This involves implementing strategies to reduce reliance on private vehicles, such as developing and optimizing public transit systems, designing pedestrian-friendly urban spaces, and encouraging alternative modes of transportation like cycling and walking.
As the world continues to face challenges related to urbanization and population growth, transportation engineering becomes increasingly important. By improving the efficiency and sustainability of transportation systems, transportation engineers contribute to reducing traffic congestion, improving air quality, and enhancing the overall quality of life in communities.
Ultimately, transportation engineering is crucial for creating transportation systems that are safe, reliable, and effective in meeting the needs of people and businesses, both now and in the future.
Environmental Engineering
Environmental engineering is a specialized branch of civil engineering that focuses on protecting and preserving the natural environment while promoting sustainable development. It involves the application of scientific and engineering principles to address environmental challenges and improve the quality of our surroundings.
Environmental engineers work on a wide range of projects, including the design and implementation of wastewater treatment systems, air pollution control measures, and solid waste management strategies. They also play a crucial role in assessing and mitigating the environmental impacts of various industries and infrastructure projects.
One of the key responsibilities of environmental engineers is to ensure that water resources are managed effectively and protected from contamination. This involves designing and operating systems for water supply, sewage treatment, and stormwater management. Environmental engineers also work towards developing sustainable solutions for water scarcity, watershed management, and water reclamation.
Additionally, environmental engineers are involved in the assessment and management of air quality. They develop techniques to monitor and control emissions from industrial plants, vehicles, and other sources. This includes designing and implementing air pollution control systems, such as filters and scrubbers, to reduce harmful pollutants and improve air quality.
Another important aspect of environmental engineering is waste management. Environmental engineers design and implement waste disposal and recycling systems to minimize the environmental impact of solid waste. They also work on developing innovative approaches, such as waste-to-energy technologies and composting methods, to reduce landfill usage and promote sustainable waste management practices.
Environmental engineers play a critical role in addressing the challenges posed by climate change and promoting sustainability. They are involved in assessing and mitigating the environmental impacts of projects and helping communities adapt to changing environmental conditions. This includes evaluating the risks associated with rising sea levels, extreme weather events, and other climate-related factors.
By integrating scientific knowledge with engineering principles, environmental engineers contribute to creating a more sustainable and resilient future. Their work helps protect ecosystems, promote public health, and ensure a healthy and sustainable environment for future generations.
Water Resources Engineering
Water resources engineering is a specialized branch of civil engineering that focuses on the management and utilization of water resources. It involves the planning, design, and implementation of infrastructure to ensure the availability of clean water for various purposes, such as drinking, irrigation, and industrial use.
Water resources engineers work on a wide range of projects, including the design and construction of dams, reservoirs, and water supply systems. Their goal is to optimize the allocation and distribution of water resources while considering factors such as sustainability, efficiency, and environmental impact.
One of the key responsibilities of water resources engineers is to develop systems for water supply and distribution. This includes designing pipelines, pumping stations, and water treatment plants to ensure a reliable and safe water supply for communities. They also work on managing and implementing technologies for water conservation and efficiency, such as rainwater harvesting and water reuse systems.
In addition to water supply, water resources engineers are involved in flood and stormwater management. They design and implement systems for flood control, including levees, flood channels, and drainage networks. By considering factors such as topography, rainfall patterns, and climate change projections, water resources engineers help reduce the risk and impact of flooding on communities.
Furthermore, water resources engineers play a crucial role in managing and protecting natural water resources such as rivers, lakes, and wetlands. They develop strategies for sustainable water management, watershed protection, and ecosystem restoration. By considering the ecological needs of these water bodies, water resources engineers help maintain the balance between human water usage and environmental sustainability.
Advancements in technology have greatly influenced water resources engineering. The use of computer modeling, remote sensing, and geographic information systems (GIS) allows for more accurate predictions and analysis of water flow, sedimentation patterns, and water quality. These tools aid in the design and management of water resources systems, ensuring efficient and sustainable water utilization.
Water resources engineering plays a vital role in addressing the global water crisis, as population growth and climate change put increasing pressure on water supplies. By managing and optimizing water resources, water resources engineers contribute to ensuring a reliable and sustainable water supply for present and future generations.
When studying civil engineering, it’s important to understand the different types, including structural, transportation, geotechnical, environmental, and water resources engineering. Each specialization has its own unique focus and applications in the field.
Construction Management
Construction management is a specialized branch of civil engineering that focuses on the planning, coordination, and execution of construction projects. It involves the management of resources, schedules, and budgets to ensure that construction projects are completed successfully and efficiently.
Construction managers play a crucial role in overseeing the entire construction process, from the initial project planning to the final delivery. They work closely with architects, engineers, contractors, and subcontractors to ensure that the project is executed in accordance with the design specifications, local regulations, and safety standards.
One of the primary responsibilities of construction managers is to create a detailed project plan and schedule. This includes outlining the timeline for each phase of construction, coordinating the activities of different trades, and ensuring that materials and equipment are available when needed. Construction managers must also manage potential risks and anticipate challenges that may arise during the construction process.
In addition to scheduling, construction managers are responsible for managing the project budget. They estimate the costs of labor, materials, and equipment, and closely monitor expenses to ensure that the project remains within budgetary constraints. Construction managers also work to optimize resource allocation and identify cost-saving opportunities.
Communication and coordination are essential skills for construction managers. They act as a liaison between the project team, stakeholders, and clients, ensuring that everyone is aligned with the project objectives and informed of any changes or updates. Construction managers also manage relationships with subcontractors and suppliers, overseeing the bidding process and negotiation of contracts.
With the advancements in technology, construction management has been greatly enhanced. Digital project management tools, Building Information Modeling (BIM), and remote collaboration software allow for better communication, real-time tracking of progress, and improved coordination among team members and stakeholders.
Construction management requires a combination of technical knowledge, leadership skills, and problem-solving abilities. Successful construction managers are adept at managing multiple tasks, resolving conflicts, and adapting to the ever-changing nature of construction projects.
By effectively managing construction projects, construction managers play a critical role in delivering projects on time, within budget, and to the desired quality standards. Their expertise and leadership help ensure the successful completion of infrastructure projects that shape our communities and improve the built environment.
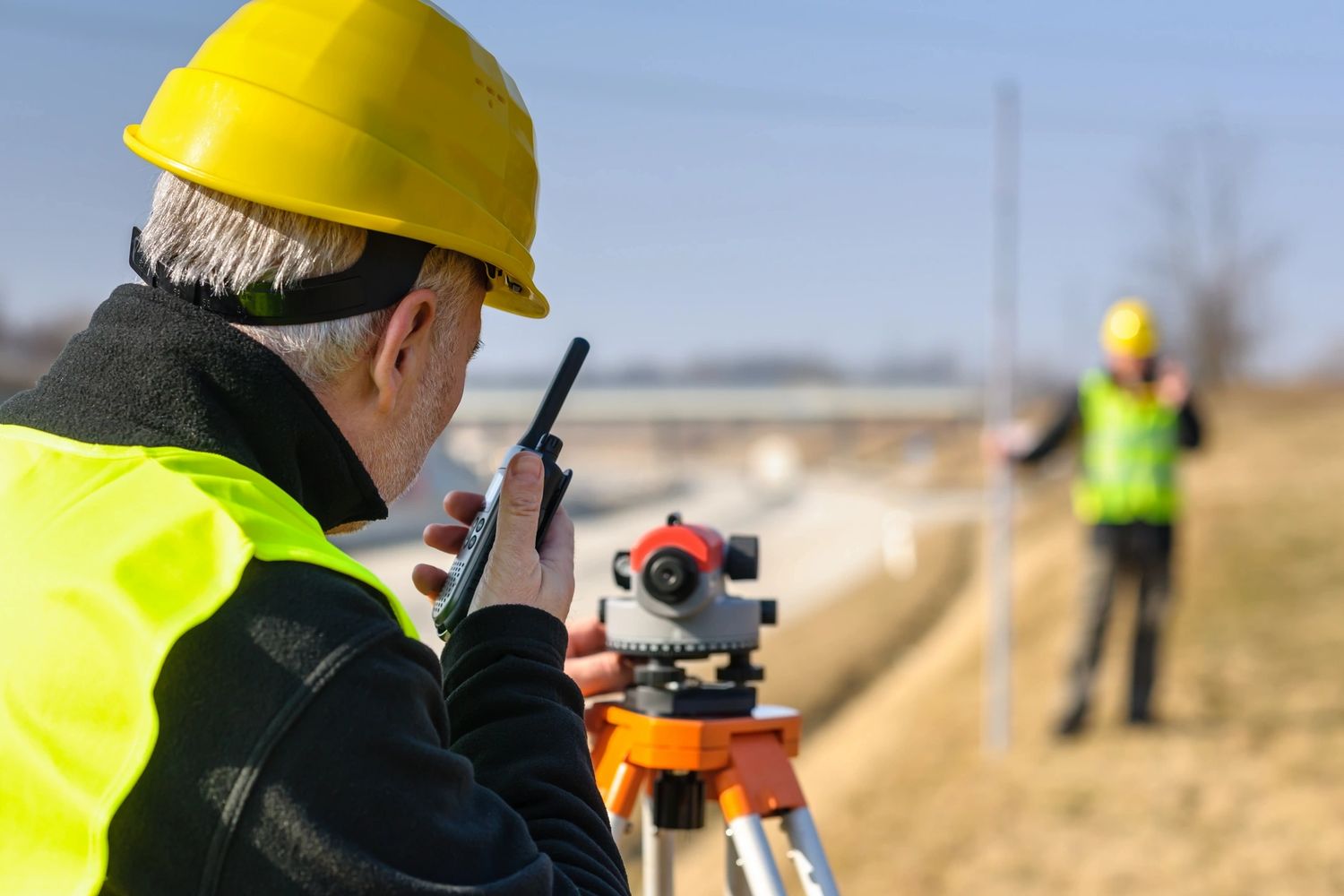
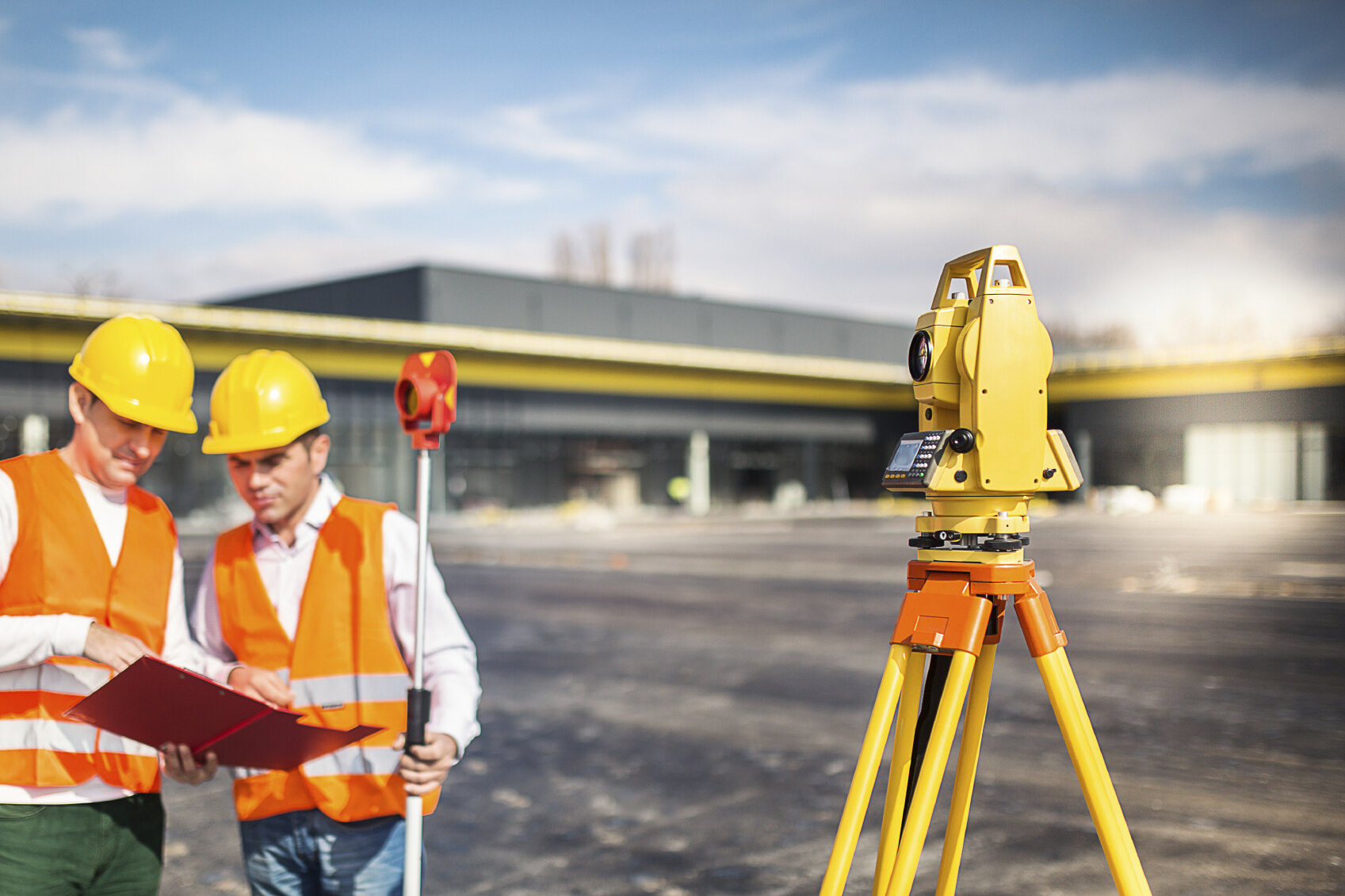
Surveying and Mapping Engineering
Surveying and mapping engineering is a specialized branch of civil engineering that focuses on accurately measuring and mapping the earth’s surface and its features. It involves the use of advanced instruments and technologies to gather data and create detailed maps, plans, and 3D models of land areas.
Surveying plays a crucial role in the design, construction, and maintenance of infrastructure projects. Surveyors are responsible for determining the exact boundaries, elevations, and positions of land parcels, buildings, and other structures. This information is essential for creating accurate site plans, designing transportation systems, and ensuring proper alignment of construction activities.
Surveyors utilize a variety of tools and techniques to collect data, including total stations, GPS receivers, LiDAR scanners, and drones. They measure distances, angles, and elevations to create precise measurements and reference points. These measurements are then used to create maps, topographic surveys, and digital terrain models.
In addition to measuring land and structures, surveying and mapping engineers also play a crucial role in geospatial data management. They collect and analyze geographic data related to natural resources, property values, and environmental conditions. This data is used in various applications, such as urban planning, land management, and disaster management.
One of the rapidly evolving areas in surveying and mapping engineering is the use of drones for aerial surveying and mapping. Drones equipped with high-resolution cameras and LiDAR sensors can quickly and accurately capture detailed imagery and terrain data. This technology has revolutionized the field, enabling surveyors to collect data more efficiently and safely.
Surveying and mapping engineering requires expertise in geomatics, geodesy, and geographic information systems (GIS). Surveyors must have a strong understanding of mathematical concepts, spatial analysis, and the use of surveying equipment and software.
Accuracy and precision are at the core of surveying and mapping engineering. By providing accurate measurements and detailed mapping data, surveying and mapping engineers play a crucial role in the planning and development of infrastructure projects. Their work ensures the proper utilization of land resources, supports accurate land valuation, aids in disaster management, and helps create a sustainable and efficient built environment.
Coastal Engineering
Coastal engineering is a specialized branch of civil engineering that focuses on the design and management of coastal areas, including coastlines, beaches, and waterfront structures. It involves understanding and addressing the unique challenges associated with coastal environments, such as erosion, sediment transport, and sea-level rise.
Coastal engineers are responsible for designing and constructing structures that protect coastlines from erosion and mitigate the impact of storms and flooding. These structures can include breakwaters, seawalls, groins, and revetments. By effectively managing sediment movement and controlling wave energy, coastal engineers help maintain the stability and integrity of coastal areas.
One of the key aspects of coastal engineering is coastal erosion and shoreline management. Coastal engineers analyze the forces and processes that cause erosion and implement measures to prevent or mitigate its effects. This can include beach nourishment projects, dune stabilization, and vegetation management to maintain and enhance the natural defenses of coastal areas.
Additionally, coastal engineers play a vital role in the design and development of coastal infrastructure. This can include harbors, ports, and marinas, where they ensure that these structures can withstand the forces of waves, tides, and currents. By designing navigational channels and improving harbor layouts, coastal engineers facilitate safe and efficient maritime transportation.
Coastal engineering also involves addressing the challenges associated with sea-level rise and climate change. Coastal engineers assess the vulnerability of coastal areas to rising sea levels and develop strategies for adaptation and resilience. This includes devising sustainable coastal protection measures and incorporating climate change considerations into coastal planning and engineering projects.
The complex nature of coastal environments requires the use of advanced modeling and simulation tools. Coastal engineers utilize numerical models and computer simulations to understand the behavior of waves, currents, and sediment transport. These tools aid in predicting the impact of coastal engineering interventions and help guide decision-making processes.
Coastal engineering plays a vital role in managing and protecting coastal regions, which are of immense ecological, economic, and recreational value. By designing coastal infrastructure, managing erosion, and mitigating the effects of climate change, coastal engineers ensure the long-term sustainability and resilience of coastal areas.
Urban Planning
Urban planning is a specialized field within civil engineering that focuses on the design, development, and management of cities and urban areas. It involves creating sustainable and livable environments by considering various factors such as land use, transportation, infrastructure, and community needs.
Urban planners work on a wide range of projects, from creating long-term city plans to designing specific neighborhoods or public spaces. They strive to balance the needs of residents, businesses, and the environment to create vibrant and functional urban spaces.
One of the key responsibilities of urban planners is land use planning. They analyze the existing land conditions, population growth projections, and economic factors to determine the appropriate allocation of land for residential, commercial, industrial, and recreational purposes. This helps create a well-organized and efficient urban fabric.
Transportation planning is another critical aspect of urban planning. Urban planners evaluate the transportation needs of communities and develop strategies to improve mobility and accessibility. This can include designing efficient road networks, implementing public transit systems, and promoting alternative modes of transportation such as walking and cycling.
Sustainability and environmental considerations are integral to urban planning. Urban planners strive to create environmentally friendly cities by integrating green spaces, promoting energy-efficient buildings, and implementing strategies for water conservation and waste management. They also focus on preserving natural resources and protecting ecologically sensitive areas within urban environments.
Community engagement and social equity are important principles in urban planning. Planners work closely with community members to understand their needs and aspirations, ensuring that the planning process is inclusive and responsive to the diverse needs of the population. They aim to create neighborhoods that are socially cohesive, safe, and accessible to all residents.
Urban planners utilize various tools and techniques to aid in the planning process. Geographic Information Systems (GIS), data analysis, and computer modeling allow for the visualization and analysis of urban data, enabling informed decision-making and predicting future urban growth patterns.
Urban planning plays a crucial role in shaping cities to be sustainable, resilient, and enjoyable places to live, work, and play. By integrating economic, social, and environmental factors, urban planners strive to create cities that meet the needs of present and future generations, fostering healthy and thriving communities.
Conclusion
Civil engineering encompasses a wide range of disciplines, each playing a unique role in shaping our built environment and improving the quality of our lives. From structural engineering and geotechnical engineering to transportation engineering and environmental engineering, these specializations work together to create safe, sustainable, and efficient infrastructure systems.
Structural engineering ensures the stability and safety of buildings and structures, while geotechnical engineering focuses on the properties and behavior of soil and rocks to determine the suitability of construction sites. Transportation engineering optimizes movement and accessibility in our cities, while environmental engineering protects and preserves our natural surroundings.
Water resources engineering manages and utilizes water resources effectively, and coastal engineering protects vulnerable coastlines and structures against erosion and flooding. Construction management ensures the successful execution and completion of construction projects, and surveying and mapping engineering provides accurate measurements and mapping data of the land.
Lastly, urban planning brings all of these disciplines together to create sustainable, equitable, and livable cities that meet the needs of their residents now and in the future. It integrates land use planning, transportation planning, and social and environmental considerations to create vibrant and functional urban spaces.
As technology continues to advance, civil engineering will continue to evolve, incorporating innovations such as computer simulations, data analysis, and remote sensing. These advancements will enhance the precision, efficiency, and sustainability of civil engineering practices, paving the way for a more interconnected and resilient built environment.
In conclusion, civil engineering plays a crucial role in shaping our modern world. Through the expertise and dedication of civil engineers, we can build structures, develop infrastructure systems, and create cities that stand the test of time while minimizing their environmental impact. As the field continues to evolve, civil engineers will play a vital role in tackling the challenges of population growth, urbanization, and climate change, ensuring that our built environment remains safe, sustainable, and enjoyable for generations to come.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Are The Different Types Of Civil Engineering
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.













0 thoughts on “What Are The Different Types Of Civil Engineering”